Thin basement membrane disease biopsy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Renal Biopsy== | ==Renal Biopsy== | ||
[[Thin Basement Membrane Disease.jpg|300px|right|1(A) and 1(B) showing [[light microscopy]] of [[Thin basement membrane disease]] with cystic dilation. | [[File:Thin Basement Membrane Disease.jpg|300px|right|1(A) and 1(B) showing [[light microscopy]] of [[Thin basement membrane disease]] with cystic dilation. | ||
1(C), 1(D), 1(E) showing [[GBM]] using different [[Immunofluoroscence]] | 1(C), 1(D), 1(E) showing [[GBM]] using different [[Immunofluoroscence]] | ||
1(F), 1(G) showing thin [[GBM]] without [[electron]] deposition using [[Electron microscope]] | 1(F), 1(G) showing thin [[GBM]] without [[electron]] deposition using [[Electron microscope]] | ||
Revision as of 07:06, 20 October 2020
|
Thin basement membrane disease Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Thin basement membrane disease from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Thin basement membrane disease biopsy On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Thin basement membrane disease biopsy |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Thin basement membrane disease |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Thin basement membrane disease biopsy |
Overview
The WHO guideline for normal GBM thickness is 250nm for adult and 180nm for children of 2-11 years of age. Diffuse thinning of 50% of glomerular basement membrane in glomerular capillaries is the criteria for diagnosing TBMD on Electron microscopy.
Renal Biopsy
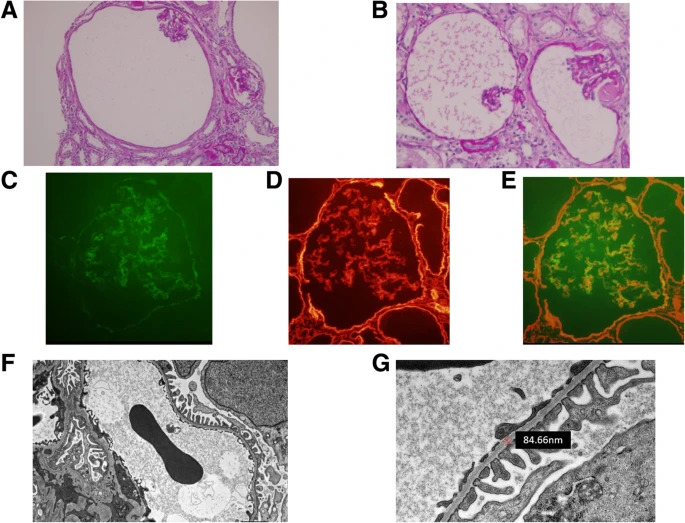
- Light Microscopy of renal samples shows usually normal glomerular histopathology with minimally showing nonspecific findings including matrix expansion, mesangial cellular proferation, RBCs in glomerular spaces with focal segmental glomerulo sclerosis or fibrosis on rare occasions.[1]
- Electron microscopy of renal samples shows diffuse thinning of 50% of glomerular basement membrane in glomerular capillaries. GBM thickness should be measured according to age.The WHO guideline for normal GBM thickness is 250nm for adult and 180nm for children of 2-11 years of age. [2] Early stages of X-linked alport syndrome is similar to TBMD, so differential features including lamellation/thickening must be ruled out on electron microscopy. [3]
- Immunohistochemistry of renal samples evaluates Type 4 collagen alpha 3-alpha5 chains to differentiate TBMD and early stage of alport syndrome.[4]
References
- ↑ Foster K, Markowitz GS, D'Agati VD (May 2005). "Pathology of thin basement membrane nephropathy". Semin Nephrol. 25 (3): 149–58. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2005.01.006. PMID 15880325.
- ↑ Vogler C, McAdams AJ, Homan SM (1987). "Glomerular basement membrane and lamina densa in infants and children: an ultrastructural evaluation". Pediatr Pathol. 7 (5–6): 527–34. doi:10.3109/15513818709161416. PMID 3449814.
- ↑ "Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy | American Society of Nephrology".
- ↑ Gubler MC, Knebelmann B, Beziau A, Broyer M, Pirson Y, Haddoum F, Kleppel MM, Antignac C (April 1995). "Autosomal recessive Alport syndrome: immunohistochemical study of type IV collagen chain distribution". Kidney Int. 47 (4): 1142–7. doi:10.1038/ki.1995.163. PMID 7783412.