Balsalazide: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{DrugProjectFormSinglePage | ||
| | |authorTag= | ||
| | |||
| | {{VP}} | ||
| | |||
| | <!--Overview--> | ||
| | |||
| | |genericName= | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |aOrAn= | ||
| | |||
| | a | ||
| | |||
| | |drugClass= | ||
| | |||
| | locally acting aminosalicylate | ||
| | |||
}} | |indication= | ||
mildly to moderately active [[ulcerative colitis]] in adults | |||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |||
|adverseReactions= | |||
[[headache]], [[abdominal pain]], [[diarrhea]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[respiratory infection]], and [[arthralgia]] | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | |||
|blackBoxWarningTitle= | |||
Title | |||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | |||
* Content | |||
<!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |||
=====Ulcerative Colitis===== | |||
* For treatment of active ulcerative colitis in adult patients, the usual dose is three 750 mg balsalazide disodium capsules to be taken 3 times a day (6.75 g per day) for up to 8 weeks. Some patients in the adult clinical trials required treatment for up to 12 weeks. | |||
*Balsalazide disodium capsules may also be administered by carefully opening the capsule and sprinkling the capsule contents on applesauce. The entire drug/applesauce mixture should be swallowed immediately; the contents may be chewed, if necessary, since contents of balsalazide disodium capsules are NOT coated beads/granules. Patients should be instructed not to store any drug/applesauce mixture for future use. | |||
*If the capsules are opened for sprinkling, color variation of the powder inside the capsules ranges from orange to yellow and is expected due to color variation of the active pharmaceutical ingredient. | |||
*Teeth and/or tongue staining may occur in some patients who use balsalazide disodium capsules in sprinkle form with food. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Developed by: | |||
* Class of Recommendation: | |||
* Strength of Evidence: | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
|fdaLIADPed= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Developed by: | |||
* Class of Recommendation: | |||
* Strength of Evidence: | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | |||
|contraindications= | |||
* Patients with [[hypersensitivity]] to salicylates or to any of the components of balsalazide disodium capsules or balsalazide metabolites. [[Hypersensitivity]] reactions may include, but are not limited to the following: [[anaphylaxis]], [[bronchospasm]], and skin reaction. | |||
<!--Warnings--> | |||
|warnings= | |||
====Precautions==== | |||
* Exacerbations of Ulcerative Colitis | |||
:*In the adult clinical trials, 3 out of 259 patients reported exacerbation of the symptoms of [[ulcerative colitis]]. | |||
:*Observe patients closely for worsening of these symptoms while on treatment. | |||
*Pyloric Stenosis | |||
:*Patients with [[pyloric stenosis]] may have prolonged gastric retention of balsalazide disodium capsules. | |||
*Renal | |||
:*Renal toxicity has been observed in animals and patients given other mesalamine products. Therefore, caution should be exercised when administering balsalazide capsules to patients with known [[renal dysfunction]] or a history of [[renal disease]]. | |||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | |||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | |||
|clinicalTrials= | |||
=====Adult Ulcerative Colitis===== | |||
*During clinical development, 259 adult patients with active ulcerative colitis were exposed to 6.75 g/day balsalazide in 4 controlled trials. | |||
*In the 4 controlled clinical trials patients receiving a balsalazide dose of 6.75 g/day most frequently reported the following adverse reactions: [[headache]] (8%), [[abdominal pain]] (6%), [[diarrhea]] (5%), [[nausea]] (5%), [[vomiting]] (4%), [[respiratory infection]] (4%), and [[arthralgia]] (4%). Withdrawal from therapy due to adverse reactions was comparable among patients on balsalazide and placebo. | |||
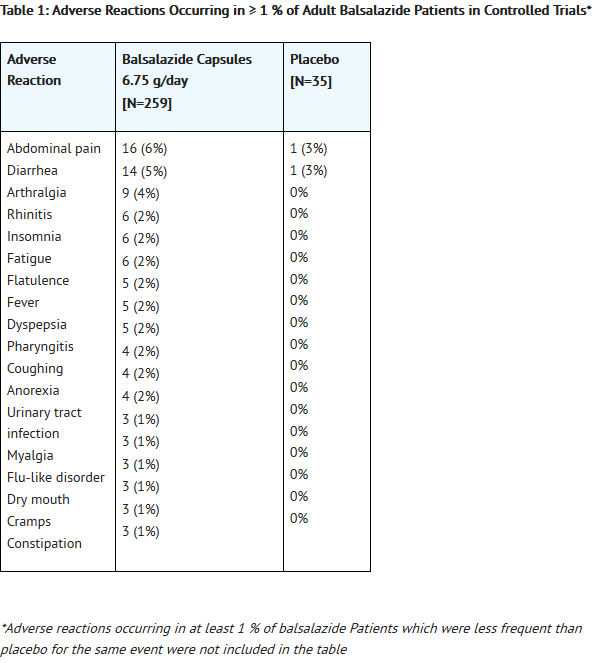
*Adverse reactions reported by 1% or more of patients who participated in the four well controlled, Phase 3 trials are presented by treatment group (Table 1). | |||
*The number of placebo patients (35), however, is too small for valid comparisons. Some adverse reactions, such as [[abdominal pain]], [[fatigue]], and [[nausea]] were reported more frequently in women than in men. [[Abdominal pain]], [[rectal bleeding]], and [[anemia]] can be part of the clinical presentation of [[ulcerative colitis]]. | |||
T1 | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | |||
|postmarketing= | |||
*The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of balsalazide in clinical practice: | |||
:*[[myocarditis]], [[pericarditis]], [[vasculitis]], [[pruritus]], [[pleural effusion]], [[pneumonia]] (with and without [[eosinophilia]]), [[alveolitis]], [[renal failure]], [[interstitial nephritis]], [[pancreatitis]], and [[alopecia]]. | |||
*Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to balsalazide. | |||
*Hepatic | |||
:*Postmarketing adverse reactions of hepatotoxicity have been reported for products which contain (or are metabolized to) [[mesalamine]], including elevated liver function tests (SGOT/AST, [[SGPT]]/[[ALT]], [[GGT]], [[LDH]], [[alkaline phosphatase]], [[bilirubin]]), [[jaundice]], [[cholestatic jaundice]], [[cirrhosis]], hepatocellular damage including [[liver necrosis]] and [[liver failure]]. Some of these cases were fatal; however, no fatalities associated with these adverse reactions were reported in balsalazide clinical trials. One case of Kawasaki-like syndrome which included hepatic function changes was also reported, however, this adverse reaction was not reported in balsalazide clinical trials. | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | |||
|drugInteractions= | |||
* In an in vitro study using human liver microsomes, balsalazide and its metabolites [5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid (N-Ac-5-ASA), 4-aminobenzoyl-β-alanine (4-ABA) and N-acetyl-4-aminobenzoyl-β–alanine (N-Ac-4-ABA)] were not shown to inhibit the major CYP enzymes evaluated (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4/5). Therefore, balsalazide and its metabolites are not expected to inhibit the metabolism of other drugs which are substrates of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4/5. | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |||
* '''Pregnancy Category B''' | |||
*Reproduction studies were performed in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 2 g/kg/day, 2.4 and 4.7 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area for the rat and rabbit, respectively, and revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to balsalazide disodium. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |||
* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | |||
|useInLaborDelivery= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | |||
|useInNursing= | |||
*It is not known whether balsalazide disodium is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when balsalazide is administered to a nursing woman. | |||
|useInPed= | |||
*Pediatric use information is protected by marketing exclusivity. | |||
|useInGeri= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to geriatric patients. | |||
|useInGender= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | |||
|useInRace= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific racial populations. | |||
|useInRenalImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with renal impairment. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with hepatic impairment. | |||
|useInReproPotential= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | |||
|useInImmunocomp= | |||
There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are immunocompromised. | |||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | |||
|administration= | |||
* Oral | |||
|monitoring= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | |||
|IVCompat= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>IV Compatibility</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Overdosage--> | |||
|overdose= | |||
===Acute Overdose=== | |||
*No case of overdose has occurred with balsalazide. A 3-year-old boy is reported to have ingested 2 g of another mesalamine product. He was treated with ipecac and activated charcoal with no adverse reactions. | |||
*If an overdose occurs with balsalazide, treatment should be supportive, with particular attention to correction of electrolyte abnormalities. | |||
===Chronic Overdose=== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Chronic Overdose</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacology--> | |||
<!--Drug box 2--> | |||
|drugBox= | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | |||
|mechAction= | |||
* Balsalazide disodium is delivered intact to the colon where it is cleaved by bacterial azoreduction to release equimolar quantities of mesalamine, which is the therapeutically active portion of the molecule, and the 4-aminobenzoyl-β-alanine carrier moiety. The carrier moiety released when balsalazide disodium is cleaved is only minimally absorbed and is largely inert. | |||
*The mechanism of action of 5-ASA is unknown, but appears to be local to the colonic mucosa rather than systemic. Mucosal production of arachidonic acid metabolites, both through the cyclooxygenase pathways, i.e., prostanoids, and through the lipoxygenase pathways, i.e., leukotrienes and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, is increased in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and it is possible that 5-ASA diminishes inflammation by blocking production of arachidonic acid metabolites in the colon. | |||
<!--Structure--> | |||
|structure= | |||
* | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | |||
|PD= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Pharmacodynamics</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | |||
|PK= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Pharmacokinetics</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | |||
|nonClinToxic= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Nonclinical Toxicology</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | |||
|clinicalStudies= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Studies</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--How Supplied--> | |||
|howSupplied= | |||
* | |||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | |||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Patient Counseling Information</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | |||
|alcohol= | |||
* Alcohol-{{PAGENAME}} interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |||
<!--Brand Names--> | |||
|brandNames= | |||
* ®<ref>{{Cite web | title = | url = }}</ref> | |||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | |||
|lookAlike= | |||
== | * A® — B®<ref name="www.ismp.org">{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://www.ismp.org | url = http://www.ismp.org | publisher = | date = }}</ref> | ||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | |||
|drugShortage= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Pill Image--> | |||
{{PillImage | |||
|fileName=No image.jpg|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
|drugName= | |||
|NDC= | |||
|drugAuthor= | |||
|ingredients= | |||
|pillImprint= | |||
|dosageValue= | |||
|dosageUnit= | |||
|pillColor= | |||
|pillShape= | |||
|pillSize= | |||
|pillScore= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Label Display Image--> | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}11.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{ | {{LabelImage | ||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}11.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
<!--Category--> | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
Revision as of 15:23, 16 February 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Balsalazide is a locally acting aminosalicylate that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis in adults. Common adverse reactions include headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, respiratory infection, and arthralgia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Ulcerative Colitis
- For treatment of active ulcerative colitis in adult patients, the usual dose is three 750 mg balsalazide disodium capsules to be taken 3 times a day (6.75 g per day) for up to 8 weeks. Some patients in the adult clinical trials required treatment for up to 12 weeks.
- Balsalazide disodium capsules may also be administered by carefully opening the capsule and sprinkling the capsule contents on applesauce. The entire drug/applesauce mixture should be swallowed immediately; the contents may be chewed, if necessary, since contents of balsalazide disodium capsules are NOT coated beads/granules. Patients should be instructed not to store any drug/applesauce mixture for future use.
- If the capsules are opened for sprinkling, color variation of the powder inside the capsules ranges from orange to yellow and is expected due to color variation of the active pharmaceutical ingredient.
- Teeth and/or tongue staining may occur in some patients who use balsalazide disodium capsules in sprinkle form with food.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Balsalazide in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Balsalazide in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Balsalazide in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Balsalazide in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Balsalazide in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Patients with hypersensitivity to salicylates or to any of the components of balsalazide disodium capsules or balsalazide metabolites. Hypersensitivity reactions may include, but are not limited to the following: anaphylaxis, bronchospasm, and skin reaction.
Warnings
Precautions
- Exacerbations of Ulcerative Colitis
- In the adult clinical trials, 3 out of 259 patients reported exacerbation of the symptoms of ulcerative colitis.
- Observe patients closely for worsening of these symptoms while on treatment.
- Pyloric Stenosis
- Patients with pyloric stenosis may have prolonged gastric retention of balsalazide disodium capsules.
- Renal
- Renal toxicity has been observed in animals and patients given other mesalamine products. Therefore, caution should be exercised when administering balsalazide capsules to patients with known renal dysfunction or a history of renal disease.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Adult Ulcerative Colitis
- During clinical development, 259 adult patients with active ulcerative colitis were exposed to 6.75 g/day balsalazide in 4 controlled trials.
- In the 4 controlled clinical trials patients receiving a balsalazide dose of 6.75 g/day most frequently reported the following adverse reactions: headache (8%), abdominal pain (6%), diarrhea (5%), nausea (5%), vomiting (4%), respiratory infection (4%), and arthralgia (4%). Withdrawal from therapy due to adverse reactions was comparable among patients on balsalazide and placebo.
- Adverse reactions reported by 1% or more of patients who participated in the four well controlled, Phase 3 trials are presented by treatment group (Table 1).
- The number of placebo patients (35), however, is too small for valid comparisons. Some adverse reactions, such as abdominal pain, fatigue, and nausea were reported more frequently in women than in men. Abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and anemia can be part of the clinical presentation of ulcerative colitis.
T1
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of balsalazide in clinical practice:
- myocarditis, pericarditis, vasculitis, pruritus, pleural effusion, pneumonia (with and without eosinophilia), alveolitis, renal failure, interstitial nephritis, pancreatitis, and alopecia.
- Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to balsalazide.
- Hepatic
- Postmarketing adverse reactions of hepatotoxicity have been reported for products which contain (or are metabolized to) mesalamine, including elevated liver function tests (SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT, GGT, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin), jaundice, cholestatic jaundice, cirrhosis, hepatocellular damage including liver necrosis and liver failure. Some of these cases were fatal; however, no fatalities associated with these adverse reactions were reported in balsalazide clinical trials. One case of Kawasaki-like syndrome which included hepatic function changes was also reported, however, this adverse reaction was not reported in balsalazide clinical trials.
Drug Interactions
- In an in vitro study using human liver microsomes, balsalazide and its metabolites [5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid (N-Ac-5-ASA), 4-aminobenzoyl-β-alanine (4-ABA) and N-acetyl-4-aminobenzoyl-β–alanine (N-Ac-4-ABA)] were not shown to inhibit the major CYP enzymes evaluated (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4/5). Therefore, balsalazide and its metabolites are not expected to inhibit the metabolism of other drugs which are substrates of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4/5.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category B
- Reproduction studies were performed in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 2 g/kg/day, 2.4 and 4.7 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area for the rat and rabbit, respectively, and revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to balsalazide disodium. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Balsalazide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Balsalazide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether balsalazide disodium is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when balsalazide is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Pediatric use information is protected by marketing exclusivity.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Balsalazide with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Balsalazide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Balsalazide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Balsalazide in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Balsalazide in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Balsalazide in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Balsalazide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Balsalazide in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Balsalazide in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
- No case of overdose has occurred with balsalazide. A 3-year-old boy is reported to have ingested 2 g of another mesalamine product. He was treated with ipecac and activated charcoal with no adverse reactions.
- If an overdose occurs with balsalazide, treatment should be supportive, with particular attention to correction of electrolyte abnormalities.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Balsalazide in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Balsalazide Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Balsalazide disodium is delivered intact to the colon where it is cleaved by bacterial azoreduction to release equimolar quantities of mesalamine, which is the therapeutically active portion of the molecule, and the 4-aminobenzoyl-β-alanine carrier moiety. The carrier moiety released when balsalazide disodium is cleaved is only minimally absorbed and is largely inert.
- The mechanism of action of 5-ASA is unknown, but appears to be local to the colonic mucosa rather than systemic. Mucosal production of arachidonic acid metabolites, both through the cyclooxygenase pathways, i.e., prostanoids, and through the lipoxygenase pathways, i.e., leukotrienes and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, is increased in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and it is possible that 5-ASA diminishes inflammation by blocking production of arachidonic acid metabolites in the colon.
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Balsalazide in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Balsalazide in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Balsalazide in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Balsalazide in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Balsalazide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Balsalazide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Balsalazide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Balsalazide in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Balsalazide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Balsalazide |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Balsalazide |Label Name=Balsalazide11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Balsalazide |Label Name=Balsalazide11.png
}}