Epiglottis
Overview
|
WikiDoc Resources for Epiglottis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Epiglottis |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Epiglottis at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Epiglottis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Epiglottis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Epiglottis Discussion groups on Epiglottis Patient Handouts on Epiglottis Directions to Hospitals Treating Epiglottis Risk calculators and risk factors for Epiglottis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Epiglottis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
The epiglottis is a lid-like flap of elastic cartilage tissue covered with a mucus membrane, attached to the root of the tongue. It projects obliquely upwards behind the tongue and the hyoid bone.
Anatomy and function
The epiglottis guards the entrance of the glottis, the opening between the vocal folds.
It is normally pointed upward, but during swallowing, elevation of the hyoid bone draws the larynx upward; as a result, the epiglottis folds down to a more horizontal position. In this manner it prevents food from going into the trachea and instead directs it to the esophagus, which is more posterior.
The epiglottis is one of three large cartilaginous structures that make up the larynx (voice box).
Clinical significance
Reflexes
The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) sends fibers to the upper epiglottis that contribute to the afferent limb of the gag reflex. The superior laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) sends fibers to the lower epiglottis that contribute to the afferent limb of the cough reflex. [1]
Infection of the epiglottis
In children, the epiglottis will occasionally become infected with Haemophilus influenzae or Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria. Although easily treated, this condition is a medical emergency because without treatment the epiglottis may swell and block the trachea, causing massive inflammation. This condition has become rare in countries where vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae (HIB) is administered.
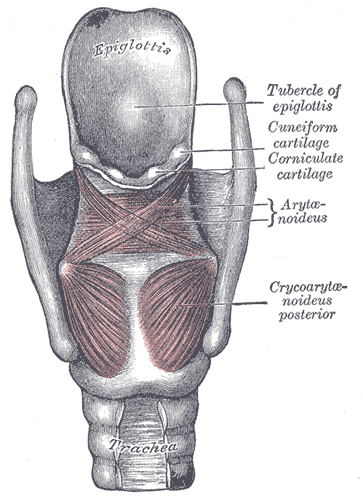
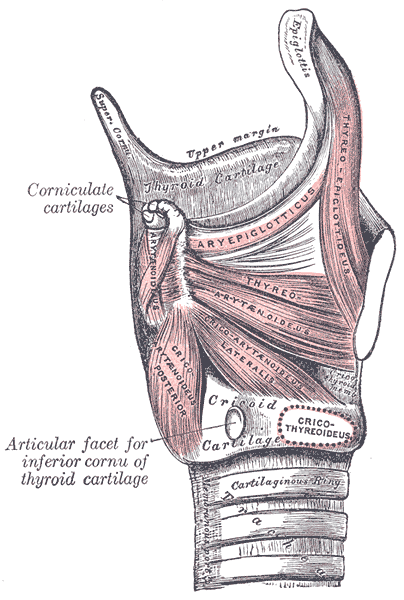
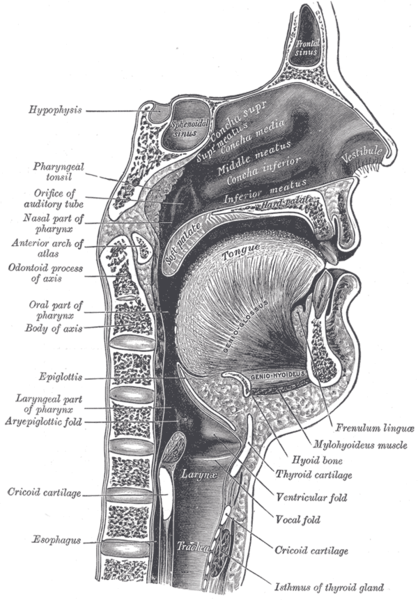
Additional images
-
Larynx
-
Cut through the larynx of a horse
-
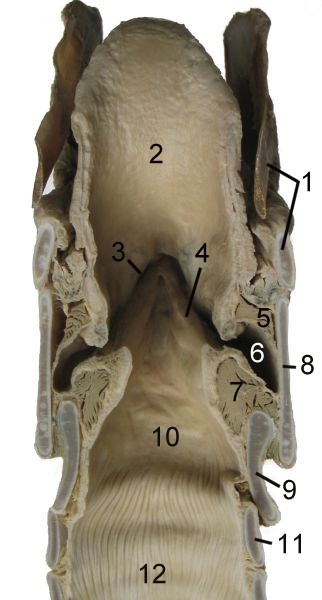
The cartilages of the larynx. Posterior view.
-
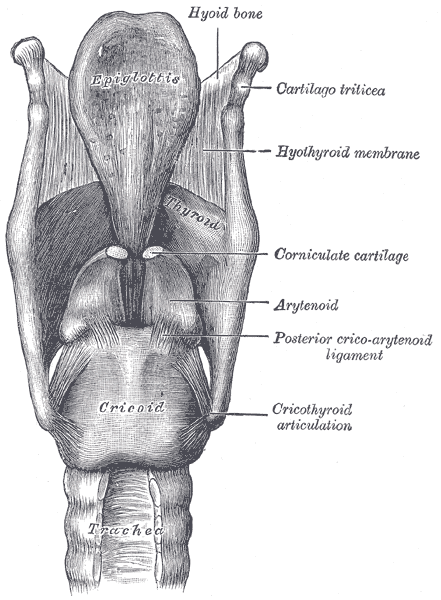
Ligaments of the larynx. Posterior view.
-
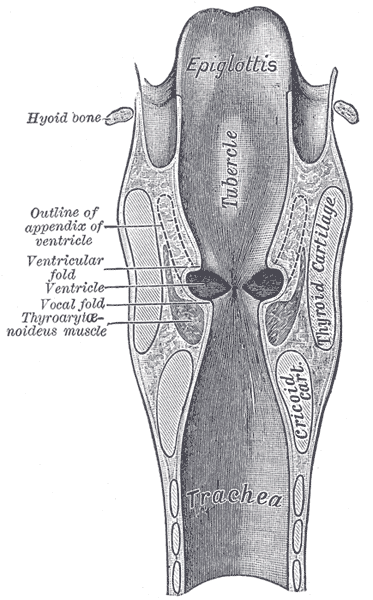
Coronal section of larynx and upper part of trachea.
-
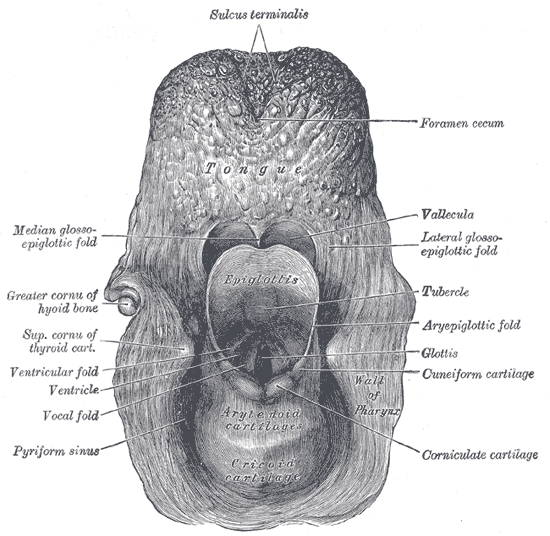
The entrance to the larynx, viewed from behind.
-
Muscles of larynx. Posterior view.
-
Muscles of larynx. Side view. Right lamina of thyroid cartilage removed.
-
Sagittal section of nose mouth, pharynx, and larynx.
References
- ↑ April, Ernest. Clinical Anatomy, 3rd ed. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins.
External links
ca:Epiglotis de:Epiglottis eo:Epigloto ko:후두개 it:Epiglottide he:מכסה הגרון nl:Strotklepje sv:Struplock uk:Надгортанник yi:אפיגלויטיס