Saxagliptin
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Saxagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Common adverse reactions include upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Monotherapy and Combination Therapy
- ONGLYZA is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in multiple clinical settings.
- The recommended dosage of ONGLYZA is 2.5 mg or 5 mg once daily taken regardless of meals.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Saxagliptin in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Saxagliptin in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Saxagliptin in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Saxagliptin in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Saxagliptin in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- ONGLYZA is contraindicated in patients with a history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to ONGLYZA, such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, or exfoliative skin conditions.
Warnings
Precautions
- There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis in patients taking ONGLYZA. After initiation of ONGLYZA, patients should be observed carefully for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, ONGLYZA should promptly be discontinued and appropriate management should be initiated. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using ONGLYZA.
- Hypoglycemia with Cocomitant Use of Sulfonylurea or Insulin
- When ONGLYZA was used in combination with a sulfonylurea or with insulin, medications known to cause hypoglycemia, the incidence of confirmed hypoglycemia was increased over that of placebo used in combination with a sulfonylurea or with insulin. Therefore, a lower dose of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with ONGLYZA.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with ONGLYZA. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with ONGLYZA, with some reports occurring after the first dose. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue ONGLYZA, assess for other potential causes for the event, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes.
- Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with ONGLYZA.
- Macrovascular Outcomes
- There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with ONGLYZA or any other antidiabetic drug.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions with Monotherapy and with Add-On Combination Therapy
- In two placebo-controlled monotherapy trials of 24-weeks duration, patients were treated with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg daily, ONGLYZA 5 mg daily, and placebo. Three 24-week, placebo-controlled, add-on combination therapy trials were also conducted: one with metformin, one with a thiazolidinedione (pioglitazone or rosiglitazone), and one with glyburide. In these three trials, patients were randomized to add-on therapy with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg daily, ONGLYZA 5 mg daily, or placebo. A saxagliptin 10 mg treatment arm was included in one of the monotherapy trials and in the add-on combination trial with metformin. The 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage.
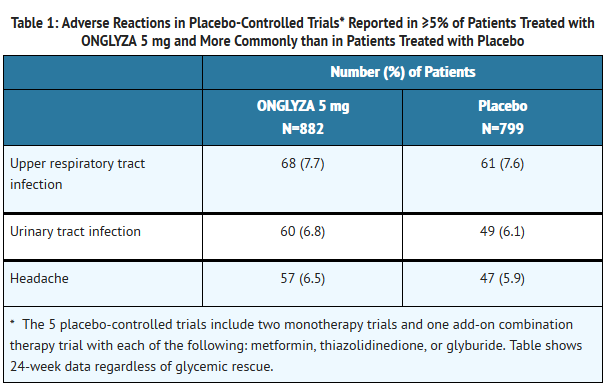
- In a prespecified pooled analysis of the 24-week data (regardless of glycemic rescue) from the two monotherapy trials, the add-on to metformin trial, the add-on to thiazolidinedione (TZD) trial, and the add-on to glyburide trial, the overall incidence of adverse events in patients treated with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg and ONGLYZA 5 mg was similar to placebo (72% and 72.2% versus 70.6%, respectively). Discontinuation of therapy due to adverse events occurred in 2.2%, 3.3%, and 1.8% of patients receiving ONGLYZA 2.5 mg, ONGLYZA 5 mg, and placebo, respectively. The most common adverse events (reported in at least 2 patients treated with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg or at least 2 patients treated with ONGLYZA 5 mg) associated with premature discontinuation of therapy included lymphopenia (0.1% and 0.5% versus 0%, respectively), rash (0.2% and 0.3% versus 0.3%), blood creatinine increased (0.3% and 0% versus 0%), and blood creatine phosphokinase increased (0.1% and 0.2% versus 0%). The adverse reactions in this pooled analysis reported (regardless of investigator assessment of causality) in ≥5% of patients treated with ONGLYZA 5 mg, and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo are shown in Table 1.
T1
- In patients treated with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg, headache (6.5%) was the only adverse reaction reported at a rate ≥5% and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo.
- In this pooled analysis, adverse reactions that were reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg or ONGLYZA 5 mg and ≥1% more frequently compared to placebo included: sinusitis (2.9% and 2.6% versus 1.6%, respectively), abdominal pain (2.4% and 1.7% versus 0.5%), gastroenteritis (1.9% and 2.3% versus 0.9%), and vomiting (2.2% and 2.3% versus 1.3%).
- In the add-on to TZD trial, the incidence of peripheral edema was higher for ONGLYZA 5 mg versus placebo (8.1% and 4.3%, respectively). The incidence of peripheral edema for ONGLYZA 2.5 mg was 3.1%. None of the reported adverse reactions of peripheral edema resulted in study drug discontinuation. Rates of peripheral edema for ONGLYZA 2.5 mg and ONGLYZA 5 mg versus placebo were 3.6% and 2% versus 3% given as monotherapy, 2.1% and 2.1% versus 2.2% given as add-on therapy to metformin, and 2.4% and 1.2% versus 2.2% given as add-on therapy to glyburide.
- The incidence rate of fractures was 1.0 and 0.6 per 100 patient-years, respectively, for ONGLYZA (pooled analysis of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg) and placebo. The 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage. The incidence rate of fracture events in patients who received ONGLYZA did not increase over time. Causality has not been established and nonclinical studies have not demonstrated adverse effects of ONGLYZA on bone.
- An event of thrombocytopenia, consistent with a diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, was observed in the clinical program. The relationship of this event to ONGLYZA is not known.
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Renal Impairment
- ONGLYZA 2.5 mg was compared to placebo in a 12-week trial in 170 patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate or severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The incidence of adverse events, including serious adverse events and discontinuations due to adverse events, was similar between ONGLYZA and placebo.
=Adverse Reactions with Concomitant Use with Insulin
- In the add-on to insulin trial, the incidence of adverse events, including serious adverse events and discontinuations due to adverse events, was similar between ONGLYZA and placebo, except for confirmed hypoglycemia.
Adverse Reactions with Concomitant Use with Metformin in Treatment-Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Table 2 shows the adverse reactions reported (regardless of investigator assessment of causality) in ≥5% of patients participating in an additional 24-week, active-controlled trial of coadministered ONGLYZA and metformin in treatment-naive patients.
Hypoglycemia
- Adverse reactions of hypoglycemia were based on all reports of hypoglycemia. A concurrent glucose measurement was not required or was normal in some patients. Therefore, it is not possible to conclusively determine that all these reports reflect true hypoglycemia.
- In the add-on to glyburide study, the overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was higher for ONGLYZA 2.5 mg and ONGLYZA 5 mg (13.3% and 14.6%) versus placebo (10.1%). The incidence of confirmed hypoglycemia in this study, defined as symptoms of hypoglycemia accompanied by a fingerstick glucose value of ≤50 mg/dL, was 2.4% and 0.8% for ONGLYZA 2.5 mg and ONGLYZA 5 mg and 0.7% for placebo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. The incidence of reported hypoglycemia for ONGLYZA 2.5 mg and ONGLYZA 5 mg versus placebo given as monotherapy was 4% and 5.6% versus 4.1%, respectively, 7.8% and 5.8% versus 5% given as add-on therapy to metformin, and 4.1% and 2.7% versus 3.8% given as add-on therapy to TZD. The incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 3.4% in treatment-naive patients given ONGLYZA 5 mg plus metformin and 4% in patients given metformin alone.
- In the active-controlled trial comparing add-on therapy with ONGLYZA 5 mg to glipizide in patients inadequately controlled on metformin alone, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 3% (19 events in 13 patients) with ONGLYZA 5 mg versus 36.3% (750 events in 156 patients) with glipizide. Confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia (accompanying fingerstick blood glucose ≤50 mg/dL) was reported in none of the ONGLYZA-treated patients and in 35 glipizide-treated patients (8.1%) (p<0.0001).
- During 12 weeks of treatment in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment or ESRD, the overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 20% among patients treated with ONGLYZA 2.5 mg and 22% among patients treated with placebo. Four ONGLYZA-treated patients (4.7%) and three placebo-treated patients (3.5%) reported at least one episode of confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia (accompanying fingerstick glucose ≤50 mg/dL).
- In the add-on to insulin trial, the overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 18.4% for ONGLYZA 5 mg and 19.9% for placebo. However, the incidence of confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia (accompanying fingerstick blood glucose ≤50 mg/dL) was higher with ONGLYZA 5 mg (5.3%) versus placebo (3.3%).
- In the add-on to metformin plus sulfonylurea trial, the overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 10.1% for ONGLYZA 5 mg and 6.3% for placebo. Confirmed hypoglycemia was reported in 1.6% of the ONGLYZA-treated patients and in none of the placebo-treated patients.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Hypersensitivity-related events, such as urticaria and facial edema in the 5-study pooled analysis up to Week 24 were reported in 1.5%, 1.5%, and 0.4% of patients who received ONGLYZA 2.5 mg, ONGLYZA 5 mg, and placebo, respectively. None of these events in patients who received ONGLYZA required hospitalization or were reported as life-threatening by the investigators. One ONGLYZA-treated patient in this pooled analysis discontinued due to generalized urticaria and facial edema.
Infections
- In the unblinded, controlled, clinical trial database for ONGLYZA to date, there have been 6 (0.12%) reports of tuberculosis among the 4959 ONGLYZA-treated patients (1.1 per 1000 patient-years) compared to no reports of tuberculosis among the 2868 comparator-treated patients. Two of these six cases were confirmed with laboratory testing. The remaining cases had limited information or had presumptive diagnoses of tuberculosis. None of the six cases occurred in the United States or in Western Europe. One case occurred in Canada in a patient originally from Indonesia who had recently visited Indonesia. The duration of treatment with ONGLYZA until report of tuberculosis ranged from 144 to 929 days. Post-treatment lymphocyte counts were consistently within the reference range for four cases. One patient had lymphopenia prior to initiation of ONGLYZA that remained stable throughout ONGLYZA treatment. The final patient had an isolated lymphocyte count below normal approximately four months prior to the report of tuberculosis. There have been no spontaneous reports of tuberculosis associated with ONGLYZA use. Causality has not been estimated and there are too few cases to date to determine whether tuberculosis is related to ONGLYZA use.
- There has been one case of a potential opportunistic infection in the unblinded, controlled clinical trial database to date in an ONGLYZA-treated patient who developed suspected foodborne fatal salmonella sepsis after approximately 600 days of ONGLYZA therapy. There have been no spontaneous reports of opportunistic infections associated with ONGLYZA use.
Vital Signs
- No clinically meaningful changes in vital signs have been observed in patients treated with ONGLYZA.
Laboratory Tests
Absolute Lymphocyte Counts
- There was a dose-related mean decrease in absolute lymphocyte count observed with ONGLYZA. From a baseline mean absolute lymphocyte count of approximately 2200 cells/microL, mean decreases of approximately 100 and 120 cells/microL with ONGLYZA 5 mg and 10 mg, respectively, relative to placebo were observed at 24 weeks in a pooled analysis of five placebo-controlled clinical studies. Similar effects were observed when ONGLYZA 5 mg was given in initial combination with metformin compared to metformin alone. There was no difference observed for ONGLYZA 2.5 mg relative to placebo. The proportion of patients who were reported to have a lymphocyte count ≤750 cells/microL was 0.5%, 1.5%, 1.4%, and 0.4% in the ONGLYZA 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. In most patients, recurrence was not observed with repeated exposure to ONGLYZA although some patients had recurrent decreases upon rechallenge that led to discontinuation of ONGLYZA. The decreases in lymphocyte count were not associated with clinically relevant adverse reactions. The 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage.
- The clinical significance of this decrease in lymphocyte count relative to placebo is not known. When clinically indicated, such as in settings of unusual or prolonged infection, lymphocyte count should be measured. The effect of ONGLYZA on lymphocyte counts in patients with lymphocyte abnormalities (e.g., human immunodeficiency virus) is unknown.
Postmarketing Experience
- Additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ONGLYZA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions.
- Acute pancreatitis.
Drug Interactions
- Strong Inhibitors of CYP3A4/5 Enzymes
- Ketoconazole significantly increased saxagliptin exposure. Similar significant increases in plasma concentrations of saxagliptin are anticipated with other strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, and telithromycin). The dose of ONGLYZA should be limited to 2.5 mg when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category B
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, ONGLYZA, like other antidiabetic medications, should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Saxagliptin was not teratogenic at any dose tested when administered to pregnant rats and rabbits during periods of organogenesis. Incomplete ossification of the pelvis, a form of developmental delay, occurred in rats at a dose of 240 mg/kg, or approximately 1503 and 66 times human exposure to saxagliptin and the active metabolite, respectively, at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 5 mg. Maternal toxicity and reduced fetal body weights were observed at 7986 and 328 times the human exposure at the MRHD for saxagliptin and the active metabolite, respectively. Minor skeletal variations in rabbits occurred at a maternally toxic dose of 200 mg/kg, or approximately 1432 and 992 times the MRHD.
- Coadministration of saxagliptin and metformin, to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis, was neither embryolethal nor teratogenic in either species when tested at doses yielding systemic exposures (AUC) up to 100 and 10 times the MRHD (saxagliptin 5 mg and metformin 2000 mg), respectively, in rats; and 249 and 1.1 times the MRHDs in rabbits. In rats, minor developmental toxicity was limited to an increased incidence of wavy ribs; associated maternal toxicity was limited to weight decrements of 11% to 17% over the course of the study, and related reductions in maternal food consumption. In rabbits, coadministration was poorly tolerated in a subset of mothers (12 of 30), resulting in death, moribundity, or abortion. However, among surviving mothers with evaluable litters, maternal toxicity was limited to marginal reductions in body weight over the course of gestation days 21 to 29; and associated developmental toxicity in these litters was limited to fetal body weight decrements of 7%, and a low incidence of delayed ossification of the fetal hyoid.
- Saxagliptin administered to female rats from gestation day 6 to lactation day 20 resulted in decreased body weights in male and female offspring only at maternally toxic doses (exposures ≥1629 and 53 times saxagliptin and its active metabolite at the MRHD). No functional or behavioral toxicity was observed in offspring of rats administered saxagliptin at any dose.
- Saxagliptin crosses the placenta into the fetus following dosing in pregnant rats.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Saxagliptin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Saxagliptin during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Saxagliptin is secreted in the milk of lactating rats at approximately a 1:1 ratio with plasma drug concentrations. It is not known whether saxagliptin is secreted in human milk. Because many drugs are secreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ONGLYZA is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness of ONGLYZA in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established. Additionally, studies characterizing the pharmacokinetics of ONGLYZA in pediatric patients have not been performed.
Geriatic Use
- In the six, double-blind, controlled clinical safety and efficacy trials of ONGLYZA, 634 (15.3%) of the 4148 randomized patients were 65 years and over, and 59 (1.4%) patients were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients ≥65 years old and the younger patients. While this clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
- Saxagliptin and its active metabolite are eliminated in part by the kidney. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection in the elderly based on renal function.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Saxagliptin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Saxagliptin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Saxagliptin in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Saxagliptin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Saxagliptin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Saxagliptin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Saxagliptin in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Saxagliptin in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- In a controlled clinical trial, once-daily, orally-administered ONGLYZA in healthy subjects at doses up to 400 mg daily for 2 weeks (80 times the MRHD) had no dose-related clinical adverse reactions and no clinically meaningful effect on QTc interval or heart rate.
Management
- In the event of an overdose, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated as dictated by the patient’s clinical status. Saxagliptin and its active metabolite are removed by hemodialysis (23% of dose over 4 hours).
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Saxagliptin in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Saxagliptin Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Increased concentrations of the incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are released into the bloodstream from the small intestine in response to meals. These hormones cause insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells in a glucose-dependent manner but are inactivated by the DPP4 enzyme within minutes. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, reducing hepatic glucose production. In patients with type 2 diabetes, concentrations of GLP-1 are reduced but the insulin response to GLP-1 is preserved. Saxagliptin is a competitive DPP4 inhibitor that slows the inactivation of the incretin hormones, thereby increasing their bloodstream concentrations and reducing fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations in a glucose-dependent manner in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Structure
- Saxagliptin is an orally-active inhibitor of the DPP4 enzyme.
- Saxagliptin monohydrate is described chemically as (1S,3S,5S)-2-[(2S)-2-Amino-2-(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]dec-1-yl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile, monohydrate or (1S,3S,5S)-2-[(2S)-2-Amino-2-(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile hydrate. The empirical formula is C18H25N3O2•H2O and the molecular weight is 333.43. The structural formula is:
- Saxagliptin monohydrate is a white to light yellow or light brown, non-hygroscopic, crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water at 24°C ± 3°C, slightly soluble in ethyl acetate, and soluble in methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, acetonitrile, acetone, and polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400).
- Each film-coated tablet of ONGLYZA for oral use contains either 2.79 mg saxagliptin hydrochloride (anhydrous) equivalent to 2.5 mg saxagliptin or 5.58 mg saxagliptin hydrochloride (anhydrous) equivalent to 5 mg saxagliptin and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate. In addition, the film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide, talc, and iron oxides.
Pharmacodynamics
- In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, administration of ONGLYZA inhibits DPP4 enzyme activity for a 24-hour period. After an oral glucose load or a meal, this DPP4 inhibition resulted in a 2- to 3-fold increase in circulating levels of active GLP-1 and GIP, decreased glucagon concentrations, and increased glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. The rise in insulin and decrease in glucagon were associated with lower fasting glucose concentrations and reduced glucose excursion following an oral glucose load or a meal.
- In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 4-way crossover, active comparator study using moxifloxacin in 40 healthy subjects, ONGLYZA was not associated with clinically meaningful prolongation of the QTc interval or heart rate at daily doses up to 40 mg (8 times the MRHD).
Pharmacokinetics
- The pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite, 5-hydroxy saxagliptin were similar in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The Cmax and AUC values of saxagliptin and its active metabolite increased proportionally in the 2.5 to 400 mg dose range. Following a 5 mg single oral dose of saxagliptin to healthy subjects, the mean plasma AUC values for saxagliptin and its active metabolite were 78 ng•h/mL and 214 ng•h/mL, respectively. The corresponding plasma Cmax values were 24 ng/mL and 47 ng/mL, respectively. The average variability (%CV) for AUC and Cmax for both saxagliptin and its active metabolite was less than 25%.
- No appreciable accumulation of either saxagliptin or its active metabolite was observed with repeated once-daily dosing at any dose level. No dose- and time-dependence were observed in the clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite over 14 days of once-daily dosing with saxagliptin at doses ranging from 2.5 to 400 mg.
- Absorption
- The median time to maximum concentration (Tmax) following the 5 mg once daily dose was 2 hours for saxagliptin and 4 hours for its active metabolite. Administration with a high-fat meal resulted in an increase in Tmax of saxagliptin by approximately 20 minutes as compared to fasted conditions. There was a 27% increase in the AUC of saxagliptin when given with a meal as compared to fasted conditions. ONGLYZA may be administered with or without food.
- Distribution
- The in vitro protein binding of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in human serum is negligible. Therefore, changes in blood protein levels in various disease states (e.g., renal or hepatic impairment) are not expected to alter the disposition of saxagliptin.
- Metabolism
- The metabolism of saxagliptin is primarily mediated by cytochrome P450 3A4/5 (CYP3A4/5). The major metabolite of saxagliptin is also a DPP4 inhibitor, which is one-half as potent as saxagliptin. Therefore, strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors and inducers will alter the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite. [See Drug Interactions (7.1).]
- Excretion
- Saxagliptin is eliminated by both renal and hepatic pathways. Following a single 50 mg dose of 14C-saxagliptin, 24%, 36%, and 75% of the dose was excreted in the urine as saxagliptin, its active metabolite, and total radioactivity, respectively. The average renal clearance of saxagliptin (~230 mL/min) was greater than the average estimated glomerular filtration rate (~120 mL/min), suggesting some active renal excretion. A total of 22% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in feces representing the fraction of the saxagliptin dose excreted in bile and/or unabsorbed drug from the gastrointestinal tract. Following a single oral dose of ONGLYZA 5 mg to healthy subjects, the mean plasma terminal half-life (t1/2) for saxagliptin and its active metabolite was 2.5 and 3.1 hours, respectively.
- Specific Populations
- Renal Impairment
- A single-dose, open-label study was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin (10 mg dose) in subjects with varying degrees of chronic renal impairment (N=8 per group) compared to subjects with normal renal function. The 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage. The study included patients with renal impairment classified on the basis of creatinine clearance as mild (>50 to ≤80 mL/min), moderate (30 to ≤50 mL/min), and severe (<30 mL/min), as well as patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Creatinine clearance was estimated from serum creatinine based on the Cockcroft-Gault formula:
F
- The degree of renal impairment did not affect the Cmax of saxagliptin or its active metabolite. In subjects with mild renal impairment, the AUC values of saxagliptin and its active metabolite were 20% and 70% higher, respectively, than AUC values in subjects with normal renal function. Because increases of this magnitude are not considered to be clinically relevant, dosage adjustment in patients with mild renal impairment is not recommended. In subjects with moderate or severe renal impairment, the AUC values of saxagliptin and its active metabolite were up to 2.1- and 4.5-fold higher, respectively, than AUC values in subjects with normal renal function. To achieve plasma exposures of saxagliptin and its active metabolite similar to those in patients with normal renal function, the recommended dose is 2.5 mg once daily in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment, as well as in patients with end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis. Saxagliptin is removed by hemodialysis.
- Hepatic Impairment
- In subjects with hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classes A, B, and C), mean Cmax and AUC of saxagliptin were up to 8% and 77% higher, respectively, compared to healthy matched controls following administration of a single 10 mg dose of saxagliptin. The 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage. The corresponding Cmax and AUC of the active metabolite were up to 59% and 33% lower, respectively, compared to healthy matched controls. These differences are not considered to be clinically meaningful. No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with hepatic impairment.
- Body Mass Index
- No dosage adjustment is recommended based on body mass index (BMI) which was not identified as a significant covariate on the apparent clearance of saxagliptin or its active metabolite in the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
- Gender
- No dosage adjustment is recommended based on gender. There were no differences observed in saxagliptin pharmacokinetics between males and females. Compared to males, females had approximately 25% higher exposure values for the active metabolite than males, but this difference is unlikely to be of clinical relevance. Gender was not identified as a significant covariate on the apparent clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
- Geriatric
- No dosage adjustment is recommended based on age alone. Elderly subjects (65-80 years) had 23% and 59% higher geometric mean Cmax and geometric mean AUC values, respectively, for saxagliptin than young subjects (18-40 years). Differences in active metabolite pharmacokinetics between elderly and young subjects generally reflected the differences observed in saxagliptin pharmacokinetics. The difference between the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and the active metabolite in young and elderly subjects is likely due to multiple factors including declining renal function and metabolic capacity with increasing age. Age was not identified as a significant covariate on the apparent clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
- Race and Ethnicity
- No dosage adjustment is recommended based on race. The population pharmacokinetic analysis compared the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in 309 Caucasian subjects with 105 non-Caucasian subjects (consisting of six racial groups). No significant difference in the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite were detected between these two populations.
- Drug Interaction Studies
- In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
- The metabolism of saxagliptin is primarily mediated by CYP3A4/5.
- In in vitro studies, saxagliptin and its active metabolite did not inhibit CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, or 3A4, or induce CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, or 3A4. Therefore, saxagliptin is not expected to alter the metabolic clearance of coadministered drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes. Saxagliptin is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate but is not a significant inhibitor or inducer of P-gp.
T3
T4
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Carcinogenesis
- Saxagliptin did not induce tumors in either mice (50, 250, and 600 mg/kg) or rats (25, 75, 150, and 300 mg/kg) at the highest doses evaluated. The highest doses evaluated in mice were equivalent to approximately 870 (males) and 1165 (females) times the human exposure at the MRHD of 5 mg/day. In rats, exposures were approximately 355 (males) and 2217 (females) times the MRHD.
- Mutagenesis
- Saxagliptin was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in an in vitro Ames bacterial assay, an in vitro cytogenetics assay in primary human lymphocytes, an in vivo oral micronucleus assay in rats, an in vivo oral DNA repair study in rats, and an oral in vivo/in vitro cytogenetics study in rat peripheral blood lymphocytes. The active metabolite was not mutagenic in an in vitro Ames bacterial assay.
- Impairment of Fertility
- In a rat fertility study, males were treated with oral gavage doses for 2 weeks prior to mating, during mating, and up to scheduled termination (approximately 4 weeks total) and females were treated with oral gavage doses for 2 weeks prior to mating through gestation day 7. No adverse effects on fertility were observed at exposures of approximately 603 (males) and 776 (females) times the MRHD. Higher doses that elicited maternal toxicity also increased fetal resorptions (approximately 2069 and 6138 times the MRHD). Additional effects on estrous cycling, fertility, ovulation, and implantation were observed at approximately 6138 times the MRHD.
- Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
- Saxagliptin produced adverse skin changes in the extremities of cynomolgus monkeys (scabs and/or ulceration of tail, digits, scrotum, and/or nose). Skin lesions were reversible at ≥20 times the MRHD but in some cases were irreversible and necrotizing at higher exposures. Adverse skin changes were not observed at exposures similar to (1 to 3 times) the MRHD of 5 mg. Clinical correlates to skin lesions in monkeys have not been observed in human clinical trials of saxagliptin.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Saxagliptin in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Saxagliptin Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Saxagliptin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Saxagliptin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Saxagliptin in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Saxagliptin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Saxagliptin |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Saxagliptin |Label Name=Saxagliptin11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Saxagliptin |Label Name=Saxagliptin11.png
}}