Mechanical ventilation types of ventilators: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
=== Types of Ventilators === | === Types of Ventilators === | ||
[[Image:Ballon ventilation 1.jpg|left|thumb|[[Bag valve mask]]]] | |||
Ventilation can be delivered via: | Ventilation can be delivered via: | ||
*Hand-controlled ventilation such as: | *Hand-controlled ventilation such as: | ||
**[[Bag valve mask]] | **[[Bag valve mask]] | ||
**Continuous-flow or Anaesthesia (or T-piece) bag | **Continuous-flow or Anaesthesia (or T-piece) bag | ||
*A mechanical ventilator. Types of mechanical ventilators include: | *A mechanical ventilator. Types of mechanical ventilators include: | ||
**Transport ventilators. These ventilators are small, more rugged, and can be powered pneumatically or via AC or DC power sources. | **Transport ventilators. These ventilators are small, more rugged, and can be powered pneumatically or via AC or DC power sources. | ||
**ICU ventilators | **ICU ventilators: These ventilators are larger and usually run on AC power (though virtually all contain a battery to facilitate intrafacility transport and as a back-up in the event of a power failure). This style of ventilator often provides greater control of a wide variety of ventilation parameters (such as inspiratory rise time). Many ICU ventilators also incorporate graphics to provide visual feedback of each breath. | ||
**[[NICU]] ventilators: Designed with the preterm neonate in mind, these are a specialized subset of ICU ventilators which are designed to deliver the smaller, more precise volumes and pressures required to ventilate these patients. | |||
**[[Positive airway pressure|PAP]] ventilators | **[[Positive airway pressure|PAP]] ventilators: These ventilators are specifically designed for non-invasive ventilation. this includes ventilators for use at home, in order to treat [[sleep apnea]]. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 1 March 2013
|
Mechanical ventilation Microchapters |
|
Mechanical ventilation types of ventilators On the Web |
|---|
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Mechanical ventilation types of ventilators |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Mechanical ventilation types of ventilators |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vishnu Vardhan Serla M.B.B.S. [2]
Classification
Types of Ventilators
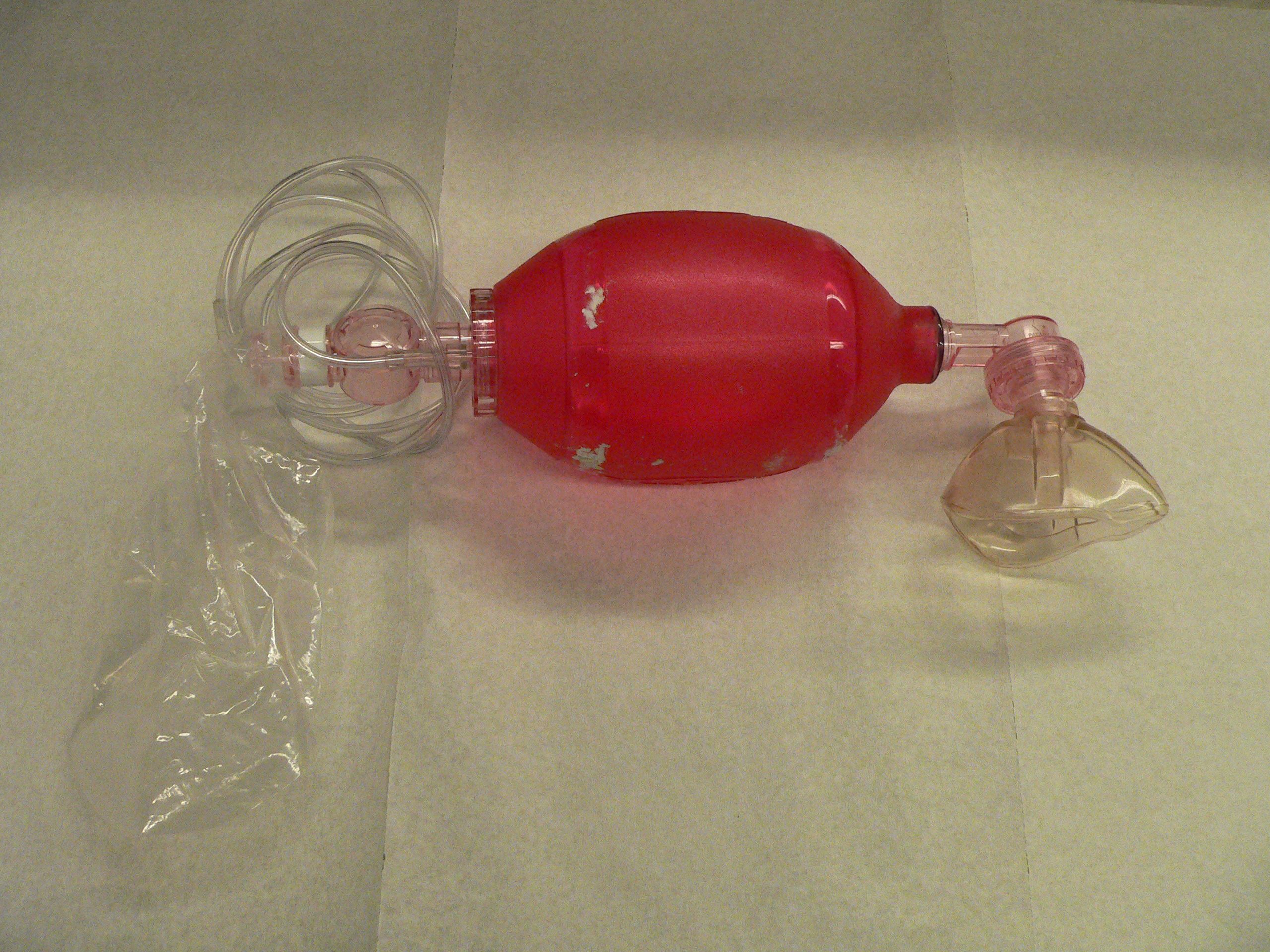
Ventilation can be delivered via:
- Hand-controlled ventilation such as:
- Bag valve mask
- Continuous-flow or Anaesthesia (or T-piece) bag
- A mechanical ventilator. Types of mechanical ventilators include:
- Transport ventilators. These ventilators are small, more rugged, and can be powered pneumatically or via AC or DC power sources.
- ICU ventilators: These ventilators are larger and usually run on AC power (though virtually all contain a battery to facilitate intrafacility transport and as a back-up in the event of a power failure). This style of ventilator often provides greater control of a wide variety of ventilation parameters (such as inspiratory rise time). Many ICU ventilators also incorporate graphics to provide visual feedback of each breath.
- NICU ventilators: Designed with the preterm neonate in mind, these are a specialized subset of ICU ventilators which are designed to deliver the smaller, more precise volumes and pressures required to ventilate these patients.
- PAP ventilators: These ventilators are specifically designed for non-invasive ventilation. this includes ventilators for use at home, in order to treat sleep apnea.