Bronchogenic cyst differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:Home_logo1.png|right|250px|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Bronchogenic_cyst]] | [[Image:Home_logo1.png|right|250px|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Bronchogenic_cyst]] | ||
==[[Bronchogenic cyst differential diagnosis|Differentiating Bronchogenic cyst from other Diseases]]== | |||
Bronchogenic cyst must be differentiated from [[Lung abscess physical examination|lung abcess]], [[Mediastinal mass differential diagnosis|thymic cyst]], and [[Mediastinal mass differential diagnosis|esophageal duplication cysts]] | |||
{| | |||
|- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | |||
! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Diseases | |||
| colspan="6" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|'''Clinical manifestations''' | |||
! colspan="7" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Para-clinical findings | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|'''Gold standard''' | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="3" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|'''Symptoms''' | |||
! colspan="3" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Physical examination | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Lab Findings | |||
! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Imaging | |||
! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Histopathology | |||
|- | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Symptom 1 | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Symptom 2 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Symptom 3 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Physical exam 1 | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Physical exam 2 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Physical exam 3 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Lab 1 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Lab 2 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Lab 3 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Imaging 1 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Imaging 2 | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;|Imaging 3 | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Lung abscess physical examination|Lung abcess]]<ref name="pmid26366400">{{cite journal| author=Kuhajda I, Zarogoulidis K, Tsirgogianni K, Tsavlis D, Kioumis I, Kosmidis C | display-authors=etal| title=Lung abscess-etiology, diagnostic and treatment options. | journal=Ann Transl Med | year= 2015 | volume= 3 | issue= 13 | pages= 183 | pmid=26366400 | doi=10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.07.08 | pmc=4543327 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26366400 }} </ref> | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Fever]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Chest pain]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Sleep hyperhidrosis|night sweats]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Dullness to [[percussion]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Rales|coarse inspiratory crackles]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Decreased [[breath sounds]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Increased [[inflammation|inflamatory markers]] ([[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]], [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Anemia of chronic disease]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File: Frontal cxr of la.gif|x200px|thumb|Frontal view of [[X-ray|CXR]] showing lung abscess with air-fluid level. Case courtesy of Dr Abu-Rahmeh Zuhair (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/lung-abscess-17?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File: Lateral cxr of LA.gif|x200px|thumb|Lateral view 0f [[X-ray|CXR]] showing lung abscess with air-fluid level. Case courtesy of Dr Abu-Rahmeh Zuhair (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/lung-abscess-17?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:Ct la.gif|x200px|thumb| Non-contrast [[Computed tomography|CT]] showing lung abscess with air-fluid levels. Case courtesy of Dr Elsayed Mohamed Elsayed (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/lung-abscess-6?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
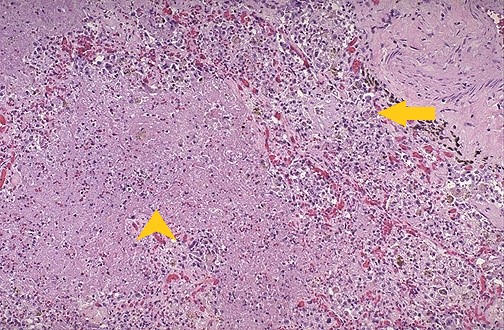
[[File:La.jpg|x200px|thumb|[[H&E]] stain showing lung abscess. Arrowhead – pink necrotic tissue with necrotic granulocytes and bacteria. Arrow – chronic inflammatory cells and dilated blood vessels (Picture courtesy: [https://webpath.med.utah.edu/LUNGHTML/LUNG023.html Webpath])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Computed tomography|CT]] with [[Radiocontrast|intravenous contrast]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Thymic cyst]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal| author=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L| title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses. | journal=Insights Imaging | year= 2013 | volume= 4 | issue= 1 | pages= 29-52 | pmid=23225215 | doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 | pmc=3579993 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23225215 }} </ref> | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | [[Cough]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | [[Chest pain]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | [[Dyspnea]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | Some patients may present with a soft compressible [[Neck masses differential diagnosis|neck mass]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
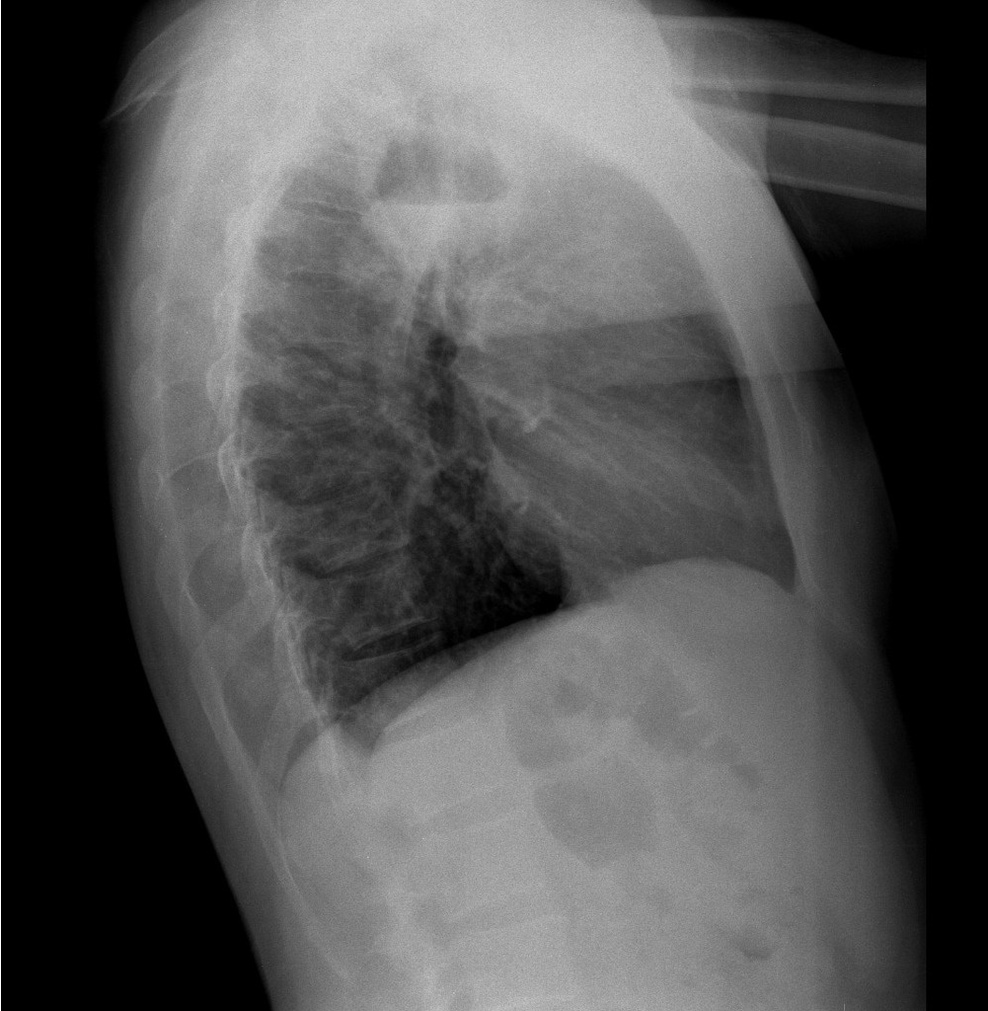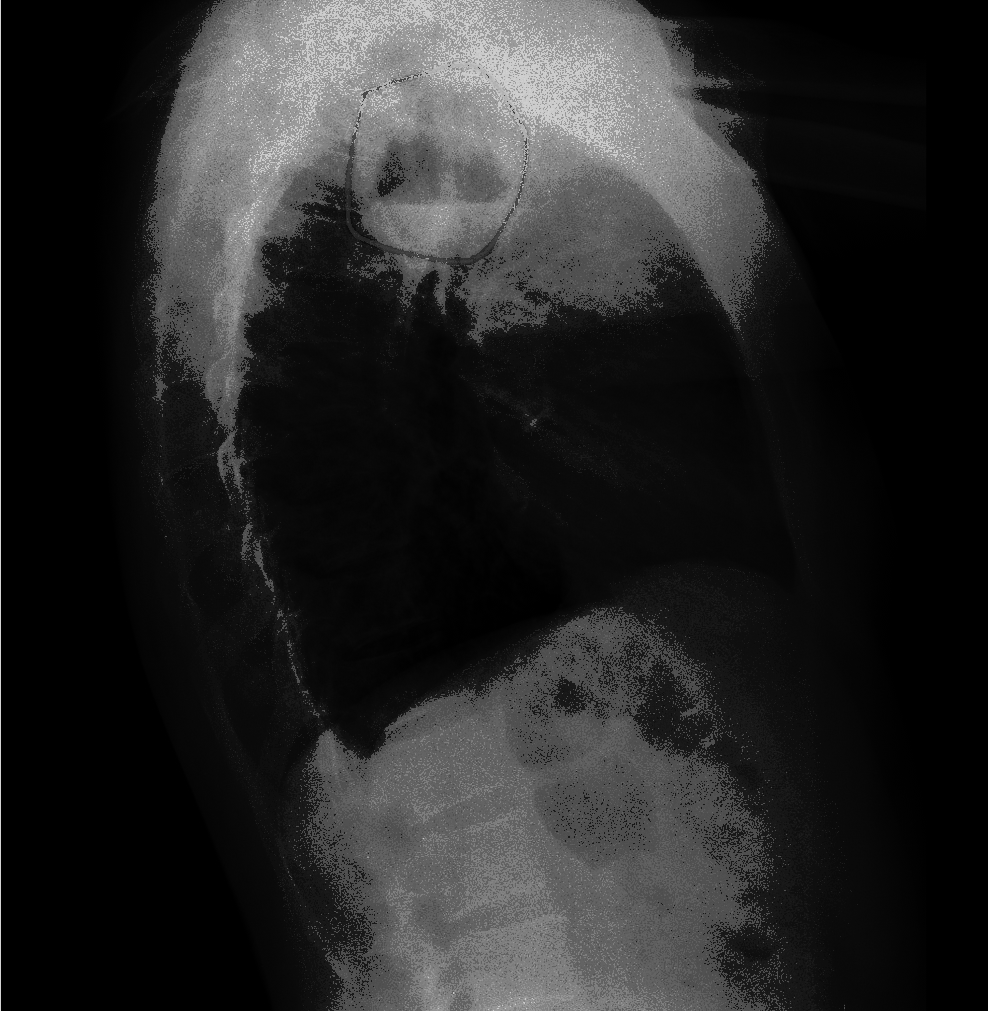
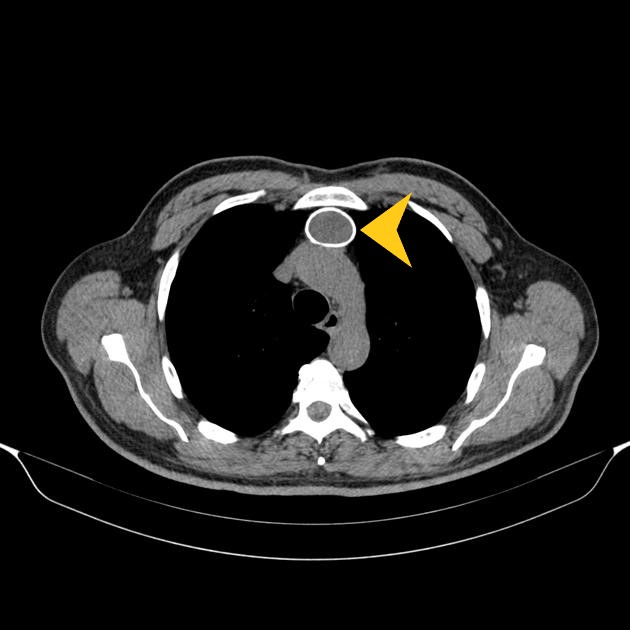
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:THYMIC CYST XRAY.jpg|x200px|thumb| [[X-ray|x-ray]] scan showing a thymic mass (yellow arrowhead). Case courtesy of Dr. Stefan Ludwig (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/thymic-cyst-1?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
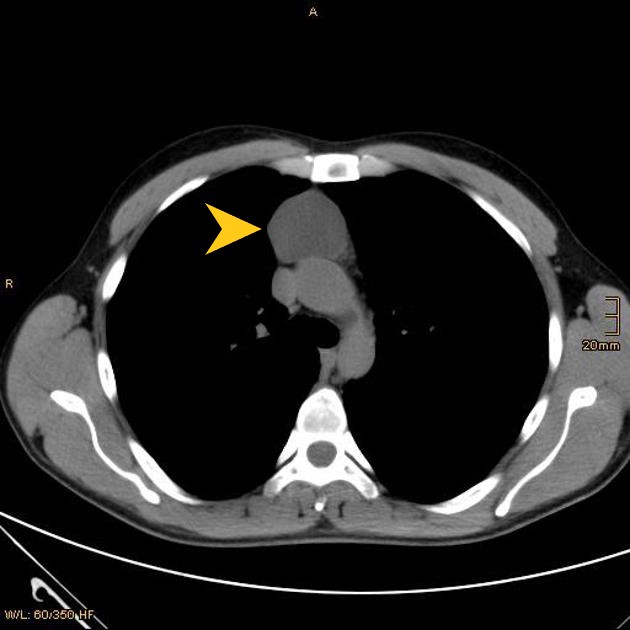
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:THYMIC CYST CT.jpg|x200px|thumb| [[Computed tomography|CT]] scan showing a thymic mass corresponds to a cystic lesion (yellowarrow head). Case courtesy of Dr. Stefan Ludwig (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/thymic-cyst-1?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:THYMIC CYST CALCIFIED.jpg|x200px|thumb| [[Computed tomography|CT]] scan showing a calcified thymic mass corresponds to a cystic lesion (yellow arrowhead). Case courtesy of Dr Bruno Di Muzio (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/thymic-cyst-probable-1?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File: Histopathology of thymic cyst.gif|x200px|thumb| H&E stain of [[thymic cyst]] showing bland squamous epithelium and some thymic tissue in its wall. Case courtesy of Dr Hanni Gulwani (Picture courtesy: [http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mediastinumthymiccyst.html Pathologyoutlines])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Biopsy]] with[[ histopathology]] and [[cytology]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinal mass differential diagnosis|Esophageal duplication cysts]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal| author=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L| title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses. | journal=Insights Imaging | year= 2013 | volume= 4 | issue= 1 | pages= 29-52 | pmid=23225215 | doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 | pmc=3579993 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23225215 }} </ref><ref name="pmid25184121">{{cite journal| author=Liu R, Adler DG| title=Duplication cysts: Diagnosis, management, and the role of endoscopic ultrasound. | journal=Endosc Ultrasound | year= 2014 | volume= 3 | issue= 3 | pages= 152-60 | pmid=25184121 | doi=10.4103/2303-9027.138783 | pmc=4145475 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=25184121 }} </ref><ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal| author=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L| title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses. | journal=Insights Imaging | year= 2013 | volume= 4 | issue= 1 | pages= 29-52 | pmid=23225215 | doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 | pmc=3579993 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23225215 }} </ref> | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[sternum|Retrosternal]] and [[chest|thoracic]] [[back pain]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Epigastric]] discomfort | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Dysphagia]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |- | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File: Endoscopic view of an esophageal duplication cyst.jpg|x200px|thumb|[[Endoscopy|endoscopic]] view of an esophageal duplication cyst (Picture courtesy: [http://www.eusjournal.com/article.asp?issn=2303-9027;year=2014;volume=3;issue=3;spage=152;epage=160;aulast=Liu#ref3 Endoscopic ultrasound])]] | |||
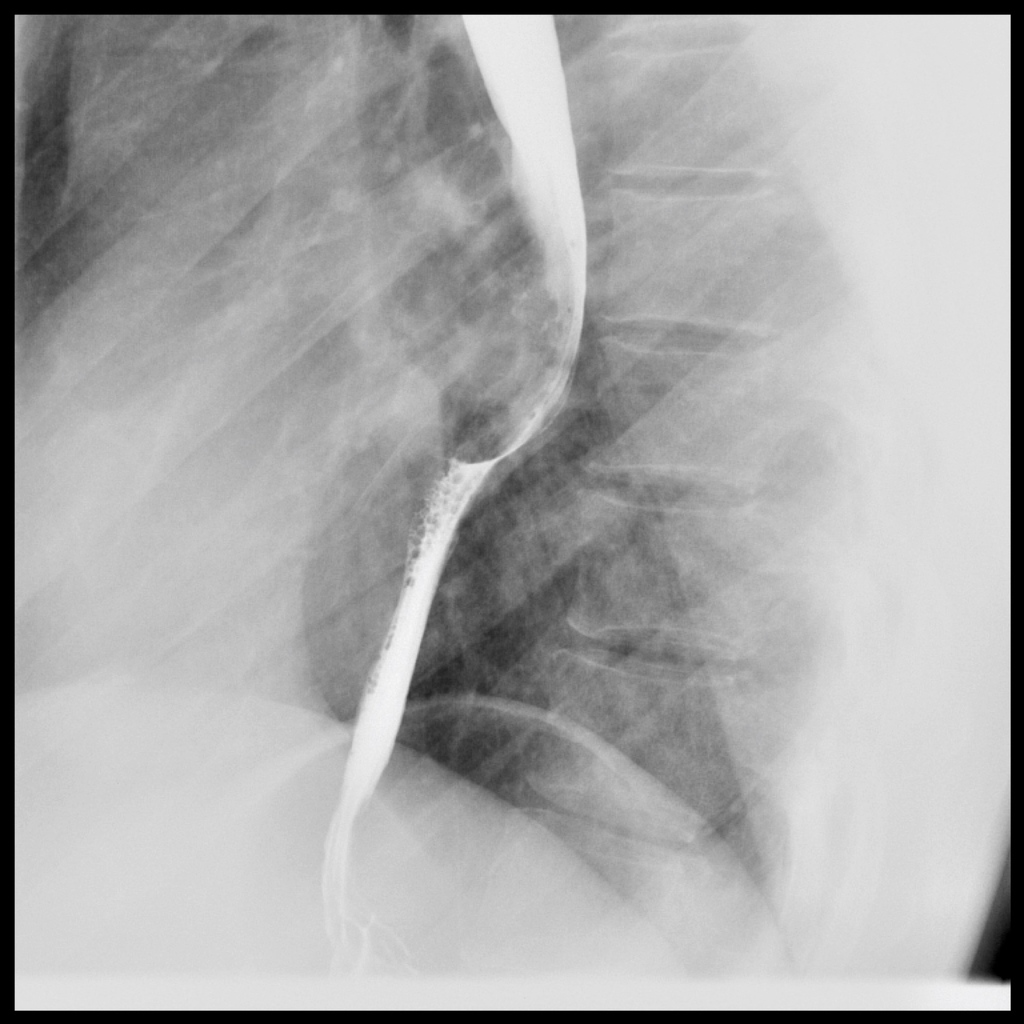
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File: Barium swallowing EDC.jpeg|x200px|thumb| [[X-rays|X-ray]] post barium swallow showing an oval mass compressing the esophagus. Case courtesy of Dr Michael P Hartung (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/oesophageal-duplication-cyst-3?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
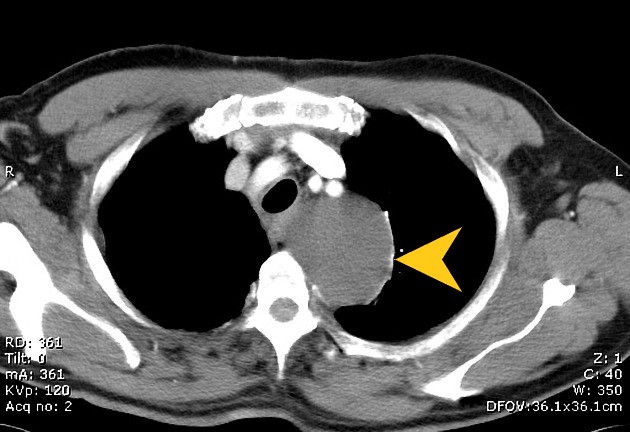
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File:EDC CT YA.jpeg|x200px|thumb|[[Computed tomography|CT]] showing an esophageal duplication cyst. Case courtesy of Assoc Prof Craig Hacking (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/superior-mediastinal-mass-due-to-oesophageal-duplication-cyst?lang=gb Radiopaedia])]] | |||
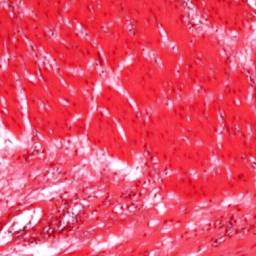
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[File: Histopath EDC.jpg|x200px|thumb|Histologic image of an esophageal duplication cyst showing two-layered muscle coat like the [[Gastrointestinal tract|GIT]], and epithelium lining of pseudo-ciliated columnar cells. (Picture courtesy: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2810603/ National Center for Biotechnology Information])]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Endoscopic ultrasound]] | |||
*Anechoic or hypoechoic, homogenous lesions | |||
*Regular margins originating from the submucosal layer or outside of the gut wall(adventitia) | |||
|- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 13 July 2020

Differentiating Bronchogenic cyst from other Diseases
Bronchogenic cyst must be differentiated from lung abcess, thymic cyst, and esophageal duplication cysts
| Diseases | Clinical manifestations | Para-clinical findings | Gold standard | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Physical examination | |||||||||||||
| Lab Findings | Imaging | Histopathology | ||||||||||||
| Symptom 1 | Symptom 2 | Symptom 3 | Physical exam 1 | Physical exam 2 | Physical exam 3 | Lab 1 | Lab 2 | Lab 3 | Imaging 1 | Imaging 2 | Imaging 3 | |||
| Lung abcess[1] | Fever | Chest pain | night sweats | Dullness to percussion | coarse inspiratory crackles | Decreased breath sounds | Leukocytosis | Increased inflamatory markers (ESR, CRP) | Anemia of chronic disease | 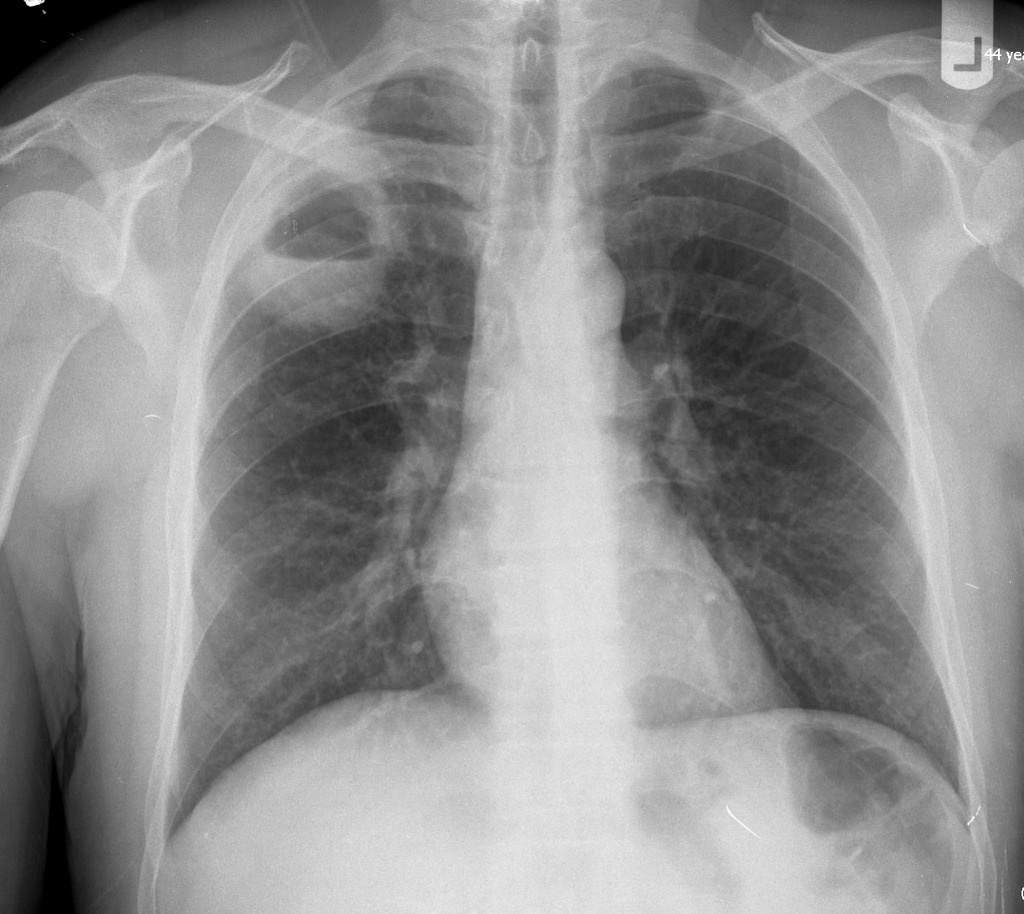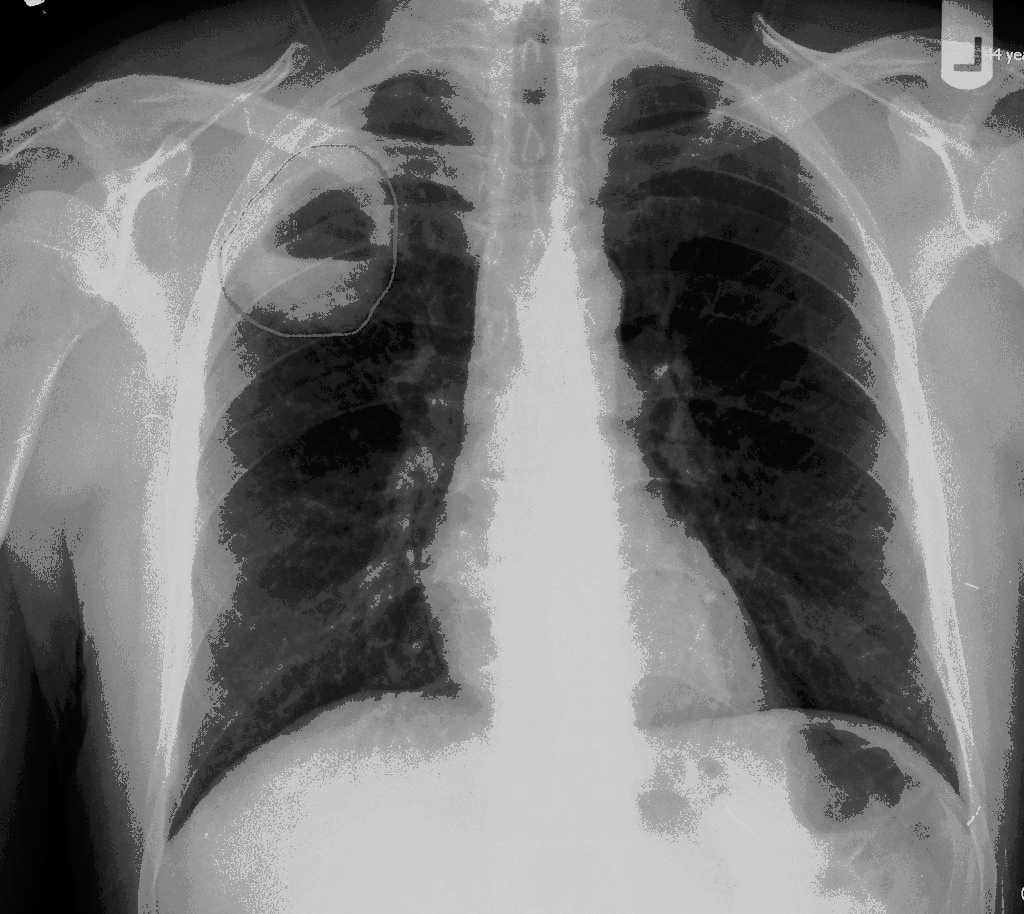 |
 |
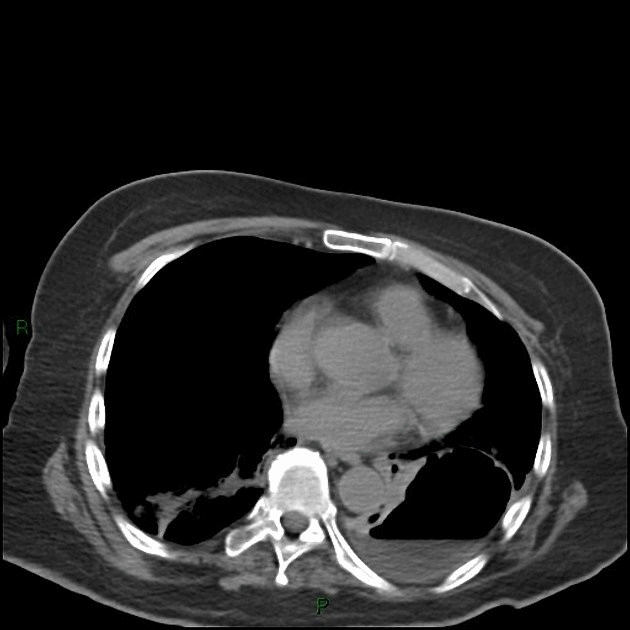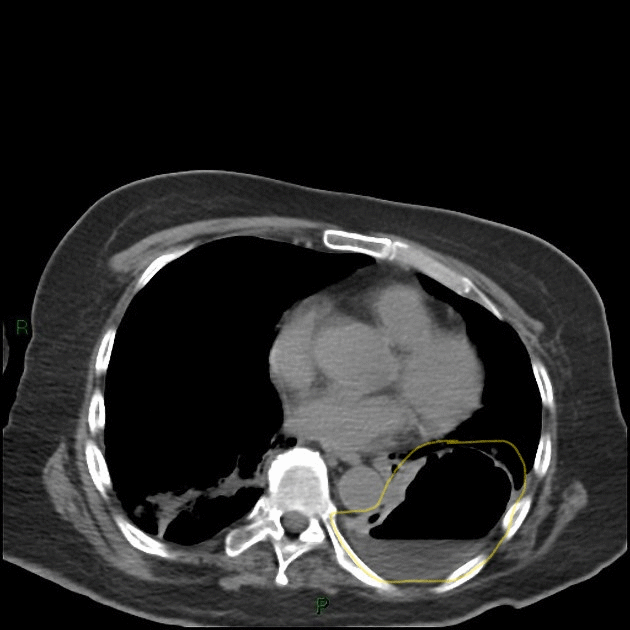 |
 |
CT with intravenous contrast |
| Thymic cyst[2] | Cough | Chest pain | Dyspnea | Some patients may present with a soft compressible neck mass | - | - | - | - | - | 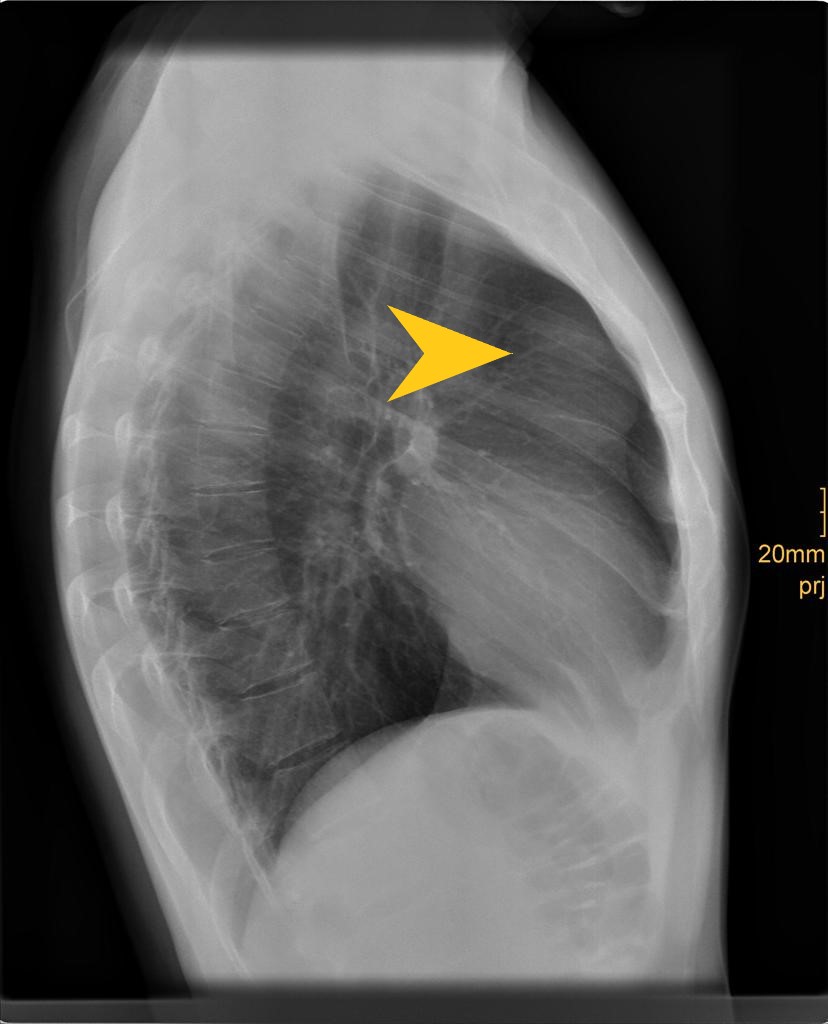 |
 |
 |
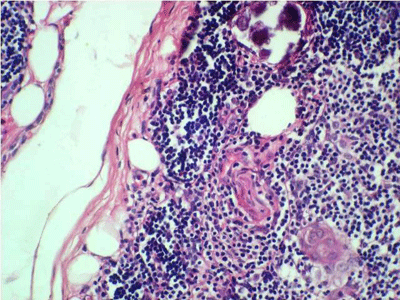 |
Biopsy withhistopathology and cytology |
| Esophageal duplication cysts[2][3][2] | Retrosternal and thoracic back pain | Epigastric discomfort | Dysphagia | - | - | - | - | - | - | 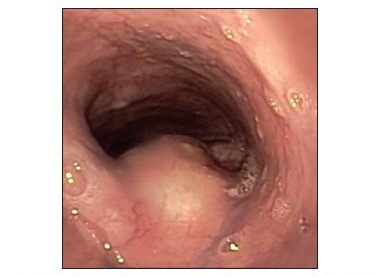 |
 |
 |
 |
Endoscopic ultrasound
|
References
- ↑ Kuhajda I, Zarogoulidis K, Tsirgogianni K, Tsavlis D, Kioumis I, Kosmidis C; et al. (2015). "Lung abscess-etiology, diagnostic and treatment options". Ann Transl Med. 3 (13): 183. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.07.08. PMC 4543327. PMID 26366400.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L (2013). "A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses". Insights Imaging. 4 (1): 29–52. doi:10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0. PMC 3579993. PMID 23225215.
- ↑ Liu R, Adler DG (2014). "Duplication cysts: Diagnosis, management, and the role of endoscopic ultrasound". Endosc Ultrasound. 3 (3): 152–60. doi:10.4103/2303-9027.138783. PMC 4145475. PMID 25184121.