Ascites ultrasound: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Ultrasound]] may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of ascites. Findings on an [[ultrasound]] [[diagnostic]] of ascites include anechoic fluid accumulation in [[abdominal cavity]] (simple [[transudate]] ascites), fluid accumulation along with floating debris ([[exudative]], [[hemoperitoneum]], or [[malignant]] ascites), and fluid accumulation along with [[Septation|septations]] ([[inflammatory]] or [[malignant]] ascites). | [[Ultrasound]] may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of ascites. Findings on an [[ultrasound]] [[diagnostic]] of ascites include anechoic fluid accumulation in [[abdominal cavity]] (simple [[transudate]] ascites), fluid accumulation along with floating debris ([[exudative]], [[hemoperitoneum]], or [[malignant]] ascites), and fluid accumulation along with [[Septation|septations]] ([[inflammatory]] or [[malignant]] ascites). | ||
==Ultrasound== | ==Ultrasound== | ||
{| align="right" | |||
| [[Image:Ascites11.jpg|400px|thumb|Ascites secondary to pancreatitis-Case courtesy of Dr Maulik S Patel, via Radiopaedia.org<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29199">rID: 29199</ref>]] | |||
|} | |||
[[Ultrasound]] may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of ascites. Findings on an [[ultrasound]] [[diagnostic]] of ascites include:<ref name="pmid3536306">{{cite journal |vauthors=Halvorsen RA, Thompson WM |title=Ascites or pleural effusion? CT and ultrasound differentiation |journal=Crit Rev Diagn Imaging |volume=26 |issue=3 |pages=201–40 |year=1986 |pmid=3536306 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | [[Ultrasound]] may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of ascites. Findings on an [[ultrasound]] [[diagnostic]] of ascites include:<ref name="pmid3536306">{{cite journal |vauthors=Halvorsen RA, Thompson WM |title=Ascites or pleural effusion? CT and ultrasound differentiation |journal=Crit Rev Diagn Imaging |volume=26 |issue=3 |pages=201–40 |year=1986 |pmid=3536306 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Anechoic fluid accumulation in [[abdominal cavity]]: Simple [[transudate]] ascites | * Anechoic fluid accumulation in [[abdominal cavity]]: Simple [[transudate]] ascites | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
* Fluid accumulation along with [[Septation|septations]] (loculated ascites): [[Inflammatory]] or [[malignant]] ascites | * Fluid accumulation along with [[Septation|septations]] (loculated ascites): [[Inflammatory]] or [[malignant]] ascites | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 18:10, 17 January 2018
|
Ascites Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ascites ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ascites ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Eiman Ghaffarpasand, M.D. [2]
Overview
Ultrasound may be helpful in the diagnosis of ascites. Findings on an ultrasound diagnostic of ascites include anechoic fluid accumulation in abdominal cavity (simple transudate ascites), fluid accumulation along with floating debris (exudative, hemoperitoneum, or malignant ascites), and fluid accumulation along with septations (inflammatory or malignant ascites).
Ultrasound
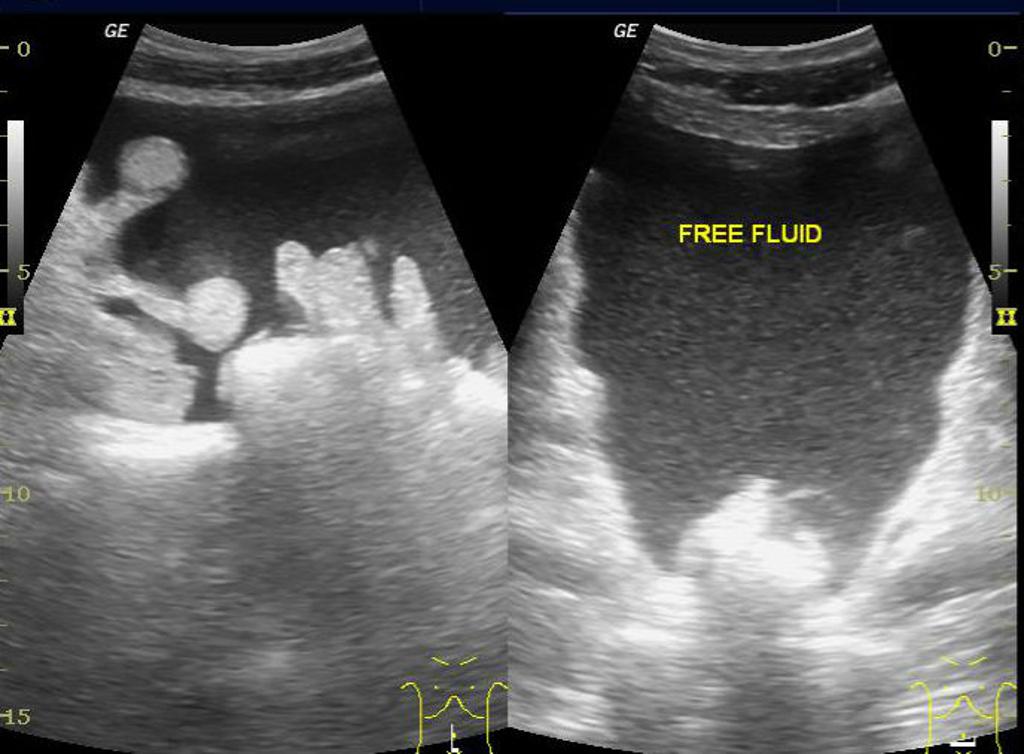 |
Ultrasound may be helpful in the diagnosis of ascites. Findings on an ultrasound diagnostic of ascites include:[2]
- Anechoic fluid accumulation in abdominal cavity: Simple transudate ascites
- Fluid accumulation along with floating debris: Exudative, hemoperitoneum, or malignant ascites
- Fluid accumulation along with septations (loculated ascites): Inflammatory or malignant ascites
References
- ↑ Radiopaedia.org. From the case <"https://radiopaedia.org/cases/29199">rID: 29199
- ↑ Halvorsen RA, Thompson WM (1986). "Ascites or pleural effusion? CT and ultrasound differentiation". Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 26 (3): 201–40. PMID 3536306.