Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung chest x ray: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Chest X Ray== | ==Chest X Ray== | ||
*Conventional chest radiograph may be helpful in the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung | |||
*The majority of squamous cell carcinomas of the lung require further evaluation with [[Computed tomography|CT scan]] and [[MRI]] | |||
*Common features of conventional radiography to perform the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include:<ref name="pmid7208937">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kundel HL |title=Predictive value and threshold detectability of lung tumors |journal=Radiology |volume=139 |issue=1 |pages=25–9 |year=1981 |pmid=7208937 |doi=10.1148/radiology.139.1.7208937 |url=}}</ref> | |||
:*Primary detection and characterization of [[Parenchyma|parenchymal]] tumor | |||
:*Assessment of [[Bronchi|main bronchi]] and tracheal involvement | |||
:*Detection of [[chest wall]] invasion | |||
:*Assessment of hiliar and [[Mediastinal tumor|mediastinal invasion]]/adenopathy | |||
:*Detection of obstructive atelectasias and signs of [[pneumonitis]] | |||
*On conventional radiography, characteristic findings of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include:<ref name="pmid7208937">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kundel HL |title=Predictive value and threshold detectability of lung tumors |journal=Radiology |volume=139 |issue=1 |pages=25–9 |year=1981 |pmid=7208937 |doi=10.1148/radiology.139.1.7208937 |url=}}</ref> | |||
:*Rounded or spiculated mass | |||
:*Bulky hilum (representing the tumor and local nodal involvement) | |||
:*Lobar collapse | |||
:*[[Cavitation]] may be seen as an air-fluid level | |||
*On conventional radiography, signs of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include:<ref name="pmid7208937">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kundel HL |title=Predictive value and threshold detectability of lung tumors |journal=Radiology |volume=139 |issue=1 |pages=25–9 |year=1981 |pmid=7208937 |doi=10.1148/radiology.139.1.7208937 |url=}}</ref> | |||
:* '''Golden "S" sign''': created by a central mass obstructing the upper lobe bronchus and should raise suspicion of a primary lung cancer. Usually seen with right upper lobe collapse. | |||
:* '''Coin lesion''': round or oval, well-circumscribed lesion | |||
:* '''Luftsichel sign''': curvilinear opacity represents compensatory hyperinflation of the lobe | |||
:* '''Bronchial cut off sign''': abrupt truncation of a bronchus from obstruction | |||
==Gallery== | |||
<div align="left"> | |||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
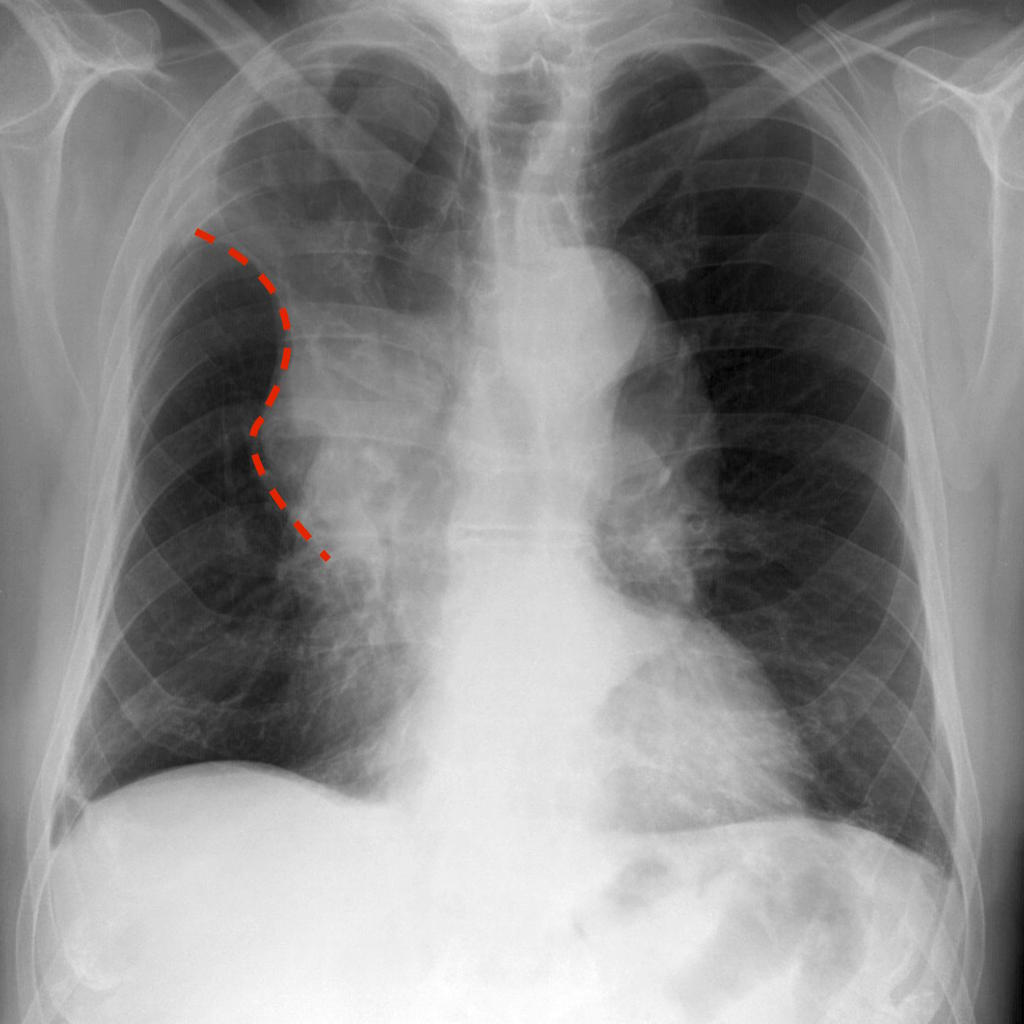
Image:Golden-s-sign marked.jpg|'''Golden "S" Sign''' (or reverse "S" sign of Golden) : right upper lobar collapse (the right upper lobe appearing dense and shifting medially and upwards, with a central mass expanding the hilum | |||
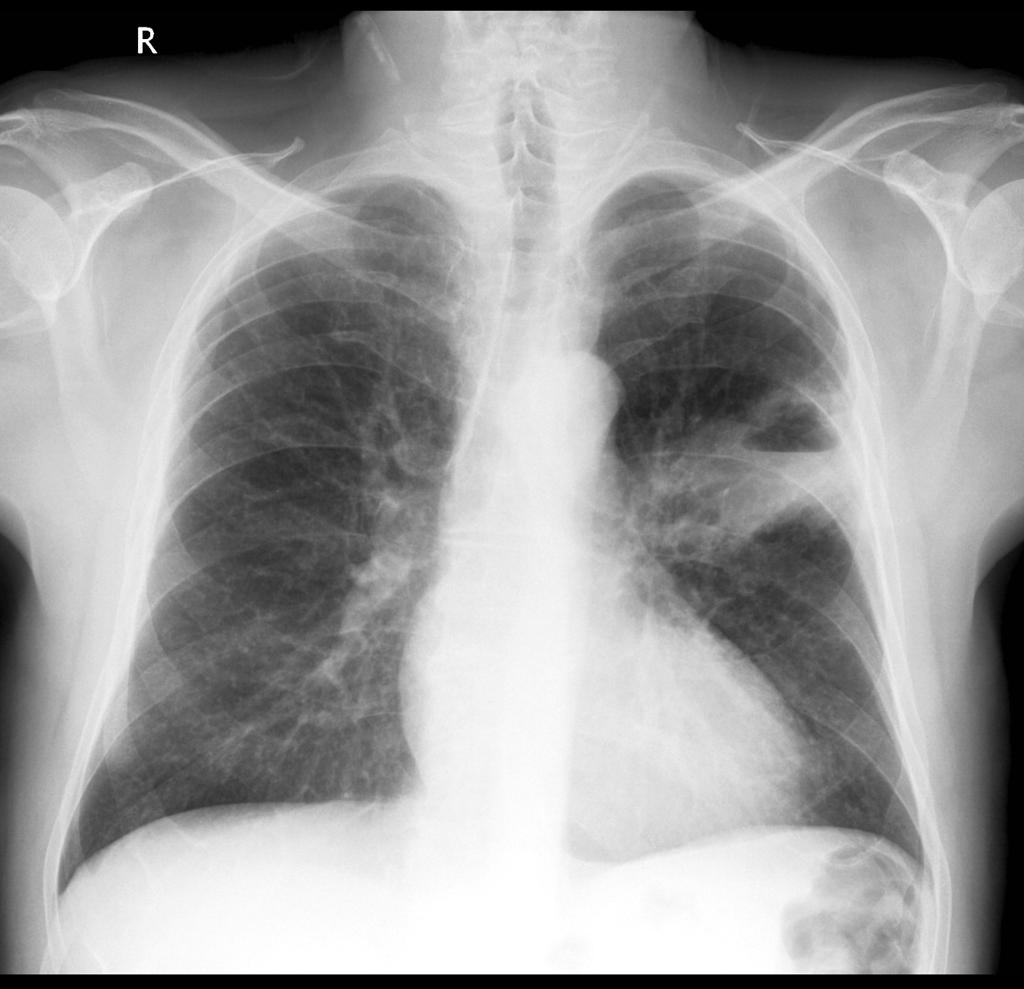
Image:Cavitating-lung-cancer.jpg|'''Squameous cell lung cancer''': lung cavitating mass left upper lobe adjacent to the oblique fissure. The prominent air-fluid level is best seen on the lateral radiograph | |||
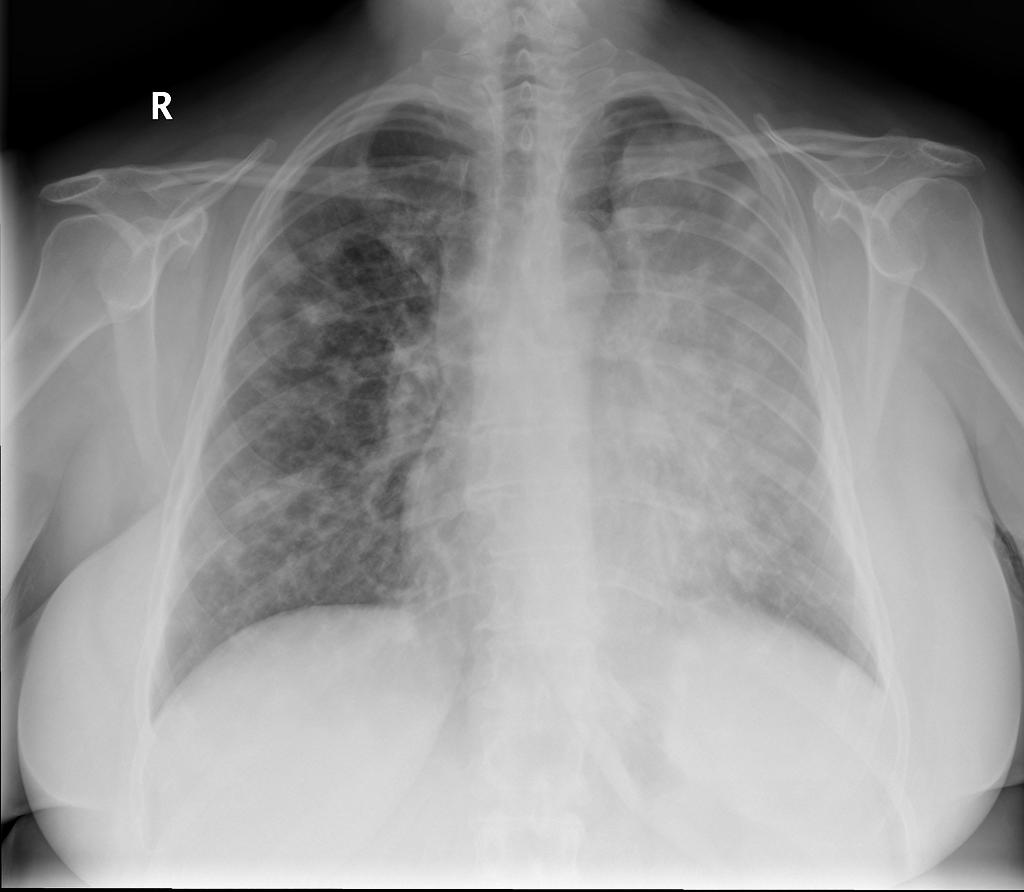
Image:Luftsichel-sign-in-lung-cancer.jpg|'''Luftsichel sign''': curvilinear opacity at the left apex represents compensatory hyperinflation of the left lower lobe | |||
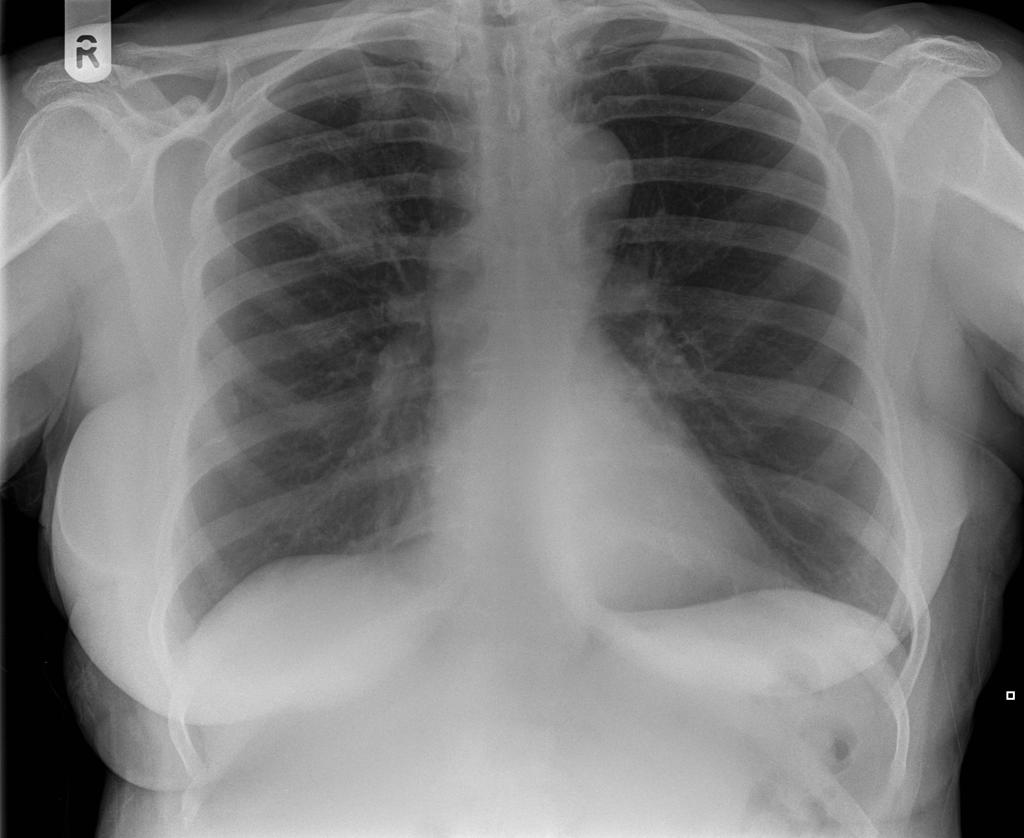
Image:Pulmonary-coin-lesion.jpg|'''Coin lesion sign''': round or oval, well-circumscribed lesion, compatible with primary lung cancer | |||
Image:Bronchial cut off sign.jpg| '''Bronchial cut off sign''': abrupt truncation of a bronchus from obstruction | |||
</gallery> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 4 March 2016
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung chest x ray |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Shanshan Cen, M.D. [2] Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [3]
Overview
On chest X ray, characteristic findings of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include: rounded or spiculated mass, bulky hilum (representing the tumor and local nodal involvement) and lobar collapse.[1]
Chest X Ray
- Conventional chest radiograph may be helpful in the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
- The majority of squamous cell carcinomas of the lung require further evaluation with CT scan and MRI
- Common features of conventional radiography to perform the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include:[2]
- Primary detection and characterization of parenchymal tumor
- Assessment of main bronchi and tracheal involvement
- Detection of chest wall invasion
- Assessment of hiliar and mediastinal invasion/adenopathy
- Detection of obstructive atelectasias and signs of pneumonitis
- On conventional radiography, characteristic findings of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include:[2]
- Rounded or spiculated mass
- Bulky hilum (representing the tumor and local nodal involvement)
- Lobar collapse
- Cavitation may be seen as an air-fluid level
- On conventional radiography, signs of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, include:[2]
- Golden "S" sign: created by a central mass obstructing the upper lobe bronchus and should raise suspicion of a primary lung cancer. Usually seen with right upper lobe collapse.
- Coin lesion: round or oval, well-circumscribed lesion
- Luftsichel sign: curvilinear opacity represents compensatory hyperinflation of the lobe
- Bronchial cut off sign: abrupt truncation of a bronchus from obstruction
Gallery
-
Golden "S" Sign (or reverse "S" sign of Golden) : right upper lobar collapse (the right upper lobe appearing dense and shifting medially and upwards, with a central mass expanding the hilum
-
Squameous cell lung cancer: lung cavitating mass left upper lobe adjacent to the oblique fissure. The prominent air-fluid level is best seen on the lateral radiograph
-
Luftsichel sign: curvilinear opacity at the left apex represents compensatory hyperinflation of the left lower lobe
-
Coin lesion sign: round or oval, well-circumscribed lesion, compatible with primary lung cancer
-
Bronchial cut off sign: abrupt truncation of a bronchus from obstruction
References
- ↑ Rosado-de-Christenson ML, Templeton PA, Moran CA (1994). "Bronchogenic carcinoma: radiologic-pathologic correlation". Radiographics. 14 (2): 429–46, quiz 447–8. doi:10.1148/radiographics.14.2.8190965. PMID 8190965.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kundel HL (1981). "Predictive value and threshold detectability of lung tumors". Radiology. 139 (1): 25–9. doi:10.1148/radiology.139.1.7208937. PMID 7208937.