Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Template:Ebstein's anomaly of the tricuspid valve}} | {{Template:Ebstein's anomaly of the tricuspid valve}} | ||
{{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}}; Claudia P. Hochberg, M.D. [mailto:chochber@bidmc.harvard.edu];[[Priyamvada Singh|Priyamvada Singh, MBBS]] [mailto:psingh13579@gmail.com] | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}}; Claudia P. Hochberg, M.D. [mailto:chochber@bidmc.harvard.edu];[[Priyamvada Singh|Priyamvada Singh, MBBS]] [mailto:psingh13579@gmail.com],{{AE}} {{M.N}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The pathophysiology of Ebstein's anomaly depends on the morphology of [[tricuspid valve]] and the [[right ventricle]]. The annulus of the valve is in normal position. The valve leaflets however, are to a varying degree attached to the walls and septum of the [[right ventricle]]. There is subsequent atrialization of a portion of the morphologic right ventricle (which is then contiguous with the [[right atrium]]). This causes the [[right atrium]] to be large and the anatomic [[right ventricle]] to be small in size. 50% of cases involve an atrial shunt (either a [[PFO]] or an [[ASD]]). | The [[pathophysiology]] of Ebstein's anomaly depends on the morphology of [[tricuspid valve]] and the [[right ventricle]]. The annulus of the [[valve]] is in normal position. The [[valve]] leaflets however, are to a varying degree attached to the walls and [[septum]] of the [[right ventricle]]. There is subsequent atrialization of a portion of the morphologic [[right ventricle]] (which is then contiguous with the [[right atrium]]). This causes the [[right atrium]] to be large and the [[anatomic]] [[right ventricle]] to be small in size. 50% of cases involve an [[atrial]] [[shunt]] (either a [[PFO]] or an [[ASD]]). | ||
[[Mutations]] in [[MYH7]], which a [[sarcomere]] [[gene]] encoding the [[cardiac]] beta[[Myosin-heavy-chain kinase|-myosin heavy chain]] have been linked in the occurence of familial Ebstein anomaly. Commonly associated conditions include [[Aortic coarctation]], Cleft anterior leaflet of the [[mitral valve]], [[Coarctation of the aorta]], corrected [[transposition of the great arteries]], [[Hypoplastic]] [[pulmonary arteries]], [[Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction|Left ventricular outflow obstruction]] etc. | |||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
*Pathophysiology mainly involves the right ventricle, right atrium and tricuspid valve.<ref name="pmid27541719">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kloesel B, DiNardo JA, Body SC |title=Cardiac Embryology and Molecular Mechanisms of Congenital Heart Disease: A Primer for Anesthesiologists |journal=Anesth. Analg. |volume=123 |issue=3 |pages=551–69 |date=September 2016 |pmid=27541719 |pmc=4996372 |doi=10.1213/ANE.0000000000001451 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21127202">{{cite journal |vauthors=Postma AV, van Engelen K, van de Meerakker J, Rahman T, Probst S, Baars MJ, Bauer U, Pickardt T, Sperling SR, Berger F, Moorman AF, Mulder BJ, Thierfelder L, Keavney B, Goodship J, Klaassen S |title=Mutations in the sarcomere gene MYH7 in Ebstein anomaly |journal=Circ Cardiovasc Genet |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=43–50 |date=February 2011 |pmid=21127202 |doi=10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.957985 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23956225">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bettinelli AL, Mulder TJ, Funke BH, Lafferty KA, Longo SA, Niyazov DM |title=Familial ebstein anomaly, left ventricular hypertrabeculation, and ventricular septal defect associated with a MYH7 mutation |journal=Am. J. Med. Genet. A |volume=161A |issue=12 |pages=3187–90 |date=December 2013 |pmid=23956225 |doi=10.1002/ajmg.a.36182 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid31384377">{{cite journal |vauthors=Holst KA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA |title=Ebstein's Anomaly |journal=Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=138–144 |date=2019 |pmid=31384377 |pmc=6668741 |doi=10.14797/mdcj-15-2-138 |url=}}</ref> | *[[Pathophysiology]] mainly involves the [[right ventricle]], [[right atrium]] and [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]].<ref name="pmid27541719">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kloesel B, DiNardo JA, Body SC |title=Cardiac Embryology and Molecular Mechanisms of Congenital Heart Disease: A Primer for Anesthesiologists |journal=Anesth. Analg. |volume=123 |issue=3 |pages=551–69 |date=September 2016 |pmid=27541719 |pmc=4996372 |doi=10.1213/ANE.0000000000001451 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21127202">{{cite journal |vauthors=Postma AV, van Engelen K, van de Meerakker J, Rahman T, Probst S, Baars MJ, Bauer U, Pickardt T, Sperling SR, Berger F, Moorman AF, Mulder BJ, Thierfelder L, Keavney B, Goodship J, Klaassen S |title=Mutations in the sarcomere gene MYH7 in Ebstein anomaly |journal=Circ Cardiovasc Genet |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=43–50 |date=February 2011 |pmid=21127202 |doi=10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.957985 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23956225">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bettinelli AL, Mulder TJ, Funke BH, Lafferty KA, Longo SA, Niyazov DM |title=Familial ebstein anomaly, left ventricular hypertrabeculation, and ventricular septal defect associated with a MYH7 mutation |journal=Am. J. Med. Genet. A |volume=161A |issue=12 |pages=3187–90 |date=December 2013 |pmid=23956225 |doi=10.1002/ajmg.a.36182 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid31384377">{{cite journal |vauthors=Holst KA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA |title=Ebstein's Anomaly |journal=Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=138–144 |date=2019 |pmid=31384377 |pmc=6668741 |doi=10.14797/mdcj-15-2-138 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*They include: | *They include: | ||
#Failure of TV leaflet delamination | #Failure of TV([[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]]) leaflet delamination | ||
#Apical descent of the functional tricuspid orifice | #Apical descent of the functional [[Tricuspid|tricuspid orifice]] | ||
#Right ventricular dilation and “atrialization” | #[[Right ventricular dilation]] and “atrialization” | ||
#Anterior leaflet abnormal fenestrations and tethering | #Anterior leaflet abnormal [[fenestrations]] and tethering | ||
#Right atrioventricular junction dilation | #[[Right atrioventricular orifice|Right atrioventricular junction]] dilation | ||
[[File:Ebstein's anomaly illustration.JPG|center|500px]] | |||
Source: National Library Of Medicine. | |||
[[Image:Pictoral depiction of ebstein anomaly.png|center]] | |||
===Tricuspid Valve=== | ===Tricuspid Valve=== | ||
*The superficial layer of the right myocardium usually delaminates to form the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve. | *The superficial layer of the right [[myocardium]] usually delaminates to form the [[septal]] and posterior leaflets of the [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]]. | ||
*Any Delamination failure might result in adherence of the leaflets to the ventricular myocardium as a result causes apical displacement of the tricuspid valve leaflets. | *Any Delamination failure might result in adherence of the leaflets to the [[ventricular]] [[myocardium]] as a result causes [[apical]] displacement of the [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]] leaflets. | ||
*The tricuspid valve orifice is in normal position. | *The [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]] orifice is in normal position. | ||
*The anterior leaflet of the tricuspid valve is attached to the [[tricuspid valve]] annulus or to the right ventricular endocardium. | *The anterior leaflet of the [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]] is attached to the [[tricuspid valve]] annulus or to the [[right ventricular]] [[endocardium]]. | ||
*The septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are absent most of the time. | *The [[septal]] and posterior leaflets of the [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]] are absent most of the time. | ||
*Due to these changes, the tricuspid valve may become funnel-shaped and incompetent or leaky. | *Due to these changes, the [[Tricuspid valves|tricuspid valve]] may become funnel-shaped and incompetent or leaky. | ||
===Right Ventricle=== | ===Right Ventricle=== | ||
The right ventricle changes secondary to the malformed [[tricuspid valve]]s. The right ventricle can be divided into two parts by the malformed valve: | The [[right ventricle]] changes secondary to the malformed [[tricuspid valve]]s. The [[right ventricle]] can be divided into two parts by the malformed [[valve]]: | ||
* The downward extension of the [[tricuspid valve]] causes 'atrialization' of the proximal part of the right ventricle | * The downward extension of the [[tricuspid valve]] causes 'atrialization' of the proximal part of the [[right ventricle]]. | ||
* The small distal part, the right ventricle proper, thus is reduced in size and sometimes comprises only of the [[right ventricular outflow tract]] | * The small distal part, the [[right ventricle]] proper, thus is reduced in size and sometimes comprises only of the [[right ventricular outflow tract]]. | ||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
*Till now the genetic basis for this condition is largely unknown or very little is known about this. | *Till now the [[genetic]] basis for this condition is largely unknown or very little is known about this.<ref name="pmid18506004">{{cite journal |vauthors=Klaassen S, Probst S, Oechslin E, Gerull B, Krings G, Schuler P, Greutmann M, Hürlimann D, Yegitbasi M, Pons L, Gramlich M, Drenckhahn JD, Heuser A, Berger F, Jenni R, Thierfelder L |title=Mutations in sarcomere protein genes in left ventricular noncompaction |journal=Circulation |volume=117 |issue=22 |pages=2893–901 |date=June 2008 |pmid=18506004 |doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.746164 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid30571578">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pierpont ME, Brueckner M, Chung WK, Garg V, Lacro RV, McGuire AL, Mital S, Priest JR, Pu WT, Roberts A, Ware SM, Gelb BD, Russell MW |title=Genetic Basis for Congenital Heart Disease: Revisited: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association |journal=Circulation |volume=138 |issue=21 |pages=e653–e711 |date=November 2018 |pmid=30571578 |pmc=6555769 |doi=10.1161/CIR.0000000000000606 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Mutations in MYH7, which a sarcomere gene encoding the cardiac beta-myosin heavy chain have been linked in the | *[[Mutations]] in [[MYH7]], which a [[sarcomere]] [[gene]] encoding the [[cardiac]] beta[[Myosin-heavy-chain kinase|-myosin heavy chain]] have been linked in the occurence of familial Ebstein anomaly. | ||
*It is formulated that embryonic cell migration may be impaired by these MYH7 mutations. | *It is formulated that [[embryonic cell]] migration may be impaired by these [[MYH7]] [[mutations]]. | ||
*[[Cardiac]] [[transcription factors]] [[NK2 homeobox 1|NK2]] [[homeobox]] 5 (NKX2-5) and [[GATA4|GATA binding protein 4]] ([[GATA4]]) [[mutations]] have also been described in some cases. | |||
==Associated Conditions== | ==Associated Conditions== | ||
Commonly associated conditions include: | Commonly associated conditions include:<ref name="pmid24701093">{{cite journal |vauthors=Siehr SL, Punn R, Priest JR, Lowenthal A |title=Ebstein anomaly and Trisomy 21: A rare association |journal=Ann Pediatr Cardiol |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=67–9 |date=January 2014 |pmid=24701093 |pmc=3959069 |doi=10.4103/0974-2069.126569 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid3925918">{{cite journal |vauthors=Davido A, Maarek M, Jullien JL, Corone P |title=[Ebstein's disease associated with Fallot's tetralogy. Apropos of a familial case, review of the literature, embryologic and genetic implications] |language=French |journal=Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss |volume=78 |issue=5 |pages=752–6 |date=May 1985 |pmid=3925918 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23707655">{{cite journal |vauthors=van Trier DC, Feenstra I, Bot P, de Leeuw N, Draaisma JM |title=Cardiac anomalies in individuals with the 18q deletion syndrome; report of a child with Ebstein anomaly and review of the literature |journal=Eur J Med Genet |volume=56 |issue=8 |pages=426–31 |date=August 2013 |pmid=23707655 |doi=10.1016/j.ejmg.2013.05.002 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23794396">{{cite journal |vauthors=Vermeer AM, van Engelen K, Postma AV, Baars MJ, Christiaans I, De Haij S, Klaassen S, Mulder BJ, Keavney B |title=Ebstein anomaly associated with left ventricular noncompaction: an autosomal dominant condition that can be caused by mutations in MYH7 |journal=Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet |volume=163C |issue=3 |pages=178–84 |date=August 2013 |pmid=23794396 |doi=10.1002/ajmg.c.31365 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* 50% of patients have an [[ASD]] or [[patent foramen ovale]] | * 50% of [[patients]] have an [[ASD]] or [[patent foramen ovale]]. | ||
* 25% have an [[accesory pathway]] | * 25% have an [[accesory pathway]] such as [[Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome]]. | ||
Listed below are the other associated conditions: | |||
* [[Aortic coarctation]] | * [[Aortic coarctation]] | ||
* | * Cleft anterior leaflet of the [[mitral valve]] | ||
* [[Coarctation of the aorta]] | * [[Coarctation of the aorta]] | ||
* | * Corrected [[transposition of the great arteries]] | ||
*[[Hypoplastic]] [[pulmonary arteries]] | |||
*[[Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction|Left ventricular outflow obstruction]] | |||
* [[Hypoplastic pulmonary arteries]] | |||
* [[Left ventricular outflow obstruction]] | |||
* [[Mitral valve prolapse]] | * [[Mitral valve prolapse]] | ||
* | * Parachute mitral valve | ||
* [[ | * Partial [[atrioventricular canal]] | ||
* [[Patent ductus arteriosus]] | * [[Patent ductus arteriosus]] | ||
* [[Pulmonary atresia]] with an intact ventricular septum | * [[Pulmonary atresia]] with an intact [[ventricular septum]] | ||
* [[Pulmonary stenosis]] | * [[Pulmonary stenosis]] | ||
* [[Subaortic stenosis]] | * [[Subaortic stenosis]] | ||
* [[Tetralogy of Fallot]] | * [[Tetralogy of Fallot]] | ||
* [[Ventricular septal defect]] ([[VSD]]) | * [[Ventricular septal defect]] ([[VSD]]) | ||
*[[Downs syndrome]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:37, 7 July 2020
|
Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve Microchapters | |
|
Diagnosis | |
|---|---|
|
Treatment | |
|
Case Studies | |
|
Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology On the Web | |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology | |
|
FDA on Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology | |
|
CDC on Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology | |
|
Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology in the news | |
|
Blogs on Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology | |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve pathophysiology | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Claudia P. Hochberg, M.D. [3];Priyamvada Singh, MBBS [4],Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Maneesha Nandimandalam, M.B.B.S.[5]
Overview
The pathophysiology of Ebstein's anomaly depends on the morphology of tricuspid valve and the right ventricle. The annulus of the valve is in normal position. The valve leaflets however, are to a varying degree attached to the walls and septum of the right ventricle. There is subsequent atrialization of a portion of the morphologic right ventricle (which is then contiguous with the right atrium). This causes the right atrium to be large and the anatomic right ventricle to be small in size. 50% of cases involve an atrial shunt (either a PFO or an ASD). Mutations in MYH7, which a sarcomere gene encoding the cardiac beta-myosin heavy chain have been linked in the occurence of familial Ebstein anomaly. Commonly associated conditions include Aortic coarctation, Cleft anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, Coarctation of the aorta, corrected transposition of the great arteries, Hypoplastic pulmonary arteries, Left ventricular outflow obstruction etc.
Pathophysiology
- Pathophysiology mainly involves the right ventricle, right atrium and tricuspid valve.[1][2][3][4]
- They include:
- Failure of TV(tricuspid valve) leaflet delamination
- Apical descent of the functional tricuspid orifice
- Right ventricular dilation and “atrialization”
- Anterior leaflet abnormal fenestrations and tethering
- Right atrioventricular junction dilation
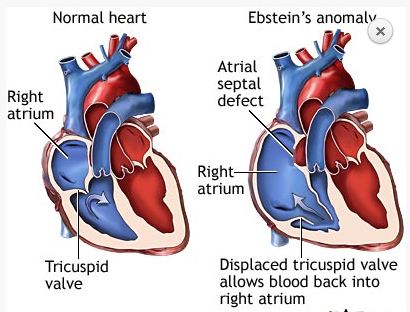
Source: National Library Of Medicine.

Tricuspid Valve
- The superficial layer of the right myocardium usually delaminates to form the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve.
- Any Delamination failure might result in adherence of the leaflets to the ventricular myocardium as a result causes apical displacement of the tricuspid valve leaflets.
- The tricuspid valve orifice is in normal position.
- The anterior leaflet of the tricuspid valve is attached to the tricuspid valve annulus or to the right ventricular endocardium.
- The septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are absent most of the time.
- Due to these changes, the tricuspid valve may become funnel-shaped and incompetent or leaky.
Right Ventricle
The right ventricle changes secondary to the malformed tricuspid valves. The right ventricle can be divided into two parts by the malformed valve:
- The downward extension of the tricuspid valve causes 'atrialization' of the proximal part of the right ventricle.
- The small distal part, the right ventricle proper, thus is reduced in size and sometimes comprises only of the right ventricular outflow tract.
Genetics
- Till now the genetic basis for this condition is largely unknown or very little is known about this.[5][6]
- Mutations in MYH7, which a sarcomere gene encoding the cardiac beta-myosin heavy chain have been linked in the occurence of familial Ebstein anomaly.
- It is formulated that embryonic cell migration may be impaired by these MYH7 mutations.
- Cardiac transcription factors NK2 homeobox 5 (NKX2-5) and GATA binding protein 4 (GATA4) mutations have also been described in some cases.
Associated Conditions
Commonly associated conditions include:[7][8][9][10]
- 50% of patients have an ASD or patent foramen ovale.
- 25% have an accesory pathway such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Listed below are the other associated conditions:
- Aortic coarctation
- Cleft anterior leaflet of the mitral valve
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Corrected transposition of the great arteries
- Hypoplastic pulmonary arteries
- Left ventricular outflow obstruction
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Parachute mitral valve
- Partial atrioventricular canal
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Subaortic stenosis
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Downs syndrome
References
- ↑ Kloesel B, DiNardo JA, Body SC (September 2016). "Cardiac Embryology and Molecular Mechanisms of Congenital Heart Disease: A Primer for Anesthesiologists". Anesth. Analg. 123 (3): 551–69. doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000001451. PMC 4996372. PMID 27541719.
- ↑ Postma AV, van Engelen K, van de Meerakker J, Rahman T, Probst S, Baars MJ, Bauer U, Pickardt T, Sperling SR, Berger F, Moorman AF, Mulder BJ, Thierfelder L, Keavney B, Goodship J, Klaassen S (February 2011). "Mutations in the sarcomere gene MYH7 in Ebstein anomaly". Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 4 (1): 43–50. doi:10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.957985. PMID 21127202.
- ↑ Bettinelli AL, Mulder TJ, Funke BH, Lafferty KA, Longo SA, Niyazov DM (December 2013). "Familial ebstein anomaly, left ventricular hypertrabeculation, and ventricular septal defect associated with a MYH7 mutation". Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 161A (12): 3187–90. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.36182. PMID 23956225.
- ↑ Holst KA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA (2019). "Ebstein's Anomaly". Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 15 (2): 138–144. doi:10.14797/mdcj-15-2-138. PMC 6668741 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 31384377. - ↑ Klaassen S, Probst S, Oechslin E, Gerull B, Krings G, Schuler P, Greutmann M, Hürlimann D, Yegitbasi M, Pons L, Gramlich M, Drenckhahn JD, Heuser A, Berger F, Jenni R, Thierfelder L (June 2008). "Mutations in sarcomere protein genes in left ventricular noncompaction". Circulation. 117 (22): 2893–901. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.746164. PMID 18506004.
- ↑ Pierpont ME, Brueckner M, Chung WK, Garg V, Lacro RV, McGuire AL, Mital S, Priest JR, Pu WT, Roberts A, Ware SM, Gelb BD, Russell MW (November 2018). "Genetic Basis for Congenital Heart Disease: Revisited: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association". Circulation. 138 (21): e653–e711. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000606. PMC 6555769 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 30571578. - ↑ Siehr SL, Punn R, Priest JR, Lowenthal A (January 2014). "Ebstein anomaly and Trisomy 21: A rare association". Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 7 (1): 67–9. doi:10.4103/0974-2069.126569. PMC 3959069. PMID 24701093.
- ↑ Davido A, Maarek M, Jullien JL, Corone P (May 1985). "[Ebstein's disease associated with Fallot's tetralogy. Apropos of a familial case, review of the literature, embryologic and genetic implications]". Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss (in French). 78 (5): 752–6. PMID 3925918.
- ↑ van Trier DC, Feenstra I, Bot P, de Leeuw N, Draaisma JM (August 2013). "Cardiac anomalies in individuals with the 18q deletion syndrome; report of a child with Ebstein anomaly and review of the literature". Eur J Med Genet. 56 (8): 426–31. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2013.05.002. PMID 23707655.
- ↑ Vermeer AM, van Engelen K, Postma AV, Baars MJ, Christiaans I, De Haij S, Klaassen S, Mulder BJ, Keavney B (August 2013). "Ebstein anomaly associated with left ventricular noncompaction: an autosomal dominant condition that can be caused by mutations in MYH7". Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 163C (3): 178–84. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31365. PMID 23794396.