Darunavir: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 482: | Line 482: | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
{{ | {{Drugbox2 | ||
| Verifiedfields = changed | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| verifiedrevid = 460773860 | | verifiedrevid = 460773860 | ||
Revision as of 15:08, 6 August 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Darunavir is a protease inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection. Common adverse reactions include diarrhea, nausea, rash, headache, abdominal pain and vomiting.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1)
- Dosing Information
- PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir to exert its therapeutic effect. Failure to correctly co-administer PREZISTA with ritonavir will result in plasma levels of darunavir that will be insufficient to achieve the desired antiviral effect and will alter some drug interactions.
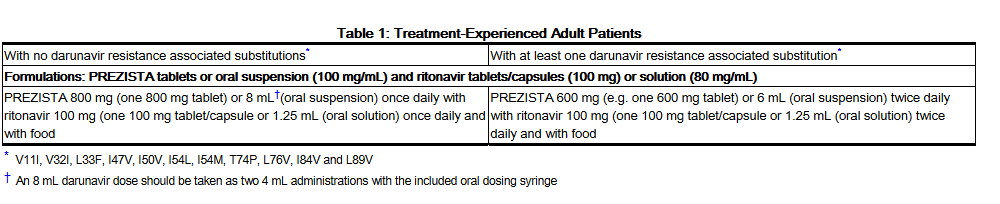
- Treatment-Naïve Adult Patients
- The recommended oral dose of PREZISTA is 800 mg (one 800 mg tablet or 8 mL of the oral suspension) taken with ritonavir 100 mg (one 100 mg tablet/capsule or 1.25 mL of a 80 mg/mL ritonavir oral solution) once daily and with food. An 8 mL darunavir dose should be taken as two 4 mL administrations with the included oral dosing syringe.
- Treatment-Experienced Adult Patients
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Darunavir in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Darunavir in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1)
- Dosing Information
- The indication for treatment-experienced pediatric patients 3 to less than 18 years of age is based on analyses of plasma HIV-1 RNA levels and CD4+ cell counts from two open-label Phase 2 trials in antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric subjects(24-week analysis for one trial in patients 6 to less than 18 years of age; 48-week analysis for one trial in patients 3 to less than 6 years of age) . The indication for treatment-naïve pediatric patients or antiretroviral treatment-experienced patients with no darunavir resistance associated substitutions is based on one open-label Phase 2 trial of 48 weeks duration in antiretroviral treatment-naïve subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age and pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation for patients 3 to less than 12 years of age.
- In treatment-experienced adult and pediatric patients, the following points should be considered when initiating therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir:
- Treatment history and, when available, genotypic or phenotypic testing should guide the use of PREZISTA/ritonavir [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
- The use of other active agents with PREZISTA/ritonavir is associated with a greater likelihood of treatment response [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4) and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
- Before prescribing PREZISTA, children weighing greater than or equal to 15 kg should be assessed for the ability to swallow tablets. If a child is unable to reliably swallow a tablet, the use of PREZISTA oral suspension should be considered.
- The recommended dose of PREZISTA/ritonavir for pediatric patients (3 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg is based on body weight (see Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5) and should not exceed the recommended adult dose. PREZISTA should be taken with ritonavir and with food.
- The recommendations for the PREZISTA/ritonavir dosage regimens were based on the following:
- Twice daily dosing
- Results from two trials in treatment-experienced pediatric subjects 3 to less 18 years of age demonstrating similar darunavir plasma exposures, virologic response rate and safety profile compared to treatment-experienced adults.
- Twice daily dosing
- Once daily dosing
- Results from one trial in treatment-naive pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age demonstrating similar darunavir plasma exposures, virologic response rate and safety profile compared to treatment-naive adults.
- Once daily dosing
Results from population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation in children 3 to less than 12 years of age predicting similar darunavir plasma exposures compared to treatment-naïve adults. Although no clinical trial was conducted to collect exposure-safety data, the predicted exposures from the once daily dosing is supported by exposures observed in a pediatric clinical trial where twice-daily dosing was administered.
- Dosing recommendations for treatment-naïve pediatric patients or antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric patients with no darunavir resistance associated substitutions
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 10 kg but less than 15 kg
- The weight-based dose in antiretroviral treatment-naïve pediatric patients or antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric patients with no darunavir resistance associated substitutions is PREZISTA 35 mg/kg once daily with ritonavir 7 mg/kg once daily using the following table.
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 15 kg
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 15 kg can be dosed with PREZISTA oral tablet(s) or suspension using the following table:
- Dosing recommendations for treatment-experienced pediatric patients with at least one darunavir resistance associated substitutions
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 10 kg but less than 15 kg
- The weight-based dose in antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric patients with at least one darunavir resistance associated substitution is PREZISTA 20 mg/kg twice daily with ritonavir 3 mg/kg twice daily using the following table:
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 15 kg
- Pediatric patients weighing at least 15 kg can be dosed with PREZISTA oral tablet(s) or suspension using the following table:
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Darunavir in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Darunavir in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (narrow therapeutic index). These drugs and other contraindicated drugs (which may lead to reduced efficacy of darunavir) are listed in Table 6
Warnings
Precautions
- General
- PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir and food to achieve the desired antiviral effect. Failure to administer PREZISTA with ritonavir and food may result in a loss of efficacy of darunavir.
- Please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for additional information on precautionary measures.
- Hepatotoxicity
- Drug-induced hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis) has been reported with PREZISTA/ritonavir. During the clinical development program (N=3063), hepatitis was reported in 0.5% of patients receiving combination therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Patients with pre-existing liver dysfunction, including chronic active hepatitis B or C, have an increased risk for liver function abnormalities including severe hepatic adverse events.
- Post-marketing cases of liver injury, including some fatalities, have been reported. These have generally occurred in patients with advanced HIV-1 disease taking multiple concomitant medications, having co-morbidities including hepatitis B or C co-infection, and/or developing immune reconstitution syndrome. A causal relationship with PREZISTA/ritonavir therapy has not been established.
- Appropriate laboratory testing should be conducted prior to initiating therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir and patients should be monitored during treatment. Increased AST/ALT monitoring should be considered in patients with underlying chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases, especially during the first several months of PREZISTA/ritonavir treatment.
- Evidence of new or worsening liver dysfunction (including clinically significant elevation of liver enzymes and/or symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, dark urine, liver tenderness, hepatomegaly) in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir should prompt consideration of interruption or discontinuation of treatment.
- Severe Skin Reactions
- During the clinical development program (n=3063), severe skin reactions, accompanied by fever and/or elevations of transaminases in some cases, have been reported in 0.4% of subjects. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome was rarely (less than 0.1%) reported during the clinical development program. During post-marketing experience toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis have been reported. Discontinue PREZISTA/ritonavir immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions develop. These can include but are not limited to severe rash or rash accompanied with fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, hepatitis and/or eosinophilia.
- Rash (all grades, regardless of causality) occurred in 10.3% of subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir [also see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Rash was mostly mild-to-moderate, often occurring within the first four weeks of treatment and resolving with continued dosing. The discontinuation rate due to rash in subjects using PREZISTA/ritonavir was 0.5%.
- Rash occurred more commonly in treatment-experienced subjects receiving regimens containing PREZISTA/ritonavir + raltegravir compared to subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir without raltegravir or raltegravir without PREZISTA/ritonavir. However, rash that was considered drug related occurred at similar rates for all three groups. These rashes were mild to moderate in severity and did not limit therapy; there were no discontinuations due to rash.
- Sulfa Allergy
- Darunavir contains a sulfonamide moiety. PREZISTA should be used with caution in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy. In clinical studies with PREZISTA/ritonavir, the incidence and severity of rash were similar in subjects with or without a history of sulfonamide allergy.
- Drug Interactions
- See Table 6 for a listing of drugs that are contraindicated for use with PREZISTA/ritonavir due to potentially life-threatening adverse events, significant drug-drug interactions, or loss of therapeutic effect to PREZISTA [see Contraindications (4)]. Please refer to Table 11 for established and other potentially significant drug-drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
- Diabetes Mellitus / Hyperglycemia
- New onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in HIV-infected patients receiving protease inhibitor (PI) therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for treatment of these events. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued PI therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and causal relationships between PI therapy and these events have not been established.
- Fat Redistribution
- Redistribution/accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and "cushingoid appearance" have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
- Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including PREZISTA. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune systems respond may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
- Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of antiretroviral treatment.
- Hemophilia
- There have been reports of increased bleeding, including spontaneous skin hematomas and hemarthrosis in patients with hemophilia type A and B treated with PIs. In some patients, additional factor VIII was given. In more than half of the reported cases, treatment with PIs was continued or reintroduced if treatment had been discontinued. A causal relationship between PI therapy and these episodes has not been established.
- Resistance/Cross-Resistance
- Because the potential for HIV cross-resistance among PIs has not been fully explored in PREZISTA/ritonavir treated patients, the effect therapy with PREZISTA will have on the activity of subsequently administered PIs is unknown [see Microbiology (12.4)].
- Pediatric Patients
- Do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age in view of toxicity and mortality observed in juvenile rats dosed with darunavir (from 20 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg) up to days 23 to 26 of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 and 8.4) Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].
- The overall safety profile of PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily and PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily is based on clinical trials and post-marketing data, and is consistent with the data presented below.
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
- Due to the need for co-administration of PREZISTA with ritonavir, please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for ritonavir-associated adverse reactions
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Treatment-Naïve Adults
- Study TMC114-C211
- The safety assessment is based on all safety data from the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C211 comparing PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily versus lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day in 689 antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects. The total mean exposure for subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily arm and in the lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day arm was 162.5 and 153.5 weeks, respectively.
- The majority of the adverse drug reactions (ADRs) reported during treatment with PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily were mild in severity. The most common clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily (greater than or equal to 5%) of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) were diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain and rash. 2.3% of subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm discontinued treatment due to ADRs.
- ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) in antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected adult subjects are presented in Table 7 and subsequent text below the table.
- Less Common Adverse Reactions
- Treatment-emergent ADRs of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) occurring in less than 2% of antiretroviral treatment-naïve subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily are listed below by body system:
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: acute pancreatitis, dyspepsia, flatulence
- General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: asthenia
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: acute hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis, hepatotoxicity)
- Immune System Disorders: (drug) hypersensitivity, immune reconstitution syndrome
- Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: diabetes mellitus
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myalgia, osteonecrosis
- Psychiatric Disorders: abnormal dreams
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: angioedema, pruritus, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, urticaria
- Laboratory abnormalities:
- Selected Grade 2 to 4 laboratory abnormalities that represent a worsening from baseline observed in antiretroviral treatment-naïve adult subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily are presented in Table 8.
Treatment-Experienced Adults
- Study TMC114-C214
- The safety assessment is based on all safety data from the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C214 comparing PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily versus lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily in 595 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult subjects. The total mean exposure for subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily arm and in the lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily arm was 80.7 and 76.4 weeks, respectively.
- The majority of the ADRs reported during treatment with PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily were mild in severity. The most common clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily (greater than or equal to 5%) of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) were diarrhea, nausea, rash, abdominal pain and vomiting. 4.7% of subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm discontinued treatment due to ADRs.
- ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult subjects are presented in Table 9 and subsequent text below the table.
- Less Common Adverse Reactions
- Treatment-emergent ADRs of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) occurring in less than 2% of antiretroviral treatment-experienced subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily are listed below by body system:
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: acute pancreatitis, flatulence
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myalgia
- Psychiatric Disorders: abnormal dreams
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: pruritus, urticaria
- Laboratory abnormalities:
- Selected Grade 2 to 4 laboratory abnormalities that represent a worsening from baseline observed in antiretroviral treatment-experienced adult subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily are presented inTable 10.
Serious ADRs
- The following serious ADRs of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) occurred in the Phase 2b studies and Phase 3 studies with PREZISTA/ritonavir: abdominal pain, acute hepatitis, acute pancreatitis, anorexia, asthenia, diabetes mellitus, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, hepatic enzyme increased, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, immune reconstitution syndrome, low density lipoprotein increased, nausea, pancreatic enzyme increased, rash, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, and vomiting.
Patients co-infected with hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus
- In subjects co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir, the incidence of adverse events and clinical chemistry abnormalities was not higher than in subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir who were not co-infected, except for increased hepatic enzymes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. The pharmacokinetic exposure in co-infected subjects was comparable to that in subjects without co-infection.
Clinical Trials Experience: Pediatric Patients
- PREZISTA/ritonavir has been studied in combination with other antiretroviral agents in 3 Phase II trials. TMC114-C212, in which 80 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 6 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 20 kg were included, TMC114-C228, in which 21 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 3 to less than 6 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg were included, and TMC114-C230 in which 12 antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric patients aged from 12 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 40 kg were included. The TMC114-C212 and C228 trials evaluated PREZISTA/ritonavir twice daily dosing and the TMC114-C230 trial evaluated PREZISTA/ritonavir once daily dosing [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Studies (14.4)].
- Frequency, type, and severity of ADRs in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adults.
- Study TMC114-C212
- Clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir (all grades, greater than or equal to 3%), were vomiting (13%), diarrhea (11%), abdominal pain (10%), headache (9%), rash (5%), nausea (4%) and fatigue (3%).
- Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were ALT increased (Grade 3: 3%; Grade 4: 1%), AST increased (Grade 3: 1%), pancreatic amylase increased (Grade 3: 4%, Grade 4: 1%), pancreatic lipase increased (Grade 3: 1%), total cholesterol increased (Grade 3: 1%), and LDL increased (Grade 3: 3%).
- Study TMC114-C228
- Clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir (all grades, greater than or equal to 5%), were diarrhea (24%), vomiting (19%),rash (19%), abdominal pain (5%) and anorexia (5%).
- There were no Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities considered as ADRs in this study.
- Study TMC114-C230
- Clinical ADRs to PREZISTA/ritonavir (all grades, greater than or equal to 3%), were vomiting (33%), nausea (25%), diarrhea (16.7%), abdominal pain (8.3%), decreased appetite (8.3%), pruritus (8.3%), and rash (8.3%).
- There were no Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities considered as ADRs in this study.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following events have been identified during post approval use of PREZISTA. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Redistribution of body fat has been reported.
- Rarely, rhabdomyolysis (associated with co-administration with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and PREZISTA/ritonavir) has been reported.
- In addition, toxic epidermal necrolysis,acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms have been reported rarely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Drug Interactions
- PREZISTA co-administered with ritonavir is an inhibitor of CYP3A and CYP2D6. Co-administration of PREZISTA and ritonavir with drugs that are primarily metabolized by CYP3A and CYP2D6 may result in increased plasma concentrations of such drugs, which could increase or prolong their therapeutic effect and adverse events (see Table 11).
- Darunavir and ritonavir are metabolized by CYP3A. Drugs that induce CYP3A activity would be expected to increase the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir, resulting in lowered plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir. Co-administration of darunavir and ritonavir and other drugs that inhibit CYP3A may decrease the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir and may result in increased plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir (see Table 11).
Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
- Table 11 provides dosing recommendations as a result of drug interactions with PREZISTA/ritonavir. These recommendations are based on either drug interaction studies or predicted interactions due to the expected magnitude of interaction and potential for serious adverse events or loss of efficacy.
- In addition to the drugs included in Table 11, the interaction between PREZISTA/ritonavir and the following drugs were evaluated in clinical studies and no dose adjustments are needed for either drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]: atazanavir, efavirenz, etravirine, nevirapine, omeprazole, ranitidine, rilpivirine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Using cross-trial comparisons to historical pharmacokinetic data, dolutegravir did not appear to affect the pharmacokinetics of darunavir. Darunavir/ritonavir had no clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of dolutegravir.
- Other nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs):
- Based on the different elimination pathways of the other NRTIs (zidovudine, zalcitabine, emtricitabine, stavudine, lamivudine and abacavir) that are primarily renally excreted, no drug interactions are expected for these drugs and PREZISTA/ritonavir.
- Other PIs:
- The co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir and PIs other than lopinavir/ritonavir, saquinavir, atazanavir, and indinavir has not been studied. Therefore, such co-administration is not recommended.
- Integrase strand transfer inhibitors:
- Based on the pharmacokinetic data from literature references, either no clinically significant changes in darunavir concentrations or decreases in darunavir concentrations were observed with concomitant use of raltegravir. The potential decrease in darunavir concentrations does not appear to be clinically relevant. PREZISTA/ritonavir and raltegravir can be used without dose adjustments.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- No adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted in pregnant women. Reproduction studies conducted with darunavir showed no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity in mice and rats in the presence or absence of ritonavir as well as in rabbits with darunavir alone. In these studies, darunavir exposures (based on AUC) were higher in rats (3-fold), whereas in mice and rabbits, exposures were lower (less than 1-fold) compared to those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose of darunavir boosted with ritonavir.
- In the rat pre- and postnatal development study, a reduction in pup body weight gain was observed with darunavir alone or in combination with ritonavir during lactation. This was due to exposure of pups to drug substances via the milk. Sexual development, fertility and mating performance of offspring were not affected by maternal treatment with darunavir alone or in combination with ritonavir. The maximal plasma exposures achieved in rats were approximately 50% of those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose boosted with ritonavir.
- In the juvenile toxicity study where rats were directly dosed with darunavir, deaths occurred from post-natal day 5 through 11 at plasma exposure levels ranging from 0.1 to 1.0 of the human exposure levels. In a 4-week rat toxicology study, when dosing was initiated on post-natal day 23 (the human equivalent of 2 to 3 years of age), no deaths were observed with a plasma exposure (in combination with ritonavir) of 0.1 of the human plasma exposure levels.
- Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry: To monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to PREZISTA, an Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry has been established. Physicians are encouraged to register patients by calling 1-800-258-4263.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Darunavir in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Darunavir during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers in the United States not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. Although it is not known whether darunavir is secreted in human milk, darunavir is secreted into the milk of lactating rats. Because of both the potential for HIV transmission and the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should be instructed not to breastfeed if they are receiving PREZISTA.
Pediatric Use
- Do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age because of toxicity and mortality observed in juvenile rats dosed with darunavir (from 20 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg) up to days 23 to 26 of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11), Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)].
- The safety, pharmacokinetic profile, and virologic and immunologic responses of PREZISTA/ritonavir were evaluated in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 3 to less than 18 years of age and weighting at least 10 kg. These subjects were evaluated in clinical trials TMC114-C212 (80 subjects, 6 to less than 18 years of age) and TMC114-228 (21 subjects, 3 to less than 6 years of age) [see Adverse Reactions (6.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.4)]. Frequency, type, and severity of adverse drug reactions in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. Please see Dosage and Administration (2.2) for twice-daily dosing recommendations for pediatric subjects 3 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg.
- In clinical trial TMC114-C230, the safety, pharmacokinetic profile and virologic and immunologic responses of PREZISTA/ritonavir administered once daily were evaluated in treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age (12 subjects) [see Adverse Reactions (6.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.4)]. Frequency, type, and severity of adverse drug reactions in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. Once daily dosing recommendations for pediatric patients 3 to less than 12 years of age were derived using population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation. Although a PREZISTA/ritonavir once daily dosing pediatric trial was not conducted in children less than 12 years of age, there is sufficient clinical safety data to support the predicted PREZISTA exposures for the dosing recommendations in this age group [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Please see Dosage and Administration (2.2) for once-daily dosing recommendations for pediatric subjects 3 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of PREZISTA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, caution should be exercised in the administration and monitoring of PREZISTA in elderly patients, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Darunavir with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Darunavir with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that the pharmacokinetics of darunavir were not significantly affected in HIV-infected subjects with moderate renal impairment (CrCL between 30–60 mL/min, n=20). No pharmacokinetic data are available in HIV-1-infected patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease; however, because the renal clearance of darunavir is limited, a decrease in total body clearance is not expected in patients with renal impairment. As darunavir and ritonavir are highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that they will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Hepatic Impairment
- No dose adjustment of PREZISTA/ritonavir is necessary for patients with either mild or moderate hepatic impairment. No pharmacokinetic or safety data are available regarding the use of PREZISTA/ritonavir in subjects with severe hepatic impairment. Therefore, PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Darunavir in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Darunavir in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Darunavir in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Darunavir in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Human experience of acute overdose with PREZISTA/ritonavir is limited. Single doses up to 3200 mg of the oral solution of darunavir alone and up to 1600 mg of the tablet formulation of darunavir in combination with ritonavir have been administered to healthy volunteers without untoward symptomatic effects.
Management
- No specific antidote is available for overdose with PREZISTA. Treatment of overdose with PREZISTA consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed active substance is to be achieved by emesis. Administration of activated charcoal may also be used to aid in removal of unabsorbed active substance. Since PREZISTA is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to be beneficial in significant removal of the active substance.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Darunavir in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Darunavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease. It selectively inhibits the cleavage of HIV-1 encoded Gag-Pol polyproteins in infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature virus particles.
Structure
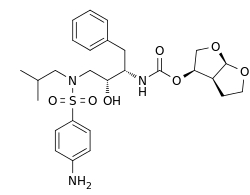
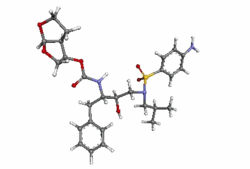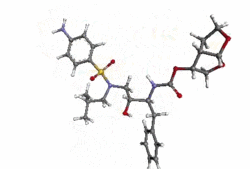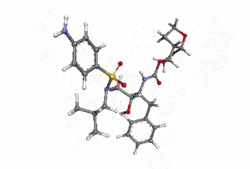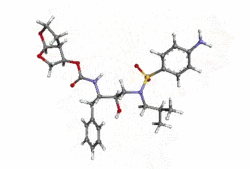
- PREZISTA (darunavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease.
- PREZISTA (darunavir), in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-carbamic acid (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester monoethanolate. Its molecular formula is C27H37N3O7S • C2H5OH and its molecular weight is 593.73. Darunavir ethanolate has the following structural formula:
- Darunavir ethanolate is a white to off-white powder with a solubility of approximately 0.15 mg/mL in water at 20°C.
- PREZISTA 100 mg/mL oral suspension is available as a white to off-white opaque suspension for oral administration.
- PREZISTA 75 mg tablets are available as white, caplet-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration. PREZISTA 150 mg tablets are available as white, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration. PREZISTA 600 mg tablets are available as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration. PREZISTA 800 mg tablets are available as dark red, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets for oral administration.
- Each mL of the oral suspension contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 100 mg darunavir. In addition, each mL contains the inactive ingredients hydroxypropyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, methylparaben sodium, citric acid monohydrate, sucralose, masking flavor, strawberry cream flavor, hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) and purified water.
- Each 75 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 75 mg of darunavir. Each 150 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 150 mg of darunavir. Each 600 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 600 mg of darunavir. Each 800 mg tablet contains darunavir ethanolate equivalent to 800 mg of darunavir. During storage, partial conversion from ethanolate to hydrate may occur; however, this does not affect product quality or performance. Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The 800 mg tablet also contains hypromellose. The 75 and 150 mg tablet film coating, OPADRY® White, contains polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide. The 600 mg tablet film coating, OPADRY® Orange, contains FD&C Yellow No. 6, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide. The 800 mg tablet film coating, OPADRY® Dark Red, contains iron oxide red, polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
- All dosages for PREZISTA are expressed in terms of the free form of darunavir.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Darunavir in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Darunavir in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
- Darunavir was evaluated for carcinogenic potential by oral gavage administration to mice and rats up to 104 weeks. Daily doses of 150, 450 and 1000 mg/kg were administered to mice and doses of 50, 150 and 500 mg/kg was administered to rats. A dose-related increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas were observed in males and females of both species as well as an increase in thyroid follicular cell adenomas in male rats. The observed hepatocellular findings in rodents are considered to be of limited relevance to humans. Repeated administration of darunavir to rats caused hepatic microsomal enzyme induction and increased thyroid hormone elimination, which predispose rats, but not humans, to thyroid neoplasms. At the highest tested doses, the systemic exposures to darunavir (based on AUC) were between 0.4- and 0.7-fold (mice) and 0.7- and 1-fold (rats), relative to those observed in humans at the recommended therapeutic doses (600/100 mg twice daily or 800/100 mg once daily).
- Darunavir was not mutagenic or genotoxic in a battery of in vitro and in vivo assays including bacterial reserve mutation (Ames), chromosomal aberration in human lymphocytes and in vivo micronucleus test in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
- No effects on fertility or early embryonic development were observed with darunavir in rats and darunavir has shown no teratogenic potential in mice or rats (in the presence or absence of ritonavir), and rabbits.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
- In juvenile rats single doses of darunavir (20 mg/kg to 160 mg/kg at ages 5–11 days) or multiple doses of darunavir (40 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg at age 12 days) caused mortality. The mortalities were associated with convulsions in some of the animals. Within this age range exposures in plasma, liver and brain were dose and age dependent and were considerably greater than those observed in adult rats. These findings were attributed to the ontogeny of the CYP450 liver enzymes involved in the metabolism of darunavir and the immaturity of the blood-brain barrier. No treatment-related mortalities were noted in juvenile rats after a single dose of darunavir at 1000 mg/kg on day 26 of age or after repeat dosing at 500 mg/kg from day 23 to 50 of age. The exposures and toxicity profile in the older animals (day 23 or day 26) were comparable to those observed in adult rats. Due to uncertainties regarding the rate of development of the human blood-brain barrier and liver enzymes, do not administer PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Darunavir in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Darunavir Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Darunavir |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Darunavir |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Darunavir in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Darunavir interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Darunavir |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Darunavir |Label Name=Darunavir11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Darunavir |Label Name=Darunavir11.png
}}