Mitral stenosis electrocardiogram
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.; Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan, M.B.B.S.
|
Mitral Stenosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Mitral stenosis electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Mitral stenosis electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Mitral stenosis electrocardiogram |
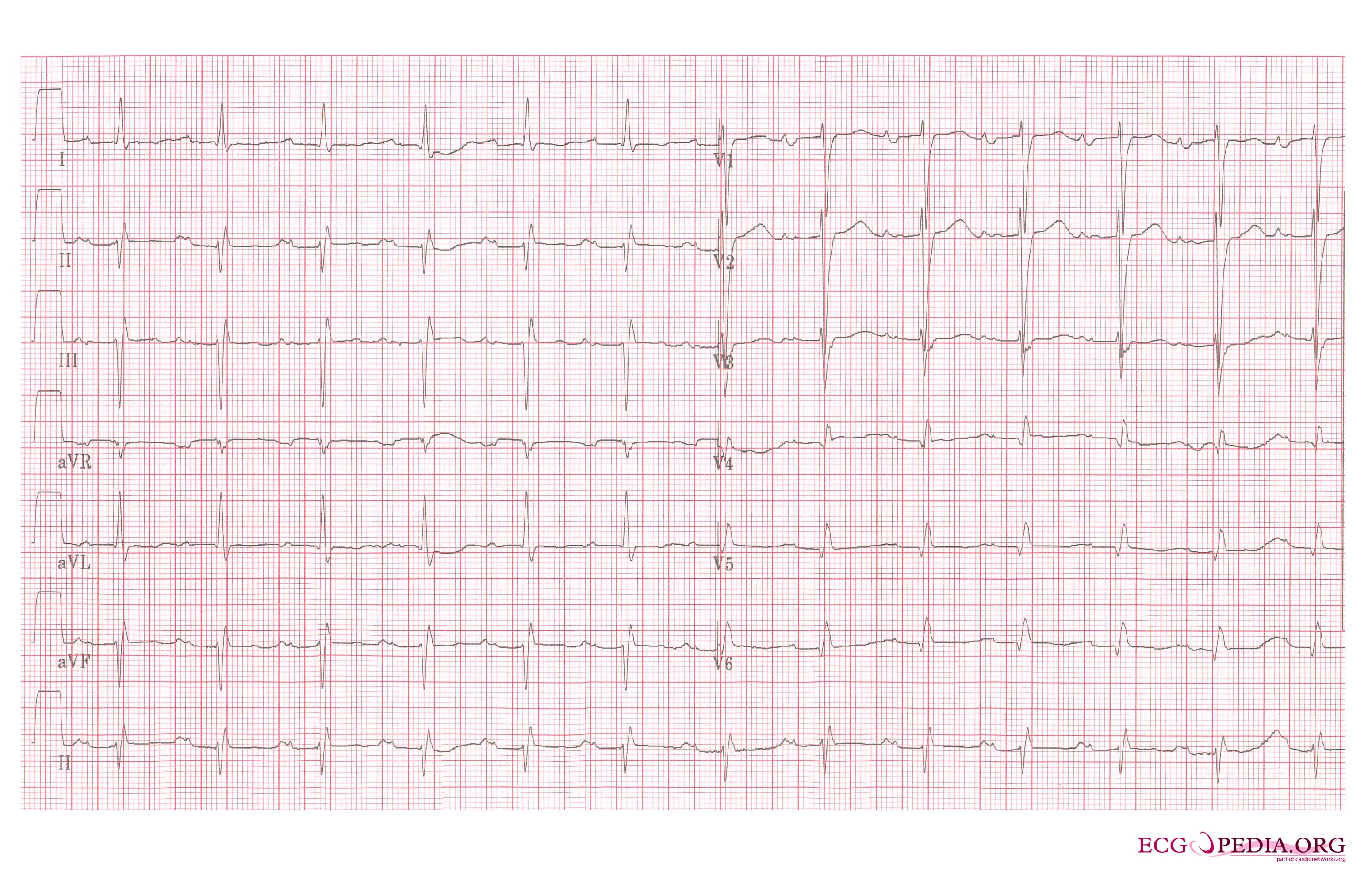
Electrocardiographic findings in Mitral stenosis
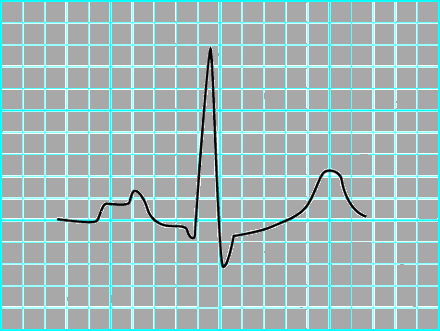
1. LA enlargement: Left atrial enlargement produces a broad, bifid P wave in lead II (P mitrale) and enlarges the terminal negative portion of the P wave in VI.
In lead II following may be seen:
- Bifid P wave with > 40 ms between the two peaks
- Total P wave duration > 110 ms
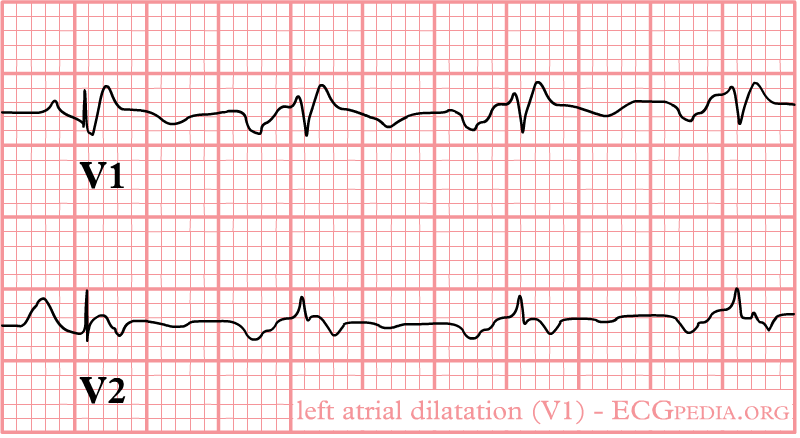
In lead V1 follwing may be seen:
- Biphasic P wave with terminal negative portion > 40 ms duration
- Biphasic P wave with terminal negative portion > 1mm deep
2. Right ventricular hypertrophy: A mean QRS axis in the frontal plane is greater than 80 and an R-to-S ratio of greater than 1 in lead V1.
3. Right axis deviation: mean QRS axis in the frontal plane moves toward the right as pulmonary hypertension worsens.
4. Atrial fibrillation is commonly seen with mitral stenosis: Irregularly irregular rhythm with absence P waves.
Below is an ECG in mitral stenosis