Cirrhosis pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Cirrhosis}} | {{Cirrhosis}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} | {{CMG}};{{AE}}{{Cherry}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Cirrhosis occurs due to long term [[liver]] injury which causes an imbalance between [[matrix]] production and degradation. The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of [[scar tissue]] which leads to replacement of normal [[liver]] [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of [[Portal vein|portal blood flow]] and disturbance of normal [[liver]] function. When [[fibrosis]] of the [[liver]] reaches an advanced stage where distortion of the [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Circulatory system|vasculature]] also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the [[liver]]. The pathogenesis of cirrhosis involves [[ | Cirrhosis occurs due to long term [[liver]] injury which causes an imbalance between [[matrix]] production and degradation. The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of [[scar tissue]] which leads to replacement of normal [[liver]] [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of [[Portal vein|portal blood flow]] and disturbance of normal [[liver]] function. When [[fibrosis]] of the [[liver]] reaches an advanced stage where distortion of the [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Circulatory system|vasculature]] also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the [[liver]]. The [[pathogenesis]] of cirrhosis involves [[inflammation]], [[Ito cell|hepatic stellate cell]] activation, [[angiogenesis]], and [[Fibrosis|fibrogenesis]]. [[Kupffer cell|Kupffer cells]] are [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Macrophage|macrophages]] responsible for [[Ito cell|hepatic stellate cell]] activation during injury. [[Ito cell|Hepatic stellate cells (HSC)]] which are located in the [[Space of Disse|subendothelial space of Disse]], become activated in areas of [[liver]] injury and secrete [[TGF-beta|transforming growth factor-beta 1]] ([[TGF beta 1|TGF-β<sub>1</sub>]]), which leads to a [[Fibrosis|fibrotic]] response and proliferation of [[connective tissue]]. Cirrhosis may also lead to [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Microvascular bed|microvascular]] changes including the formation of intra-[[Liver|hepatic]] [[Shunt (medical)|shunts]] (due to [[angiogenesis]] and loss of [[Parenchyma|parenchymal cells]]) and [[Endothelium|endothelial]] dysfunction. [[Fibrosis]] eventually leads to formation of [[Septum (disambiguation)|septae]] that grossly distort the [[liver]] architecture which includes both the [[liver]] [[parenchyma]] and the [[Circulatory system|vasculature]], accompanied by regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation. HAYOP | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
The pathogenesis of cirrhosis is as follows: <ref name="pmid7932316">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ, Iredale JP |title=Hepatic lipocytes, TIMP-1 and liver fibrosis |journal=J R Coll Physicians Lond |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=200–8 |year=1994 |pmid=7932316 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8502273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Friedman SL |title=Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=328 |issue=25 |pages=1828–35 |year=1993 |pmid=8502273 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199306243282508 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8682489">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Matrix turnover in fibrogenesis |journal=Hepatogastroenterology |volume=43 |issue=7 |pages=56–71 |year=1996 |pmid=8682489 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7959178">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gressner AM |title=Perisinusoidal lipocytes and fibrogenesis |journal=Gut |volume=35 |issue=10 |pages=1331–3 |year=1994 |pmid=7959178 |pmc=1374996 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17332881">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=117 |issue=3 |pages=539–48 |year=2007 |pmid=17332881 |pmc=1804370 |doi=10.1172/JCI30542 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | The [[pathogenesis]] of cirrhosis is as follows:<ref name="pmid7932316">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ, Iredale JP |title=Hepatic lipocytes, TIMP-1 and liver fibrosis |journal=J R Coll Physicians Lond |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=200–8 |year=1994 |pmid=7932316 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8502273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Friedman SL |title=Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=328 |issue=25 |pages=1828–35 |year=1993 |pmid=8502273 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199306243282508 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid8682489">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Matrix turnover in fibrogenesis |journal=Hepatogastroenterology |volume=43 |issue=7 |pages=56–71 |year=1996 |pmid=8682489 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7959178">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gressner AM |title=Perisinusoidal lipocytes and fibrogenesis |journal=Gut |volume=35 |issue=10 |pages=1331–3 |year=1994 |pmid=7959178 |pmc=1374996 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17332881">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iredale JP |title=Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=117 |issue=3 |pages=539–48 |year=2007 |pmid=17332881 |pmc=1804370 |doi=10.1172/JCI30542 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* When an injured [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] is replaced by a [[Collagen|collagenous]] [[scar]], it is termed as [[fibrosis]]. The development of [[fibrosis]] requires several months, or even years | * When an injured [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] is replaced by a [[Collagen|collagenous]] [[scar]], it is termed as [[fibrosis]]. The development of [[fibrosis]] requires several months, or even years of ongoing [[injury]]. | ||
* The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of [[scar tissue]] that leads to replacement of normal [[liver]] [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of [[Portal vein|portal blood flow]] and disturbance of normal [[liver]] function. | * The [[pathological]] hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of [[scar tissue]] that leads to replacement of normal [[liver]] [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of [[Portal vein|portal blood flow]] and disturbance of normal [[liver]] function. | ||
* When [[fibrosis]] of the [[liver]] reaches | * When [[fibrosis]] of the [[liver]] reaches a point where distortion of the [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Circulatory system|vasculature]] also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the [[liver]]. If the damage progresses, panlobular cirrhosis may result. | ||
* The cellular mechanisms responsible for cirrhosis are similar regardless of the type of initial insult and site of injury within the [[Hepatic lobule|liver lobule]]. | * The [[cellular]] mechanisms responsible for cirrhosis are similar regardless of the type of initial insult and site of injury within the [[Hepatic lobule|liver lobule]]. | ||
* [[Hepatitis|Viral hepatitis]] involves the periportal region, whereas involvement in [[alcoholic liver disease]] is largely pericentral. | * [[Hepatitis|Viral hepatitis]] involves the periportal region, whereas involvement in [[alcoholic liver disease]] is largely pericentral. | ||
* Cirrhosis involves the following steps:<ref name="pmid7737629">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G |title=Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension |journal=Hepatology |volume=21 |issue=5 |pages=1238–47 |year=1995 |pmid=7737629 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * Cirrhosis involves the following steps:<ref name="pmid7737629">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G |title=Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension |journal=Hepatology |volume=21 |issue=5 |pages=1238–47 |year=1995 |pmid=7737629 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
** [[Angiogenesis]] | ** [[Angiogenesis]] | ||
** [[Fibrosis|Fibrogenesis]] | ** [[Fibrosis|Fibrogenesis]] | ||
'''Hepatic stellate cell activation''' | |||
The role of [[Kupffer cell|hepatic stellate cells]] in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis is described below: | |||
* [[Kupffer cell|Kupffer cells]] are [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Macrophage|macrophages]] responsible for [[Ito cell|hepatic stellate cell]] activation during injury. | * [[Kupffer cell|Kupffer cells]] are [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Macrophage|macrophages]] responsible for [[Ito cell|hepatic stellate cell]] activation during injury. | ||
* The [[Ito cell|stellate cell]], (also known as the [[Ito cell|perisinusoidal cell]] or [[Ito cell]]) is a cell | * The [[Ito cell|stellate cell]], (also known as the [[Ito cell|perisinusoidal cell]] or [[Ito cell]]) is a type of [[cell]] that normally stores [[vitamin A]] and plays a pivotal role in the development of cirrhosis. | ||
* [[Ito cell|Hepatic stellate cells (HSC)]] are usually located in the subendothelial space of Disse and become activated to a [[myofibroblast]]-like | * [[Ito cell|Hepatic stellate cells (HSC)]] are usually located in the [[Space of Disse|subendothelial space of Disse]] and become activated to a [[myofibroblast]]-like [[cell]] in areas of [[liver]] injury. This contractile [[Cell (biology)|cell]] (known as a [[myofibroblast]]) obstructs [[blood flow]] in the [[Circulatory system|circulation]]. | ||
* The [[stellate cell]] secretes [[TGF beta 1|TGF-β<sub>1</sub>]], which leads to a [[Fibrosis|fibrotic]] response and proliferation of [[connective tissue]]. | * The [[stellate cell]] secretes [[TGF-β|transforming growth factor-beta 1]] ([[TGF beta 1|TGF-β<sub>1</sub>]]), which leads to a [[Fibrosis|fibrotic]] response and [[proliferation]] of [[connective tissue]]. | ||
* [[Connective tissue]] proliferation leads to the formation of [[extracellular matrix]] around [[hepatocytes]] | * [[Connective tissue]] [[proliferation]] leads to the formation of [[extracellular matrix]] around [[hepatocytes]] that is composed of [[collagen]]s (especially type I, III, IV), [[glycoprotein]] and [[proteoglycan]]s. | ||
* [[Collagen]] and non collagenous [[matrix]] [[Protein|proteins]] responsible for [[fibrosis]] are produced by the activated [[ | * [[Collagen]] and non-[[collagenous]] [[matrix]] [[Protein|proteins]] responsible for [[fibrosis]] are produced by the activated [[Stellate cell|hepatic stellate cells]] ([[Ito cell|HSC]]). | ||
* [[Hepatocyte]] damage causes the release of [[lipid]] [[Peroxidase|peroxidases]] from injured [[Cell membrane|cell membranes]] leading to [[necrosis]] of [[Parenchyma|parenchymal cells]]. | * [[Hepatocyte]] damage causes the release of [[lipid]] [[Peroxidase|peroxidases]] from injured [[Cell membrane|cell membranes]] leading to [[necrosis]] of [[Parenchyma|parenchymal cells]]. | ||
* Activated [[Ito cell|HSC]] | * Activated [[Ito cell|HSC]] induce the production of numerous [[Cytokine|cytokines]] and their receptors, such as [[platelet-derived growth factor]] ([[Platelet-derived growth factor|PDGF]]) and [[Transforming growth factor|TGF-f31]], which are responsible for [[Fibrosis|fibrogenesis]]. | ||
* The matrix formed due to [[Ito cell|HSC]] activation is deposited in the space of Disse and leads to loss of fenestrations of [[Endothelium|endothelial cells]], | * The matrix formed due to [[Ito cell|HSC]] activation is deposited in the [[space of Disse]] and leads to loss of fenestrations of [[Endothelium|endothelial cells]], through a process called capillarization. | ||
* [[Stellate cell]] activation leads to disturbance of the balance between [[matrix metalloproteinase]]s and the naturally occurring inhibitors (TIMP 1 and | * [[Stellate cell]] activation leads to disturbance of the balance between [[matrix metalloproteinase]]s and the naturally occurring inhibitors ([[TIMP1|TIMP 1]] and [[TIMP2]]). This is followed by [[matrix (biology)|matrix]] breakdown and replacement by [[connective tissue]]-secreted [[matrix]].<ref>Iredale JP. Cirrhosis: new research provides a basis for rational and targeted treatments. [[British Medical Journal|BMJ]] 2003;327:143-7.[http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/327/7407/143 Fulltext.] PMID 12869458.</ref> | ||
* [[Matrix metalloproteinase]] (MMP) are [[calcium]] dependent [[enzymes]] that specifically degrade [[collagen]] and non [[Collagen|collagenous]] substrate. | * [[Matrix metalloproteinase]] (MMP) are [[calcium]] dependent [[enzymes]] that specifically degrade [[collagen]] and non [[Collagen|collagenous]] substrate. | ||
* MMP-2 and stromyelysin-1 are produced by [[Ito cell|stellate cells]]. | * [[Matrix metalloproteinase|MMP]]-2 and stromyelysin-1 are produced by [[Ito cell|stellate cells]]. | ||
* MMP-2 degrades [[collagen]] and stromelysin-1 degrades [[proteoglycan]] and [[glycoprotein]]. | * [[Matrix metalloproteinase|MMP]]-2 degrades [[collagen]] and stromelysin-1 degrades [[proteoglycan]] and [[glycoprotein]]. | ||
'''Microvascular changes''' | |||
Cirrhosis leads to [[Liver|hepatic]] microvascular changes characterised by:<ref name="pmid19157625">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I, Pinzani M, Bosch J |title=Angiogenesis in liver disease |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=50 |issue=3 |pages=604–20 |year=2009 |pmid=19157625 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.011 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Formation of intra [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Shunt (medical)|shunts]] (due to [[angiogenesis]] and loss of [[Parenchyma|parenchymal cells]]) | |||
* [[Liver|Hepatic]] [[Endothelium|endothelial]] dysfunction | |||
* [[Sinusoid (blood vessel)|Sinusoidal]] [[Endothelium|endothelial cells]] are also important contributors of early [[fibrosis]]. [[Endothelial cell]]s from a normal [[liver]] produces [[collagen]], [[laminin]] and [[fibronectin]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Maher JJ, McGuire RF |title=Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=86 |issue=5 |pages=1641–8 |year=1990 |month=November |pmid=2243137 |pmc=296914 |doi=10.1172/JCI114886 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Herbst H, Frey A, Heinrichs O, ''et al.'' |title=Heterogeneity of liver cells expressing procollagen types I and IV in vivo |journal=Histochem. Cell Biol. |volume=107 |issue=5 |pages=399–409 |year=1997 |month=May |pmid=9208331 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * [[Sinusoid (blood vessel)|Sinusoidal]] [[Endothelium|endothelial cells]] are also important contributors of early [[fibrosis]]. [[Endothelial cell]]s from a normal [[liver]] produces [[collagen]], [[laminin]] and [[fibronectin]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Maher JJ, McGuire RF |title=Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=86 |issue=5 |pages=1641–8 |year=1990 |month=November |pmid=2243137 |pmc=296914 |doi=10.1172/JCI114886 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Herbst H, Frey A, Heinrichs O, ''et al.'' |title=Heterogeneity of liver cells expressing procollagen types I and IV in vivo |journal=Histochem. Cell Biol. |volume=107 |issue=5 |pages=399–409 |year=1997 |month=May |pmid=9208331 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* The [[Endothelium|endothelial]] dysfunction is characterised by<ref name="pmid22504334">{{cite journal |vauthors=García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J |title=Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=57 |issue=2 |pages=458–61 |year=2012 |pmid=22504334 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007 |url=}}</ref> | * The [[Endothelium|endothelial]] dysfunction is characterised by:<ref name="pmid22504334">{{cite journal |vauthors=García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J |title=Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=57 |issue=2 |pages=458–61 |year=2012 |pmid=22504334 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007 |url=}}</ref> | ||
** Insufficient release of [[Vasodilator|vasodilators]], such as [[nitric oxide]] due to [[oxidative stress]] | ** Insufficient release of [[Vasodilator|vasodilators]], such as [[nitric oxide]] due to [[oxidative stress]] | ||
** Increased production of [[Vasoconstrictor|vasoconstrictors]] (mainly [[adrenergic]] stimulation and activation of [[Endothelin|endothelins]] and [[Renin-angiotensin system|RAAS]]) | ** Increased production of [[Vasoconstrictor|vasoconstrictors]] (mainly [[adrenergic]] stimulation and activation of [[Endothelin|endothelins]] and [[Renin-angiotensin system|RAAS]]) | ||
| Line 49: | Line 55: | ||
**[[Nitric oxide]] | **[[Nitric oxide]] | ||
**[[Carbon monoxide]] | **[[Carbon monoxide]] | ||
*[[Angiogenesis]] in cirrhosis results in the production of immature and permeable [[Vascular endothelial growth factor|VEGF]] induced neo-[[Blood vessel|vessels]] that further exacerbate [[liver]] injury. <ref>{{cite journal |author=Lee JS, Semela D, Iredale J, Shah VH |title=Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: a new function for the liver-specific pericyte? |journal=Hepatology |volume=45 |issue=3 |pages=817–25 |year=2007 |month=March |pmid=17326208 |doi=10.1002/hep.21564 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Rosmorduc O, Housset C |title=Hypoxia: a link between fibrogenesis, angiogenesis, and carcinogenesis in liver disease |journal=Semin. Liver Dis. |volume=30 |issue=3 |pages=258–70 |year=2010 |month=August |pmid=20665378 |doi=10.1055/s-0030-1255355 |url=}}</ref> | '''Angiogenesis''' | ||
*[[Angiogenesis]] in cirrhosis results in the production of immature and permeable [[vascular endothelial growth factor]] ([[Vascular endothelial growth factor|VEGF]]) induced neo-[[Blood vessel|vessels]] that further exacerbate [[liver]] injury.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Lee JS, Semela D, Iredale J, Shah VH |title=Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: a new function for the liver-specific pericyte? |journal=Hepatology |volume=45 |issue=3 |pages=817–25 |year=2007 |month=March |pmid=17326208 |doi=10.1002/hep.21564 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Rosmorduc O, Housset C |title=Hypoxia: a link between fibrogenesis, angiogenesis, and carcinogenesis in liver disease |journal=Semin. Liver Dis. |volume=30 |issue=3 |pages=258–70 |year=2010 |month=August |pmid=20665378 |doi=10.1055/s-0030-1255355 |url=}}</ref> | |||
'''Fibrosis''' | |||
The role of [[fibrosis]] in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis is described below: | |||
* [[Fibrosis]] eventually leads to formation of [[Septum (disambiguation)|septae]] that grossly distort the [[liver]] architecture which includes both the [[liver]] [[parenchyma]] and the [[Circulatory system|vasculature]]. | * [[Fibrosis]] eventually leads to formation of [[Septum (disambiguation)|septae]] that grossly distort the [[liver]] architecture which includes both the [[liver]] [[parenchyma]] and the [[Circulatory system|vasculature]]. | ||
* A cirrhotic [[liver]] compromises [[ | * A cirrhotic [[liver]] compromises [[Hepatic sinusoids|hepatic sinusoidal]] exchange by shunting [[Artery|arterial]] and [[Portal vein|portal blood]] directly into the [[Central vein|central veins]] ([[Liver|hepatic]] outflow). | ||
* Vascularized [[Fiber|fibrous]] [[Septum (disambiguation)|septa]] connect [[Central vein|central veins]] with [[Portal triad|portal tracts]] leading to islands of [[Hepatocyte|hepatocytes]] surrounded by [[Fiber|fibrous]] bands without [[Central vein|central veins]].<ref name="pmid18328931">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schuppan D, Afdhal NH |title=Liver cirrhosis |journal=Lancet |volume=371 |issue=9615 |pages=838–51 |year=2008 |pmid=18328931 |pmc=2271178 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15094237">{{cite journal |vauthors=Desmet VJ, Roskams T |title=Cirrhosis reversal: a duel between dogma and myth |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=40 |issue=5 |pages=860–7 |year=2004 |pmid=15094237 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2004.03.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11079009">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M |title=Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=124 |issue=11 |pages=1599–607 |year=2000 |pmid=11079009 |doi=10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<1599:ROHC>2.0.CO;2 |url=}}</ref> | * [[Vascularity|Vascularized]] [[Fiber|fibrous]] [[Septum (disambiguation)|septa]] connect [[Central vein|central veins]] with [[Portal triad|portal tracts]] leading to islands of [[Hepatocyte|hepatocytes]] surrounded by [[Fiber|fibrous]] bands without [[Central vein|central veins]].<ref name="pmid18328931">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schuppan D, Afdhal NH |title=Liver cirrhosis |journal=Lancet |volume=371 |issue=9615 |pages=838–51 |year=2008 |pmid=18328931 |pmc=2271178 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15094237">{{cite journal |vauthors=Desmet VJ, Roskams T |title=Cirrhosis reversal: a duel between dogma and myth |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=40 |issue=5 |pages=860–7 |year=2004 |pmid=15094237 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2004.03.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11079009">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M |title=Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=124 |issue=11 |pages=1599–607 |year=2000 |pmid=11079009 |doi=10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<1599:ROHC>2.0.CO;2 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* These mechanisms simultaneously occurring in the [[liver]] lead to [[Fibrous tissue|fibrous tissue band]] (septa) and regenerative [[hepatocyte]] [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation, which eventually replace the entire [[liver]] architecture, leading to decreased [[blood flow]] throughout. | * These mechanisms simultaneously occurring in the [[liver]] lead to [[Fibrous tissue|fibrous tissue band]] (septa) and regenerative [[hepatocyte]] [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation, which eventually replace the entire [[liver]] architecture, leading to decreased [[blood flow]] throughout. | ||
* The formation of [[Fibrosis|fibrotic]] bands is accompanied by regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation in the [[Liver|hepatic]] [[parenchyma]]. | * The formation of [[Fibrosis|fibrotic]] bands is accompanied by regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation in the [[Liver|hepatic]] [[parenchyma]]. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 68: | ||
* The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of [[scar tissue]] that replaces normal [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of [[Portal vein|portal blood flow]] and disturbance of normal [[liver]] function. | * The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of [[scar tissue]] that replaces normal [[parenchyma]], leading to blockade of [[Portal vein|portal blood flow]] and disturbance of normal [[liver]] function. | ||
* Due to [[portal hypertension]], the [[spleen]] becomes congested, which leads to [[hypersplenism]] and increased [[platelet]] sequestration. | * Due to [[portal hypertension]], the [[spleen]] becomes congested, which leads to [[hypersplenism]] and increased [[platelet]] sequestration. | ||
'''Pathogenesis of cirrhosis according to cause''' | |||
[[Pathogenesis]] of cirrhosis based upon the underlying cause is as follows: | |||
* '''[[Alcoholic liver disease]]''': [[Alcohol]] seems to injure the [[liver]] by blocking the normal metabolism of [[protein]], [[fat]]s, and [[carbohydrate]]s. Patients may also have concurrent [[alcoholic hepatitis]] with [[fever]], [[hepatomegaly]], [[jaundice]], and [[anorexia]]. [[Liver]] damage due to [[alcoholic hepatitis]] may progress to cirrhosis. | |||
* '''Chronic hepatitis C''': Infection with the [[hepatitis C]] virus causes [[inflammation]] and low grade damage to the [[liver]] that may eventually lead to cirrhosis after decades. | |||
* '''[[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease|Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis]]''' (NASH): In [[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease|NASH]], fat builds up in the [[liver]] and eventually causes [[scar tissue]]. This type of [[hepatitis]] appears to be associated with [[diabetes]], [[protein malnutrition]], [[obesity]], [[coronary artery disease]], and treatment with [[corticosteroid]] medications. | |||
* '''[[Primary sclerosing cholangitis]] (PSC):''' [[Primary sclerosing cholangitis|PSC]] is a progressive [[Cholestasis|cholestatic]] disorder presenting with [[pruritus]], [[steatorrhea]], [[Fat soluble vitamins|fat soluble vitamin]] deficiencies, and [[metabolic]] bone disease. | |||
** There is a strong association with [[inflammatory bowel disease]] (IBD), especially [[ulcerative colitis]]. | |||
* '''[[Autoimmune hepatitis]]''': [[Immunological|Immunologic]] damage to the [[liver]] leads to [[inflammation]], [[Scar|scarring]] and cirrhosis. | |||
* [[Portal hypertension]] may result from a combination of the following: | * [[Portal hypertension]] may result from a combination of the following: | ||
| Line 70: | Line 82: | ||
** Functional abnormalities such as [[Endothelium|endothelial]] dysfunction and increased [[Liver|hepatic]] [[vascular]] tone account for 30% of total [[Liver|hepatic]] [[vascular resistance]]. | ** Functional abnormalities such as [[Endothelium|endothelial]] dysfunction and increased [[Liver|hepatic]] [[vascular]] tone account for 30% of total [[Liver|hepatic]] [[vascular resistance]]. | ||
===Pathophysiology of Cirrhosis due to Alcohol=== | |||
Mechanisms of [[alcohol]]-induced [[liver]] damage include:<ref name="pmid25548474">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ceni E, Mello T, Galli A |title=Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism |journal=World J. Gastroenterol. |volume=20 |issue=47 |pages=17756–72 |year=2014 |pmid=25548474 |pmc=4273126 |doi=10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17756 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15194557">{{cite journal |vauthors=You M, Crabb DW |title=Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease II. Minireview: molecular mechanisms of alcoholic fatty liver |journal=Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. |volume=287 |issue=1 |pages=G1–6 |year=2004 |pmid=15194557 |doi=10.1152/ajpgi.00056.2004 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16088993">{{cite journal |vauthors=Freeman TL, Tuma DJ, Thiele GM, Klassen LW, Worrall S, Niemelä O, Parkkila S, Emery PW, Preedy VR |title=Recent advances in alcohol-induced adduct formation |journal=Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. |volume=29 |issue=7 |pages=1310–6 |year=2005 |pmid=16088993 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17590995">{{cite journal |vauthors=Niemelä O |title=Acetaldehyde adducts in circulation |journal=Novartis Found. Symp. |volume=285 |issue= |pages=183–92; discussion 193–7 |year=2007 |pmid=17590995 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Impairment of: | |||
** [[Protein synthesis]] | |||
** [[Secretion]] | |||
** [[Glycosylation]] | |||
* [[Ethanol]] intake leads to elevated accumulation of intracellular [[Triglyceride|triglycerides]] by:<ref name="pmid12791698">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fischer M, You M, Matsumoto M, Crabb DW |title=Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) agonist treatment reverses PPARalpha dysfunction and abnormalities in hepatic lipid metabolism in ethanol-fed mice |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=278 |issue=30 |pages=27997–8004 |year=2003 |pmid=12791698 |doi=10.1074/jbc.M302140200 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15578517">{{cite journal |vauthors=You M, Matsumoto M, Pacold CM, Cho WK, Crabb DW |title=The role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the action of ethanol in the liver |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=127 |issue=6 |pages=1798–808 |year=2004 |pmid=15578517 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16879892">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ji C, Chan C, Kaplowitz N |title=Predominant role of sterol response element binding proteins (SREBP) lipogenic pathways in hepatic steatosis in the murine intragastric ethanol feeding model |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=45 |issue=5 |pages=717–24 |year=2006 |pmid=16879892 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2006.05.009 |url=}}</ref> | * [[Ethanol]] intake leads to elevated accumulation of intracellular [[Triglyceride|triglycerides]] by:<ref name="pmid12791698">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fischer M, You M, Matsumoto M, Crabb DW |title=Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) agonist treatment reverses PPARalpha dysfunction and abnormalities in hepatic lipid metabolism in ethanol-fed mice |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=278 |issue=30 |pages=27997–8004 |year=2003 |pmid=12791698 |doi=10.1074/jbc.M302140200 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15578517">{{cite journal |vauthors=You M, Matsumoto M, Pacold CM, Cho WK, Crabb DW |title=The role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the action of ethanol in the liver |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=127 |issue=6 |pages=1798–808 |year=2004 |pmid=15578517 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16879892">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ji C, Chan C, Kaplowitz N |title=Predominant role of sterol response element binding proteins (SREBP) lipogenic pathways in hepatic steatosis in the murine intragastric ethanol feeding model |journal=J. Hepatol. |volume=45 |issue=5 |pages=717–24 |year=2006 |pmid=16879892 |doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2006.05.009 |url=}}</ref> | ||
** [[Lipoprotein]] secretion | ** [[Lipoprotein]] secretion | ||
** Decreased [[fatty acid]] [[Redox|oxidation]] | ** Decreased [[fatty acid]] [[Redox|oxidation]] | ||
** Increased [[fatty acid]] uptake | ** Increased [[fatty acid]] uptake | ||
* [[Alcohol]] is converted by [[ | * [[Alcohol]] is converted by [[alcohol dehydrogenase]] to [[acetaldehyde]]. | ||
* Due to the high reactivity of [[acetaldehyde]], it forms [[acetaldehyde]]-[[protein]] adducts which cause damage to cells by: | * Due to the high reactivity of [[acetaldehyde]], it forms [[acetaldehyde]]-[[protein]] adducts which cause damage to [[Cells (biology)|cells]] by: | ||
** Trafficking of [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Protein|proteins]] | ** Trafficking of [[Liver|hepatic]] [[Protein|proteins]] | ||
** Interrupting [[microtubule]] formation | ** Interrupting [[microtubule]] formation | ||
** Interfering with enzyme activities | ** Interfering with [[enzyme]] activities | ||
* [[Reactive oxygen species]] begin to form as a result of [[hepatocyte]] damage that activate [[Kupffer cell|Kupffer cells]].<ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * [[Reactive oxygen species]] begin to form as a result of [[hepatocyte]] damage that activate [[Kupffer cell|Kupffer cells]].<ref name="pmid11984538">{{cite journal |vauthors=Arthur MJ |title=Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=122 |issue=5 |pages=1525–8 |year=2002 |pmid=11984538 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*[[Kupffer cell]] activation leads to the production of profibrogenic [[Cytokine|cytokines]] which in turn, stimulates [[Stellate cell|stellate]] | *[[Kupffer cell]] activation leads to the production of profibrogenic [[Cytokine|cytokines]] which in turn, stimulates [[Stellate cell|stellate cells]]. | ||
*[[Stellate cell]] activation leads to [[connective tissue]] formation due to deposition [[extracellular matrix]] and [[collagen]]. | *[[Stellate cell]] activation leads to [[connective tissue]] formation due to deposition [[extracellular matrix]] and [[collagen]]. | ||
* [[Portal triad|Portal triads]] develop connections with central veins due to [[connective tissue]] formation in pericentral and periportal zones, leading to the formation of regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]]. | * [[Portal triad|Portal triads]] develop connections with central [[veins]] due to [[connective tissue]] formation in pericentral and periportal zones, leading to the formation of regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]]. | ||
* Shrinkage of the [[liver]] occurs over years due to repeated insults that lead to: | * Shrinkage of the [[liver]] occurs over years due to repeated insults that lead to: | ||
** Loss of [[Hepatocyte|hepatocytes]] | ** Loss of [[Hepatocyte|hepatocytes]] | ||
** Increased production and deposition of [[collagen]] and regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation | ** Increased production and deposition of [[collagen]] and regenerative [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] formation on a background of [[fibrosis]] | ||
==Pathophysiology of Portal Hypertension== | ===Pathophysiology of Portal Hypertension due to Cirrhosis=== | ||
==== Increased resistance ==== | ==== Increased resistance ==== | ||
* Portal hypertension is related to elevation of [[Portal venous system|portal vasculature]] | * Portal hypertension is related to elevation of resistance in the [[Portal venous system|portal vasculature]]. | ||
* Increased resistance in [[Portal venous system|portal system]] may be due to both intra-[[hepatic]] and also portosystemic collateral resistance. | * Increased resistance in [[Portal venous system|portal system]] may be due to both intra-[[hepatic]] and also [[Portocaval anastomoses|portosystemic collateral]] resistance. | ||
** '''Intra-hepatic resistance''' | ** '''Intra-hepatic resistance''' | ||
*** The main factor responsible for intra-[[hepatic]] resistance is [[hepatic]] vascular [[compliance]], which is greatly decreased in | *** The main factor responsible for intra-[[hepatic]] resistance is [[hepatic]] vascular [[compliance]], which is greatly decreased in liver [[fibrosis]] or [[cirrhosis]]. | ||
*** Portal hypertension occurs when [[compliance]] is decreased and [[blood flow]] is increased in [[liver]].<ref name="pmid5543903">{{cite journal |vauthors=Greenway CV, Stark RD |title=Hepatic vascular bed |journal=Physiol. Rev. |volume=51 |issue=1 |pages=23–65 |year=1971 |pmid=5543903 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** [[Portal hypertension]] occurs when [[compliance]] is decreased and [[blood flow]] is increased in [[liver]].<ref name="pmid5543903">{{cite journal |vauthors=Greenway CV, Stark RD |title=Hepatic vascular bed |journal=Physiol. Rev. |volume=51 |issue=1 |pages=23–65 |year=1971 |pmid=5543903 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*** Pre-[[hepatic]] and post-[[hepatic]] portal hypertension arise due to some secondary obstruction before or after [[liver]] [[vasculature]], respectively.<ref>{{cite book | last = Schiff | first = Eugene | title = Schiff's diseases of the liver | publisher = John Wiley & Sons | location = Chichester, West Sussex, UK | year = 2012 | isbn = 9780470654682 | *** Pre-[[hepatic]] and post-[[hepatic]] [[portal hypertension]] arise due to some secondary obstruction before or after [[liver]] [[vasculature]], respectively.<ref>{{cite book | last = Schiff | first = Eugene | title = Schiff's diseases of the liver | publisher = John Wiley & Sons | location = Chichester, West Sussex, UK | year = 2012 | isbn = 9780470654682 }}</ref> | ||
*** [[Alcoholic hepatitis]] causes both [[sinusoidal]] and post-[[sinusoidal]] pathologies.<ref name="pmid13976646">{{cite journal |vauthors=SCHAFFNER F, POPER H |title=Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=44 |issue= |pages=239–42 |year=1963 |pmid=13976646 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid5775031">{{cite journal |vauthors=Reynolds TB, Hidemura R, Michel H, Peters R |title=Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=70 |issue=3 |pages=497–506 |year=1969 |pmid=5775031 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** [[Alcoholic hepatitis]] causes both [[sinusoidal]] and post-[[sinusoidal]] pathologies.<ref name="pmid13976646">{{cite journal |vauthors=SCHAFFNER F, POPER H |title=Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=44 |issue= |pages=239–42 |year=1963 |pmid=13976646 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid5775031">{{cite journal |vauthors=Reynolds TB, Hidemura R, Michel H, Peters R |title=Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=70 |issue=3 |pages=497–506 |year=1969 |pmid=5775031 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*** [[Hepatic]] vascular [[endothelium]] synthesizes and secretes both [[Vasodilator|vasodilators]] (e.g., [[nitric oxide]], [[Prostacyclin|prostacyclins]]) and [[Vasoconstrictor|vasoconstrictors]] (e.g., [[endothelin]] and [[Prostanoid|prostanoids]]).<ref name="pmid1874796">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rubanyi GM |title=Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors |journal=J. Cell. Biochem. |volume=46 |issue=1 |pages=27–36 |year=1991 |pmid=1874796 |doi=10.1002/jcb.240460106 |url=}}</ref><ref name="EpsteinVane1990">{{cite journal|last1=Epstein|first1=Franklin H.|last2=Vane|first2=John R.|last3=Änggård|first3=Erik E.|last4=Botting|first4=Regina M.|title=Regulatory Functions of the Vascular Endothelium|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=323|issue=1|year=1990|pages=27–36|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJM199007053230106}}</ref> | *** [[Hepatic]] vascular [[endothelium]] synthesizes and secretes both [[Vasodilator|vasodilators]] (e.g., [[nitric oxide]], [[Prostacyclin|prostacyclins]]) and [[Vasoconstrictor|vasoconstrictors]] (e.g., [[endothelin]] and [[Prostanoid|prostanoids]]).<ref name="pmid1874796">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rubanyi GM |title=Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors |journal=J. Cell. Biochem. |volume=46 |issue=1 |pages=27–36 |year=1991 |pmid=1874796 |doi=10.1002/jcb.240460106 |url=}}</ref><ref name="EpsteinVane1990">{{cite journal|last1=Epstein|first1=Franklin H.|last2=Vane|first2=John R.|last3=Änggård|first3=Erik E.|last4=Botting|first4=Regina M.|title=Regulatory Functions of the Vascular Endothelium|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=323|issue=1|year=1990|pages=27–36|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJM199007053230106}}</ref> | ||
*** Increased resistance due to the elevation of [[vascular]] tone may be caused by excess of [[vasoconstrictors]] or lack of [[vasodilators]]. | *** Increased resistance due to the elevation of [[vascular]] tone may be caused by excess of [[vasoconstrictors]] or lack of [[vasodilators]]. | ||
*** It is postulated that in [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]] the [[nitric oxide]] level is lower and the response to [[endothelin]] | *** It is postulated that in [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]] the [[nitric oxide]] level is lower and the response to [[endothelin]] in [[myofibrils]] is stronger than in normal [[liver]].<ref name="pmid8707268">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rockey DC, Weisiger RA |title=Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance |journal=Hepatology |volume=24 |issue=1 |pages=233–40 |year=1996 |pmid=8707268 |doi=10.1002/hep.510240137 |url=}}</ref> | ||
** '''Portosystemic collateral resistance''' | ** '''Portosystemic collateral resistance''' | ||
*** [[Collateral]] blood circulation develops as a consequence of portal hypertension which is the main contributor to [[esophageal varices]] | *** [[Collateral]] blood circulation develops as a consequence of [[portal hypertension]] which is the main contributor to [[Gastrointestinal varices|esophageal and gastric varices]] | ||
*** The main purpose of the [[collaterals]] is to decompress and bypass [[portal]] blood flow. | *** The main purpose of the [[collaterals]] is to decompress and bypass [[portal]] [[blood]] flow. | ||
*** However, [[Portocaval anastomoses|portosystemic collaterals]] may not lead to a complete decompression. | *** However, [[Portocaval anastomoses|portosystemic collaterals]] may not lead to a complete decompression. | ||
*** [[Portocaval anastomoses|Portosystemic | *** [[Portocaval anastomoses|Portosystemic circulation]] occurs between the [[short gastric]], [[left gastric vein]], and the [[esophageal]], [[azygos]] and the [[intercostal veins]]; the superior, the middle, and the inferior [[Hemorrhoidal plexus|hemorrhoidal veins]]; the [[Paraumbilical veins|paraumbilical venous plexus]], the [[venous]] system of [[abdominal]] [[organs]] juxtaposed with the [[retroperitoneum]] and [[abdominal wall]]; the left [[renal vein]], the [[splanchnic]], the [[adrenal]], and the [[spermatic veins]].<ref name="pmid1415713">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mosca P, Lee FY, Kaumann AJ, Groszmann RJ |title=Pharmacology of portal-systemic collaterals in portal hypertensive rats: role of endothelium |journal=Am. J. Physiol. |volume=263 |issue=4 Pt 1 |pages=G544–50 |year=1992 |pmid=1415713 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
==== Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertension ==== | ==== Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertension ==== | ||
* Peripheral [[vasodilatation]] is the basis for decreased systemic [[vascular resistance]] and [[mean arterial pressure]], plasma volume expansion, elevated [[splanchnic]] [[blood flow]], and elevated [[cardiac index]].<ref name="pmid1735537">{{cite journal |vauthors=Colombato LA, Albillos A, Groszmann RJ |title=Temporal relationship of peripheral vasodilatation, plasma volume expansion and the hyperdynamic circulatory state in portal-hypertensive rats |journal=Hepatology |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=323–8 |year=1992 |pmid=1735537 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * Peripheral [[vasodilatation]] is the basis for decreased systemic [[vascular resistance]] and [[mean arterial pressure]], [[plasma]] volume expansion, elevated [[splanchnic]] [[blood flow]], and elevated [[cardiac index]].<ref name="pmid1735537">{{cite journal |vauthors=Colombato LA, Albillos A, Groszmann RJ |title=Temporal relationship of peripheral vasodilatation, plasma volume expansion and the hyperdynamic circulatory state in portal-hypertensive rats |journal=Hepatology |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=323–8 |year=1992 |pmid=1735537 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* '''Systemic vasodilation''' | * '''Systemic vasodilation''' | ||
** Three main mechanisms which contribute to the peripheral vasodilation are as | ** Three main mechanisms which contribute to the peripheral [[vasodilation]] are as follows: | ||
*** Increased [[vasodilators]] production in systemic circulation<ref name="pmid2372062">{{cite journal |vauthors=Genecin P, Polio J, Colombato LA, Ferraioli G, Reuben A, Groszmann RJ |title=Bile acids do not mediate the hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertensive rats |journal=Am. J. Physiol. |volume=259 |issue=1 Pt 1 |pages=G21–5 |year=1990 |pmid=2372062 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** Increased [[vasodilators]] production in systemic circulation<ref name="pmid2372062">{{cite journal |vauthors=Genecin P, Polio J, Colombato LA, Ferraioli G, Reuben A, Groszmann RJ |title=Bile acids do not mediate the hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertensive rats |journal=Am. J. Physiol. |volume=259 |issue=1 Pt 1 |pages=G21–5 |year=1990 |pmid=2372062 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
*** Increased [[vasodilators]] production in local [[endothelium]]<ref name="CasadevallPanés1993">{{cite journal|last1=Casadevall|first1=María|last2=Panés|first2=Julián|last3=Piqué|first3=Josep M.|last4=Marroni|first4=Norma|last5=Bosch|first5=Jaume|last6=Whittle|first6=Brendan J. R.|title=Involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandins in gastric mucosal hyperemia of portal-hypertensive anesthetized rats|journal=Hepatology|volume=18|issue=3|year=1993|pages=628–634|issn=02709139|doi=10.1002/hep.1840180323}}</ref> | *** Increased [[vasodilators]] production in local [[endothelium]]<ref name="CasadevallPanés1993">{{cite journal|last1=Casadevall|first1=María|last2=Panés|first2=Julián|last3=Piqué|first3=Josep M.|last4=Marroni|first4=Norma|last5=Bosch|first5=Jaume|last6=Whittle|first6=Brendan J. R.|title=Involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandins in gastric mucosal hyperemia of portal-hypertensive anesthetized rats|journal=Hepatology|volume=18|issue=3|year=1993|pages=628–634|issn=02709139|doi=10.1002/hep.1840180323}}</ref> | ||
*** Decreased vascular response to local [[vasoconstrictors]]<ref name="pmid1616049">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sieber CC, Groszmann RJ |title=In vitro hyporeactivity to methoxamine in portal hypertensive rats: reversal by nitric oxide blockade |journal=Am. J. Physiol. |volume=262 |issue=6 Pt 1 |pages=G996–1001 |year=1992 |pmid=1616049 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** Decreased [[vascular]] response to local [[vasoconstrictors]]<ref name="pmid1616049">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sieber CC, Groszmann RJ |title=In vitro hyporeactivity to methoxamine in portal hypertensive rats: reversal by nitric oxide blockade |journal=Am. J. Physiol. |volume=262 |issue=6 Pt 1 |pages=G996–1001 |year=1992 |pmid=1616049 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* '''Plasma volume''' | * '''Plasma volume''' | ||
** There are several events which contribute to the [[hyperdynamic circulation]] such as: | ** There are several events which contribute to the [[hyperdynamic circulation]] such as: | ||
*** Initial [[vasodilatation]], induced by systemic and local [[endothelial]] factors | *** Initial [[vasodilatation]], induced by [[systemic]] and local [[endothelial]] factors | ||
*** Subsequent [[Blood plasma|plasma]] volume expansion<ref name="pmid8425700">{{cite journal |vauthors=Albillos A, Colombato LA, Lee FY, Groszmann RJ |title=Octreotide ameliorates vasodilatation and Na+ retention in portal hypertensive rats |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=104 |issue=2 |pages=575–9 |year=1993 |pmid=8425700 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | *** Subsequent [[Blood plasma|plasma]] volume expansion<ref name="pmid8425700">{{cite journal |vauthors=Albillos A, Colombato LA, Lee FY, Groszmann RJ |title=Octreotide ameliorates vasodilatation and Na+ retention in portal hypertensive rats |journal=Gastroenterology |volume=104 |issue=2 |pages=575–9 |year=1993 |pmid=8425700 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Genetics== | |||
* Certain TERT (Telomerase reverese transcriptase) gene variants resulting in reduced telomerase activity have been found to be a risk factor for sporadic cirrhosis<ref>{{cite journal |author=Calado RT, Brudno J, Mehta P, ''et al.'' |title=Constitutional telomerase mutations are genetic risk factors for cirrhosis |journal=Hepatology |volume=53 |issue=5 |pages=1600–7 |year=2011 |month=May |pmid=21520173 |pmc=3082730 |doi=10.1002/hep.24173 |url=}}</ref> | * Certain [[TERT]] ([[Telomerase reverse transcriptase|Telomerase reverese transcriptase]]) [[gene]] variants resulting in reduced [[telomerase]] activity have been found to be a [[risk factor]] for sporadic cirrhosis<ref>{{cite journal |author=Calado RT, Brudno J, Mehta P, ''et al.'' |title=Constitutional telomerase mutations are genetic risk factors for cirrhosis |journal=Hepatology |volume=53 |issue=5 |pages=1600–7 |year=2011 |month=May |pmid=21520173 |pmc=3082730 |doi=10.1002/hep.24173 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* An uncharacterized nucleolar protein, NOL11, has a role in the pathogenesis of North American Indian childhood cirrhosis<ref>{{cite journal |author=Freed EF, Prieto JL, McCann KL, McStay B, Baserga SJ |title=NOL11, Implicated in the Pathogenesis of North American Indian Childhood Cirrhosis, Is Required for Pre-rRNA Transcription and Processing |journal=PLoS Genet. |volume=8 |issue=8 |pages=e1002892 |year=2012 |month=August |pmid=22916032 |pmc=3420923 |doi=10.1371/journal.pgen.1002892 |url=}}</ref> | * An uncharacterized [[Nucleolar protein, member A1|nucleolar protein]], NOL11, has a role in the [[pathogenesis]] of North American Indian childhood cirrhosis<ref>{{cite journal |author=Freed EF, Prieto JL, McCann KL, McStay B, Baserga SJ |title=NOL11, Implicated in the Pathogenesis of North American Indian Childhood Cirrhosis, Is Required for Pre-rRNA Transcription and Processing |journal=PLoS Genet. |volume=8 |issue=8 |pages=e1002892 |year=2012 |month=August |pmid=22916032 |pmc=3420923 |doi=10.1371/journal.pgen.1002892 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Loss of interaction between the C-terminus of Utp4/cirhin and other SSU processome proteins may cause | * Loss of interaction between the [[C-terminus]] of a protein called Utp4/cirhin and other SSU processome [[proteins]] may cause cirrhosis in children<ref>{{cite journal |author=Freed EF, Baserga SJ |title=The C-terminus of Utp4, mutated in childhood cirrhosis, is essential for ribosome biogenesis |journal=Nucleic Acids Res. |volume=38 |issue=14 |pages=4798–806 |year=2010 |month=August |pmid=20385600 |pmc=2919705 |doi=10.1093/nar/gkq185 |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Gross Pathology== | |||
On [[gross examination]], the [[liver]] may initially be enlarged, but with progression of the disease, it becomes smaller. Its surface is irregular, the consistency is firm, and the color is often yellow (if associates [[steatosis]]). Depending on the size of the [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] there are three macroscopic types: micronodular, macronodular and mixed cirrhosis. | |||
* In the micronodular form ([[René Laennec|Laennec]]'s cirrhosis or portal cirrhosis) regenerating [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] are under 3 mm. | * In the micronodular form ([[René Laennec|Laennec]]'s cirrhosis or portal cirrhosis) regenerating [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] are under 3 mm. | ||
* In macronodular cirrhosis (post-necrotic cirrhosis), the [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] are larger than 3 mm. | * In macronodular cirrhosis (post-necrotic cirrhosis), the [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] are larger than 3 mm. | ||
* The mixed cirrhosis consists of a variety of [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] with different sizes. | * The mixed cirrhosis consists of a variety of [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] with different sizes. | ||
On [[gross pathology]], [[Cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]], [[splenomegaly]], and [[esophageal varices]] are characteristic findings in portal hypertension. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 300: | Line 171: | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Images of gross pathology of cirrhosis === | |||
[http://www.peir.net Images courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] | [http://www.peir.net Images courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 367: | Line 239: | ||
*Dilated ducts contain inspissated bile which appears as bile casts or bile thrombi (brown-green, amorphous). | *Dilated ducts contain inspissated bile which appears as bile casts or bile thrombi (brown-green, amorphous). | ||
*Bile retention may be found also in the parenchyma and are referred to as "bile lakes".<ref>[http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/Cirrhosis.html Pathology atlas], "cirrhosis".</ref> | *Bile retention may be found also in the parenchyma and are referred to as "bile lakes".<ref>[http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/Cirrhosis.html Pathology atlas], "cirrhosis".</ref> | ||
== Microscopic pathology == | |||
The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in portal hypertension are related to [[Cirrhosis (patient information)|cirrhosis]], [[esophageal varices]], [[Hepatic amyloidosis with intrahepatic cholestasis|hepatic amyloidosis]], and congestive [[hepatopathy]] due to [[heart failure]] or [[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
=== Cirrhosis === | === Cirrhosis === | ||
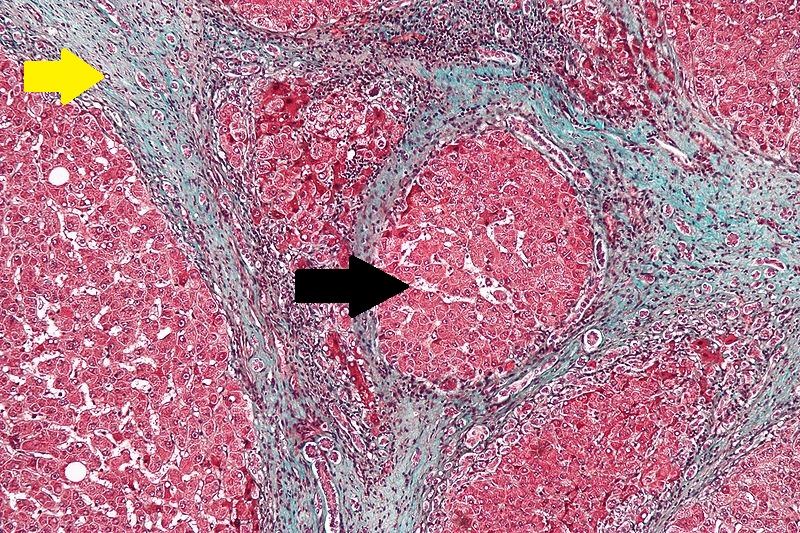
Robbins definition of microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in cirrhosis includes (all three is needed for diagnosis):<ref>{{cite book | last = Mitchell | first = Richard | title = Pocket companion to Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease | publisher = Elsevier Saunders | location = Philadelphia, PA | year = 2012 | isbn = 978-1416054542 }}</ref> | Robbins definition of [[microscopic]] [[histopathological]] findings in cirrhosis includes (all three is needed for diagnosis):<ref>{{cite book | last = Mitchell | first = Richard | title = Pocket companion to Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease | publisher = Elsevier Saunders | location = Philadelphia, PA | year = 2012 | isbn = 978-1416054542 }}</ref> | ||
* Bridging [[fibrosis]] | * Bridging [[fibrosis]] | ||
* [[Nodule]] formation | * [[Nodule]] formation | ||
| Line 383: | Line 256: | ||
=== Esophageal varices === | === Esophageal varices === | ||
The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in [[esophageal varices]] are: | The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in [[esophageal varices]] are: | ||
* Large dilated | * Large dilated [[submucosal]] [[veins]] ('''key feature''') | ||
* [[Blood]] (fresh) | * [[Blood]] (fresh) | ||
* [[Hemosiderin]]-laden [[macrophages]]. | * [[Hemosiderin]]-laden [[macrophages]]. | ||
| Line 391: | Line 264: | ||
| | | | ||
=== Hepatic amyloidosis === | === Hepatic amyloidosis === | ||
The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in [[Hepatic amyloidosis with intrahepatic cholestasis|hepatic amyloidosis]] is amorphous extracellular pink stuff on H&E staining. | The main [[microscopic]] [[histopathological]] findings in [[Hepatic amyloidosis with intrahepatic cholestasis|hepatic amyloidosis]] is amorphous extracellular pink stuff on [[H&E stain|H&E]] staining. | ||
| | | | ||
[[image:Amyloidosis - high mag.jpg|thumb|200px|Hepatic amyloidosis with amorphous amyloids (black arrow) and normal hepatocytes (blue arrow), via Librepathology.org<ref name="urlFile:Hepatic amyloidosis - high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology">{{cite web |url=https://librepathology.org/wiki/File:Hepatic_amyloidosis_-_high_mag.jpg |title=File:Hepatic amyloidosis - high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | [[image:Amyloidosis - high mag.jpg|thumb|200px|Hepatic amyloidosis with amorphous amyloids (black arrow) and normal hepatocytes (blue arrow), via Librepathology.org<ref name="urlFile:Hepatic amyloidosis - high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology">{{cite web |url=https://librepathology.org/wiki/File:Hepatic_amyloidosis_-_high_mag.jpg |title=File:Hepatic amyloidosis - high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | ||
| Line 397: | Line 270: | ||
| | | | ||
=== Congestive hepatopathy === | === Congestive hepatopathy === | ||
The main microscopic [[histopathological]] findings in congestive [[hepatopathy]] (due to [[heart failure]] or [[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]) are: | The main [[microscopic]] [[histopathological]] findings in congestive [[hepatopathy]] (due to [[heart failure]] or [[Budd-Chiari syndrome]]) are: | ||
* [[Atrophy]] of zone III | * [[Atrophy]] of the centrilobular zone (zone III) | ||
* Distension of portal [[venule]] ([[central vein]]) | * Distension of portal [[venule]] ([[central vein]]) | ||
* Perisinusoidal [[fibrosis]] which may progress to centrilobular [[fibrosis]] and then diffuse [[fibrosis]] | * Perisinusoidal [[fibrosis]] which may progress to centrilobular [[fibrosis]] and then diffuse [[fibrosis]] | ||
* [[Sinusoidal]] dilation | * [[Sinusoidal]] dilation in all zone III areas ('''key feature)''' | ||
| | | | ||
[[image:Congestive hepatopathy.jpg|thumb|200px|Congestive hepatopathy with central vein (yellow arrowhead), inflammatory cells, Councilman body (green arrowhead), and hepatocyte with mitotic figure (red arrowhead), via Librepathology.org<ref name="urlFile:2 CEN NEC 1 680x512px.tif - Libre Pathology">{{cite web |url=https://librepathology.org/wiki/File:2_CEN_NEC_1_680x512px.tif |title=File:2 CEN NEC 1 680x512px.tif - Libre Pathology |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | [[image:Congestive hepatopathy.jpg|thumb|200px|Congestive hepatopathy with central vein (yellow arrowhead), inflammatory cells, Councilman body (green arrowhead), and hepatocyte with mitotic figure (red arrowhead), via Librepathology.org<ref name="urlFile:2 CEN NEC 1 680x512px.tif - Libre Pathology">{{cite web |url=https://librepathology.org/wiki/File:2_CEN_NEC_1_680x512px.tif |title=File:2 CEN NEC 1 680x512px.tif - Libre Pathology |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Videos === | |||
{{#ev:youtube|CzKGvWZrUpU}} | {{#ev:youtube|CzKGvWZrUpU}} | ||
| Line 414: | Line 289: | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:51, 11 October 2022
| https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5szNmKtyBW4%7C350}} |
|
Cirrhosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Cirrhosis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cirrhosis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cirrhosis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sudarshana Datta, MD [2]
Overview
Cirrhosis occurs due to long term liver injury which causes an imbalance between matrix production and degradation. The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of scar tissue which leads to replacement of normal liver parenchyma, leading to blockade of portal blood flow and disturbance of normal liver function. When fibrosis of the liver reaches an advanced stage where distortion of the hepatic vasculature also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the liver. The pathogenesis of cirrhosis involves inflammation, hepatic stellate cell activation, angiogenesis, and fibrogenesis. Kupffer cells are hepatic macrophages responsible for hepatic stellate cell activation during injury. Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) which are located in the subendothelial space of Disse, become activated in areas of liver injury and secrete transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), which leads to a fibrotic response and proliferation of connective tissue. Cirrhosis may also lead to hepatic microvascular changes including the formation of intra-hepatic shunts (due to angiogenesis and loss of parenchymal cells) and endothelial dysfunction. Fibrosis eventually leads to formation of septae that grossly distort the liver architecture which includes both the liver parenchyma and the vasculature, accompanied by regenerative nodule formation. HAYOP
Pathophysiology
The pathogenesis of cirrhosis is as follows:[1][2][3][4][5][6]
- When an injured tissue is replaced by a collagenous scar, it is termed as fibrosis. The development of fibrosis requires several months, or even years of ongoing injury.
- The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of scar tissue that leads to replacement of normal liver parenchyma, leading to blockade of portal blood flow and disturbance of normal liver function.
- When fibrosis of the liver reaches a point where distortion of the hepatic vasculature also occurs, it is termed as cirrhosis of the liver. If the damage progresses, panlobular cirrhosis may result.
- The cellular mechanisms responsible for cirrhosis are similar regardless of the type of initial insult and site of injury within the liver lobule.
- Viral hepatitis involves the periportal region, whereas involvement in alcoholic liver disease is largely pericentral.
- Cirrhosis involves the following steps:[7]
Hepatic stellate cell activation
The role of hepatic stellate cells in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis is described below:
- Kupffer cells are hepatic macrophages responsible for hepatic stellate cell activation during injury.
- The stellate cell, (also known as the perisinusoidal cell or Ito cell) is a type of cell that normally stores vitamin A and plays a pivotal role in the development of cirrhosis.
- Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are usually located in the subendothelial space of Disse and become activated to a myofibroblast-like cell in areas of liver injury. This contractile cell (known as a myofibroblast) obstructs blood flow in the circulation.
- The stellate cell secretes transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1), which leads to a fibrotic response and proliferation of connective tissue.
- Connective tissue proliferation leads to the formation of extracellular matrix around hepatocytes that is composed of collagens (especially type I, III, IV), glycoprotein and proteoglycans.
- Collagen and non-collagenous matrix proteins responsible for fibrosis are produced by the activated hepatic stellate cells (HSC).
- Hepatocyte damage causes the release of lipid peroxidases from injured cell membranes leading to necrosis of parenchymal cells.
- Activated HSC induce the production of numerous cytokines and their receptors, such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and TGF-f31, which are responsible for fibrogenesis.
- The matrix formed due to HSC activation is deposited in the space of Disse and leads to loss of fenestrations of endothelial cells, through a process called capillarization.
- Stellate cell activation leads to disturbance of the balance between matrix metalloproteinases and the naturally occurring inhibitors (TIMP 1 and TIMP2). This is followed by matrix breakdown and replacement by connective tissue-secreted matrix.[8]
- Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) are calcium dependent enzymes that specifically degrade collagen and non collagenous substrate.
- MMP-2 and stromyelysin-1 are produced by stellate cells.
- MMP-2 degrades collagen and stromelysin-1 degrades proteoglycan and glycoprotein.
Microvascular changes
Cirrhosis leads to hepatic microvascular changes characterised by:[9]
- Formation of intra hepatic shunts (due to angiogenesis and loss of parenchymal cells)
- Hepatic endothelial dysfunction
- Sinusoidal endothelial cells are also important contributors of early fibrosis. Endothelial cells from a normal liver produces collagen, laminin and fibronectin.[10][11]
- The endothelial dysfunction is characterised by:[12]
- Insufficient release of vasodilators, such as nitric oxide due to oxidative stress
- Increased production of vasoconstrictors (mainly adrenergic stimulation and activation of endothelins and RAAS)
- The liver responds to injury with new blood vessel formation. Mediators involved in angiogenesis include:
Angiogenesis
- Angiogenesis in cirrhosis results in the production of immature and permeable vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced neo-vessels that further exacerbate liver injury.[13][14]
Fibrosis
The role of fibrosis in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis is described below:
- Fibrosis eventually leads to formation of septae that grossly distort the liver architecture which includes both the liver parenchyma and the vasculature.
- A cirrhotic liver compromises hepatic sinusoidal exchange by shunting arterial and portal blood directly into the central veins (hepatic outflow).
- Vascularized fibrous septa connect central veins with portal tracts leading to islands of hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous bands without central veins.[15][16][17]
- These mechanisms simultaneously occurring in the liver lead to fibrous tissue band (septa) and regenerative hepatocyte nodule formation, which eventually replace the entire liver architecture, leading to decreased blood flow throughout.
- The formation of fibrotic bands is accompanied by regenerative nodule formation in the hepatic parenchyma.
- Advancement of cirrhosis may lead to parenchymal dysfunction and development of portal hypertension.
- The pathological hallmark of cirrhosis is the development of scar tissue that replaces normal parenchyma, leading to blockade of portal blood flow and disturbance of normal liver function.
- Due to portal hypertension, the spleen becomes congested, which leads to hypersplenism and increased platelet sequestration.
Pathogenesis of cirrhosis according to cause
Pathogenesis of cirrhosis based upon the underlying cause is as follows:
- Alcoholic liver disease: Alcohol seems to injure the liver by blocking the normal metabolism of protein, fats, and carbohydrates. Patients may also have concurrent alcoholic hepatitis with fever, hepatomegaly, jaundice, and anorexia. Liver damage due to alcoholic hepatitis may progress to cirrhosis.
- Chronic hepatitis C: Infection with the hepatitis C virus causes inflammation and low grade damage to the liver that may eventually lead to cirrhosis after decades.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): In NASH, fat builds up in the liver and eventually causes scar tissue. This type of hepatitis appears to be associated with diabetes, protein malnutrition, obesity, coronary artery disease, and treatment with corticosteroid medications.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC): PSC is a progressive cholestatic disorder presenting with pruritus, steatorrhea, fat soluble vitamin deficiencies, and metabolic bone disease.
- There is a strong association with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), especially ulcerative colitis.
- Autoimmune hepatitis: Immunologic damage to the liver leads to inflammation, scarring and cirrhosis.
- Portal hypertension may result from a combination of the following:
- Structural disturbances associated with advanced liver disease account for 70% of total hepatic vascular resistance.
- Functional abnormalities such as endothelial dysfunction and increased hepatic vascular tone account for 30% of total hepatic vascular resistance.
Pathophysiology of Cirrhosis due to Alcohol
Mechanisms of alcohol-induced liver damage include:[18][19][20][21]
- Impairment of:
- Ethanol intake leads to elevated accumulation of intracellular triglycerides by:[22][23][24]
- Lipoprotein secretion
- Decreased fatty acid oxidation
- Increased fatty acid uptake
- Alcohol is converted by alcohol dehydrogenase to acetaldehyde.
- Due to the high reactivity of acetaldehyde, it forms acetaldehyde-protein adducts which cause damage to cells by:
- Trafficking of hepatic proteins
- Interrupting microtubule formation
- Interfering with enzyme activities
- Reactive oxygen species begin to form as a result of hepatocyte damage that activate Kupffer cells.[6]
- Kupffer cell activation leads to the production of profibrogenic cytokines which in turn, stimulates stellate cells.
- Stellate cell activation leads to connective tissue formation due to deposition extracellular matrix and collagen.
- Portal triads develop connections with central veins due to connective tissue formation in pericentral and periportal zones, leading to the formation of regenerative nodules.
- Shrinkage of the liver occurs over years due to repeated insults that lead to:
- Loss of hepatocytes
- Increased production and deposition of collagen and regenerative nodule formation on a background of fibrosis
Pathophysiology of Portal Hypertension due to Cirrhosis
Increased resistance
- Portal hypertension is related to elevation of resistance in the portal vasculature.
- Increased resistance in portal system may be due to both intra-hepatic and also portosystemic collateral resistance.
- Intra-hepatic resistance
- The main factor responsible for intra-hepatic resistance is hepatic vascular compliance, which is greatly decreased in liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
- Portal hypertension occurs when compliance is decreased and blood flow is increased in liver.[25]
- Pre-hepatic and post-hepatic portal hypertension arise due to some secondary obstruction before or after liver vasculature, respectively.[26]
- Alcoholic hepatitis causes both sinusoidal and post-sinusoidal pathologies.[27][28]
- Hepatic vascular endothelium synthesizes and secretes both vasodilators (e.g., nitric oxide, prostacyclins) and vasoconstrictors (e.g., endothelin and prostanoids).[29][30]
- Increased resistance due to the elevation of vascular tone may be caused by excess of vasoconstrictors or lack of vasodilators.
- It is postulated that in cirrhotic liver the nitric oxide level is lower and the response to endothelin in myofibrils is stronger than in normal liver.[31]
- Portosystemic collateral resistance
- Collateral blood circulation develops as a consequence of portal hypertension which is the main contributor to esophageal and gastric varices
- The main purpose of the collaterals is to decompress and bypass portal blood flow.
- However, portosystemic collaterals may not lead to a complete decompression.
- Portosystemic circulation occurs between the short gastric, left gastric vein, and the esophageal, azygos and the intercostal veins; the superior, the middle, and the inferior hemorrhoidal veins; the paraumbilical venous plexus, the venous system of abdominal organs juxtaposed with the retroperitoneum and abdominal wall; the left renal vein, the splanchnic, the adrenal, and the spermatic veins.[32]
- Intra-hepatic resistance
Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertension
- Peripheral vasodilatation is the basis for decreased systemic vascular resistance and mean arterial pressure, plasma volume expansion, elevated splanchnic blood flow, and elevated cardiac index.[33]
- Systemic vasodilation
- Three main mechanisms which contribute to the peripheral vasodilation are as follows:
- Increased vasodilators production in systemic circulation[34]
- Increased vasodilators production in local endothelium[35]
- Decreased vascular response to local vasoconstrictors[36]
- Three main mechanisms which contribute to the peripheral vasodilation are as follows:
- Plasma volume
- There are several events which contribute to the hyperdynamic circulation such as:
- Initial vasodilatation, induced by systemic and local endothelial factors
- Subsequent plasma volume expansion[37]
- There are several events which contribute to the hyperdynamic circulation such as:
Genetics
- Certain TERT (Telomerase reverese transcriptase) gene variants resulting in reduced telomerase activity have been found to be a risk factor for sporadic cirrhosis[38]
- An uncharacterized nucleolar protein, NOL11, has a role in the pathogenesis of North American Indian childhood cirrhosis[39]
- Loss of interaction between the C-terminus of a protein called Utp4/cirhin and other SSU processome proteins may cause cirrhosis in children[40]
Gross Pathology
On gross examination, the liver may initially be enlarged, but with progression of the disease, it becomes smaller. Its surface is irregular, the consistency is firm, and the color is often yellow (if associates steatosis). Depending on the size of the nodules there are three macroscopic types: micronodular, macronodular and mixed cirrhosis.
- In the micronodular form (Laennec's cirrhosis or portal cirrhosis) regenerating nodules are under 3 mm.
- In macronodular cirrhosis (post-necrotic cirrhosis), the nodules are larger than 3 mm.
- The mixed cirrhosis consists of a variety of nodules with different sizes.
On gross pathology, cirrhotic liver, splenomegaly, and esophageal varices are characteristic findings in portal hypertension.
CirrhosisOn gross pathology there are two types of cirrhosis:
|
 |
 |
SplenomegalyOn gross pathology, diffuse enlargement and congestion of the spleen are characteristic findings of splenomegaly. |
 | |
Esophageal VaricesOn gross pathology, prominent, congested, and tortoise veins in the lower parts of esophagus are characteristic findings of esophageal varices. |
 | |
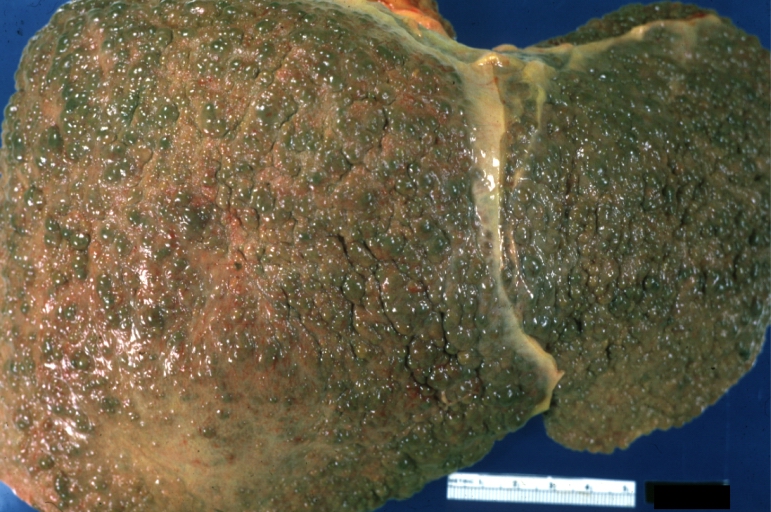
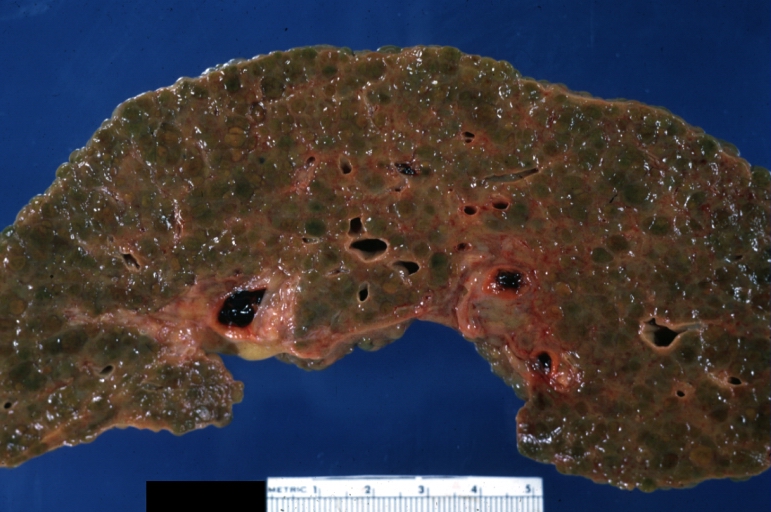
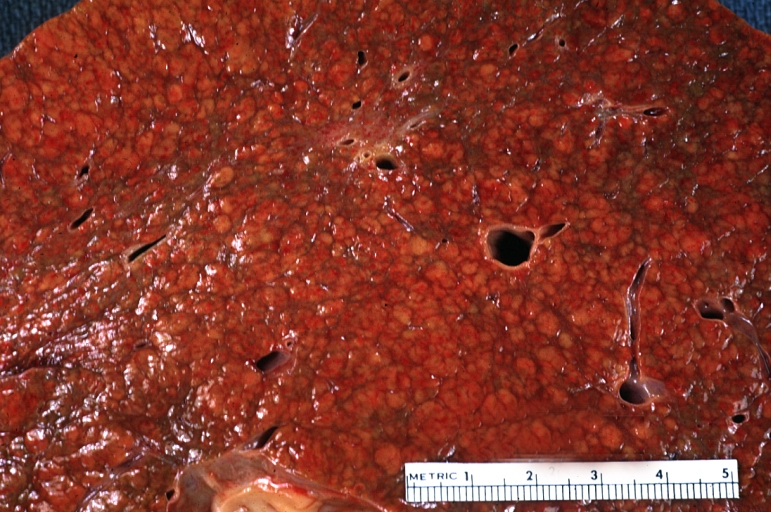
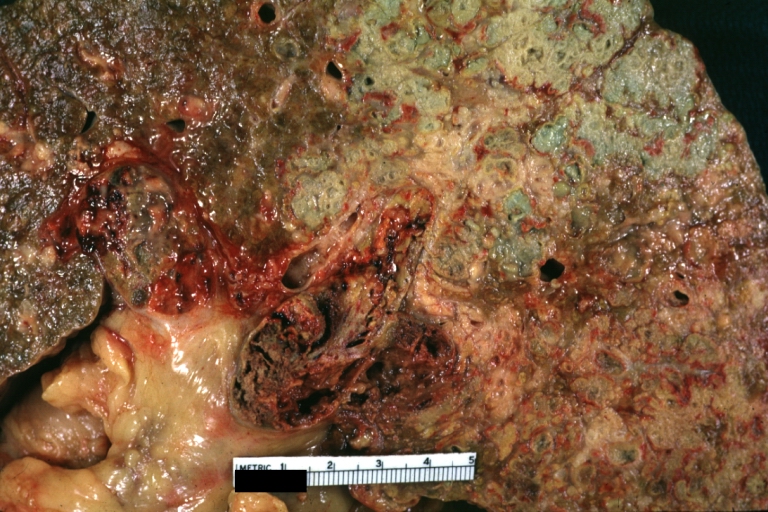
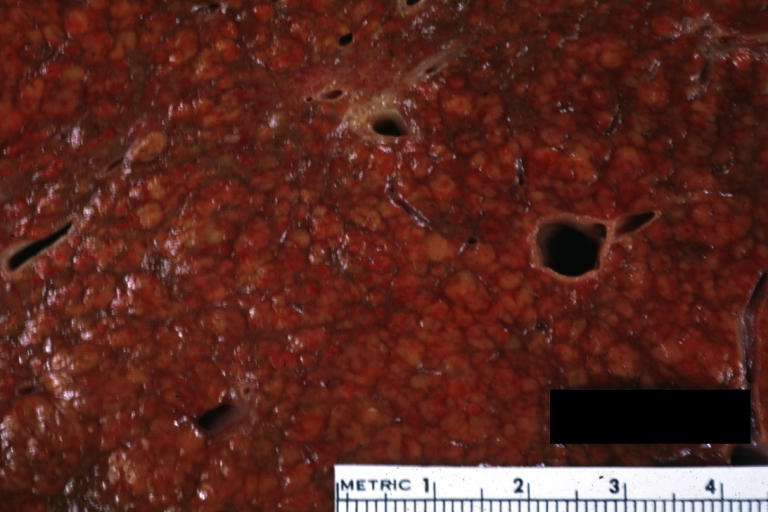
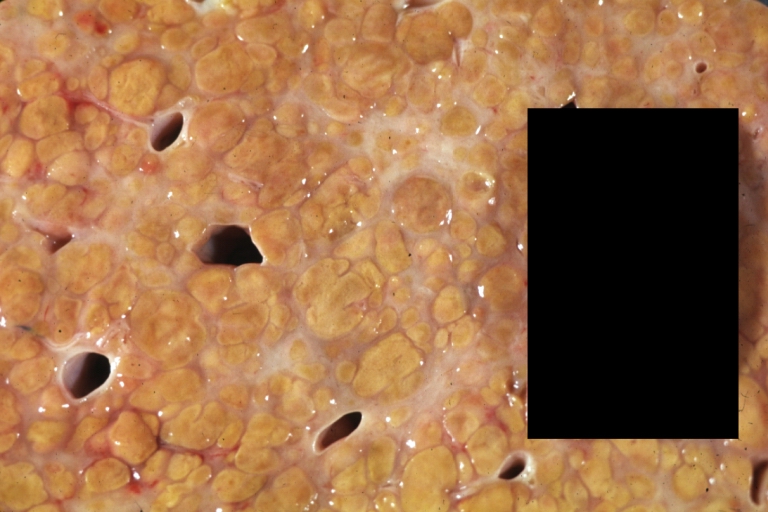
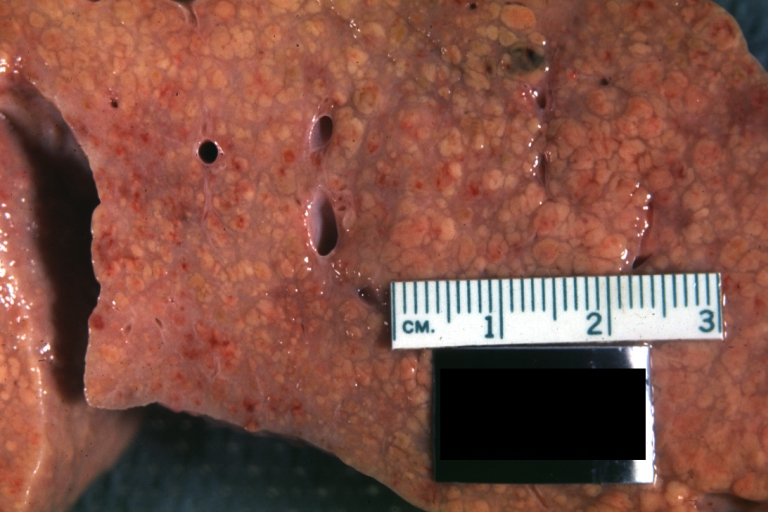
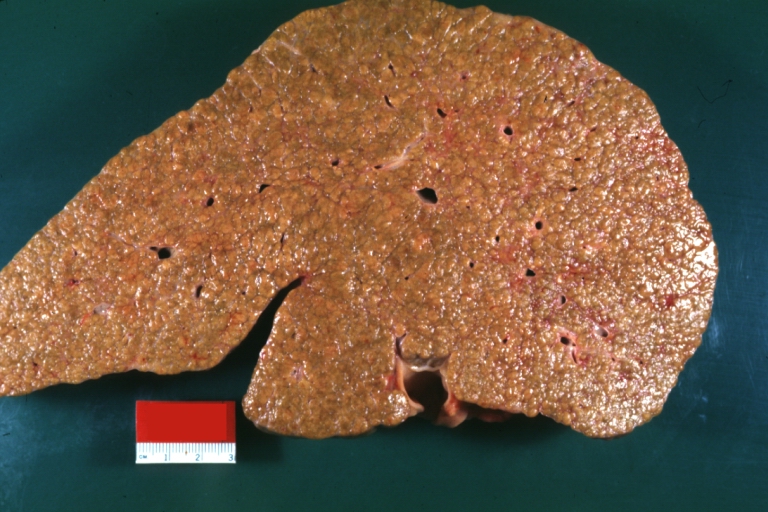
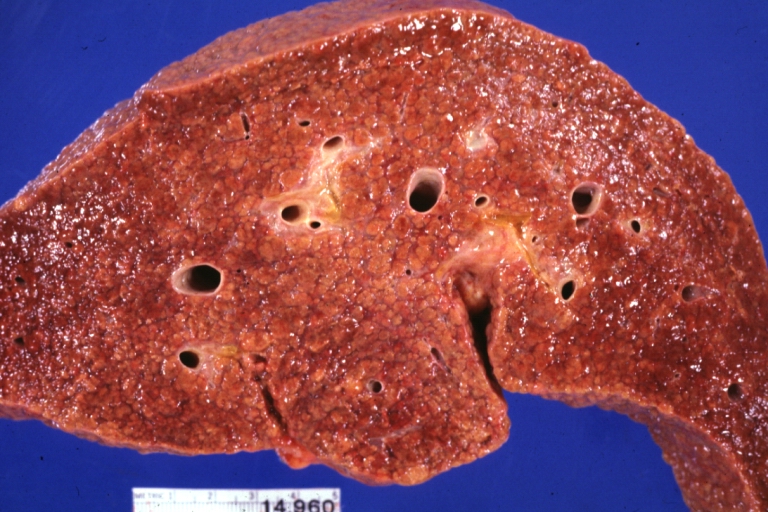
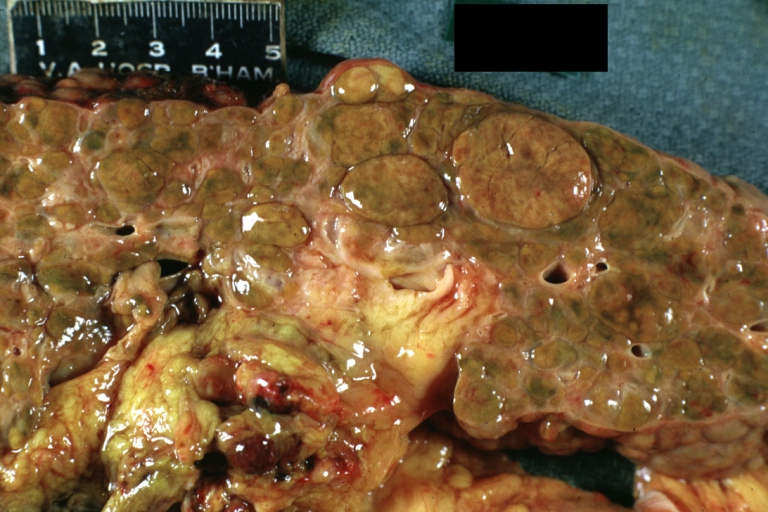
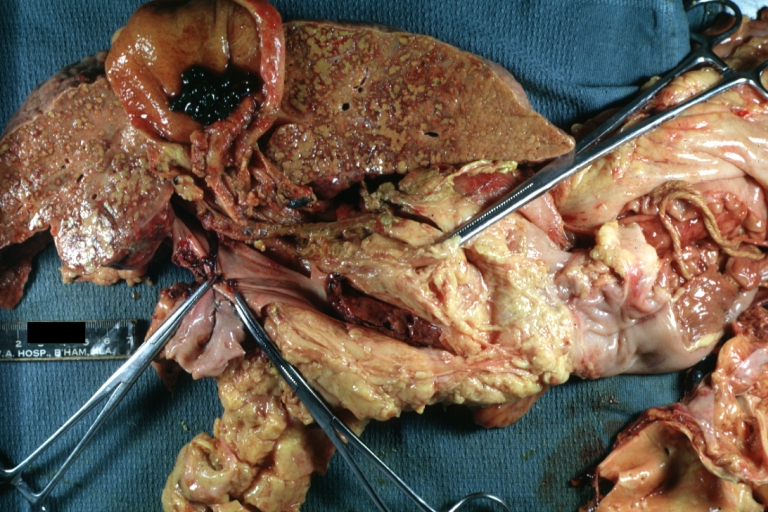
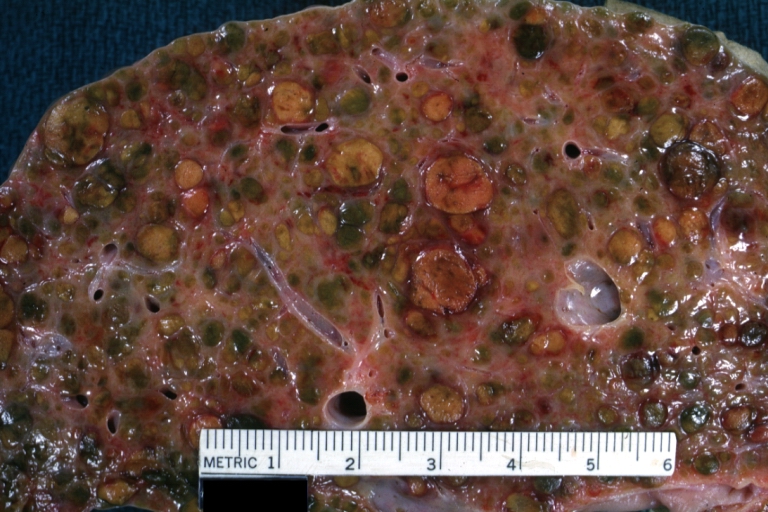
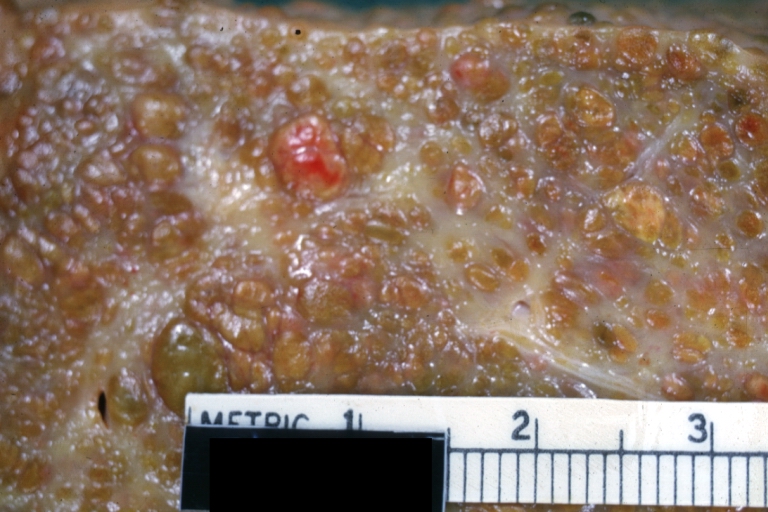
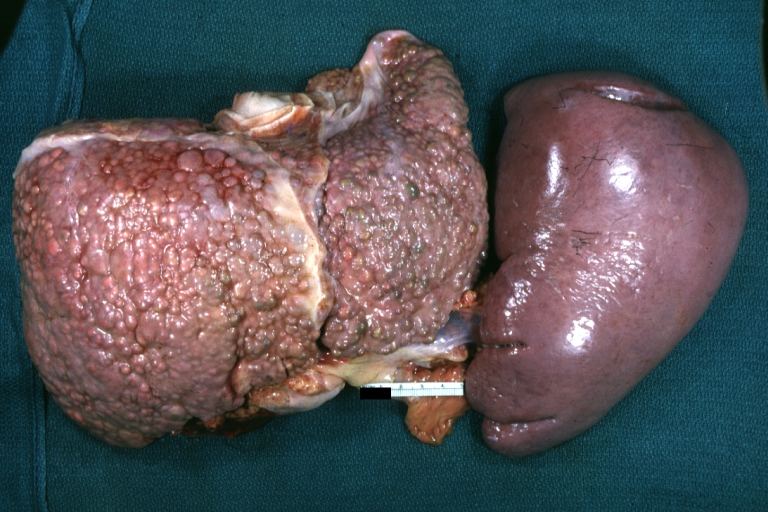
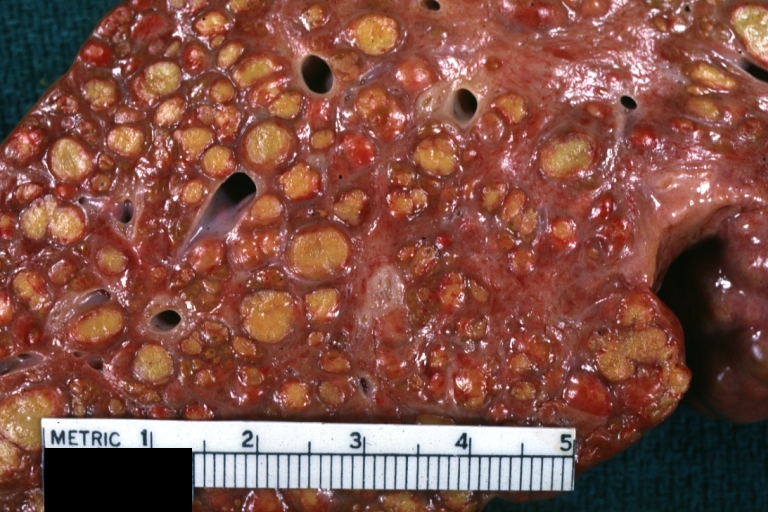
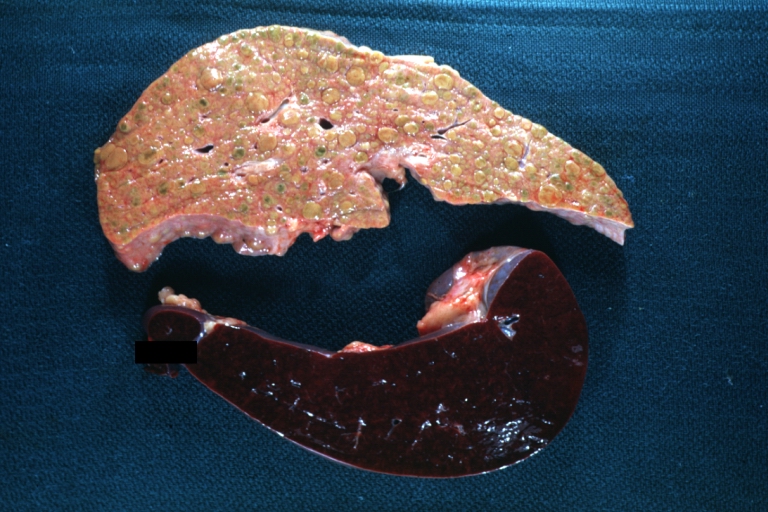
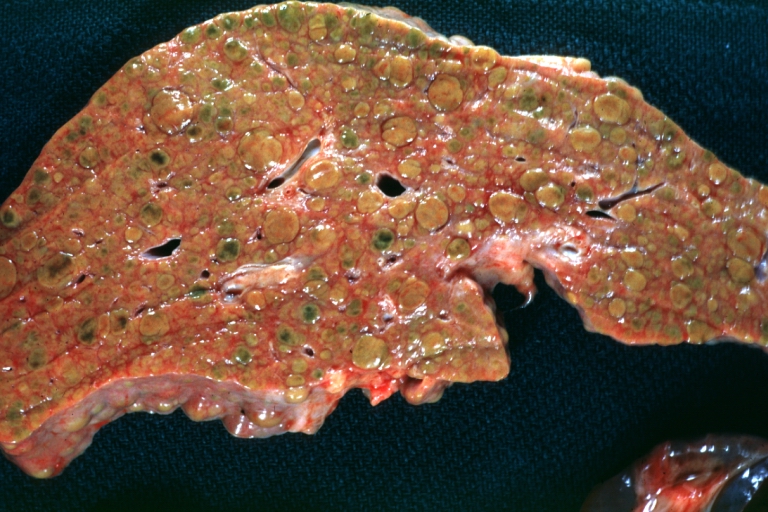
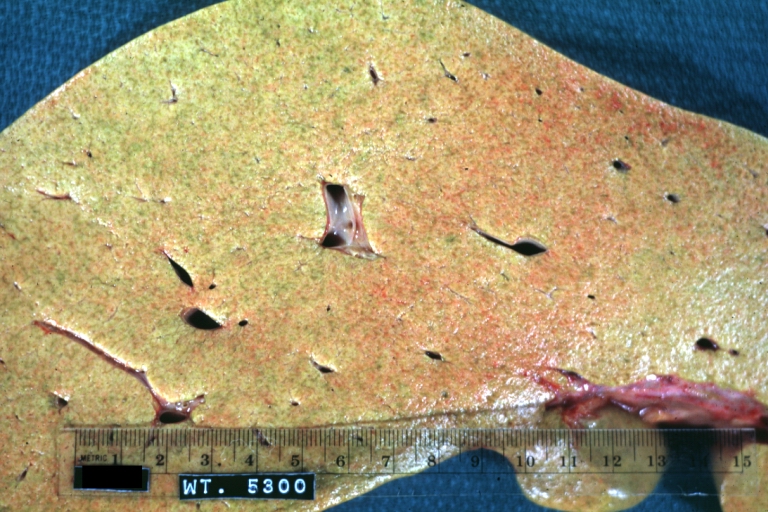
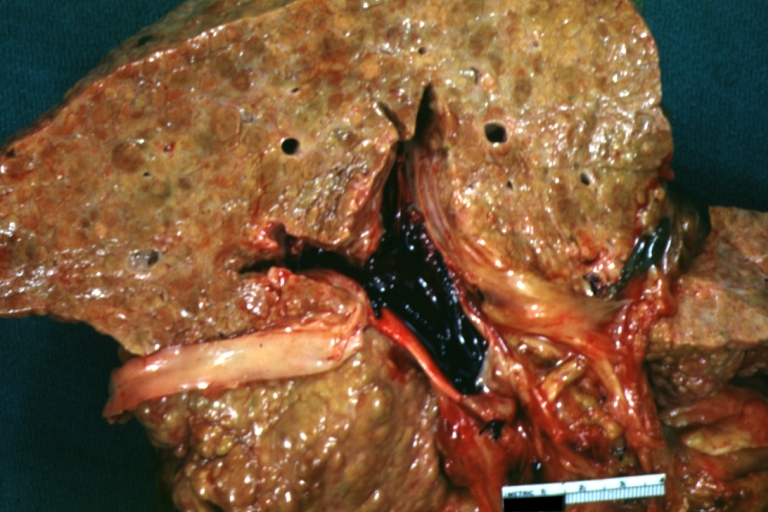
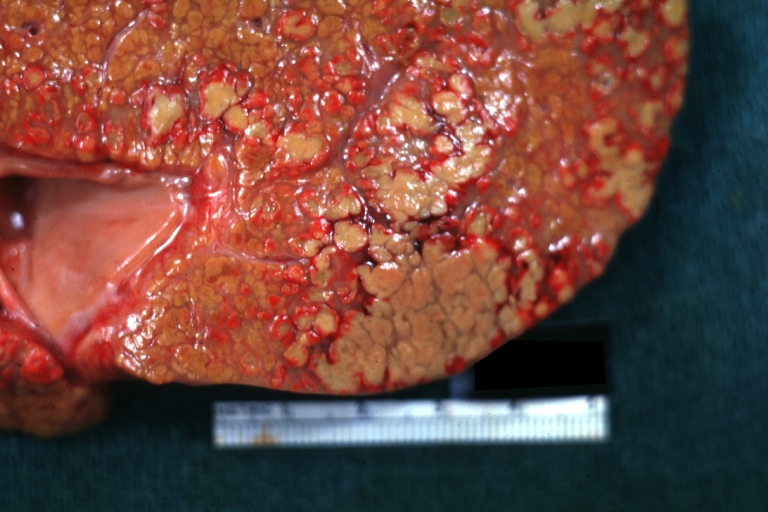
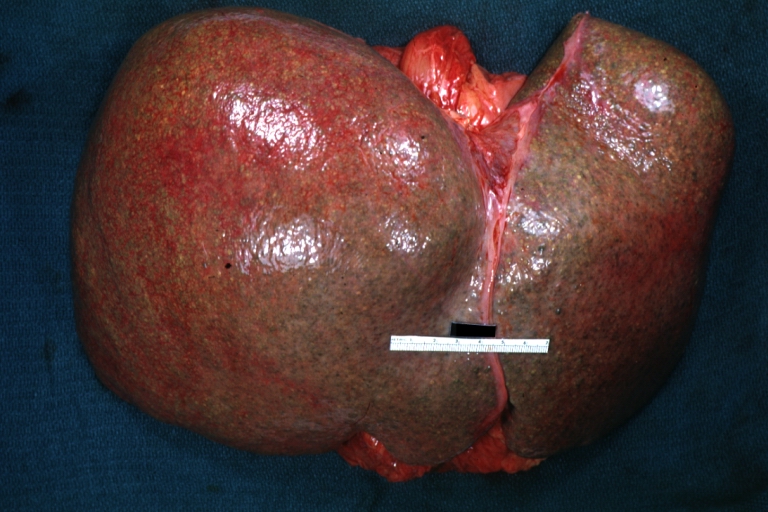
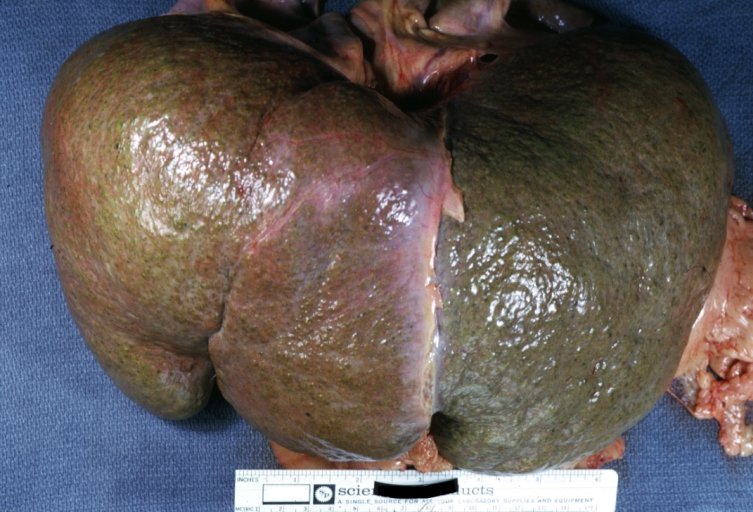
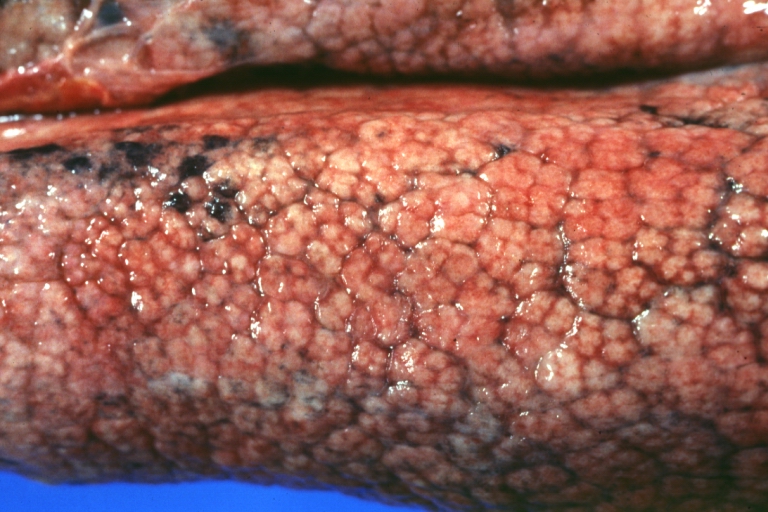
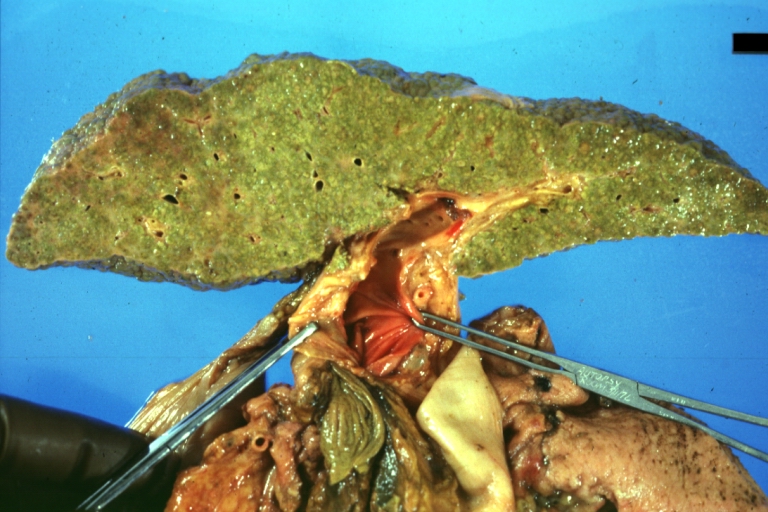
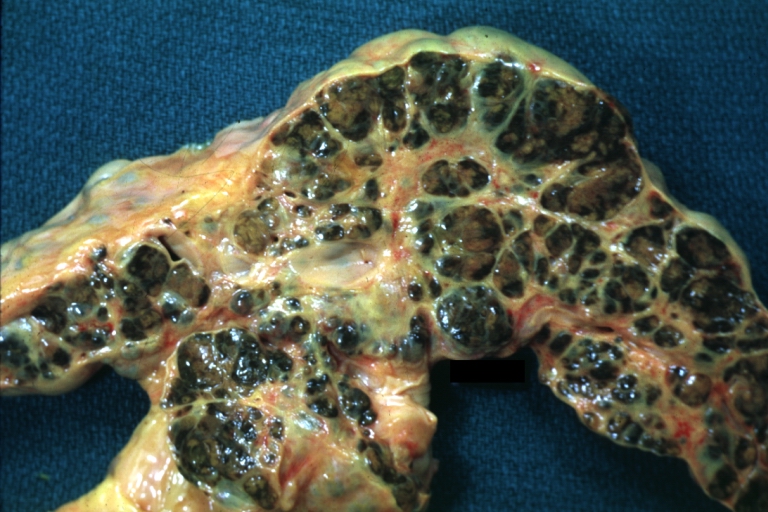
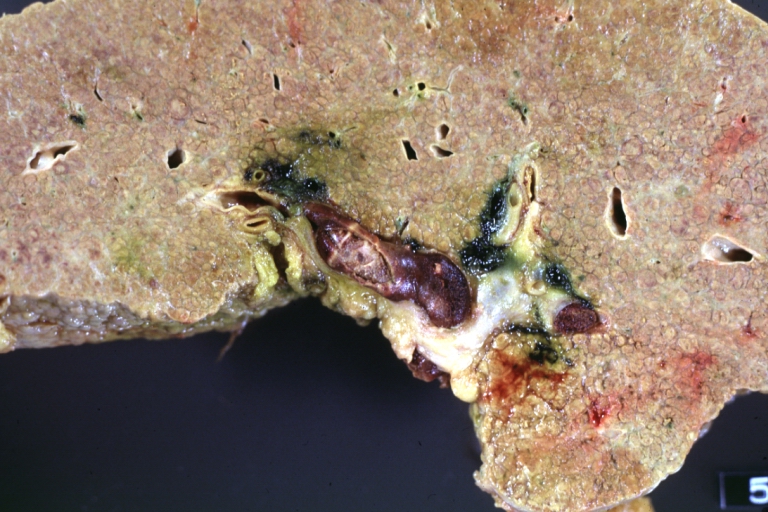
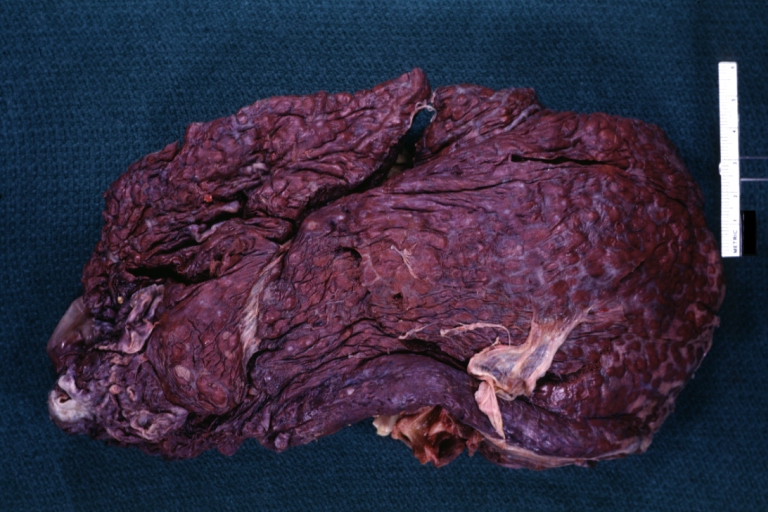
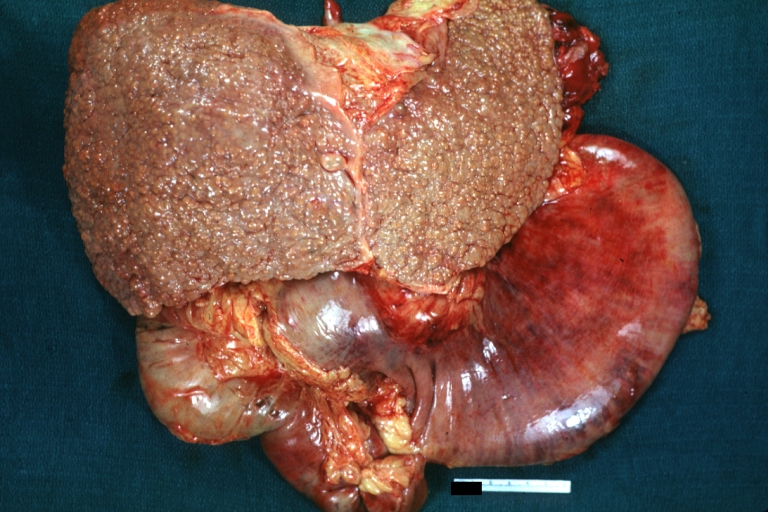
Images of gross pathology of cirrhosis
-
Cirrhosis: Gross, external view of micronodular cirrhosis
-
Cirrhosis: Gross, cut section of previous one (an excellent example)
-
Cirrhosis: Gross, close-up image
-
Macronodular cirrhosis and hepatoma
-
Cirrhosis: Gross, close-up, natural color (an excellent example)
-
Cirrhosis: Gross, close-up (an excellent example)
-
Cirrhosis: Gross, close-up view
-
Micronodular cirrhosis: Gross, external view (an excellent example)
-
Micronodular cirrhosis: Gross, close-up image
-
Micronodular cirrhosis: Gross (an excellent example)
-
Macronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color (perfect color for cirrhosis), close-up, an excellent example
-
Cirrhosis with portocaval shunt: Gross, severe cirrhosis with extensive liver necrosis due to thrombosis of portocaval shunt (well shown)
-
Endstage cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, close-up (an excellent example)
-
Endstage cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, close-up view is an excellent example for nodules of yellow-orange liver tissue and broad irregular bands of fibrosis
-
Endstage cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, close-up cut surface, very well shown nodules of yellow and necrotic opaque liver tissue with broad and irregular bands of fibrosis (an excellent example)
-
Macronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, external view of liver and very enlarged spleen (liver has variable size nodules up to about 2 cm)
-
Macronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, cut surface, large irregular bands of fibrosis with variable size liver cell nodules up to about 8 mm and all necrotic appears to be an end stage liver disease.
-
Macronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color view of frontal sections of liver and spleen showing a contracted macronodular liver and an enlarged spleen as large as the liver
-
Macronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color slab of liver
-
Fatty change and early cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, rather close-up image showing typical fatty color, and in lighting at lower right of micrography micronodularity is evident (quite good example)
-
Cirrhosis with portal vein thrombosis: Gross, natural color, sectioned liver with portal vein exposed and filled with red thrombus. A good example of end stage cirrhosis.
-
Endstage cirrhosis with lobular necrosis: Gross, natural color, very close-up view (an excellent example of alcoholic cirrhosis)
-
Micronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color view of whole liver through capsule with obvious cirrhosis (note to quite large liver)
-
Micronodular cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, view of whole liver showing external surface typical cirrhotic liver (history of alcoholism)
-
Lung: Idiopathic Interstitial Fibrosis: Gross, natural color, an excellent photo of lung cirrhosis (close-up view)
-
Endstage cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, slice of liver. Portal vein is opened to show size and patency.
-
Endstage cirrhosis: Gross, natural color, severe cirrhosis with bile stasis
-
Portal Vein Thrombosis with cirrhosis: Gross, close-up, micronodular cirrhosis with portal vein thrombosis
-
Lung: Hematite: Gross, natural color, external view of "pulmonary cirrhosis" with typical hematite color
-
Gross, natural color of liver and stomach view from external surfaces, micronodular cirrhosis and hemorrhagic gastritis (as the surgeon would see these in natural color)
Microscopic Pathology
- Microscopic pathology reveals the four stages of cirrhosis as it progresses:
- Chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis: inflammation and necrosis of portal tracts with lymphocyte infiltration leads to the destruction of the bile ducts
- Development of biliary stasis and fibrosis
- Periportal fibrosis progresses to bridging fibrosis
- Increased proliferation of smaller bile ductules leads to regenerative nodule formation
- Microscopically, cirrhosis is characterized by regeneration nodules surrounded by fibrous septa.
- In these nodules, regenerating hepatocytes are present.
- Portal tracts, central veins and the radial pattern of hepatocytes are absent.
- Fibrous septa are present and inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and macrophages) are also visible.
- If the underlying cause is secondary biliary cirrhosis, biliary ducts are damaged, proliferated or distended leading to bile stasis.
- Dilated ducts contain inspissated bile which appears as bile casts or bile thrombi (brown-green, amorphous).
- Bile retention may be found also in the parenchyma and are referred to as "bile lakes".[45]
Microscopic pathology
The main microscopic histopathological findings in portal hypertension are related to cirrhosis, esophageal varices, hepatic amyloidosis, and congestive hepatopathy due to heart failure or Budd-Chiari syndrome.
CirrhosisRobbins definition of microscopic histopathological findings in cirrhosis includes (all three is needed for diagnosis):[46] |
 |
Esophageal varicesThe main microscopic histopathological findings in esophageal varices are:
|
 |
Hepatic amyloidosisThe main microscopic histopathological findings in hepatic amyloidosis is amorphous extracellular pink stuff on H&E staining. |
 |
Congestive hepatopathyThe main microscopic histopathological findings in congestive hepatopathy (due to heart failure or Budd-Chiari syndrome) are:
|
 |
Videos
{{#ev:youtube|CzKGvWZrUpU}}
{{#ev:youtube|CV8OYeIUXko}}
{{#ev:youtube|Jj8ozr_IttM}}
References
- ↑ Arthur MJ, Iredale JP (1994). "Hepatic lipocytes, TIMP-1 and liver fibrosis". J R Coll Physicians Lond. 28 (3): 200–8. PMID 7932316.
- ↑ Friedman SL (1993). "Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies". N. Engl. J. Med. 328 (25): 1828–35. doi:10.1056/NEJM199306243282508. PMID 8502273.
- ↑ Iredale JP (1996). "Matrix turnover in fibrogenesis". Hepatogastroenterology. 43 (7): 56–71. PMID 8682489.
- ↑ Gressner AM (1994). "Perisinusoidal lipocytes and fibrogenesis". Gut. 35 (10): 1331–3. PMC 1374996. PMID 7959178.
- ↑ Iredale JP (2007). "Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ". J. Clin. Invest. 117 (3): 539–48. doi:10.1172/JCI30542. PMC 1804370. PMID 17332881.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Arthur MJ (2002). "Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C". Gastroenterology. 122 (5): 1525–8. PMID 11984538.
- ↑ Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G (1995). "Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension". Hepatology. 21 (5): 1238–47. PMID 7737629.
- ↑ Iredale JP. Cirrhosis: new research provides a basis for rational and targeted treatments. BMJ 2003;327:143-7.Fulltext. PMID 12869458.
- ↑ Fernández M, Semela D, Bruix J, Colle I, Pinzani M, Bosch J (2009). "Angiogenesis in liver disease". J. Hepatol. 50 (3): 604–20. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.011. PMID 19157625.
- ↑ Maher JJ, McGuire RF (1990). "Extracellular matrix gene expression increases preferentially in rat lipocytes and sinusoidal endothelial cells during hepatic fibrosis in vivo". J. Clin. Invest. 86 (5): 1641–8. doi:10.1172/JCI114886. PMC 296914. PMID 2243137. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Herbst H, Frey A, Heinrichs O; et al. (1997). "Heterogeneity of liver cells expressing procollagen types I and IV in vivo". Histochem. Cell Biol. 107 (5): 399–409. PMID 9208331. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J (2012). "Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis". J. Hepatol. 57 (2): 458–61. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007. PMID 22504334.
- ↑ Lee JS, Semela D, Iredale J, Shah VH (2007). "Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: a new function for the liver-specific pericyte?". Hepatology. 45 (3): 817–25. doi:10.1002/hep.21564. PMID 17326208. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Rosmorduc O, Housset C (2010). "Hypoxia: a link between fibrogenesis, angiogenesis, and carcinogenesis in liver disease". Semin. Liver Dis. 30 (3): 258–70. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1255355. PMID 20665378. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Schuppan D, Afdhal NH (2008). "Liver cirrhosis". Lancet. 371 (9615): 838–51. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9. PMC 2271178. PMID 18328931.
- ↑ Desmet VJ, Roskams T (2004). "Cirrhosis reversal: a duel between dogma and myth". J. Hepatol. 40 (5): 860–7. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2004.03.007. PMID 15094237.
- ↑ Wanless IR, Nakashima E, Sherman M (2000). "Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 124 (11): 1599–607. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<1599:ROHC>2.0.CO;2. PMID 11079009.
- ↑ Ceni E, Mello T, Galli A (2014). "Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism". World J. Gastroenterol. 20 (47): 17756–72. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17756. PMC 4273126. PMID 25548474.
- ↑ You M, Crabb DW (2004). "Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease II. Minireview: molecular mechanisms of alcoholic fatty liver". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 287 (1): G1–6. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00056.2004. PMID 15194557.
- ↑ Freeman TL, Tuma DJ, Thiele GM, Klassen LW, Worrall S, Niemelä O, Parkkila S, Emery PW, Preedy VR (2005). "Recent advances in alcohol-induced adduct formation". Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 29 (7): 1310–6. PMID 16088993.
- ↑ Niemelä O (2007). "Acetaldehyde adducts in circulation". Novartis Found. Symp. 285: 183–92, discussion 193–7. PMID 17590995.
- ↑ Fischer M, You M, Matsumoto M, Crabb DW (2003). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) agonist treatment reverses PPARalpha dysfunction and abnormalities in hepatic lipid metabolism in ethanol-fed mice". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (30): 27997–8004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302140200. PMID 12791698.
- ↑ You M, Matsumoto M, Pacold CM, Cho WK, Crabb DW (2004). "The role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the action of ethanol in the liver". Gastroenterology. 127 (6): 1798–808. PMID 15578517.
- ↑ Ji C, Chan C, Kaplowitz N (2006). "Predominant role of sterol response element binding proteins (SREBP) lipogenic pathways in hepatic steatosis in the murine intragastric ethanol feeding model". J. Hepatol. 45 (5): 717–24. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2006.05.009. PMID 16879892.
- ↑ Greenway CV, Stark RD (1971). "Hepatic vascular bed". Physiol. Rev. 51 (1): 23–65. PMID 5543903.
- ↑ Schiff, Eugene (2012). Schiff's diseases of the liver. Chichester, West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9780470654682.
- ↑ SCHAFFNER F, POPER H (1963). "Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man". Gastroenterology. 44: 239–42. PMID 13976646.
- ↑ Reynolds TB, Hidemura R, Michel H, Peters R (1969). "Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease". Ann. Intern. Med. 70 (3): 497–506. PMID 5775031.
- ↑ Rubanyi GM (1991). "Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors". J. Cell. Biochem. 46 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1002/jcb.240460106. PMID 1874796.
- ↑ Epstein, Franklin H.; Vane, John R.; Änggård, Erik E.; Botting, Regina M. (1990). "Regulatory Functions of the Vascular Endothelium". New England Journal of Medicine. 323 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ Rockey DC, Weisiger RA (1996). "Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance". Hepatology. 24 (1): 233–40. doi:10.1002/hep.510240137. PMID 8707268.
- ↑ Mosca P, Lee FY, Kaumann AJ, Groszmann RJ (1992). "Pharmacology of portal-systemic collaterals in portal hypertensive rats: role of endothelium". Am. J. Physiol. 263 (4 Pt 1): G544–50. PMID 1415713.
- ↑ Colombato LA, Albillos A, Groszmann RJ (1992). "Temporal relationship of peripheral vasodilatation, plasma volume expansion and the hyperdynamic circulatory state in portal-hypertensive rats". Hepatology. 15 (2): 323–8. PMID 1735537.
- ↑ Genecin P, Polio J, Colombato LA, Ferraioli G, Reuben A, Groszmann RJ (1990). "Bile acids do not mediate the hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertensive rats". Am. J. Physiol. 259 (1 Pt 1): G21–5. PMID 2372062.
- ↑ Casadevall, María; Panés, Julián; Piqué, Josep M.; Marroni, Norma; Bosch, Jaume; Whittle, Brendan J. R. (1993). "Involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandins in gastric mucosal hyperemia of portal-hypertensive anesthetized rats". Hepatology. 18 (3): 628–634. doi:10.1002/hep.1840180323. ISSN 0270-9139.
- ↑ Sieber CC, Groszmann RJ (1992). "In vitro hyporeactivity to methoxamine in portal hypertensive rats: reversal by nitric oxide blockade". Am. J. Physiol. 262 (6 Pt 1): G996–1001. PMID 1616049.
- ↑ Albillos A, Colombato LA, Lee FY, Groszmann RJ (1993). "Octreotide ameliorates vasodilatation and Na+ retention in portal hypertensive rats". Gastroenterology. 104 (2): 575–9. PMID 8425700.
- ↑ Calado RT, Brudno J, Mehta P; et al. (2011). "Constitutional telomerase mutations are genetic risk factors for cirrhosis". Hepatology. 53 (5): 1600–7. doi:10.1002/hep.24173. PMC 3082730. PMID 21520173. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Freed EF, Prieto JL, McCann KL, McStay B, Baserga SJ (2012). "NOL11, Implicated in the Pathogenesis of North American Indian Childhood Cirrhosis, Is Required for Pre-rRNA Transcription and Processing". PLoS Genet. 8 (8): e1002892. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002892. PMC 3420923. PMID 22916032. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Freed EF, Baserga SJ (2010). "The C-terminus of Utp4, mutated in childhood cirrhosis, is essential for ribosome biogenesis". Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (14): 4798–806. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq185. PMC 2919705. PMID 20385600. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ <CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)>
- ↑ "www.meddean.luc.edu".
- ↑ Amadalvarez - Own work, <"https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0" title="Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0">CC BY-SA 4.0, <"https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=49669333">Link
- ↑ <http://wellcomeimages.org/indexplus/obf_images/29/b4/13f38971164f946a97f9d32ddd93.jpg>Gallery: <"http://wellcomeimages.org/indexplus/image/L0074357.html"><"http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0> CC BY 4.0, <"https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=36297209">
- ↑ Pathology atlas, "cirrhosis".
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard (2012). Pocket companion to Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ "File:Cirrhosis high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology".
- ↑ "Esophageal varices - Libre Pathology".
- ↑ "File:Hepatic amyloidosis - high mag.jpg - Libre Pathology".
- ↑ "File:2 CEN NEC 1 680x512px.tif - Libre Pathology".