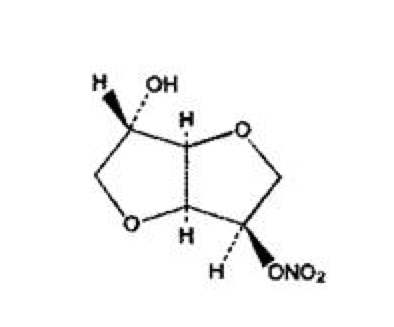
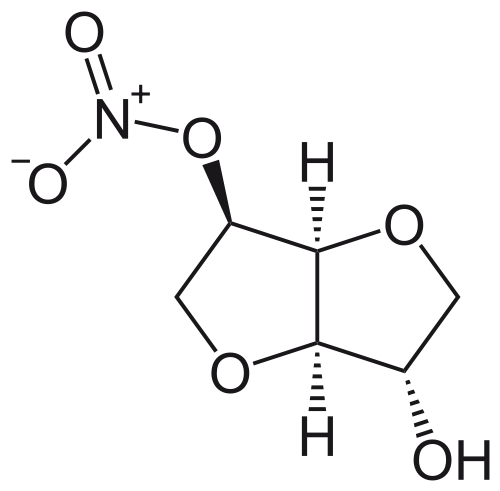
Isosorbide mononitrate
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Isosorbide mononitrate is an anti-anginal nitrate that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of angina pectoris due to coronary artery disease.. Common adverse reactions include dizziness and headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Prophylaxis of Angina Pectoris
- Dosing Information
- The recommended starting dose is 30 mg (given as a single 30 mg tablet or as 1/2 of a 60 mg tablet) or 60 mg (given as a single tablet) once daily.
- After several days, the dosage may be increased to 120 mg (given as a single 120 mg tablet or as two 60 mg tablets) once daily. Rarely, 240 mg may be required.
- The daily dose of IMDUR Tablets should be taken in the morning on arising.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Isosorbide mononitrate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Prophylaxis of Rebleeding of Esophageal Varices
- Dosing Information
- 10 mg twice daily and titrated to 20 mg twice daily unless hypotension or headache occurred.[1]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Isosorbide mononitrate in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Isosorbide mononitrate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Isosorbide mononitrate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity or idiosyncratic reactions to other nitrates or nitrites.
Warnings
- Amplification of the vasodilatory effects of IMDUR by sildenafil can result in severe hypotension. The time course and dose dependence of this interaction have not been studied. Appropriate supportive care has not been studied, but it seems reasonable to treat this as a nitrate overdose, with elevation of the extremities and with central volume expansion.
- The benefits of ISMN in patients with acute myocardial infarction or congestive heart failure have not been established; because the effects of isosorbide mononitrate are difficult to terminate rapidly, this drug is not recommended in these settings.
- If isosorbide mononitrate is used in these conditions, careful clinical or hemodynamic monitoring must be used to avoid the hazards of hypotension and tachycardia.
Precautions
- Severe hypotension, particularly with upright posture, may occur with even small doses of isosorbide mononitrate. This drug should, therefore, be used with caution in patients who may be volume depleted or who, for whatever reason, are already hypotensive. Hypotension induced by isosorbide mononitrate may be accompanied by paradoxical bradycardia and increased angina pectoris.
- Nitrate therapy may aggravate the angina caused by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- In industrial workers who have had long-term exposure to unknown (presumably high) doses of organic nitrates, tolerance clearly occurs. Chest pain, acute myocardial infarction, and even sudden death have occurred during temporary withdrawal of nitrates from these workers, demonstrating the existence of true physical dependence. The importance of these observations to the routine, clinical use of oral isosorbide mononitrate is not known.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
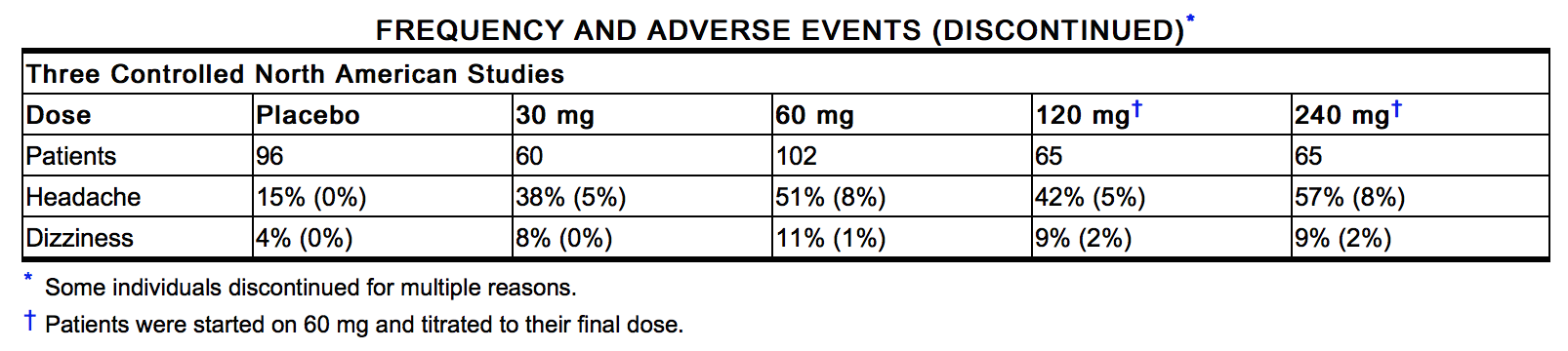
- The table below shows the frequencies of the adverse events that occurred in >5% of the subjects in three placebo-controlled North American studies in which patients in the active treatment arm received 30 mg, 60 mg, 120 mg, or 240 mg of isosorbide mononitrate as IMDUR Tablets once daily. In parentheses, the same table shows the frequencies with which these adverse events were associated with the discontinuation of treatment. Overall, 8% of the patients who received 30 mg, 60 mg, 120 mg, or 240 mg of isosorbide mononitrate in the three placebo-controlled North American studies discontinued treatment because of adverse events. Most of these discontinued because of headache. Dizziness was rarely associated with withdrawal from these studies. Since headache appears to be a dose-related adverse effect and tends to disappear with continued treatment, it is recommended that IMDUR treatment be initiated at low doses for several days before being increased to desired levels.
- In addition, the three North American trials were pooled with 11 controlled trials conducted in Europe. Among the 14 controlled trials, a total of 711 patients were randomized to IMDUR Tablets. When the pooled data were reviewed, headache and dizziness were the only adverse events that were reported by >5% of patients. Other adverse events, each reported by ≤5% of exposed patients, and in many cases of uncertain relation to drug treatment, were:
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- The vasodilating effects of isosorbide mononitrate may be additive with those of other vasodilators. Alcohol, in particular, has been found to exhibit additive effects of this variety.
- Marked symptomatic orthostatic hypotension has been reported when calcium channel blockers and organic nitrates were used in combination. Dose adjustments of either class of agents may be necessary.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
- Nitrates and nitrites may interfere with the Zlatkis-Zak color reaction, causing falsely low readings in serum cholesterol determinations.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category B
- In studies designed to detect effects of isosorbide mononitrate on embryo-fetal development, doses of up to 240 or 248 mg/kg/day, administered to pregnant rats and rabbits, were unassociated with evidence of such effects. These animal doses are about 100 times the maximum recommended human dose (120 mg in a 50 kg woman) when comparison is based on body weight; when comparison is based on body surface area, the rat dose is about 17 times the human dose and the rabbit dose is about 38 times the human dose. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, IMDUR Tablets should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Neonatal survival and development and incidence of stillbirths were adversely affected when pregnant rats were administered oral doses of 750 (but not 300) mg isosorbide mononitrate/kg/day during late gestation and lactation. This dose (about 312 times the human dose when comparison is based on body weight and 54 times the human dose when comparison is based on body surface area) was associated with decreases in maternal weight gain and motor activity and evidence of impaired lactation.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Isosorbide mononitrate in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Isosorbide mononitrate during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ISMN is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of ISMN in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of IMDUR Tablets did not include sufficient information on patients age 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience for IMDUR has not identified differences in response between elderly and younger patients. Clinical experience for organic nitrates reported in the literature identified a potential for severe hypotension and increased sensitivity to nitrates in the elderly. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
- Elderly patients may have reduced baroreceptor function and may develop severe orthostatic hypotension when vasodilators are used. IMDUR should therefore be used with caution in elderly patients who may be volume depleted, on multiple medications or who, for whatever reason, are already hypotensive. Hypotension induced by isosorbide mononitrate may be accompanied by paradoxical bradycardia and increased angina pectoris.
- Elderly patients may be more susceptible to hypotension and may be at a greater risk of falling at therapeutic doses of nitroglycerin.
- Nitrate therapy may aggravate the angina caused by hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, particularly in the elderly.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isosorbide mononitrate with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isosorbide mononitrate with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isosorbide mononitrate in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isosorbide mononitrate in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Isosorbide mononitrate in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Isosorbide mononitrate in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- IMDUR Extended Release Tablets should not be chewed or crushed and should be swallowed together with a half-glassful of fluid. Do not break the 30 mg tablet.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Pharmacology
| |
Isosorbide mononitrate
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 8-nitrooxy-2,6-dioxabicyclo[3.3.0]octan-4-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C01 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 191.139 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | >95% |
| Protein binding | <5% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half life | 5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal: 93% |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C (USA) |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed in rats exposed to isosorbide mononitrate in their diets at doses of up to 900 mg/kg/day for the first 6 months and 500 mg/kg/day for the remaining duration of a study in which males were dosed for up to 121 weeks and females were dosed for up to 137 weeks. No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed in mice exposed to isosorbide mononitrate in their diets for up to 104 weeks at doses of up to 900 mg/kg/day.
- Isosorbide mononitrate did not produce gene mutations (Ames test, mouse lymphoma test) or chromosome aberrations (human lymphocyte and mouse micronucleus tests) at biologically relevant concentrations.
- No effects on fertility were observed in a study in which male and female rats were administered doses of up to 750 mg/kg/day beginning, in males, 9 weeks prior to mating, and in females, 2 weeks prior to mating.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Isosorbide mononitrate in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Isosorbide mononitrate Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Isosorbide mononitrate |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Isosorbide mononitrate |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients should be told that the antianginal efficacy of IMDUR Tablets can be maintained by carefully following the prescribed schedule of dosing. For most patients, this can be accomplished by taking the dose on arising.
- As with other nitrates, daily headaches sometimes accompany treatment with isosorbide mononitrate. In patients who get these headaches, the headaches are a marker of the activity of the drug. Patients should resist the temptation to avoid headaches by altering the schedule of their treatment with isosorbide mononitrate, since loss of headache may be associated with simultaneous loss of antianginal efficacy. Aspirin or acetaminophen often successfully relieves isosorbide mononitrate-induced headaches with no deleterious effect on isosorbide mononitrate's antianginal efficacy.
- Treatment with isosorbide mononitrate may be associated with light-headedness on standing, especially just after rising from a recumbent or seated position. This effect may be more frequent in patients who have also consumed alcohol.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Isosorbide mononitrate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- IMDUR®[2]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[3]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Merkel, C. (1996-12-21). "Randomised trial of nadolol alone or with isosorbide mononitrate for primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Gruppo-Triveneto per L'ipertensione portale (GTIP)". Lancet. 348 (9043): 1677–1681. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 8973428. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ "IMDUR (isosorbide mononitrate) tablet, extended release".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Isosorbide mononitrate |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Isosorbide mononitrate |Label Name=Isosorbide mononitrate11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Isosorbide mononitrate |Label Name=Isosorbide mononitrate11.png
}}