Cefadroxil
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Cefadroxil is a cephalosporin that is FDA approved for the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by E. coli, P. mirabilis, and Klebsiella species, skin and skin structure infections caused by staphylococci and/or 4streptococci, pharyngitis and/or tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci). Common adverse reactions include {{{adverseReactions}}}.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Urinary Tract Infections
- For uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections (i.e., cystitis) the usual dosage is 1 or 2 g per day in a single (q.d.) or divided doses (b.i.d.).
- For all other urinary tract infections the usual dosage is 2 g per day in divided doses (b.i.d.).
Skin and Skin Structure Infections
For skin and skin structure infections the usual dosage is 1 g per day in single (q.d.) or divided doses (b.i.d.).
Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis
Treatment of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis and tonsillitis-1 g per day in single (q.d.) or divided doses (b.i.d.) for 10 days.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Cefadroxil in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Osteomyelitis[1]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
For urinary tract infections, the recommended daily dosage for children is 30 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours. For pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and impetigo, the recommended daily dosage for children is 30 mg/kg/day in a single dose or in equally divided doses every 12 hours. For other skin and skin structure infections, the recommended daily dosage is 30 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses every 12 hours. In the treatment of beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections, a therapeutic dosage of Cefadroxil should be administered for at least 10 days.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Cefadroxil in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Osteomyelitis[1]
Contraindications
Cefadroxil monohydrate is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
Warnings
Before therapy with Cefadroxil monohydrate is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefadroxil, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. if this product is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross-sensitivity among beta-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to Cefadroxil monohydrate occurs, discontinue the drug. serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefadroxil, and may range from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicated that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is a primary cause of “antibiotic-associated colitis’’. After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to discontinuation of the drug alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation and treatment with an antibacterial drug effective against Clostridium difficile.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Gastrointestinal
Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment. Dyspepsia, nausea and vomiting have been reported rarely. Diarrhea has also occurred.
Hypersensitivity
Allergies (in the form of rash, urticaria, angioedema, and pruritus) have been observed. These reactions usually subsided upon discontinuation of the drug. Anaphylaxis has also been reported.
Other
Other reactions have included hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis and elevations in serum transaminase, genital pruritus, genital moniliasis, vaginitis, moderate transient neutropenia, fever. Agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, idiosyncratic hepatic failure, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, serum sickness, and arthralgia have been rarely reported.
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with cefadroxil, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin-class antibiotics: Toxic epidermal necrolysis, abdominal pain, superinfection, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, prolonged prothrombin time, positive Coombs’ test, increased BUN, increased creatinine, elevated alkaline phosphatase, elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST), elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), elevated bilirubin, elevated LDH, eosinophilia, pancytopenia, neutropenia.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment, when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): B
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 11 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefadroxil monohydrate. There are, however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Cefadroxil in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
Cefadroxil monohydrate has not been studied for use during labor and delivery. Treatment should only be given if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when cefadroxil monohydrate is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cefadroxil in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
Of approximately 650 patients who received cefadroxil for the treatment of urinary tract infections in three clinical trials, 28% were 60 years and older, while 16% were 70 years and older. Of approximately 1000 patients who received cefadroxil for the treatment of skin and skin structure infection in 14 clinical trials, 12% were 60 years and older while 4% were 70 years and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between the elderly patients in these studies and younger patients. Clinical studies of cefadroxil for the treatment of pharyngitis or tonsillitis did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience with cefadroxil has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Cefadroxil is substantially excreted by the kidney, and dosage adjustment is indicated for patients with renal impairment. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cefadroxil with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cefadroxil with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
In patients with renal impairment, the dosage of cefadroxil monohydrate should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance rates to prevent drug accumulation. The following schedule is suggested. In adults, the initial dose is 1000 mg of cefadroxil monohydrate and the maintenance dose (based on the creatinine clearance rate [mL/min/1.73 m2]) is 500 mg at the time intervals listed below.
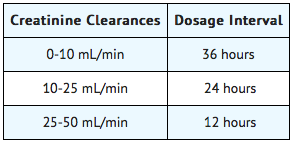
Patients with creatinine clearance rates over 50 mL/min may be treated as if they were patients having normal renal function.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cefadroxil in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Cefadroxil in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Cefadroxil in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Cefadroxil and IV administrations.
Overdosage
A study of children under six years of age suggested that ingestion of less than 250 mg/kg of cephalosporins is not associated with significant outcomes. No action is required other than general support and observation. For amounts greater than 250 mg/kg, induce gastric emptying.
In five anuric patients, it was demonstrated that an average of 63% of a 1 g oral dose is extracted from the body during a 6 to 8 hour hemodialysis session.
Pharmacology
| |
Cefadroxil
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (6R,7R)-7-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino}-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | J01 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 363.389 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Protein binding | plasma protein |
| Metabolism | unknown |
| Half life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
Rx Only |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
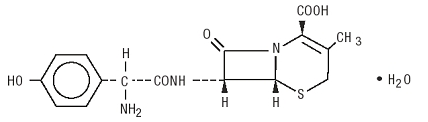
It is chemically designated as 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[amino (4-hydroxyphenyl) acetyl] amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-, monohydrate, [6R-[6α, 7β(R*)]]-. It has the molecular formula C16H17N3O5S•H2O and the molecular weight of 381.40. It has the following structural formula:

Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
Cefadroxil monohydrate is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Following single doses of 500 mg and 1000 mg, average peak serum concentrations were approximately 16 and 28 mcg/mL, respectively. Measurable levels were present 12 hours after administration. Over 90% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine within 24 hours. Peak urine concentrations are approximately 1800 mcg/mL during the period following a single 500 mg oral dose. Increases in dosage generally produce a proportionate increase in cefadroxil urinary concentration. The urine antibiotic concentration, following a 1 g dose, was maintained well above the MIC of susceptible urinary pathogens for 20 to 22 hours.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
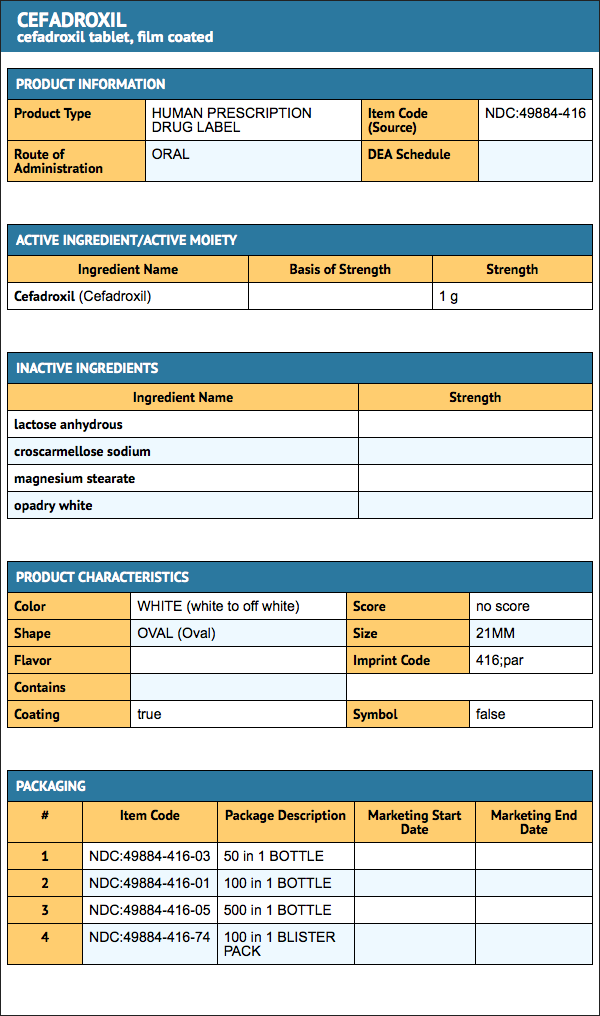
Cefadroxil Tablets, USP 1 gram: White to off-white, film-coated, oval shaped tablets with ‘416’ and ‘par’ on either side of the breakline on one side and plain on the other side. Tablets are supplied as follows:
- NDC 49884-416-03: Bottle of 50
- NDC 49884-416-01: Bottle of 100
- NDC 49884-416-05: Bottle of 500
- NDC 49884-416-74: Carton of 100 [10 x 10s (2 x 5 cards)]
Storage
Store at 20° – 25° C (68° – 77° F)
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Cefadroxil |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Cefadroxil |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Cefadroxil interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Cefadroxil Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Schwob MF, Jimenez-Shehab M (1980). "Cefadroxil in the treatment of osteomyelitis in children". J Int Med Res. 8 (Suppl 1): 106–10. PMID 7439498.