WBR0505
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Gonzalo A. Romero, M.D. [1] (Reviewed by Alison Leibowitz)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Neurology, SubCategory::Oncology, SubCategory::Reproductive |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 57-year-old male patient comes to the ER after presenting with visual deficits. The symptoms have been gradually worsening over the last 6 months. His wife denies any history of trauma or drug ingestion. You preform a physical examination and find that his vitals are within normal limits. On neurological exam, you encounter a right hemianopsia with macular sparing, and becomes concerned that the patient may have a stroke or a tumor. A CT scan is ordered and shows a mass in the posterior fossa. Forty-eight hours following admission, the patient develops a Grand-mal seizure and undergoes respiratory arrest. Despite aggressive resuscitation measures, the patient dies. Concerned about malpraxis, you order an autopsy. Upon entering the skull, the pathologist notices a tumor arising from the membranes covering the brain. A specimen under the microscope shows the picture below. Which of the following ovarian tumors is also associated with the latter histologic findings of this tumor?
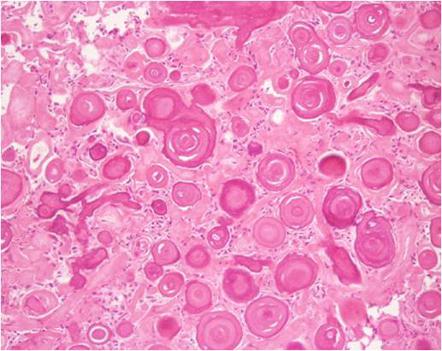 |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Granulosa cell tumor |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::A Granulosa cell tumor is a non-germ cell ovarian tumor which secretes estrogen and can cause precocious puberty in children and endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma in adults. Histologically Granulosa cell tumors are characterized by Call-Exner bodies, which are small follicles filled with eosinophilic secretions. It often presents with abnormal uterine bleeding.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Brenner tumor |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::A Brenner tumor is a benign and unilateral ovarian tumor. It originates from the surface epithelial-stromal. Macroscopically Brenner tumors are solid, pale yellow-tan and encapsulated. Histologically Brenner tumors contains clusters of cells resembling transitional epithelium of the bladder with "coffee bean" shaped nuclei.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Serous cystadenocarcinoma |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Just under half of ovarian tumors are serous cystadenocarcinoma. They are malignant and frequently bilateral with Psammoma bodies appearing on histology.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Serous cystadenoma |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Approximately 1/5 of ovarian tumors are serous cystadenoma. They are benign tumors and it appear bilaterally. On microscopic examination serous cystadenoma are lined with fallopian tube-like epithelium.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Kruckenberg tumor |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::A Kruckenberg tumor is a malignant ovarian tumor resulting from GI malignancy metastasis, which causes a mucin-secreting signet cell adenocarcinoma.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::C |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::This patient presents with hallucinations and visual deficits which worsened over time and right hemianopsia with macular sparing. The CT scan displays a tumor rising from the occipital region of the meninges, which correlates with the clinical findings. The histo-pathologic findings of laminated, concentric, calcific spherules are also known as Psammoma bodies, which are associated with meningioma compressing the occipital lobe. Psammoma bodies are also found in:
WikiDoc Mnemonic: PSaMMoma :
Educational Objective:
Psammoma bodies are often present in meningiomas within the central nervous system.
References: First Aid 2013 reproductive chapter |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Psammoma bodies |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |