Myxoma echocardiography or ultrasound: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} {{MV}} | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} {{MV}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
On cardiac [[ultrasound]], myxoma is characterized by the presence of a [[heterogeneous]] pedunculated mass that is commonly located in the [[left atrium]]. Cardiac myxomas appear as hyperechogenic lesions with a well-defined stalk. Moreover, [[echocardiography]] can be useful to assess the mobility of the tumor, as it often | On cardiac [[ultrasound]], myxoma is characterized by the presence of a [[heterogeneous]] pedunculated mass that is commonly located in the [[left atrium]]. Cardiac myxomas appear as hyperechogenic lesions with a well-defined stalk. Moreover, [[echocardiography]] can be useful to assess the mobility of the tumor, as it often protrudes through valve flaps. Echocardiography is useful to evaluate the function identification and evaluation of cardiac myxomas. As an imaging modality, [[two-dimensional echocardiography]] is often coupled with other testing modalities (such as, Doppler echocardiography) to detect vascular abnormalities that frequently occur in cardiac myxomas. <ref name="pmid2605587">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bentivoglio M, Savino K, Corea L, Verdecchia P, Porcellati C |title=[Doppler echocardiography in atrial myxoma] |language=Italian |journal=Cardiologia |volume=34 |issue=9 |pages=783–6 |year=1989 |pmid=2605587 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Echocardiography== | ==Echocardiography== | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 30 November 2015
|
Myxoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Myxoma echocardiography or ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Myxoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Myxoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2] Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [3]
Overview
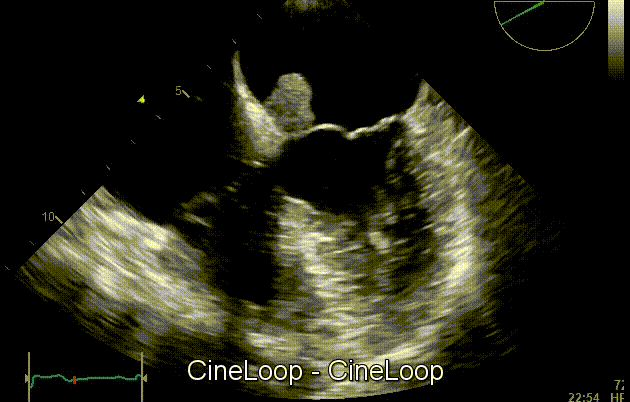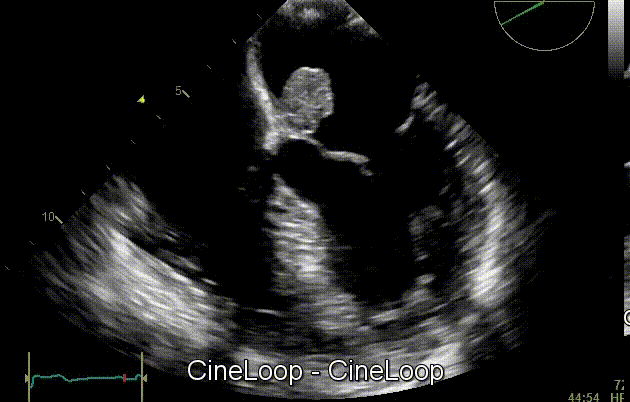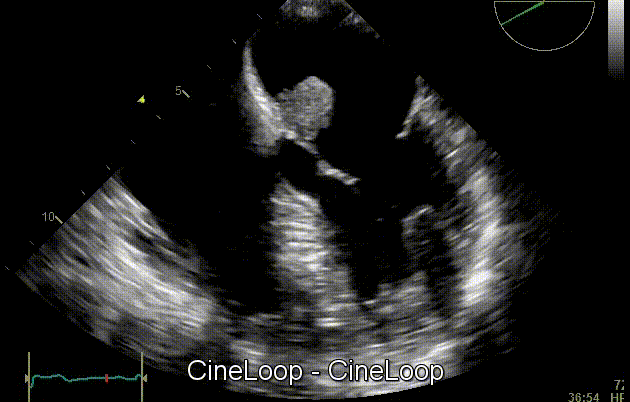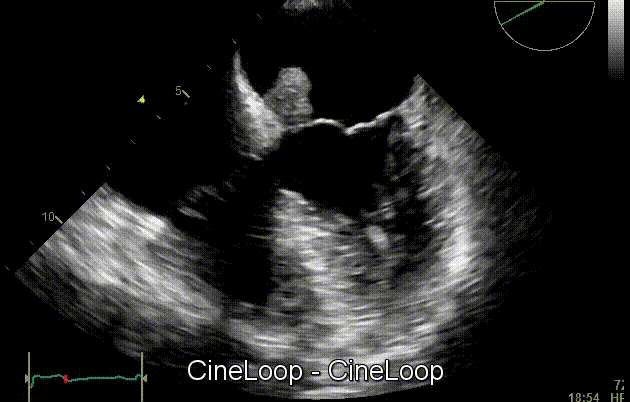
On cardiac ultrasound, myxoma is characterized by the presence of a heterogeneous pedunculated mass that is commonly located in the left atrium. Cardiac myxomas appear as hyperechogenic lesions with a well-defined stalk. Moreover, echocardiography can be useful to assess the mobility of the tumor, as it often protrudes through valve flaps. Echocardiography is useful to evaluate the function identification and evaluation of cardiac myxomas. As an imaging modality, two-dimensional echocardiography is often coupled with other testing modalities (such as, Doppler echocardiography) to detect vascular abnormalities that frequently occur in cardiac myxomas. [1]
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is useful to evaluate tumor mobility on of cardiac myxoma, as it often protrude through valve flaps. As a test modality, two-dimensional echocardiography is often coupled with other modalities (such as, Doppler echocardiography) to detect vascular abnormalities that frequently occur in cardiac myxomas. [1]
Gallery
| Imaging Technique | Features | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two- or three-dimensional echocardiography | Echocardiography is usually the initial modality used for identification and evaluation of cardiac myxomas |
|
|
|
| MRI | Evaluation of cardiac masses and is of greatest value when echocardiographic findings are suboptimal or when the lesion has an atypical location or appearance |
|
|
|
| CT | CT can be used to accurately image the heart and surrounding mediastinum |
|
|
|
| Angiography | Coronary angiography may be helpful to detect vascular supply of the tumor by the coronary arteries |
|
|
|
| Chest x-ray | Chest x-ray has no particular findings associated with cardiac myxoma |
|
|
|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bentivoglio M, Savino K, Corea L, Verdecchia P, Porcellati C (1989). "[Doppler echocardiography in atrial myxoma]". Cardiologia (in Italian). 34 (9): 783–6. PMID 2605587.
- ↑ Atrial Myxoma. Wikipedia.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrial_myxoma Accessed November 25,2015 on
- ↑ Reeder GS, Khandheria BK, Seward JB, Tajik AJ (1991). "Transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac masses". Mayo Clin. Proc. 66 (11): 1101–9. PMID 1943240.
- ↑ Araoz PA, Eklund HE, Welch TJ, Breen JF (1999). "CT and MR imaging of primary cardiac malignancies". Radiographics. 19 (6): 1421–34. doi:10.1148/radiographics.19.6.g99no031421. PMID 10555666.