Aarskog-Scott syndrome: Difference between revisions
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
==== HEENT ==== | ==== HEENT ==== | ||
[[Facial]] features are very prominent and important for the diagnosis of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) which include:<ref name="Reza JabalameliBriceno20163">{{cite journal|last1=Reza Jabalameli|first1=M.|last2=Briceno|first2=Ignacio|last3=Martinez|first3=Julio|last4=Briceno|first4=Ignacio|last5=J. Pengelly|first5=Reuben|last6=Ennis|first6=Sarah|last7=Collins|first7=Andrew|title=Aarskog-Scott syndrome: phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity|journal=AIMS Genetics|volume=3|issue=1|year=2016|pages=49–59|issn=2377-1143|doi=10.3934/genet.2016.1.49}}</ref><ref name="pmid19110080">{{cite journal| author=Bedoyan JK, Friez MJ, DuPont B, Ahmad A| title=First case of deletion of the faciogenital dysplasia 1 (FGD1) gene in a patient with Aarskog-Scott syndrome. | journal=Eur J Med Genet | year= 2009 | volume= 52 | issue= 4 | pages= 262-4 | pmid=19110080 | doi=10.1016/j.ejmg.2008.12.001 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19110080 }}</ref> | [[Facial]] features are very prominent and important for the diagnosis of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) which include:<ref name="Reza JabalameliBriceno20163">{{cite journal|last1=Reza Jabalameli|first1=M.|last2=Briceno|first2=Ignacio|last3=Martinez|first3=Julio|last4=Briceno|first4=Ignacio|last5=J. Pengelly|first5=Reuben|last6=Ennis|first6=Sarah|last7=Collins|first7=Andrew|title=Aarskog-Scott syndrome: phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity|journal=AIMS Genetics|volume=3|issue=1|year=2016|pages=49–59|issn=2377-1143|doi=10.3934/genet.2016.1.49}}</ref><ref name="pmid19110080">{{cite journal| author=Bedoyan JK, Friez MJ, DuPont B, Ahmad A| title=First case of deletion of the faciogenital dysplasia 1 (FGD1) gene in a patient with Aarskog-Scott syndrome. | journal=Eur J Med Genet | year= 2009 | volume= 52 | issue= 4 | pages= 262-4 | pmid=19110080 | doi=10.1016/j.ejmg.2008.12.001 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19110080 }}</ref><ref name="pmid8322809">{{cite journal| author=Teebi AS, Rucquoi JK, Meyn MS| title=Aarskog syndrome: report of a family with review and discussion of nosology. | journal=Am J Med Genet | year= 1993 | volume= 46 | issue= 5 | pages= 501-9 | pmid=8322809 | doi=10.1002/ajmg.1320460508 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8322809 }}</ref> | ||
* Round face | * Round face | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 9 September 2019
Synonyms and Keywords: Aarskog disease, Aarskog-Scott syndrome, AAS, Faciodigitogenital syndrome, Faciogenital dysplasia, FGDY, Scott Aarskog syndrome
| Aarskog-Scott syndrome | |
| ICD-10 | Q87.1 |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 759.89 |
| OMIM | 100050 |
| DiseasesDB | 29329 |
Overview
Aarskog-Scott syndrome is a rare inherited disease distinguish by short stature, facial abnormalities, skeletal and genital anomalies. The Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is also known as the Aarskog syndrome, faciodigitogenital syndrome, shawl scrotum syndrome and facial genital dysplasia. In The United States of America in order to categorise a condition as a rare disease it should affect fewer than 200,000 people. Rare diseases also called as orphan diseases. Orphan Drug Act was passed on 1983 by congress for the rare diseases. Today an average of 25-30 million americans have been reported with rare diseases. The number of people with individual rare disease may be less but overall the number of people with rare diseases are large in number.
Historical Perspective
- In 1970, Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) was first described by Aarskog, a Norwegian pediatrician and human geneticist.
- In 1971, Scott described the association between ligamentous laxity which results in hyperextensibility of the fingers, genu recurvatum, flat feet and Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).[1]
- In 1973, Sugarman et al described an Mexican-American family in which 2 half brothers and their 2 maternal uncles had Aarskog syndrome.
- In 1993, Teebi et al suggested that the disease Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) follows autosomal dominant inheritance.[2]
- In 1978, Escobar and Weaver described a patient who is had symptoms of Noonan syndrome than Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).[3]
- In 1981, Grier et al. suggested that Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) follows autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance.[4]
- In 1984, Van den Bergh et al. mentioned a patient with Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) development of syndrome of benign intracranial hypertension after minor head trauma.[5]
- In 1994, Fernandez et al. mentioned 10 Japanese patients who are positive with Aarskog syndrome.[6]
- In 1998, Logie and Porteous concluded that in patients with Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) have normal intelligence.[7]
- In 2002, Lebel et al. is the one who found a missense mutation in the FGD1 gene.[8]
- In 2005, Orrico et al. described attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in patient with Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).[9]
- In 2010, Orrico et al. genetically confirmed 11 patients for Aarskog-Scott syndrome.[10]
Classification
- There is no established system for the classification of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).[11]
Pathophysiology
- Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is transmitted in X-linked recessive mode of inheritance.[12][13][14]
- In some cases Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is transmitted in autosomal dominant mode of inheritance.[15]
- It is understood that Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is the result caused by a mutation in FGD1 gene.
- FGD1 gene mapped to the Xp11.21 region is located on X chromosome.
- Normally, in most of the situations males have one X chromosome and females have two X chromosomes.
- When mutation occurs in FGD1 gene of males may result in the Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
- But, in females the mutation had to occur in both X chromosomes to manifest the disease Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
- In females if the mutation occurs in only one X chromosome then it results in mild features of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
- The gene FGD1 specifically encodes for guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF).[16]
- Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) inturn activates Cdc42 which belongs to Ras homology of the p21 GTPases.[17][18][19]
- Upon activation of Cdc42, FGD1 proteins they activate the following:[20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28]
- Fibroblasts
- Cytoskeletal elements which are involved in
- Cellular signaling
- Adhesion
- Migration
- c- N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling cascade which involves:
- Cell growth
- Apoptosis
- Cellular differentiation
- These abnormalities of FGD1/Cdc42 signaling pathway may produce an defective embryonic development and abnormal endochondral and intramembranous bone formation and leads to Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
Causes
Genetic Cause
Differentiating Aarskog-Scott syndrome from other Diseases
- Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) must be differentiated from Robinow syndrome, Noonan syndrome, pseudohypoparathyroidism, Silver-Russell and SHORT syndrome.[29][30]
Epidemiology and Demographics
Incidence
- The incidence of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is unknown.[31]
- Till now there are less than 100 cases of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) had been diagnosed worldwide.
Prevalence
- The prevalence of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is 1/25 000 worldwide.[32]
- The prevalence of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is 1-9 per 1,000,000 in Europe.
Age
- Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) commonly affects individuals of younger age especially in childwood.
Race
- There is no racial predilection to Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
Gender
- Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) affects men more commonly than in women.[33]
Risk Factors
There are no established risk factors for Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
Screening
There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine screening for Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Natural History
- The symptoms of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) usually develop in the first decade of life, and start with symptoms such as delayed growth spurt.
- The symptoms of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) typically develop in 2 to 4 years of age.
Complications
- Common complications of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) include:[34][35][36]
- Cryptorchidism
- Spina bifida occulta
- Cervical spine abnormalities
- Scoliosis
- Camptodactyly
- Lymphoedema
- Optic nerve hypoplasia
- Retinal vessel tortuosity
Prognosis
- Prognosis is generally good with Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) patients.
Diagnostic study of choice
- Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) is primarily diagnosed based on clinical presentation based on Teebi criteria which includes:[37][38]
- Short stature
- Hypertelorism
- Fold of the lower lip
- Brachydactyly
- Interdigital webbing
- Shawl scrotum
- Long philtrum
- Mild facial hypoplasia
History and Symptoms
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) include:[22][39]
- Short stature (evident by 1-3 years of age)
- Mental retardation
- Hypertelorism
- Umbilical hernia
- Shawl scrotum
- Hypospadias
- Undescended testes
Physical Examination
HEENT
Facial features are very prominent and important for the diagnosis of Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS) which include:[40][41][42]
- Round face
- Facial edema with downward slanting palpebral fissures
- Short nose along with anteverted nares
- Long philtrum
- Ocular hypertelorism with ptosis
- Maxillary hypoplasia
- A broad upper lip with a crease below the lower lip
- Abnormal auriculares
Neck
- Short neck
- Webbing of sides of the neck
Chest
- Mild pectus excavatum (sunken chest)
Abdomen
- Protruding navel
- Inguinal hernias
Genitourinary
- Shawl Scrotum
- Undescended testicles
Extremities
- Small, broad hands and feet
- Short fingers and toes (brachydactyly)
- Clinodactyly
- Mild webbing between the fingers and toes
- Simian crease
- Broad thumbs and big toes
Laboratory Findings
- There are no diagnostic laboratory findings associated with Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
Electrocardiogram
- There are no ECG findings associated with Aarskog-Scott syndrome (AAS).
X-Ray Findings
Echocardiography and Ultrasound
CT-Scan Findings
MRI Findings
Other Imaging Findings
Other Diagnostic Studies
Medical Therapy
Interventions
Surgery
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy
Future or Investigational Therapies
Genetic
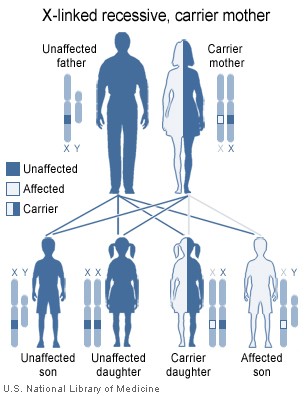
Aarskog-Scott syndrome is transmitted in an X-linked recessive manner. The sons of female carriers are at 50% risk of being affected with the syndrome. The daughters of female carriers are at 50% risk of being carriers themselves. Females may have mild manifestations of the syndrome. The syndrome is caused by mutation in a gene called FGDY1 in band p11.21 on the X chromosome.
Eponym
The syndrome is named for Dagfinn Aarskog, a Norwegian pediatrician and human geneticist who first described it in 1970, and for Charles I. Scott, Jr., an American medical geneticist who independently described the syndrome in 1971.
Description
The Aarskog-Scott syndrome is a disorder with short stature, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, anteverted nostrils, joint laxity, shawl scrotum, and mental retardation. The physical phenotype varies with age and postpuberal males may have only minor remnant manifestations of the prepuberal phenotype.
Diagnosis
Genetic testing may be available for mutations in the FGDY1 gene. Genetic counseling is indicated for individuals or families who may carry this condition, as there are overlapping features with Fetal alcohol syndrome.
Treatment
Surgery may be required to correct some of the anomalies, and orthodontic treatment may be used to correct some of the facial abnormalities. Trials of growth hormone have not been effective to treat short stature in this disorder.
Support Group
The MAGIC Foundation for Children's Growth is a support group for Aarskog-Scott syndrome and can be found at www.magicfoundation.org.
Prognosis
Mild degrees of mental slowness may be present, but affected children usually have good social skills. Some males may exhibit reduced fertility.
Complications
Some recent findings have included cystic changes in the brain and generalized seizures. There may be difficulty growing in the first year of life in up to one-third of cases. Misaligned teeth may require orthodontic correction. An undescended testicle will require surgery.
Molecular biology
The Aarskog-Scott syndrome is due to mutation in the FGD1 gene. FGD1 encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that specifically activates Cdc42, a member of the Rho (Ras homology) family of the p21 GTPases. By activating Cdc42, FGD1 protein stimulates fibroblasts to form filopodia, cytoskeletal elements involved in cellular signaling, adhesion, and migration. Through Cdc42, FGD1 protein also activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling cascade, a pathway that regulates cell growth, apoptosis, and cellular differentiation.
Within the developing mouse skeleton, FGD1 protein is expressed in precartilaginous mesenchymal condensations, the perichondrium and periostium, proliferating chondrocytes, and osteoblasts. These results suggest that FGD1 signaling may play a role in the biology of several different skeletal cell types including mesenchymal prechondrocytes, chondrocytes, and osteoblasts. The characterization of the spatiotemporal pattern of FGD1 expression in mouse embryos has provided important clues to the understanding of the pathogenesis of Aarskog-Scott syndrome. It appears likely that the primary defect in Aarskog-Scott syndrome is an abnormality of FGD1/Cdc42 signaling resulting in anomalous embryonic development and abnormal endochondral and intramembranous bone formation
References
- ↑ Scott CI (1971). "Unusual facies, joint hypermobility, genital anomaly and short stature: a new dysmorphic syndrome". Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 7 (6): 240–6. PMID 5173168.
- ↑ Grier RE, Farrington FH, Kendig R, Mamunes P (1983). "Autosomal dominant inheritance of the Aarskog syndrome". Am J Med Genet. 15 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150105. PMID 6344635.
- ↑ Escobar V, Weaver DD (1978). "Aarskog syndrome. New findings and genetic analysis". JAMA. 240 (24): 2638–41. doi:10.1001/jama.240.24.2638. PMID 712980.
- ↑ Grier, Robert E.; Farrington, Frank H.; Kendig, Robert; Mamunes, Peter; Opitz, John M. (1983). "Autosomal dominant inheritance of the Aarskog syndrome". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 15 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150105. ISSN 0148-7299.
- ↑ van den Bergh P, Fryns JP, Wilms G, Piot R, Dralands G, van den Bergh R (1984). "Anomalous cerebral venous drainage in Aarskog syndrome". Clin Genet. 25 (3): 288–94. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01991.x. PMID 6705262.
- ↑ Fernandez I, Tsukahara M, Mito H, Yoshii H, Uchida M, Matsuo K; et al. (1994). "Congenital heart defects in Aarskog syndrome". Am J Med Genet. 50 (4): 318–22. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320500404. PMID 8209909.
- ↑ Logie LJ, Porteous ME (1998). "Intelligence and development in Aarskog syndrome". Arch Dis Child. 79 (4): 359–60. doi:10.1136/adc.79.4.359. PMC 1717704. PMID 9875050.
- ↑ Lebel RR, May M, Pouls S, Lubs HA, Stevenson RE, Schwartz CE (2002). "Non-syndromic X-linked mental retardation associated with a missense mutation (P312L) in the FGD1 gene". Clin Genet. 61 (2): 139–45. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0004.2002.610209.x. PMID 11940089.
- ↑ Orrico A, Galli L, Buoni S, Hayek G, Luchetti A, Lorenzini S; et al. (2005). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and variable clinical expression of Aarskog-Scott syndrome due to a novel FGD1 gene mutation (R408Q)". Am J Med Genet A. 135 (1): 99–102. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.30700. PMID 15809997.
- ↑ Orrico A, Galli L, Faivre L, Clayton-Smith J, Azzarello-Burri SM, Hertz JM; et al. (2010). "Aarskog-Scott syndrome: clinical update and report of nine novel mutations of the FGD1 gene". Am J Med Genet A. 152A (2): 313–8. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33199. PMID 20082460.
- ↑ Estrada L, Caron E, Gorski JL (2001). "Fgd1, the Cdc42 guanine nucleotide exchange factor responsible for faciogenital dysplasia, is localized to the subcortical actin cytoskeleton and Golgi membrane". Hum Mol Genet. 10 (5): 485–95. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.5.485. PMID 11181572.
- ↑ Pasteris NG, Cadle A, Logie LJ, Porteous ME, Schwartz CE, Stevenson RE; et al. (1994). "Isolation and characterization of the faciogenital dysplasia (Aarskog-Scott syndrome) gene: a putative Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor". Cell. 79 (4): 669–78. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90552-5. PMID 7954831.
- ↑ Pasteris NG, Buckler J, Cadle AB, Gorski JL (1997). "Genomic organization of the faciogenital dysplasia (FGD1; Aarskog syndrome) gene". Genomics. 43 (3): 390–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4837. PMID 9268645.
- ↑ Aarskog D (1971). "A familial syndrome of short stature associated with facial dysplasia and genital anomalies". Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 7 (6): 235–9. PMID 4155960.
- ↑ Grier RE, Farrington FH, Kendig R, Mamunes P (1983). "Autosomal dominant inheritance of the Aarskog syndrome". Am J Med Genet. 15 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150105. PMID 6344635.
- ↑ Orrico A, Galli L, Cavaliere ML, Garavelli L, Fryns JP, Crushell E; et al. (2004). "Phenotypic and molecular characterisation of the Aarskog-Scott syndrome: a survey of the clinical variability in light of FGD1 mutation analysis in 46 patients". Eur J Hum Genet. 12 (1): 16–23. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201081. PMID 14560308.
- ↑ Pedigo NG, Van Delden D, Walters L, Farrell CL (2016). "Minireview: Role of genetic changes of faciogenital dysplasia protein 1 in human disease". Physiol Genomics. 48 (7): 446–54. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00101.2015. PMID 27199457.
- ↑ Pasteris NG, Nagata K, Hall A, Gorski JL (2000). "Isolation, characterization, and mapping of the mouse Fgd3 gene, a new Faciogenital Dysplasia (FGD1; Aarskog Syndrome) gene homologue". Gene. 242 (1–2): 237–47. doi:10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00518-1. PMID 10721717.
- ↑ Rajnicek AM, Foubister LE, McCaig CD (2006). "Temporally and spatially coordinated roles for Rho, Rac, Cdc42 and their effectors in growth cone guidance by a physiological electric field". J Cell Sci. 119 (Pt 9): 1723–35. doi:10.1242/jcs.02896. PMID 16595546.
- ↑ Pasteris NG, Gorski JL (1999). "Isolation, characterization, and mapping of the mouse and human Fgd2 genes, faciogenital dysplasia (FGD1; Aarskog syndrome) gene homologues". Genomics. 60 (1): 57–66. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5903. PMID 10458911.
- ↑ Orrico A, Galli L, Falciani M, Bracci M, Cavaliere ML, Rinaldi MM; et al. (2000). "A mutation in the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of the FGD1 gene in an Italian family with faciogenital dysplasia (Aarskog-Scott syndrome)". FEBS Lett. 478 (3): 216–20. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01857-3. PMID 10930571.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Schwartz CE, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, May M, Cappa M, Gorski J, Steindl K; et al. (2000). "Two novel mutations confirm FGD1 is responsible for the Aarskog syndrome". Eur J Hum Genet. 8 (11): 869–74. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200553. PMID 11093277.
- ↑ Pasteris NG, Buckler J, Cadle AB, Gorski JL (1997). "Genomic organization of the faciogenital dysplasia (FGD1; Aarskog syndrome) gene". Genomics. 43 (3): 390–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4837. PMID 9268645.
- ↑ Hall A (2005). "Rho GTPases and the control of cell behaviour". Biochem Soc Trans. 33 (Pt 5): 891–5. doi:10.1042/BST20050891. PMID 16246005.
- ↑ Ridley AJ, Allen WE, Peppelenbosch M, Jones GE (1999). "Rho family proteins and cell migration". Biochem Soc Symp. 65: 111–23. PMID 10320936.
- ↑ Linseman DA, Laessig T, Meintzer MK, McClure M, Barth H, Aktories K; et al. (2001). "An essential role for Rac/Cdc42 GTPases in cerebellar granule neuron survival". J Biol Chem. 276 (42): 39123–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103959200. PMID 11509562.
- ↑ Bishop AL, Hall A (2000). "Rho GTPases and their effector proteins". Biochem J. 348 Pt 2: 241–55. PMC 1221060. PMID 10816416.
- ↑ Orrico, A.; Galli, L.; Faivre, L.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Azzarello-Burri, S.M.; Hertz, J.M.; Jacquemont, S.; Taurisano, R.; Arroyo Carrera, I.; Tarantino, E.; Devriendt, K.; Melis, D.; Thelle, T.; Meinhardt, U.; Sorrentino, V. (2010). "Aarskog-Scott syndrome: Clinical update and report of nine novel mutations of theFGD1gene". American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A. 152A (2): 313–318. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33199. ISSN 1552-4825.
- ↑ Parıltay E, Hazan F, Ataman E, Demir K, Etlik Ö, Özbek E; et al. (2016). "A novel splice site mutation of FGD1 gene in an Aarskog-Scott syndrome patient with a large anterior fontanel". J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 29 (9): 1111–4. doi:10.1515/jpem-2015-0482. PMID 27544718.
- ↑ Weinstein, Lee S. (2016). "GNAS and McCune-Albright/Fibrous Dysplasia, Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy, and Pseudohypoparathyroidism": 1178–1181. doi:10.1093/med/9780199934522.003.0179.
- ↑ Reza Jabalameli, M.; Briceno, Ignacio; Martinez, Julio; Briceno, Ignacio; J. Pengelly, Reuben; Ennis, Sarah; Collins, Andrew (2016). "Aarskog-Scott syndrome: phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity". AIMS Genetics. 3 (1): 49–59. doi:10.3934/genet.2016.1.49. ISSN 2377-1143.
- ↑ Orrico A, Galli L, Clayton-Smith J, Fryns JP (2015) Clinical utility gene card for: Aarskog-Scott Syndrome (faciogenital dysplasia) - update 2015. Eur J Hum Genet 23 (4):. DOI:10.1038/ejhg.2014.178 PMID: 25227149
- ↑ Reza Jabalameli, M.; Briceno, Ignacio; Martinez, Julio; Briceno, Ignacio; J. Pengelly, Reuben; Ennis, Sarah; Collins, Andrew (2016). "Aarskog-Scott syndrome: phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity". AIMS Genetics. 3 (1): 49–59. doi:10.3934/genet.2016.1.49. ISSN 2377-1143.
- ↑ Jogiya, Aryan; Sandy, Charles (2009). "Mild Optic Nerve Hypoplasia with Retinal Venous Tortuosity in Aarskog (Facial-Digital-Genital) Syndrome". Ophthalmic Genetics. 26 (3): 139–141. doi:10.1080/13816810500229025. ISSN 1381-6810.
- ↑ Pizio HF, Scott MH, Richard JM (1994). "Tortuosity of the retinal vessels in Aarskog syndrome (faciogenital dysplasia)". Ophthalmic Genet. 15 (1): 37–40. PMID 7953251.
- ↑ Grier RE, Farrington FH, Kendig R, Mamunes P (1983). "Autosomal dominant inheritance of the Aarskog syndrome". Am J Med Genet. 15 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150105. PMID 6344635.
- ↑ Grier RE, Farrington FH, Kendig R, Mamunes P (1983). "Autosomal dominant inheritance of the Aarskog syndrome". Am J Med Genet. 15 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150105. PMID 6344635.
- ↑ Darendeliler F, Larsson P, Neyzi O, Price AD, Hagenäs L, Sipilä I; et al. (2003). "Growth hormone treatment in Aarskog syndrome: analysis of the KIGS (Pharmacia International Growth Database) data". J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 16 (8): 1137–42. PMID 14594174.
- ↑ Şıklar Z, Berberoğlu M (2014). "Syndromic disorders with short stature". J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 6 (1): 1–8. doi:10.4274/Jcrpe.1149. PMC 3986733. PMID 24637303.
- ↑ Reza Jabalameli, M.; Briceno, Ignacio; Martinez, Julio; Briceno, Ignacio; J. Pengelly, Reuben; Ennis, Sarah; Collins, Andrew (2016). "Aarskog-Scott syndrome: phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity". AIMS Genetics. 3 (1): 49–59. doi:10.3934/genet.2016.1.49. ISSN 2377-1143.
- ↑ Bedoyan JK, Friez MJ, DuPont B, Ahmad A (2009). "First case of deletion of the faciogenital dysplasia 1 (FGD1) gene in a patient with Aarskog-Scott syndrome". Eur J Med Genet. 52 (4): 262–4. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2008.12.001. PMID 19110080.
- ↑ Teebi AS, Rucquoi JK, Meyn MS (1993). "Aarskog syndrome: report of a family with review and discussion of nosology". Am J Med Genet. 46 (5): 501–9. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320460508. PMID 8322809.