Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases: Difference between revisions
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) |
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Hirschsprung disease must be differentiated from other diseases that cause failure to pass meconium and abdominal distension in infants, such as meconium plug syndrome, small left colon syndrome and congenital hypothyroidism. | Hirschsprung disease must be differentiated from other diseases that cause failure to pass meconium and abdominal distension in infants, such as meconium plug syndrome, small left colon syndrome and congenital hypothyroidism. | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
Hirschprung's disease must be differentiated from other diseases in infancy presenting with similar features such as failure to pass meconium, abdominal distension and non-bilious vomiting. | Hirschprung's disease must be differentiated from other diseases in infancy presenting with similar features such as failure to pass meconium, abdominal distension, and non-bilious vomiting. | ||
*Meconium plug syndrome | *Meconium plug syndrome | ||
*Small left colon syndrome | *Small left colon syndrome | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
* Usually seen in premature infants. | * Usually seen in premature infants. | ||
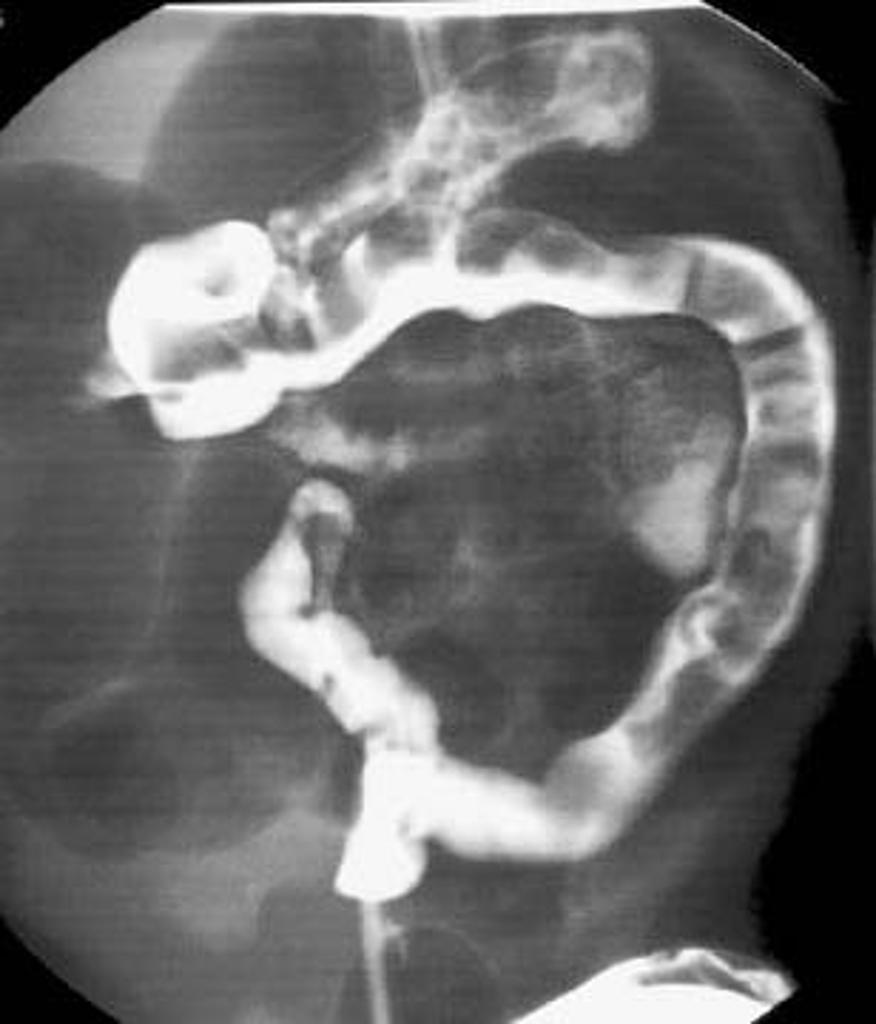
|[[Image: | |[[Image:Meconium-plug-syndrome - Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID 11606.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Abdominal X-ray with contrast showing inspissated meconium in the intestine proximal to the colon - Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID 11606]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Small left colon syndrome | |Small left colon syndrome | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* Usually associated with gestational diabetes. | * Usually associated with gestational diabetes. | ||
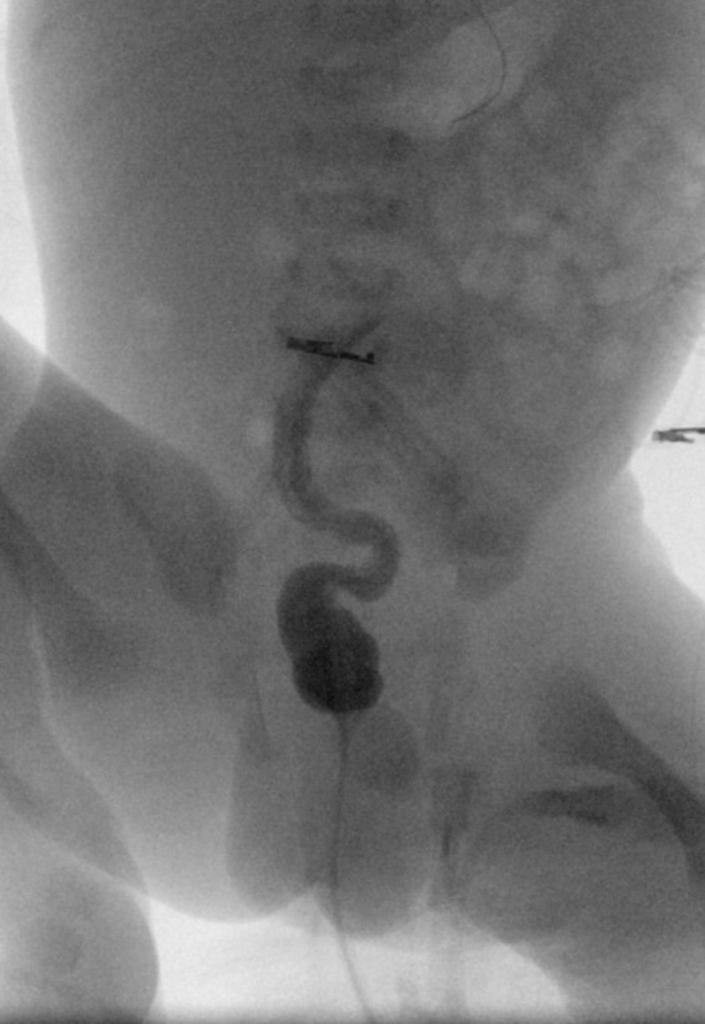
|[[Image: | |[[Image:Small-left-colon-syndrome-1 - Case courtesy of Dr Eric F Greif, Radiopaedia.org, rID 30024.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Abdominal X-ray with contrast shows decreased caliber of the descending and sigmoid colon, loss of haustration along with filling defects corresponding to retained feces - Case courtesy of Dr Eric F Greif, Radiopaedia.org, rID 30024]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Distal small bowel /colonic atresia | |Distal small bowel /colonic atresia | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
* Colonic atresia may affect normal children or may be associated with other abnormalities as Hirschsprung disease or gastroschisis. | * Colonic atresia may affect normal children or may be associated with other abnormalities as Hirschsprung disease or gastroschisis. | ||
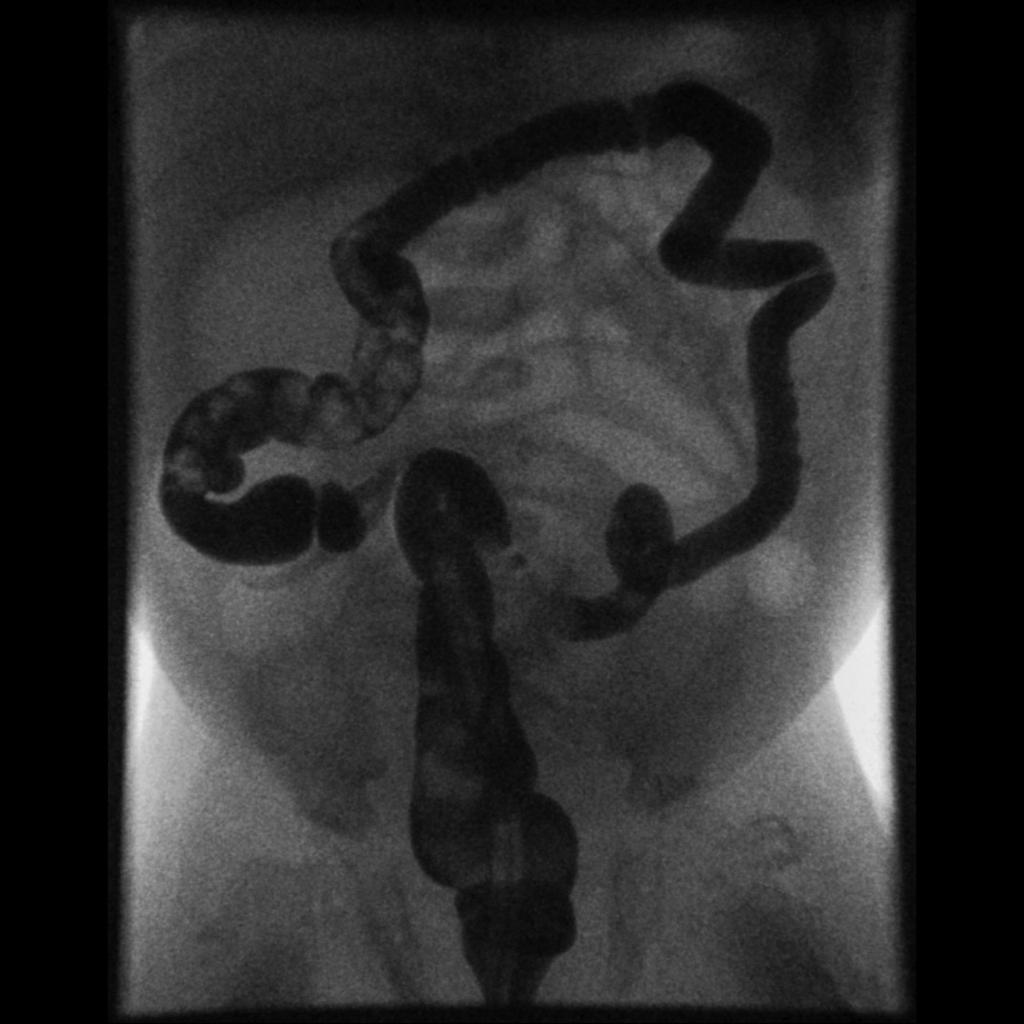
|[[Image: | |[[Image:Small-bowel-atresia - Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID 5959.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Normal appearing colon that is small and unused. Contrast fills the whole colon and passes to the ileum - Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID 5959]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Meconium ileus | |Meconium ileus | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
* Meconium ileus may first present with complications perforation and volvulus. | * Meconium ileus may first present with complications perforation and volvulus. | ||
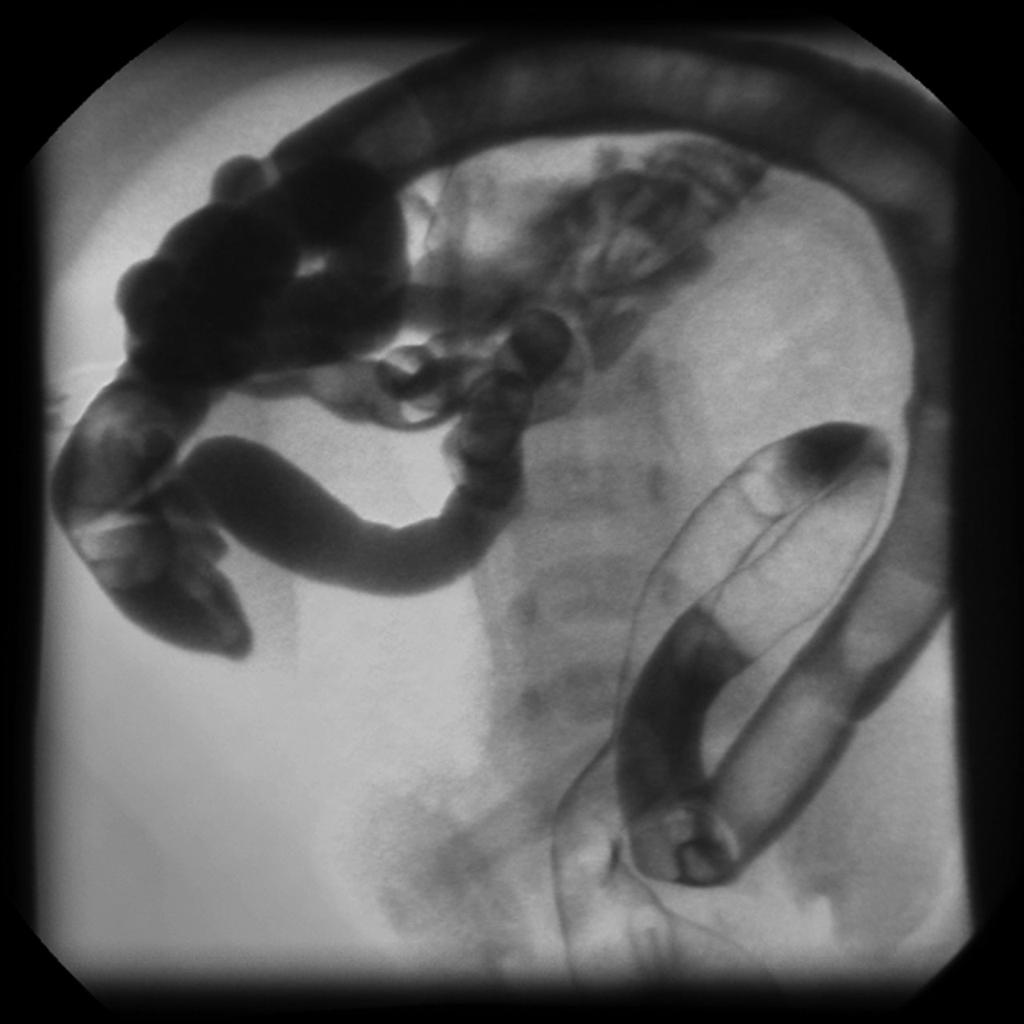
|[[Image: | |[[Image:Meconium-ileus-neonate-with-cystic-fibrosis - Case courtesy of Dr Michael Sargent, Radiopaedia.org, rID 6009.jpg|center|300px|thumb|Contrast enema shows inspissated meconium starting from the mid sigmoid colon and going up till the splenic flexure. The colon is normal in diameter ruling out microcolon]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Congenital hypothyroidism | |Congenital hypothyroidism | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 15 June 2017
|
Hirschsprung's disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases |
|
FDA on Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases |
|
CDC on Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases |
|
Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases in the news |
|
Blogs on Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Differentiating Hirschsprung's Disease from other Diseases |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Younes M.B.B.CH [2]
Overview
Hirschsprung disease must be differentiated from other diseases that cause failure to pass meconium and abdominal distension in infants, such as meconium plug syndrome, small left colon syndrome and congenital hypothyroidism.
Differential Diagnosis
Hirschprung's disease must be differentiated from other diseases in infancy presenting with similar features such as failure to pass meconium, abdominal distension, and non-bilious vomiting.
- Meconium plug syndrome
- Small left colon syndrome
- Distal small bowel /colonic atresia
- Meconium ileus and cystic fibrosis complex
- Congenital hypothyroidism