Blalock-Taussig shunt: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CMG}} '''[http://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/User:Usmanaliakbar Associate Editor-In-Chief: Usman Ali Akbar, M.B.B.S],'''{{SI}} | {{CMG}} '''[http://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/User:Usmanaliakbar Associate Editor-In-Chief: Usman Ali Akbar, M.B.B.S],'''{{SI}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The '''Blalock-Taussig shunt''' is a surgical procedure that are done as palliative procedures for [[cyanotic heart defect]]s . This procedure is used to deviate blood flow to lungs from systemic circulation to relieve cyanosis while a definitive | The '''Blalock-Taussig shunt''' is a [[surgical procedure]] that are done as [[Palliative treatment|palliative]] procedures for [[cyanotic heart defect]]s . This procedure is used to deviate blood flow to lungs from systemic circulation to relieve [[cyanosis]] while a definitive [[corrective surgery]] can be performed at later time. Connection between [[subclavian artery]] and [[pulmonary artery]] is usually made . There are usually two types of [[Shunt (medical)|shunts]] that are used i.e classic or original Blalock-Taussig shunt and modified Blalock Taussig shunt. The classic or original BT shunt has been modified into modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt (mBTS). In this modified procedure a [[graft]] from [[innominate artery]] or [[subclavian artery]] is placed to the corresponding [[pulmonary artery]]. <ref name="pmid28701598" />This type of BT shunt has superior [[Prognosis|prognostic]] value over classical shunt leading to greater rate of shunt patency at 3-5 years as compared to classic or original BT Shunt.<ref name="pmid19040408" /> | ||
== Historical Perspective == | == Historical Perspective == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
=== Classic or Original Shunt === | === Classic or Original Shunt === | ||
The classic or original BT shunt procedure was named for [[Alfred Blalock]], surgeon, Baltimore, (1899–1964) and [[Helen B. Taussig]], cardiologist, Baltimore/Boston, (1898–1986) who, along with Blalock's African American laboratory technician [[Vivien Thomas]] (1910–1985), developed and described the procedure. Taussig noticed that | The classic or original BT shunt procedure was named for [[Alfred Blalock]], surgeon, Baltimore, (1899–1964) and [[Helen B. Taussig]], cardiologist, Baltimore/Boston, (1898–1986) who, along with Blalock's African American laboratory technician [[Vivien Thomas]] (1910–1985), developed and described the procedure. Taussig noticed that the children with cyanosis along with [[congenital heart disease]] accompanied by [[patent ductus arteriosus]] have longer life time than those without PDA. Dr. Taussig approached Blalock and Thomas in their Hopkins laboratory in 1943 to work upon in this shunt as it was hypothesized that a shunt mimicking [[PDA]] can relieve the cyanosis and improve [[oxygenation]] in [[congential cyanotic diseases]]. {{cite book | last = Thomas | first = Vivien | title = Partners of the heart : Vivien Thomas and his work with Alfred Blalock : an autobiography | publisher = University of Pennsylvania Press | location = Philadelphia | year = 1985 | isbn = 0812216342 }} | ||
=== Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt === | === Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt === | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Indications == | == Indications == | ||
* Tricuspid atresia | *[[Tricuspid atresia]] | ||
* | *[[Tetralogy of Fallot:|Tetralogy of Fallot]] | ||
* Ebstein's | *[[Ebstein's anomaly of the tricuspid valve|Ebstein's Anomaly]] | ||
* Hypoplastic Left Heart syndrome | *[[Hypoplastic Left Heart syndrome]] | ||
* Pulmonary atresia | *[[Pulmonary atresia]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
=== Classic/Orginal Blalock-Taussig Shunt <ref name="pmid28701598">{{cite journal| author=Kiran U, Aggarwal S, Choudhary A, Uma B, Kapoor PM| title=The blalock and taussig shunt revisited. | journal=Ann Card Anaesth | year= 2017 | volume= 20 | issue= 3 | pages= 323-330 | pmid=28701598 | doi=10.4103/aca.ACA_80_17 | pmc=5535574 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28701598 }} </ref> === | === Classic/Orginal Blalock-Taussig Shunt <ref name="pmid28701598">{{cite journal| author=Kiran U, Aggarwal S, Choudhary A, Uma B, Kapoor PM| title=The blalock and taussig shunt revisited. | journal=Ann Card Anaesth | year= 2017 | volume= 20 | issue= 3 | pages= 323-330 | pmid=28701598 | doi=10.4103/aca.ACA_80_17 | pmc=5535574 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28701598 }} </ref> === | ||
* For classic Blalock-Taussig shunt end to end anastomosis between the subclavian and pulmonary arteries is performed on opposite to the aortic arch to minimize the kinking of subclavian artery as it crosses aortic prominence | * For classic Blalock-Taussig shunt end to end [[anastomosis]] between the [[subclavian]] and [[Pulmonary artery|pulmonary arteries]] is performed on opposite to the [[aortic arch]] to minimize the [[kinking]] of [[subclavian artery]] as it crosses [[Aorta|aortic]] prominence. | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
!Disadvantages | !Disadvantages | ||
|- | |- | ||
|The relative diameter of | |The relative [[diameter]] of [[subclavian artery]] prevents excessive blood flow to lungs | ||
|Thrombosis of shunt due to less diameter | |[[Thrombosis]] of shunt due to less diameter | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Easily Reversible | |Easily Reversible | ||
|Risk of Dissection | |Risk of [[Dissection (medical)|Dissection]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Increased rate of anastomosis growth | |Increased rate of anastomosis growth | ||
| Line 54: | Line 55: | ||
=== Modified Blalock Taussig Shunt <ref name="pmid28701598">{{cite journal| author=Kiran U, Aggarwal S, Choudhary A, Uma B, Kapoor PM| title=The blalock and taussig shunt revisited. | journal=Ann Card Anaesth | year= 2017 | volume= 20 | issue= 3 | pages= 323-330 | pmid=28701598 | doi=10.4103/aca.ACA_80_17 | pmc=5535574 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28701598 }} </ref> === | === Modified Blalock Taussig Shunt <ref name="pmid28701598">{{cite journal| author=Kiran U, Aggarwal S, Choudhary A, Uma B, Kapoor PM| title=The blalock and taussig shunt revisited. | journal=Ann Card Anaesth | year= 2017 | volume= 20 | issue= 3 | pages= 323-330 | pmid=28701598 | doi=10.4103/aca.ACA_80_17 | pmc=5535574 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28701598 }} </ref> === | ||
It is the most commonly used procedure now a days. First described and performed by Klinner et. al in 1962, this procedure hold superb prognosis over classic one. An Interposition PTFE or Gore-Tex graft is placed between the | It is the most commonly used procedure now a days. First described and performed by Klinner et. al in 1962, this procedure hold superb [[prognosis]] over classic one. An [[Interposition]] PTFE or Gore-Tex graft is placed between the [[subclavian artery]] and the [[pulmonary artery]]. Hence no [[scarring]] of [[subclavian artery]] results. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+Modified Blalock Taussig Shunt | |+Modified Blalock Taussig Shunt | ||
| Line 61: | Line 62: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|It can be done on the same side of the arch | |It can be done on the same side of the arch | ||
|Thrombosis | |[[Thrombosis]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|More patency than Classic BT shunt i.e >90 % at 2 years | |More [[patency]] than Classic BT shunt i.e >90 % at 2 years | ||
|Pseudoaneurysm | |[[Pseudoaneurysm]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Pulmonary artery is less disorted | |[[Pulmonary artery]] is less disorted | ||
|Chylothorax, Chylopericardium, chylous ascites | |[[Chylothorax]], [[Chylopericardium|Chylopericardium,]] [[Ascites|chylous ascites]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Complications == | == Complications == | ||
[[File:Unilateral-pulmonary-oedema-blalock-taussig-shunt-in-pulmonary-atresia-with-ventricular-septal-defect-1.jpg|left|thumb|220x220px|Case courtesy of Dr Charlie Chia-Tsong Hsu,. From the case https://radiopaedia.org/cases/18390, rID: 18390</a>]] | [[File:Unilateral-pulmonary-oedema-blalock-taussig-shunt-in-pulmonary-atresia-with-ventricular-septal-defect-1.jpg|left|thumb|220x220px|Case courtesy of Dr Charlie Chia-Tsong Hsu,. From the case https://radiopaedia.org/cases/18390, rID: 18390</a>]] | ||
The immediate post-operative complications include <ref name="pmid19040408">{{cite journal| author=Yuan SM, Shinfeld A, Raanani E| title=The Blalock-Taussig shunt. | journal=J Card Surg | year= 2009 | volume= 24 | issue= 2 | pages= 101-8 | pmid=19040408 | doi=10.1111/j.1540-8191.2008.00758.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19040408 }} </ref> | The immediate [[Post operative complications|post-operative complications]] include <ref name="pmid19040408">{{cite journal| author=Yuan SM, Shinfeld A, Raanani E| title=The Blalock-Taussig shunt. | journal=J Card Surg | year= 2009 | volume= 24 | issue= 2 | pages= 101-8 | pmid=19040408 | doi=10.1111/j.1540-8191.2008.00758.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19040408 }} </ref> | ||
* Development of chylothorax, chylopericardium and chylous ascites | * Development of [[chylothorax]], [[chylopericardium]] and [[Ascites|chylous ascites]] | ||
* Phrenic nerve resection leading to paralysis | *[[Phrenic nerve|Phrenic nerve resection]] leading to [[paralysis]] | ||
* Anemia | *[[Anemia]] | ||
* Congestive Heart | *[[Congestive heart failure|Congestive Heart failure]] resulting from excessive blood flow | ||
* Modified PTFE grafts can result in formation seroma or shunt occlusion due to hyperplasia of | * Modified PTFE grafts can result in formation of [[seroma]] or shunt [[occlusion]] due to [[hyperplasia]] of [[neo-intima]] | ||
* Stenosis of innominate artery | *[[Stenosis]] of [[innominate artery]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 89: | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
[[File:Blalock-taussig-shunt-annotated-image.png|left|thumb|202x202px|Case courtesy of Dr Vincent Tatco,From the case https://radiopaedia.org/cases/41040<nowiki/>,rID: 41040]] | [[File:Blalock-taussig-shunt-annotated-image.png|left|thumb|202x202px|Case courtesy of Dr Vincent Tatco,From the case https://radiopaedia.org/cases/41040<nowiki/>,rID: 41040]] | ||
Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt has superior prognostic value over classic Blalock-Taussig Shunts. Following prognostic factors are compared between the two procedures in multiple studies. <ref name="pmid9855103">{{cite journal| author=Al Jubair KA, Al Fagih MR, Al Jarallah AS, Al Yousef S, Ali Khan MA, Ashmeg A | display-authors=etal| title=Results of 546 Blalock-Taussig shunts performed in 478 patients. | journal=Cardiol Young | year= 1998 | volume= 8 | issue= 4 | pages= 486-90 | pmid=9855103 | doi=10.1017/s1047951100007150 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9855103 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid16337132">{{cite journal| author=Kim HK, Kim WH, Kim SC, Lim C, Lee CH, Kim SJ| title=Surgical strategy for pulmonary coarctation in the univentricular heart. | journal=Eur J Cardiothorac Surg | year= 2006 | volume= 29 | issue= 1 | pages= 100-4 | pmid=16337132 | doi=10.1016/j.ejcts.2005.10.032 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16337132 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid3968910">{{cite journal| author=Karpawich PP, Bush CP, Antillon JR, Amato JJ, Marbey ML, Agarwal KC| title=Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt in infants and young children. Clinical and catheterization assessment. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1985 | volume= 89 | issue= 2 | pages= 275-9 | pmid=3968910 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3968910 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid10707705">{{cite journal| author=Kulkarni H, Rajani R, Dalvi B, Gupta KG, Vora A, Kelkar P| title=Effect of Blalock Taussig shunt on clinical parameters, left ventricular function and pulmonary arteries. | journal=J Postgrad Med | year= 1995 | volume= 41 | issue= 2 | pages= 34-6 | pmid=10707705 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10707705 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid2441893">{{cite journal| author=Bove EL, Kohman L, Sereika S, Byrum CJ, Kavey RE, Blackman MS | display-authors=etal| title=The modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: analysis of adequacy and duration of palliation. | journal=Circulation | year= 1987 | volume= 76 | issue= 3 Pt 2 | pages= III19-23 | pmid=2441893 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2441893 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid3675059">{{cite journal| author=Ullom RL, Sade RM, Crawford FA, Ross BA, Spinale F| title=The Blalock-Taussig shunt in infants: standard versus modified. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 1987 | volume= 44 | issue= 5 | pages= 539-43 | pmid=3675059 | doi=10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62119-4 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3675059 }} </ref> | Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt has superior [[Prognosis|prognostic]] value over classic Blalock-Taussig Shunts. Following prognostic factors are compared between the two procedures in multiple studies. <ref name="pmid9855103">{{cite journal| author=Al Jubair KA, Al Fagih MR, Al Jarallah AS, Al Yousef S, Ali Khan MA, Ashmeg A | display-authors=etal| title=Results of 546 Blalock-Taussig shunts performed in 478 patients. | journal=Cardiol Young | year= 1998 | volume= 8 | issue= 4 | pages= 486-90 | pmid=9855103 | doi=10.1017/s1047951100007150 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9855103 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid16337132">{{cite journal| author=Kim HK, Kim WH, Kim SC, Lim C, Lee CH, Kim SJ| title=Surgical strategy for pulmonary coarctation in the univentricular heart. | journal=Eur J Cardiothorac Surg | year= 2006 | volume= 29 | issue= 1 | pages= 100-4 | pmid=16337132 | doi=10.1016/j.ejcts.2005.10.032 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16337132 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid3968910">{{cite journal| author=Karpawich PP, Bush CP, Antillon JR, Amato JJ, Marbey ML, Agarwal KC| title=Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt in infants and young children. Clinical and catheterization assessment. | journal=J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | year= 1985 | volume= 89 | issue= 2 | pages= 275-9 | pmid=3968910 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3968910 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid10707705">{{cite journal| author=Kulkarni H, Rajani R, Dalvi B, Gupta KG, Vora A, Kelkar P| title=Effect of Blalock Taussig shunt on clinical parameters, left ventricular function and pulmonary arteries. | journal=J Postgrad Med | year= 1995 | volume= 41 | issue= 2 | pages= 34-6 | pmid=10707705 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10707705 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid2441893">{{cite journal| author=Bove EL, Kohman L, Sereika S, Byrum CJ, Kavey RE, Blackman MS | display-authors=etal| title=The modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: analysis of adequacy and duration of palliation. | journal=Circulation | year= 1987 | volume= 76 | issue= 3 Pt 2 | pages= III19-23 | pmid=2441893 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2441893 }} </ref> <ref name="pmid3675059">{{cite journal| author=Ullom RL, Sade RM, Crawford FA, Ross BA, Spinale F| title=The Blalock-Taussig shunt in infants: standard versus modified. | journal=Ann Thorac Surg | year= 1987 | volume= 44 | issue= 5 | pages= 539-43 | pmid=3675059 | doi=10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62119-4 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=3675059 }} </ref> | ||
* Rise in saturation of oxygen is greater in modified than in classic shunt | * Rise in [[Oxygen saturation|saturation of oxygen]] is greater in modified than in classic shunt | ||
* Shunt patency is 88.8 % in modified for 3-5 years versus 90 % in first year, 62 % in two years and 78.0 % in 3 years for classic shunt. | * Shunt patency is 88.8 % in modified for 3-5 years versus 90 % in first year, 62 % in two years and 78.0 % in 3 years for classic shunt. | ||
* The risk of early shunt faliure is 20.8 % in modified and 51.7% in classic shunt. | * The risk of early shunt faliure is 20.8 % in modified and 51.7% in classic shunt. | ||
* Post-shunt increase in pulmonary arterial index (mm2/m2) is 158 +/- 21 versus 117 +/- 52 in classic Blalock-Taussig shunt. <br /> | * Post-shunt increase in [[Pulmonary artery|pulmonary arterial index]] (mm2/m2) is 158 +/- 21 versus 117 +/- 52 in classic Blalock-Taussig shunt. <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 03:35, 8 June 2020
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor-In-Chief: Usman Ali Akbar, M.B.B.S,
Overview
The Blalock-Taussig shunt is a surgical procedure that are done as palliative procedures for cyanotic heart defects . This procedure is used to deviate blood flow to lungs from systemic circulation to relieve cyanosis while a definitive corrective surgery can be performed at later time. Connection between subclavian artery and pulmonary artery is usually made . There are usually two types of shunts that are used i.e classic or original Blalock-Taussig shunt and modified Blalock Taussig shunt. The classic or original BT shunt has been modified into modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt (mBTS). In this modified procedure a graft from innominate artery or subclavian artery is placed to the corresponding pulmonary artery. [1]This type of BT shunt has superior prognostic value over classical shunt leading to greater rate of shunt patency at 3-5 years as compared to classic or original BT Shunt.[2]
Historical Perspective
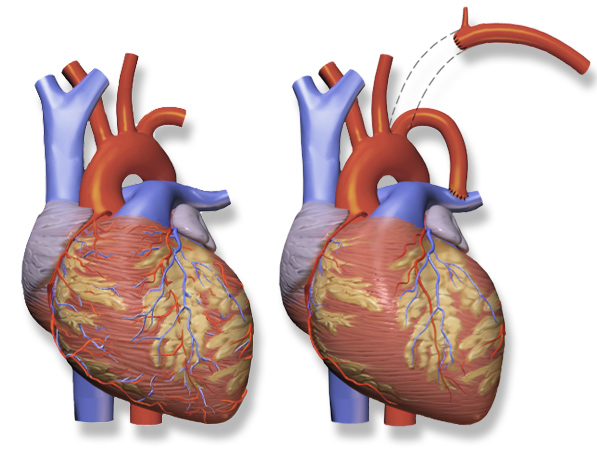
Classic or Original Shunt
The classic or original BT shunt procedure was named for Alfred Blalock, surgeon, Baltimore, (1899–1964) and Helen B. Taussig, cardiologist, Baltimore/Boston, (1898–1986) who, along with Blalock's African American laboratory technician Vivien Thomas (1910–1985), developed and described the procedure. Taussig noticed that the children with cyanosis along with congenital heart disease accompanied by patent ductus arteriosus have longer life time than those without PDA. Dr. Taussig approached Blalock and Thomas in their Hopkins laboratory in 1943 to work upon in this shunt as it was hypothesized that a shunt mimicking PDA can relieve the cyanosis and improve oxygenation in congential cyanotic diseases. Thomas, Vivien (1985). Partners of the heart : Vivien Thomas and his work with Alfred Blalock : an autobiography. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0812216342.
Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt

A modified method of inserting a shunt was developed in 1962 by Klinner using teflon as prosthetic graft material between the subclavian artery and the pulmonary artery is used to prevent scarring of the subclavian artery. [3]
Indications
- Tricuspid atresia
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Ebstein's Anomaly
- Hypoplastic Left Heart syndrome
- Pulmonary atresia
Procedure
Classic/Orginal Blalock-Taussig Shunt [1]
- For classic Blalock-Taussig shunt end to end anastomosis between the subclavian and pulmonary arteries is performed on opposite to the aortic arch to minimize the kinking of subclavian artery as it crosses aortic prominence.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| The relative diameter of subclavian artery prevents excessive blood flow to lungs | Thrombosis of shunt due to less diameter |
| Easily Reversible | Risk of Dissection |
| Increased rate of anastomosis growth | Subclavian artery is lost during the procedure |
Modified Blalock Taussig Shunt [1]
It is the most commonly used procedure now a days. First described and performed by Klinner et. al in 1962, this procedure hold superb prognosis over classic one. An Interposition PTFE or Gore-Tex graft is placed between the subclavian artery and the pulmonary artery. Hence no scarring of subclavian artery results.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| It can be done on the same side of the arch | Thrombosis |
| More patency than Classic BT shunt i.e >90 % at 2 years | Pseudoaneurysm |
| Pulmonary artery is less disorted | Chylothorax, Chylopericardium, chylous ascites |
Complications

The immediate post-operative complications include [2]
- Development of chylothorax, chylopericardium and chylous ascites
- Phrenic nerve resection leading to paralysis
- Anemia
- Congestive Heart failure resulting from excessive blood flow
- Modified PTFE grafts can result in formation of seroma or shunt occlusion due to hyperplasia of neo-intima
- Stenosis of innominate artery
Prognosis
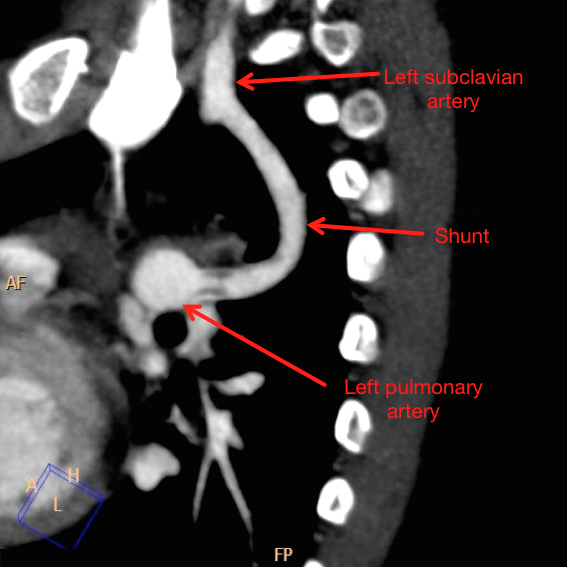
Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt has superior prognostic value over classic Blalock-Taussig Shunts. Following prognostic factors are compared between the two procedures in multiple studies. [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
- Rise in saturation of oxygen is greater in modified than in classic shunt
- Shunt patency is 88.8 % in modified for 3-5 years versus 90 % in first year, 62 % in two years and 78.0 % in 3 years for classic shunt.
- The risk of early shunt faliure is 20.8 % in modified and 51.7% in classic shunt.
- Post-shunt increase in pulmonary arterial index (mm2/m2) is 158 +/- 21 versus 117 +/- 52 in classic Blalock-Taussig shunt.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kiran U, Aggarwal S, Choudhary A, Uma B, Kapoor PM (2017). "The blalock and taussig shunt revisited". Ann Card Anaesth. 20 (3): 323–330. doi:10.4103/aca.ACA_80_17. PMC 5535574. PMID 28701598.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yuan SM, Shinfeld A, Raanani E (2009). "The Blalock-Taussig shunt". J Card Surg. 24 (2): 101–8. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8191.2008.00758.x. PMID 19040408.
- ↑ KLINNER W, PASINI M, SCHAUDIG A (1962). "[Anastomosis between systemic and pulmonary arteries with the aid of plastic prostheses in cyanotic heart diseases]". Thoraxchirurgie. 10: 68–75. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1096482. PMID 14457041.
- ↑ Al Jubair KA, Al Fagih MR, Al Jarallah AS, Al Yousef S, Ali Khan MA, Ashmeg A; et al. (1998). "Results of 546 Blalock-Taussig shunts performed in 478 patients". Cardiol Young. 8 (4): 486–90. doi:10.1017/s1047951100007150. PMID 9855103.
- ↑ Kim HK, Kim WH, Kim SC, Lim C, Lee CH, Kim SJ (2006). "Surgical strategy for pulmonary coarctation in the univentricular heart". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 29 (1): 100–4. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2005.10.032. PMID 16337132.
- ↑ Karpawich PP, Bush CP, Antillon JR, Amato JJ, Marbey ML, Agarwal KC (1985). "Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt in infants and young children. Clinical and catheterization assessment". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 89 (2): 275–9. PMID 3968910.
- ↑ Kulkarni H, Rajani R, Dalvi B, Gupta KG, Vora A, Kelkar P (1995). "Effect of Blalock Taussig shunt on clinical parameters, left ventricular function and pulmonary arteries". J Postgrad Med. 41 (2): 34–6. PMID 10707705.
- ↑ Bove EL, Kohman L, Sereika S, Byrum CJ, Kavey RE, Blackman MS; et al. (1987). "The modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: analysis of adequacy and duration of palliation". Circulation. 76 (3 Pt 2): III19–23. PMID 2441893.
- ↑ Ullom RL, Sade RM, Crawford FA, Ross BA, Spinale F (1987). "The Blalock-Taussig shunt in infants: standard versus modified". Ann Thorac Surg. 44 (5): 539–43. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62119-4. PMID 3675059.