Lyme disease primary prevention: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Primary Prevention== | ==Primary Prevention== | ||
===Management of | ===Management of host animals=== | ||
Lyme and all other deer-tick borne diseases can be prevented on a regional level by reducing the deer population that the ticks depend on for reproductive success. This has been effectively demonstrated in the communities of Monhegan, Maine<ref name="Rand">{{cite journal |author=Rand PW, Lubelczyk C, Holman MS, Lacombe EH, Smith RP |title=Abundance of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) after the complete removal of deer from an isolated offshore island, endemic for Lyme Disease |journal=J. Med. Entomol. |volume=41 |issue=4 |pages=779-84 |year=2004 |pmid=15311475 }}</ref> and in Mumford Cove, CT.<ref>Figure 2. p.4. DEP Wildlife Division: Managing Urban Deer in Connecticut 2nd edition June 2007</ref> | * Lyme and all other deer-tick borne diseases can be prevented on a regional level by reducing the deer population that the ticks depend on for reproductive success. | ||
* This has been effectively demonstrated in the communities of Monhegan, Maine<ref name="Rand">{{cite journal |author=Rand PW, Lubelczyk C, Holman MS, Lacombe EH, Smith RP |title=Abundance of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) after the complete removal of deer from an isolated offshore island, endemic for Lyme Disease |journal=J. Med. Entomol. |volume=41 |issue=4 |pages=779-84 |year=2004 |pmid=15311475 }}</ref> and in Mumford Cove, CT.<ref>Figure 2. p.4. DEP Wildlife Division: Managing Urban Deer in Connecticut 2nd edition June 2007</ref> | |||
* The black-legged or deer tick (''Ixodes scapularis'') depends on the white-tailed deer for successful reproduction. | |||
By reducing the deer population back to healthy levels of 8 to 10 per square mile (from the current levels of 60 or more deer per square mile in the areas of the country with the highest Lyme disease rates) the tick numbers can be brought down to very low levels, too few to spread Lyme and other tick-borne diseases.<ref>{{cite web | author = Stafford KC | title = Tick Management Handbook | url = http://www.ct.gov/caes/lib/caes/documents/special_features/TickHandbook.pdf | format = PDF | year = 2004 | publisher = Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station and Connecticut Department of Public Health | pages = p. 46 | accessdate = 2007-08-21}}</ref> | * By reducing the deer population back to healthy levels of 8 to 10 per square mile (from the current levels of 60 or more deer per square mile in the areas of the country with the highest Lyme disease rates) the tick numbers can be brought down to very low levels, too few to spread Lyme and other tick-borne diseases.<ref>{{cite web | author = Stafford KC | title = Tick Management Handbook | url = http://www.ct.gov/caes/lib/caes/documents/special_features/TickHandbook.pdf | format = PDF | year = 2004 | publisher = Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station and Connecticut Department of Public Health | pages = p. 46 | accessdate = 2007-08-21}}</ref> | ||
===Minimizing tick exposure=== | |||
=== | |||
[[Image:SOCKS.jpg|left|thumb|180px|Tuck pants into socks]] | [[Image:SOCKS.jpg|left|thumb|180px|Tuck pants into socks]] | ||
It is unreasonable to assume that a person can completely eliminate activities that may result in tick exposure. Therefore, prevention measures should emphasize personal protection when exposed to natural areas where ticks are present: | It is unreasonable to assume that a person can completely eliminate activities that may result in tick exposure. Therefore, prevention measures should emphasize personal protection when exposed to natural areas where ticks are present: | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
===Vaccination=== | ===Vaccination=== | ||
A [[vaccine]], called Lymerix, against a North American strain of the spirochetal bacteria was available from 1998 to 2002. It was produced by [[GlaxoSmithKline]] (GSK) and was based on the outer surface protein A (Osp-A) of ''Borrelia''. Osp-A causes the human [[immune system]] to create [[antibody|antibodies]] that attack that protein. | * A [[vaccine]], called Lymerix, against a North American strain of the spirochetal bacteria was available from 1998 to 2002. | ||
* It was produced by [[GlaxoSmithKline]] (GSK) and was based on the outer surface protein A (Osp-A) of ''Borrelia''. Osp-A causes the human [[immune system]] to create [[antibody|antibodies]] that attack that protein. | |||
* A group of patients who been administered Lymerix developed [[arthritis]], muscle pain and other troubling symptoms post-vaccination. Class-action litigation against GSK followed. Cassidy v. SmithKline Beecham, No. 99-10423 (Ct. Common Pleas, PA state court) (common settlement case).<ref name="LymeInfo-Vaccine">Safety/Efficacy concerns re: Lyme vaccine: LYMErix [http://www.lymeinfo.net/vaccine2.html Controversy] ''LymeInfo.net''</ref><!-- This ref does not appear to meet WP:RS standards (MarcoTolo - 2007-08-21) --> | |||
It was later learned that patients with the genetic [[allele]] HLA-DR4 were susceptible to T-cell cross-reactivity between [[epitope]]s of OspA and lymphocyte function-associated antigen in these patients causing an autoimmune reaction.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Willett TA, Meyer AL, Brown EL, Huber BT |title=An effective second-generation outer surface protein A-derived Lyme vaccine that eliminates a potentially autoreactive T cell epitope |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=101 |issue=5 |pages=1303-8 |year=2004 |pmid=14742868 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0305680101 | url = http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=14742868}}</ref> | * It was later learned that patients with the genetic [[allele]] HLA-DR4 were susceptible to T-cell cross-reactivity between [[epitope]]s of OspA and lymphocyte function-associated antigen in these patients causing an autoimmune reaction.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Willett TA, Meyer AL, Brown EL, Huber BT |title=An effective second-generation outer surface protein A-derived Lyme vaccine that eliminates a potentially autoreactive T cell epitope |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=101 |issue=5 |pages=1303-8 |year=2004 |pmid=14742868 |doi=10.1073/pnas.0305680101 | url = http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=14742868}}</ref> | ||
New vaccines are being researched using outer surface protein C (Osp-C) and [[Glycolipid|glycolipoprotein]] as methods of immunization.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Earnhart CG, Marconi RT |title=OspC phylogenetic analyses support the feasibility of a broadly protective polyvalent chimeric Lyme disease vaccine |journal=Clin. Vaccine Immunol. |volume=14 |issue=5 |pages=628-34 |year=2007 |pmid=17360854 |doi=10.1128/CVI.00409-06}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Pozsgay V, Kubler-Kielb J |title=Synthesis of an experimental glycolipoprotein vaccine against Lyme disease |journal=Carbohydr. Res. |volume=342 |issue=3-4 |pages=621-6 |year=2007 |pmid=17182019 |doi=10.1016/j.carres.2006.11.014 | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=17182019&query_hl=35&itool=pubmed_docsum}}</ref> | * New vaccines are being researched using outer surface protein C (Osp-C) and [[Glycolipid|glycolipoprotein]] as methods of immunization.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Earnhart CG, Marconi RT |title=OspC phylogenetic analyses support the feasibility of a broadly protective polyvalent chimeric Lyme disease vaccine |journal=Clin. Vaccine Immunol. |volume=14 |issue=5 |pages=628-34 |year=2007 |pmid=17360854 |doi=10.1128/CVI.00409-06}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Pozsgay V, Kubler-Kielb J |title=Synthesis of an experimental glycolipoprotein vaccine against Lyme disease |journal=Carbohydr. Res. |volume=342 |issue=3-4 |pages=621-6 |year=2007 |pmid=17182019 |doi=10.1016/j.carres.2006.11.014 | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=17182019&query_hl=35&itool=pubmed_docsum}}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 21:28, 9 February 2016
|
Lyme disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Lyme disease primary prevention On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Lyme disease primary prevention |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Lyme disease primary prevention |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Primary prevention of Lyme disease involves reducing exposure to ticks. Scientists have been developing all-natural chemical compounds made from plants that can repel or kill ticks. A Lyme disease vaccine is no longer available.
Primary Prevention
Management of host animals
- Lyme and all other deer-tick borne diseases can be prevented on a regional level by reducing the deer population that the ticks depend on for reproductive success.
- This has been effectively demonstrated in the communities of Monhegan, Maine[1] and in Mumford Cove, CT.[2]
- The black-legged or deer tick (Ixodes scapularis) depends on the white-tailed deer for successful reproduction.
- By reducing the deer population back to healthy levels of 8 to 10 per square mile (from the current levels of 60 or more deer per square mile in the areas of the country with the highest Lyme disease rates) the tick numbers can be brought down to very low levels, too few to spread Lyme and other tick-borne diseases.[3]
Minimizing tick exposure

It is unreasonable to assume that a person can completely eliminate activities that may result in tick exposure. Therefore, prevention measures should emphasize personal protection when exposed to natural areas where ticks are present:
- Wear light-colored clothing which allows you to see ticks that are crawling on your clothing.
- Tuck your pants legs into your socks so that ticks cannot crawl up the inside of your pants legs.
- Apply repellents to discourage tick attachment. Repellents containing permethrin can be sprayed on boots and clothing, and will last for several days. Repellents containing DEET (n, n-diethyl-m-toluamide) can be applied to the skin, but will last only a few hours before reapplication is necessary. Use DEET with caution on children. Application of large amounts of DEET on children has been associated with adverse reactions.
- Conduct a body check upon return from potentially tick-infested areas by searching your entire body for ticks. Use a hand-held or full-length mirror to view all parts of your body. Remove any tick you find on your body.
- Parents should check their children for ticks, especially in the hair, when returning from potentially tick-infested areas.
- Ticks may also be carried into the household on clothing and pets and only attach later, so both should be examined carefully to exclude ticks.[4]
The best way to remove a tick
- Use fine-tipped tweezers or notched tick extractor, and protect your fingers with a tissue, paper towel, or latex gloves. Persons should avoid removing ticks with bare hands.
- Grasp the tick as close to the skin surface as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. Do not twist or jerk the tick; this may cause the mouth-parts to break off and remain in the skin. (If this happens, remove mouth-parts with tweezers. Consult your health care provider if illness occurs.)
- After removing the tick, thoroughly disinfect the bite site and wash your hands with soap and water.
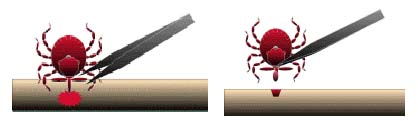
- Do not squeeze, crush, or puncture the body of the tick because its fluids may contain infectious organisms. Skin accidentally exposed to tick fluids can be disinfected with iodine scrub, rubbing alcohol, or water containing detergents.
- Save the tick for identification in case you become ill. This may help your doctor to make an accurate diagnosis. Place the tick in a sealable plastic bag and put it in your freezer. Write the date of the bite on a piece of paper with a pencil and place it in the bag. [5]
Vaccination
- A vaccine, called Lymerix, against a North American strain of the spirochetal bacteria was available from 1998 to 2002.
- It was produced by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and was based on the outer surface protein A (Osp-A) of Borrelia. Osp-A causes the human immune system to create antibodies that attack that protein.
- A group of patients who been administered Lymerix developed arthritis, muscle pain and other troubling symptoms post-vaccination. Class-action litigation against GSK followed. Cassidy v. SmithKline Beecham, No. 99-10423 (Ct. Common Pleas, PA state court) (common settlement case).[6]
- It was later learned that patients with the genetic allele HLA-DR4 were susceptible to T-cell cross-reactivity between epitopes of OspA and lymphocyte function-associated antigen in these patients causing an autoimmune reaction.[7]
- New vaccines are being researched using outer surface protein C (Osp-C) and glycolipoprotein as methods of immunization.[8][9]
References
- ↑ Rand PW, Lubelczyk C, Holman MS, Lacombe EH, Smith RP (2004). "Abundance of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) after the complete removal of deer from an isolated offshore island, endemic for Lyme Disease". J. Med. Entomol. 41 (4): 779–84. PMID 15311475.
- ↑ Figure 2. p.4. DEP Wildlife Division: Managing Urban Deer in Connecticut 2nd edition June 2007
- ↑ Stafford KC (2004). "Tick Management Handbook" (PDF). Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station and Connecticut Department of Public Health. pp. p. 46. Retrieved 2007-08-21.
- ↑ General Tick Disease Information. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2015). http://www.cdc.gov/ticks/symptoms.html Accessed on December 30, 2015
- ↑ Tick Removal. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2015). http://www.cdc.gov/ticks/removing_a_tick.html Accessed on December 30, 2015
- ↑ Safety/Efficacy concerns re: Lyme vaccine: LYMErix Controversy LymeInfo.net
- ↑ Willett TA, Meyer AL, Brown EL, Huber BT (2004). "An effective second-generation outer surface protein A-derived Lyme vaccine that eliminates a potentially autoreactive T cell epitope". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (5): 1303–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0305680101. PMID 14742868.
- ↑ Earnhart CG, Marconi RT (2007). "OspC phylogenetic analyses support the feasibility of a broadly protective polyvalent chimeric Lyme disease vaccine". Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 14 (5): 628–34. doi:10.1128/CVI.00409-06. PMID 17360854.
- ↑ Pozsgay V, Kubler-Kielb J (2007). "Synthesis of an experimental glycolipoprotein vaccine against Lyme disease". Carbohydr. Res. 342 (3–4): 621–6. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2006.11.014. PMID 17182019.