Cardiac tamponade echocardiography: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The role of echocardiography in the evaluation of the patient with pericarditis is to chracterize the presence, size, location and hemodynamic impact of a pericardial effusion. | The role of echocardiography in the evaluation of the patient with pericarditis is to chracterize the presence, size, location and hemodynamic impact of a pericardial effusion. | ||
==Echocardiography== | ==Echocardiography== | ||
* | * As part of their recommendations for echocardiography, the [[American College of Cardiology]] ([[ACC]]), the [[American Heart Association]] ([[AHA]]), and the [[American Society of Echocardiography]] gave strong recommendations for [[echocardiography]] in [[pericardial]] diseases. <ref name="pmid12952829">{{cite journal |author=Cheitlin MD, Armstrong WF, Aurigemma GP, Beller GA, Bierman FZ, Davis JL, Douglas PS, Faxon DP, Gillam LD, Kimball TR, Kussmaul WG, Pearlman AS, Philbrick JT, Rakowski H, Thys DM, Antman EM, Smith SC, Alpert JS, Gregoratos G, Anderson JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Fuster V, Jacobs AK, Gibbons RJ, Russell RO |title=ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 guideline update for the clinical application of echocardiography: summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASE Committee to Update the 1997 Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography) |journal=[[Circulation]] |volume=108 |issue=9 |pages=1146–62 |year=2003 |month=September |pmid=12952829 |doi=10.1161/01.CIR.0000073597.57414.A9 |url=http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12952829 |accessdate=2012-09-14}}</ref> | ||
* Two dimensional and Doppler echocardiography should be done in all suspected cases of cardiac tamponade and [[pericardial effusion]]. | * Two dimensional echocardiography and Doppler echocardiography should be done in all suspected cases of cardiac tamponade and [[pericardial effusion]]. | ||
* Follow up / sequential echocardiography for assessment of impending cardiac tamponade should be considered. | * Follow up / sequential echocardiography for assessment of impending cardiac tamponade should be considered. | ||
* Helps in diagnosing pericardial disease | * Helps in diagnosing pericardial disease and hemodynamic parameters (pressure in different cardiac chambers). | ||
==Echocardiographic findings in cardiac tamponade== | ==Echocardiographic findings in cardiac tamponade== | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 19 September 2012
|
Cardiac tamponade Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Cardiac tamponade echocardiography On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cardiac tamponade echocardiography |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cardiac tamponade echocardiography |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Priyamvada Singh, M.D. [2]
Overview
The role of echocardiography in the evaluation of the patient with pericarditis is to chracterize the presence, size, location and hemodynamic impact of a pericardial effusion.
Echocardiography
- As part of their recommendations for echocardiography, the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the American Society of Echocardiography gave strong recommendations for echocardiography in pericardial diseases. [1]
- Two dimensional echocardiography and Doppler echocardiography should be done in all suspected cases of cardiac tamponade and pericardial effusion.
- Follow up / sequential echocardiography for assessment of impending cardiac tamponade should be considered.
- Helps in diagnosing pericardial disease and hemodynamic parameters (pressure in different cardiac chambers).
Echocardiographic findings in cardiac tamponade
- Presence of moderate and large pericardial effusion.
- Swinging of the heart within the effusion
- Reversal of right atrial and right ventricular diastolic transmural pressures.
- Cardiac chamber collapse is a common finding in cardiac tamponade.
- Right atrium and right ventricle are the commonest to collapse when intrapericardial pressure exceeds intracardiac pressure within any particular chamber.
- Right atrial collapse
- Right atrial pressure is minimal during diastole. However, pericardial pressure is maximal in diastole. Due to this the first signs of collapse could be seen during right atrial diastole.
- Right atrial collapse if persists for > 1/3rd of cardiac cycle is a good indicator of impending tamponade.
- Transient right atrial collapse can occur normally also.
- Diastolic collapse of right ventricle is very specific for cardiac tamponade.
- Diastolic left atrial collapse are very specific for cardiac tampoande
- Left ventricle collapse is uncommon due to high thickness of ventricular wall.
- The respiratory variation of inflow and outflow across mitral valve and tricuspid valve is increased
- Normal respiratory variation in inflow and outflow across mitral and tricuspid valve ranges between 20 - 25 percent.
- Inflow outflow respiratory variation across mitral flow > 35 percent
- Tricuspid valve flow > 80 to 100 percent.
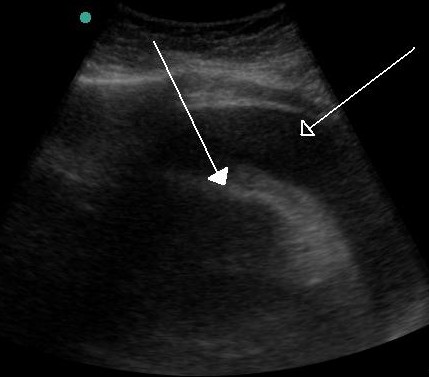
Pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade
In pericardial effusion, large hypoechoic regions are seen surrounding the heart with presence of oscillatory motion of heart.
The echocardiogram below demonstrates swinging motion of the heart in cardiac tamponade. {{#ev:youtube|U4xQ3-VRiNg}}
Echocardiography of heart with loculated pericardial effusion compressing the left ventricle. {{#ev:youtube|unnmmlCyyZM}}
Cardiac tamponade {{#ev:youtube|YWVI6rRTIzU}}
Cardiac tamponade {{#ev:youtube|_az8_V6bHE8}}
Left ventricular free wall rupture with cardiac tamponade {{#ev:youtube|g9TdKcFRiLo}}
Collapse of right ventricle in patient with cardiac tamponade {{#ev:youtube|dwJkJr00v5c}}
References
- ↑ Cheitlin MD, Armstrong WF, Aurigemma GP, Beller GA, Bierman FZ, Davis JL, Douglas PS, Faxon DP, Gillam LD, Kimball TR, Kussmaul WG, Pearlman AS, Philbrick JT, Rakowski H, Thys DM, Antman EM, Smith SC, Alpert JS, Gregoratos G, Anderson JL, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Fuster V, Jacobs AK, Gibbons RJ, Russell RO (2003). "ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 guideline update for the clinical application of echocardiography: summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASE Committee to Update the 1997 Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography)". Circulation. 108 (9): 1146–62. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000073597.57414.A9. PMID 12952829. Retrieved 2012-09-14. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)