Dicyclomine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
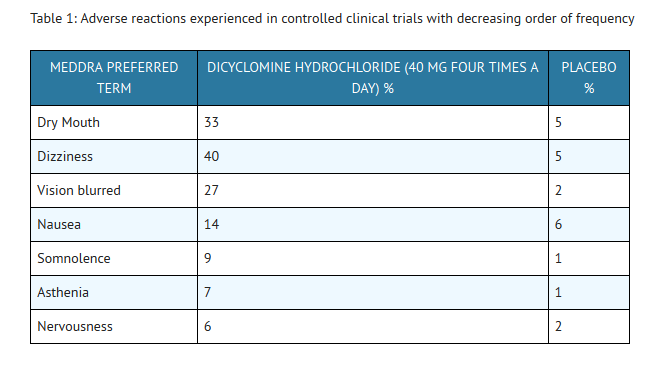
Dicyclomine is an antispasmodic and anticholinergic agent that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of functional bowel/irritable bowel syndrome. Common adverse reactions include dizziness, dry mouth, vision blurred, nausea, somnolence, asthenia and nervousness.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Dosing Information
- Oral Dosage and Administration in Adults
- The recommended initial dose is 20 mg four times a day. After one week treatment with the initial dose, the dose may be increased to 40 mg four times a day unless side effects limit dosage escalation.
If efficacy is not achieved within 2 weeks or side effects require doses below 80 mg per day, the drug should be discontinued. Documented safety data are not available for doses above 80 mg daily for periods longer than 2 weeks.
- Intramuscular Dosage and Administration in Adults
- BENTYL Intramuscular Injection must be administered via intramuscular route only. Do not administer by an other route. The recommended intramuscular dose is 10 mg to 20 mg four times a day. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]
The intramuscular injection is to be used only for 1 or 2 days when the patient cannot take oral medication.
- Intramuscular injection is about twice as bioavailable as oral dosage forms.
- Preparation for Intramuscular Administration
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- Aspirate the syringe before injecting to avoid intravascular injection, since thrombosis may occur if the drug is inadvertently injected intravascularly.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Dicyclomine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Dicyclomine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Dicyclomine in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Dicyclomine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Dicyclomine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- BENTYL is contraindicated in infants less than 6 months of age, nursing mothers], and in patients with:
- unstable cardiovascular status in acute hemorrhage
- myasthenia gravis
- glaucoma
- obstructive uropathy
- obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract
- severe ulcerative colitis
- reflux esophagitis
Warnings
Precautions
- Inadvertent Intravenous Administration
- BENTYL solution is for intramuscular administration only. Do not administer by any other route. Inadvertent intravenous administration may result in thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and injection site reactions such as pain, edema, skin color change, and reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Cardiovascular Conditions
- Dicyclomine hydrochloride needs to be used with caution in conditions characterized by tachyarrhythmia such as thyrotoxicosis, congestive heart failure and in cardiac surgery, where they may further accelerate the heart rate. Investigate any tachycardia before administration of dicyclomine hydrochloride. Care is required in patients with coronary heart disease, as ischemia and infarction may be worsened, and in patients with hypertension [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)].
- Peripheral and Central Nervous System
- The peripheral effects of dicyclomine hydrochloride are a consequence of their inhibitory effect on muscarinic receptors of the autonomic nervous system. They include dryness of the mouth with difficulty in swallowing and talking, thirst, reduced bronchial secretions, dilatation of the pupils (mydriasis) with loss of accommodation (cycloplegia) and photophobia, flushing and dryness of the skin, transient bradycardia followed by tachycardia, with palpitations and arrhythmias, and difficulty in micturition, as well as reduction in the tone and motility of the gastrointestinal tract leading to constipation [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
- In the presence of high environmental temperature heat prostration can occur with drug use (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating). It should also be used cautiously in patients with fever. If symptoms occur, the drug should be discontinued and supportive measures instituted. Because of the inhibitory effect on muscarinic receptors within the autonomic nervous system, caution should be taken in patients with autonomic neuropathy.
- Central nervous system (CNS) signs and symptoms include confusional state, disorientation, amnesia, hallucinations, dysarthria, ataxia, coma, euphoria, fatigue, insomnia, agitation and mannerisms, and inappropriate affect.
- Psychosis and delirium have been reported in sensitive individuals (such as elderly patients and/or in patients with mental illness) given anticholinergic drugs. These CNS signs and symptoms usually resolve within 12 to 24 hours after discontinuation of the drug.
- BENTYL may produce drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. The patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing hazardous work while taking BENTYL.
- Myasthenia Gravis
- With overdosage, a curare-like action may occur (i.e., neuromuscular blockade leading to muscular weakness and possible paralysis). It should not be given to patients with myasthenia gravis except to reduce adverse muscarinic effects of an anticholinesterase [see Contraindications (4)]
- Intestinal Obstruction
- Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance, treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful [see Contraindications (4)].
- Rarely development of Ogilvie's syndrome (colonic pseudo-obstruction) has been reported. Ogilvie's syndrome is a clinical disorder with signs, symptoms, and radiographic appearance of an acute large bowel obstruction but with no evidence of distal colonic obstruction
- Toxic Dilatation of Intestinemegacolon
- Toxic dilatation of intestine and intestinal perforation is possible when anticholinergic agents are administered in patients with Salmonella dysentery.
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Caution should be taken in patients with ulcerative colitis. Large doses may suppress intestinal motility to the point of producing a paralytic ileus and the use of this drug may precipitate or aggravate the serious complication of toxic megacolon [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)]. BENTYL is contraindicated in patients with severe ulcerative colitis [see Contraindications (4)].
- Prostatic Hypertrophy
- BENTYL should be used with caution in patients with known or suspected prostatic enlargement, in whom prostatic enlargement may lead to urinary retention [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)]
- Hepatic and Renal Disease
- BENTYL should be used with caution in patients with known hepatic and renal impairment.
- Geriatric Population
- Dicyclomine hydrochloride should be used with caution in elderly who may be more susceptible to its adverse effects.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- The data described below reflect exposure in controlled clinical trials involving over 100 patients treated for functional bowel/irritable bowel syndrome with dicyclomine hydrochloride at initial doses of 160 mg daily (40 mg four times a day)
- In these trials most of the side effects were typically anticholinergic in nature and were reported by 61% of the patients. Table 1 presents adverse reactions (MedDRA 13.0 preferred terms) by decreasing order of frequency in a side-by-side comparison with placebo.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Dicyclomine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Dicyclomine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Dicyclomine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Dicyclomine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Dicyclomine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Dicyclomine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Dicyclomine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Dicyclomine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Dicyclomine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Dicyclomine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Dicyclomine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Dicyclomine |Label Name=Dicyclomine11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Dicyclomine |Label Name=Dicyclomine11.png
}}