Ozenoxacin
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sonya Gelfand
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Ozenoxacin is a quinolone antimicrobial that is FDA approved for the topical treatment of impetigo due to Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes in adult and pediatric patients 2 months of age and older. Common adverse reactions include rosacea and seborrheic dermatitis which were reported in 1 adult patient treated with ozenoxacin.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Ozenoxacin is indicated for the topical treatment of impetigo due to Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes in adult and pediatric patients 2 months of age and older.
Dosage and Administration
- Apply a thin layer of ozenoxacin topically to the affected area twice daily for five days. Affected area may be up to 100 cm2 in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older or 2% of the total body surface area and not exceeding 100 cm2</sup in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age.
- Wash hands after applying ozenoxacin cream.
- Ozenoxacin cream is for topical use only.
- Not for oral, ophthalmic, intranasal, or intravaginal use.
- The treated area may be covered with a sterile bandage or gauze dressing.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Cream: 1%, pale yellow cream. Each gram of ozenoxacin contains 10 mg of ozenoxacin.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding ozenoxacin Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use and Dosage (Adult) in the drug label.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding ozenoxacin Off-Label Non-Guideline-Supported Use and Dosage (Adult) in the drug label.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Indications
- Ozenoxacin is indicated for the topical treatment of impetigo due to Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes in adult and pediatric patients 2 months of age and older.
Dosage and Administration
- Apply a thin layer of ozenoxacin topically to the affected area twice daily for five days. Affected area may be up to 100 cm2 in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older or 2% of the total body surface area and not exceeding 100 cm2 in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age.
- Wash hands after applying ozenoxacin cream.
- Ozenoxacin cream is for topical use only.
- Not for oral, ophthalmic, intranasal, or intravaginal use.
- The treated area may be covered with a sterile bandage or gauze dressing.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Cream: 1%, pale yellow cream. Each gram of ozenoxacin contains 10 mg of ozenoxacin.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding ozenoxacin Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding ozenoxacin Off-Label Non-Guideline-Supported Use and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Contraindications
- None.
Warnings
Potential for Microbial Overgrowth
- The prolonged use of ozenoxacin may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible bacteria and fungi. If such infections occur during therapy, discontinue use and institute appropriate supportive measures.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- The safety profile of ozenoxacin was assessed in two clinical trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2) in 362 adult and pediatric patients two months of age and older with impetigo. The patients used at least one dose from a 5-day, twice a day regimen of ozenoxacin. Control groups included 361 patients who used placebo and 152 patients who used retapamulin ointment. The median age of the patients enrolled in the clinical trials was 10 years; 3 % of patients were 2 months to less than 2 years of age, 55 % of patients were 2 to less than 12 years of age, 11 % of patients were 12 to less than 18 years of age, and 31 % of patients were 18 years of age or older.
- Adverse reactions (rosacea and seborrheic dermatitis) were reported in 1 adult patient treated with ozenoxacin.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Ozenoxacin Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Ozenoxacin Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
- There are no available data on the use of ozenoxacin in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk. Systemic absorption of ozenoxacin in humans is negligible following topical administration of ozenoxacin (up to twice the concentration of the marketed formulation). Due to the negligible systemic exposure, it is not expected that maternal use of ozenoxacin will result in fetal exposure to the drug.
- Animal reproduction studies were not conducted with ozenoxacin. However, toxicity studies conducted in pregnant rats and rabbits administered the oral form of ozenoxacin showed no significant adverse developmental effects (at >10,000 times the maximum human plasma concentration seen with dermal application of ozenoxacin).
- The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ozenoxacin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Ozenoxacin during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Risk Summary
- No data are available regarding the presence of ozenoxacin in human milk, and the effects of ozenoxacin on the breastfed infant or on milk production. However, breastfeeding is not expected to result in exposure of the child to ozenoxacin due to the negligible systemic absorption of ozenoxacin in humans following topical administration of ozenoxacin. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ozenoxacin and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from ozenoxacin or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of ozenoxacin in the treatment of impetigo have been established in pediatric patients 2 months to 17 years of age. Use of ozenoxacin in pediatric patients (2 months to 17 years of age) is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of ozenoxacin in which 251 pediatric patients received at least one dose of ozenoxacin. The median age of the patients enrolled in the clinical trials was 10 years; 3 % of patients were 2 months to less than 2 years of age, 55 % of patients were 2 to less than 12 years of age, 11 % of patients were 12 to less than 18 years of age, and 31 % of patients were 18 years of age or older. In these studies, the maximum dose applied was approximately 0.5 g of ozenoxacin applied twice daily for up to 5 days (i.e., up to 10 applications total).
- The safety profile of ozenoxacin in pediatric patients 2 months and older was similar to that of adults.
- The safety and effectiveness of ozenoxacin in pediatric patients younger than 2 months of age have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of ozenoxacin did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ozenoxacin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ozenoxacin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ozenoxacin in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ozenoxacin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ozenoxacin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ozenoxacin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Apply a thin layer of ozenoxacin topically to the affected area twice daily for five days. Affected area may be up to 100 cm2 in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older or 2% of the total body surface area and not exceeding 100 cm2 in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age.
- Wash hands after applying ozenoxacin cream.
- Ozenoxacin cream is for topical use only.
- Not for oral, ophthalmic, intranasal, or intravaginal use.
- The treated area may be covered with a sterile bandage or gauze dressing.
Monitoring
- The absence or reduction in signs and symptoms of impetigo including, exudate or pus, crusting, tissue warmth, pain, erythema, and itching may indicate efficacy.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Ozenoxacin and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- Any sign or symptom of overdose, either topically or by accidental ingestion, should be treated symptomatically. No specific antidote is known.
Pharmacology
| |
Ozenoxacin
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
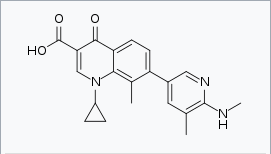
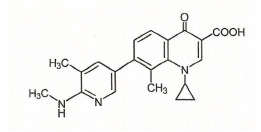
| 1-Cyclopropyl-8-methyl-7-[5-methyl-6-(methylamino)-3-pyridinyl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | D06 |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- Ozenoxacin is an antimicrobial drug.
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationship
- The exposure response relationship for ozenoxacin following topical application has not been studied, however; a relationship is unlikely because systemic exposure following topical application is negligible.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
- Four pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in 110 patients utilizing varying strengths of ozenoxacin cream, up to 2% (twice the concentration of the marketed formulation). Three of these studies assessed systemic absorption in healthy subjects and in subjects with impetigo. These studies were conducted with either single or repeated application of up to 1 g ozenoxacin cream to intact or abraded skin (up to 200 cm2 surface area). No systemic absorption was observed in 84 of 86 subjects, and negligible systemic absorption was observed at the level of detection (0.489 ng/mL) in 2 subjects.
Distribution
- Plasma protein binding of [14C]-ozenoxacin was moderate (~80 to 85%) and did not appear to be dependent on concentration. Since negligible systemic absorption was observed in clinical studies, tissue distribution has not been investigated in humans.
Elimination
Metabolism
- Ozenoxacin was not metabolized in the presence of fresh human skin discs and was minimally metabolized in human hepatocytes.
Excretion
- Studies have not been investigated in humans due to the negligible systemic absorption observed in clinical studies.
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
- Ozenoxacin is a quinolone antimicrobial drug. The mechanism of action involves the inhibition of bacterial DNA replication enzymes, DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV. Ozenoxacin has been shown to be bactericidal against S. aureus and S. pyogenes organisms.
Resistance
- The mechanism of quinolone resistance can arise through mutations of one or more of the genes that encode DNA gyrase or topoisomerase IV. Resistant organisms will typically carry a combination of mutations within gyrA and parC subunits.
- Overall the frequency of resistant mutants selected by ozenoxacin is ≤10-10.
Interaction with Other Antimicrobials
- Ozenoxacin has been tested in combination with 17 other commonly used antimicrobial agents against S. aureus and S.pyogenes. Antagonism interactions with ozenoxacin were observed with ciprofloxacin against S. aureus.
Antimicrobial Activity
- Ozenoxacin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections.
- Gram-positive bacteria
- Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant isolates)
- Streptococcus pyogenes
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted with ozenoxacin.
- Ozenoxacin demonstrated no genotoxicity when evaluated in vitro for gene mutation and/or chromosomal effects in the Ames test, mouse lymphoma cell assay, or when evaluated in vivo in a rat micronucleus test with demonstrated systemic exposure.
- Oral doses of ozenoxacin did not affect mating and fertility in male and female rats treated up to 500 mg/kg/day (about 8500 and 16,000 times respectively, the maximum human plasma concentration seen with dermal application of ozenoxacin 1% cream).
Clinical Studies
- The safety and efficacy of ozenoxacin for the treatment of impetigo was evaluated in two multi-center, randomized, double-blind placebo controlled clinical trials (Trial 1 (NCT01397461) and Trial 2, (NCT02090764)). Sevenhundred twenty-three (723) subjects two months of age and older with an affected body surface area of up to 100 cm2, and not exceeding 2% for subjects aged 2 months to 11 years were randomized to ozenoxacin or placebo. Subjects applied ozenoxacin or placebo twice daily for 5 days. Subjects with underlying skin disease (e.g., preexisting eczematous dermatitis), skin trauma, clinical evidence of secondary infection, or systemic signs and symptoms of infection (such as fever), were excluded from these studies.
- Overall clinical success was defined as no need for additional antimicrobial therapy of the baseline affected area(s) and absence/reduction in clinical signs and symptoms assessed at the end of therapy (Day 6-7), as follows: absence of exudates/pus, crusting, tissue warmth, and pain; and erythema/inflammation, tissue edema, and itching assessed as less than mild in Trial 1; and absence of blistering, exudates/pus, crusting, and itching/pain, and mild or improved erythema/inflammation in Trial 2. Table 2 below presents the results for clinical response at the end of therapy.

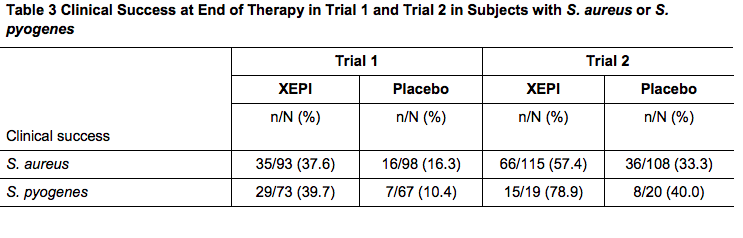
- The most commonly identified bacteria were S. aureus and S. pyogenes. Table 3 below presents the results for clinical success at end of therapy in subjects with S.aureus or S.pyogenes at baseline.
How Supplied
- Ozenoxacin cream, 1% is a pale yellow cream supplied in 10-, 30-, and 45-gram tubes. Each gram of cream contains 10 mg of ozenoxacin.
- NDC 43538-320-10 (10-gram tube)
- NDC 43538-320-30 (30-gram tube)
- NDC 43538-320-45 (45-gram tube)
Storage
- Store at 20ºC - 25ºC (68ºF - 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF - 86ºF).
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Ozenoxacin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Ozenoxacin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Advise patients (and/or their caregivers or guardians) using ozenoxacin of the following information and instructions:
- Use ozenoxacin as directed by the healthcare practitioner. As with any topical medication, patients and caregivers should wash their hands after application if the hands are not the area for treatment.
- Ozenoxacin is for external use only.Do not swallow ozenoxacin or use it in the eyes, on the mouth or lips, inside the nose, or inside the female genital area.
- The treated area may be covered by a sterile bandage or gauze dressing.
- Use the medication for the entire time recommended by the healthcare practitioner, even though symptoms may have improved.
- Notify the healthcare practitioner if there is no improvement in symptoms within 3 days after starting use of ozenoxacin.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Ozenoxacin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Xepi
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Ozenoxacin Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.