Coronary angiography left coronary artery: Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The left main coronary artery gives rise to the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the left circumflex coronary (LCx) artery. Complete visualization of these arteries and their branches requires care and rigor to ensure complete anatomical documentation. Often bifurcations and vessel foreshortening and overlap cause errors in stenosis estimation. There are no steadfast rules in which tomographic views are most useful. Generally, for circumflex and proximal epicardial visualization, the caudal views are most useful. For LAD and LAD/diagonal bifurcation visualization, the cranial views are most useful. Overall, if there is not a significant limitation on contrast utilization, standard 'around the world' angiography using a selection of the following angiographic views will document left coronary anatomy. | The [[left main coronary artery]] gives rise to the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending (LAD)]] artery and the [[Left circumflex artery|left circumflex coronary (LCx)]] artery. Complete visualization of these arteries and their branches requires care and rigor to ensure complete anatomical documentation. Often bifurcations and vessel foreshortening and overlap cause errors in stenosis estimation. There are no steadfast rules in which tomographic views are most useful. Generally, for circumflex and proximal epicardial visualization, the caudal views are most useful. For LAD and LAD/[[Left anterior descending artery#Diagonal Arteries|diagonal]] bifurcation visualization, the cranial views are most useful. Overall, if there is not a significant limitation on contrast utilization, standard 'around the world' angiography using a selection of the following angiographic views will document left coronary anatomy. | ||
==How to Engage the Left Coronary Artery== | ==How to Engage the Left Coronary Artery== | ||
The left main coronary artery is typically cannulated in the 30° RAO position. Using the femoral arterial approach, a Judkins Left 4 (JL4) catheter is used to engage the left coronary artery. The JL catheter usually requires no manipulation other than a simple forward push by the operator. Variations in aortic root size may prevent selective engagement of the left main coronary artery and catheters of different sizes may be utilized accordingly. Variations in the location of ostium and orientation of left main stems may lead to difficult catheter engagement. For superiorly directed left main stems, a shorter Judkins catheter may be used, while inferiorly directed left main stems are engaged by a longer JL catheter or a left Amplatz catheter. If the ostium of the left main coronary artery has a posterior trajectory, a left Amplatz catheter may engage better. | The [[left main coronary artery]] is typically cannulated in the 30° RAO position. Using the femoral arterial approach, a Judkins Left 4 (JL4) catheter is used to engage the left coronary artery. The JL catheter usually requires no manipulation other than a simple forward push by the operator. Variations in aortic root size may prevent selective engagement of the [[left main coronary artery]] and catheters of different sizes may be utilized accordingly. Variations in the location of ostium and orientation of [[left main coronary artery|left main]] stems may lead to difficult catheter engagement. For superiorly directed [[left main coronary artery|left main]] stems, a shorter Judkins catheter may be used, while inferiorly directed [[left main coronary artery|left main]] stems are engaged by a longer JL catheter or a left Amplatz catheter. If the ostium of the left main coronary artery has a posterior trajectory, a left Amplatz catheter may engage better. | ||
==Optimal Views of the Left Coronary Artery== | ==Optimal Views of the Left Coronary Artery== | ||
An uniform sequence of four views is obtained to visualize the left coronary artery and its branches. | An uniform sequence of four views is obtained to visualize the left coronary artery and its branches. | ||
# RAO caudal view to visualize the left main, proximal LAD, and proximal LCx | # RAO caudal view to visualize the [[left main coronary artery|left main]], proximal [[Left anterior descending artery|LAD]], and proximal [[Left circumflex artery|LCx]] | ||
# RAO cranial view to visualize the middle and distal LAD and diagonals | # RAO cranial view to visualize the middle and distal [[Left anterior descending artery|LAD]] and [[Left anterior descending artery#Diagonal Arteries|diagonals]] | ||
# LAO cranial view to visualize the middle and distal LAD in an orthogonal projection and the ostium of the left main | # LAO cranial view to visualize the middle and distal [[Left anterior descending artery|LAD]] in an orthogonal projection and the ostium of the [[left main coronary artery|left main]] | ||
# LAO caudal view to visualize the left main and proximal LAD, ramus intermedius, and LCx | # LAO caudal view to visualize the [[left main coronary artery|left main]] and proximal [[Left anterior descending artery|LAD]], [[ramus intermedius]], and [[Left circumflex artery|LCx]] | ||
===Right Anterior Oblique (RAO) Caudal=== | ===Right Anterior Oblique (RAO) Caudal=== | ||
RAO caudal is considered as the best view for the initial injection of the left system. The left main coronary artery, the ostium and proximal segment of the left anterior descending artery, and the circumflex and obtuse marginal branches are optimally visualized. RAO caudal view is also the best overall view to assess the blush of the left circumflex territory. However, this view obscures the origins of the diagonals and forshortens the middle and distal segments of the left anterior descending artery. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to the right of the spine with a slight inferior angulation. | RAO caudal is considered as the best view for the initial injection of the left system. The [[left main coronary artery]], the ostium and proximal segment of the left anterior descending artery, and the circumflex and obtuse marginal branches are optimally visualized. RAO caudal view is also the best overall view to assess the blush of the left circumflex territory. However, this view obscures the origins of the [[Left anterior descending artery#Diagonal Arteries|diagonals]] and forshortens the middle and distal segments of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending artery]]. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to the right of the spine with a slight inferior angulation. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Right Anterior Oblique (RAO) Cranial=== | ===Right Anterior Oblique (RAO) Cranial=== | ||
The RAO cranial view clearly expose the middle and distal segments of the left anterior descending artery as well as the origins of the diagonals. In general, the RAO cranial projection is not useful for visualizing the left circumflex artery except in cases of left dominant circulations since it may provide a view of the left posterior descending artery. RAO cranial is the best overall view to assess the blush of the LAD, as it minimizes intra- and inter-arterial overlap. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to the right of the spine with a slight anterior angulation. | The RAO cranial view clearly expose the middle and distal segments of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending artery]] as well as the origins of the [[Left anterior descending artery#Diagonal Arteries|diagonals]]. In general, the RAO cranial projection is not useful for visualizing the [[left circumflex artery]] except in cases of left dominant circulations since it may provide a view of the left posterior descending artery. RAO cranial is the best overall view to assess the blush of the LAD, as it minimizes intra- and inter-arterial overlap. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to the right of the spine with a slight anterior angulation. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Left Anterior Oblique (LAO) Cranial=== | ===Left Anterior Oblique (LAO) Cranial=== | ||
The LAO cranial view provides a clear view of the middle and distal segments of the left anterior descending artery and the origins of the diagonals. It also exposes the ostium of the left main coronary artery. However, the proximal segments of the left anterior descending artery is usually foreshortened thus requiring additional LAO angulation. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to lie to the left of the spine with a slight anterior angulation. | The LAO cranial view provides a clear view of the middle and distal segments of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending artery]] and the origins of the [[Left anterior descending artery#Diagonal Arteries|diagonals]]. It also exposes the ostium of the [[left main coronary artery]]. However, the proximal segments of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending artery]] is usually foreshortened thus requiring additional LAO angulation. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to lie to the left of the spine with a slight anterior angulation. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
===Left Anterior Oblique (LAO) Caudal=== | ===Left Anterior Oblique (LAO) Caudal=== | ||
The LAO caudal view is also referred to as the 'spider view' and offers visualization of the left main coronary artery and the proximal segments of the left anterior descending artery, the ramus intermedius, and the left circumflex artery. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to lie to the left of the spine with a slight inferior angulation. | The LAO caudal view is also referred to as the 'spider view' and offers visualization of the [[left main coronary artery]] and the proximal segments of the [[Left anterior descending artery|left anterior descending artery]], the [[ramus intermedius]], and the [[left circumflex artery]]. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to lie to the left of the spine with a slight inferior angulation. | ||
{| | {| | ||
Revision as of 03:26, 5 September 2013
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
The left main coronary artery gives rise to the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the left circumflex coronary (LCx) artery. Complete visualization of these arteries and their branches requires care and rigor to ensure complete anatomical documentation. Often bifurcations and vessel foreshortening and overlap cause errors in stenosis estimation. There are no steadfast rules in which tomographic views are most useful. Generally, for circumflex and proximal epicardial visualization, the caudal views are most useful. For LAD and LAD/diagonal bifurcation visualization, the cranial views are most useful. Overall, if there is not a significant limitation on contrast utilization, standard 'around the world' angiography using a selection of the following angiographic views will document left coronary anatomy.
How to Engage the Left Coronary Artery
The left main coronary artery is typically cannulated in the 30° RAO position. Using the femoral arterial approach, a Judkins Left 4 (JL4) catheter is used to engage the left coronary artery. The JL catheter usually requires no manipulation other than a simple forward push by the operator. Variations in aortic root size may prevent selective engagement of the left main coronary artery and catheters of different sizes may be utilized accordingly. Variations in the location of ostium and orientation of left main stems may lead to difficult catheter engagement. For superiorly directed left main stems, a shorter Judkins catheter may be used, while inferiorly directed left main stems are engaged by a longer JL catheter or a left Amplatz catheter. If the ostium of the left main coronary artery has a posterior trajectory, a left Amplatz catheter may engage better.
Optimal Views of the Left Coronary Artery
An uniform sequence of four views is obtained to visualize the left coronary artery and its branches.
- RAO caudal view to visualize the left main, proximal LAD, and proximal LCx
- RAO cranial view to visualize the middle and distal LAD and diagonals
- LAO cranial view to visualize the middle and distal LAD in an orthogonal projection and the ostium of the left main
- LAO caudal view to visualize the left main and proximal LAD, ramus intermedius, and LCx
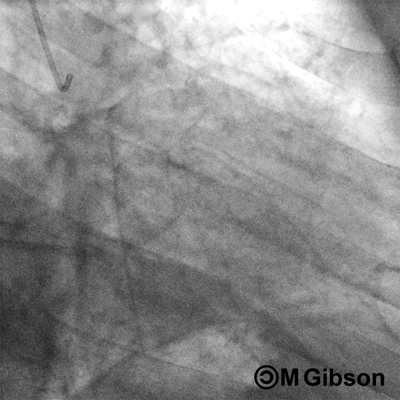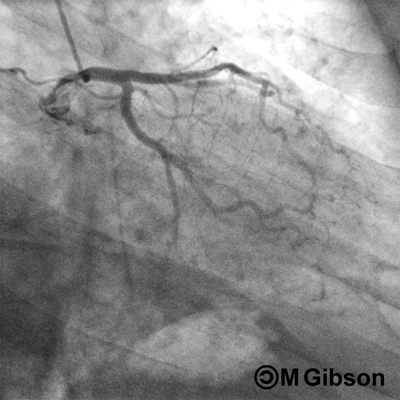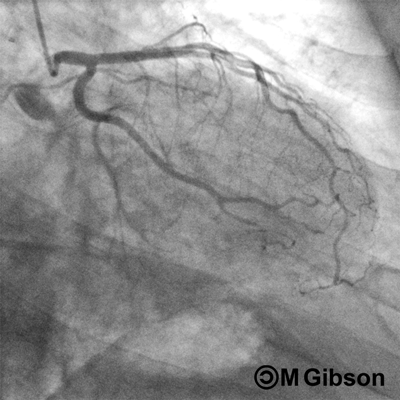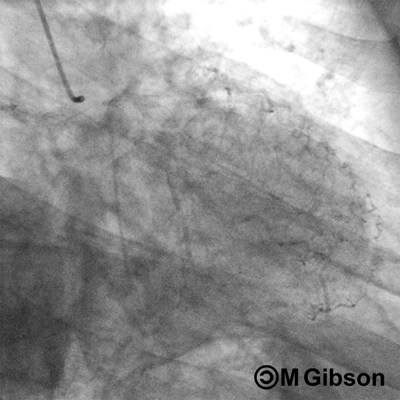
Right Anterior Oblique (RAO) Caudal
RAO caudal is considered as the best view for the initial injection of the left system. The left main coronary artery, the ostium and proximal segment of the left anterior descending artery, and the circumflex and obtuse marginal branches are optimally visualized. RAO caudal view is also the best overall view to assess the blush of the left circumflex territory. However, this view obscures the origins of the diagonals and forshortens the middle and distal segments of the left anterior descending artery. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to the right of the spine with a slight inferior angulation.
 |
 |
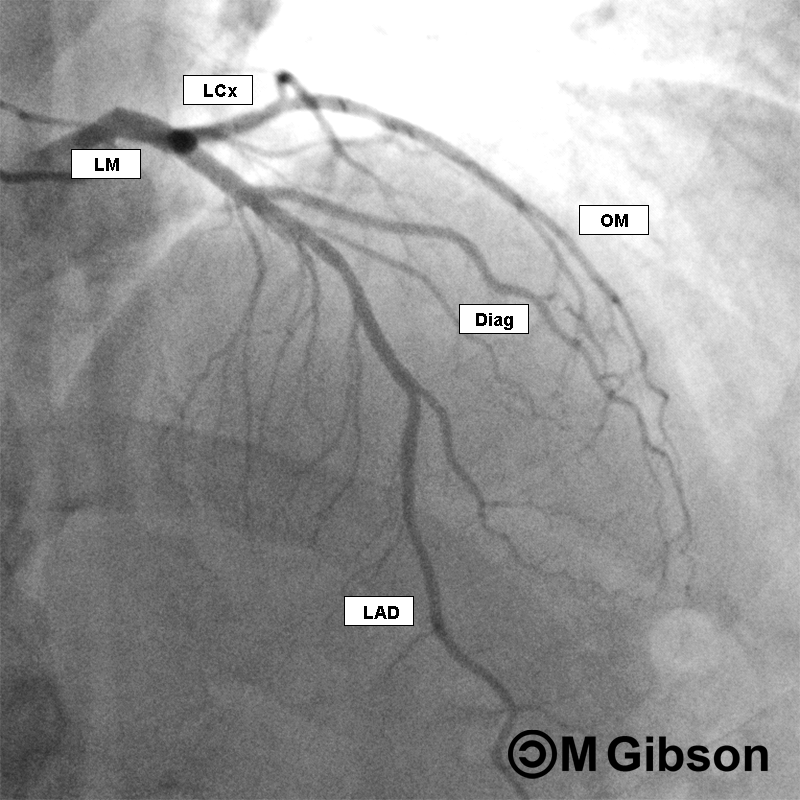
Right Anterior Oblique (RAO) Cranial
The RAO cranial view clearly expose the middle and distal segments of the left anterior descending artery as well as the origins of the diagonals. In general, the RAO cranial projection is not useful for visualizing the left circumflex artery except in cases of left dominant circulations since it may provide a view of the left posterior descending artery. RAO cranial is the best overall view to assess the blush of the LAD, as it minimizes intra- and inter-arterial overlap. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to the right of the spine with a slight anterior angulation.
 |
 |
Left Anterior Oblique (LAO) Cranial
The LAO cranial view provides a clear view of the middle and distal segments of the left anterior descending artery and the origins of the diagonals. It also exposes the ostium of the left main coronary artery. However, the proximal segments of the left anterior descending artery is usually foreshortened thus requiring additional LAO angulation. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to lie to the left of the spine with a slight anterior angulation.
 |
 |
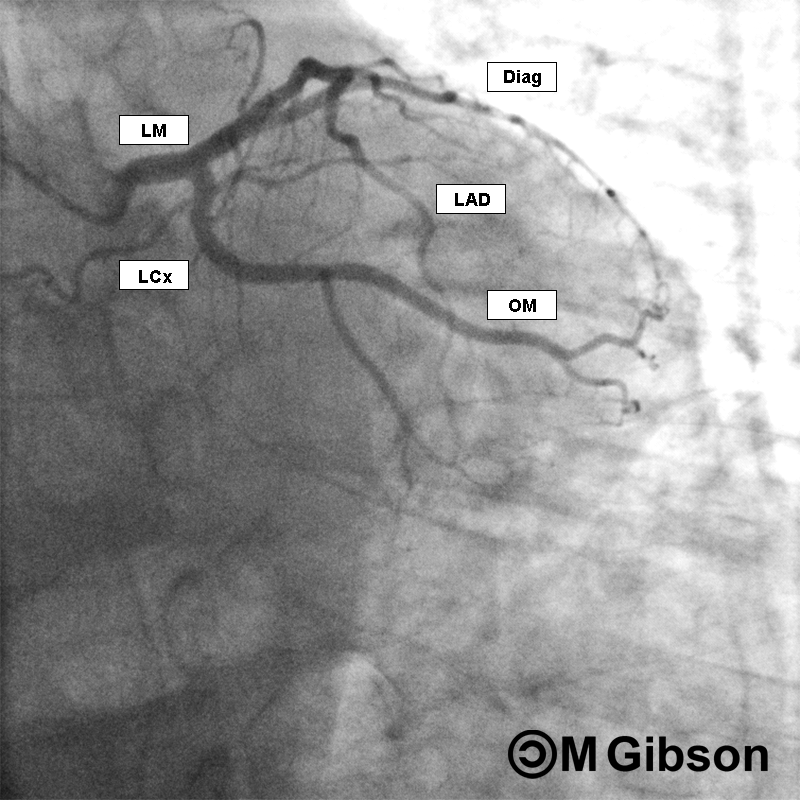
Left Anterior Oblique (LAO) Caudal
The LAO caudal view is also referred to as the 'spider view' and offers visualization of the left main coronary artery and the proximal segments of the left anterior descending artery, the ramus intermedius, and the left circumflex artery. In this view, the system in question appears angiographically to lie to the left of the spine with a slight inferior angulation.
 |
 |