Ankylosing spondylitis pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Ankylosing spondylitis}} | {{Ankylosing spondylitis}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} ; {{AE}} {{MKK}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS), a spondyloarthropathy, is a chronic, multisystem inflammatory disorder involving primarily the sacroiliac (SI) joints and the axial skeleton. The outcome in patients with a spondyloarthropathy, including AS, is generally compared with that in patients with a disease such as rheumatoid arthritis.Mostly the joints where the spine joins | [[Ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS), a [[spondyloarthropathy]], is a [[Chronic (medical)|chronic]], multisystem [[Inflammation|inflammatory]] disorder involving primarily the [[Sacroiliac joint|sacroiliac]] (SI) joints and the axial [[skeleton]]. The outcome in patients with a [[spondyloarthropathy]], including AS, is generally compared with that in patients with a disease such as [[rheumatoid arthritis]].Mostly the joints where the [[spine]] joins the [[pelvis]] are also affected.[[Back pain]] is one of the most prominent symptoms of the [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS) which is intermittent in nature.[[Stiffness]] in the affected joints gets worse.It is believed that both the combination of [[Genetics|genetic]] and environmental factors play an important role in the [[pathogenesis]] of [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS) and the underlying [[etiology]] is believed to be [[autoimmune]] or autoinflammatory. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
'''Pathogenesis'''<ref name="ShamjiBafaquh2008">{{cite journal|last1=Shamji|first1=Mohammed F.|last2=Bafaquh|first2=Mohammed|last3=Tsai|first3=Eve|title=The pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis|journal=Neurosurgical Focus|volume=24|issue=1|year=2008|pages=E3|issn=1092-0684|doi=10.3171/FOC/2008/24/1/E3}}</ref> | '''Pathogenesis'''<ref name="ShamjiBafaquh2008">{{cite journal|last1=Shamji|first1=Mohammed F.|last2=Bafaquh|first2=Mohammed|last3=Tsai|first3=Eve|title=The pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis|journal=Neurosurgical Focus|volume=24|issue=1|year=2008|pages=E3|issn=1092-0684|doi=10.3171/FOC/2008/24/1/E3}}</ref> | ||
* It is understood that ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is the result of genetic and environmental factors. | * It is understood that [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS) is the result of [[genetic]] and environmental factors. | ||
* Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect sacroiliac joints and axial skeleton and cause significant functional and structural implications of the affected joints. | * [[Ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS) is a [[Chronic inflammation|chronic inflammatory]] disease that can affect [[Sacroiliac joint|sacroiliac joints]] and [[axial]] [[skeleton]] and cause significant functional and structural implications of the affected joints. | ||
* Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) has a familial associations particularly among the patients who are positive for human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–B27 . | * [[Ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS) has a familial associations particularly among the patients who are positive for [[human leukocyte antigen]] (HLA)–B27 . | ||
== Genetics == | == Genetics == | ||
* Genes involved in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) include Human Leukocyte | * [[Gene|Genes]] involved in the [[pathogenesis]] of [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS) include [[Human leukocyte antigen|Human Leukocyte Antigen–B2]]7([[HLA-B27]]).<ref name="pmid9710228">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fiorillo MT, Greco G, Maragno M, Potolicchio I, Monizio A, Dupuis ML, Sorrentino R |title=The naturally occurring polymorphism Asp116-->His116, differentiating the ankylosing spondylitis-associated HLA-B*2705 from the non-associated HLA-B*2709 subtype, influences peptide-specific CD8 T cell recognition |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=28 |issue=8 |pages=2508–16 |date=August 1998 |pmid=9710228 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* The expression of HLA-B27 is more in the antigen presenting cells. | * The expression of [[HLA-B27]] is more in the [[Antigen-presenting cell|antigen presenting cells]]. | ||
* HLA-B27 binds to b2 microglobulin after translation and tertiary folding and then loaded with an oligopeptide. | * [[HLA-B27]] binds to b2 microglobulin after [[translation]] and tertiary folding and then loaded with an [[oligopeptide]]. | ||
* The complex now passes via Golgi apparatus to the cell surface where the antigenic peptide is presented to either CD8+ lymphocytes or NK cells.<ref name="pmid97102282">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fiorillo MT, Greco G, Maragno M, Potolicchio I, Monizio A, Dupuis ML, Sorrentino R |title=The naturally occurring polymorphism Asp116-->His116, differentiating the ankylosing spondylitis-associated HLA-B*2705 from the non-associated HLA-B*2709 subtype, influences peptide-specific CD8 T cell recognition |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=28 |issue=8 |pages=2508–16 |date=August 1998 |pmid=9710228 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * The complex now passes via Golgi apparatus to the cell surface where the [[antigenic]] [[peptide]] is presented to either CD8+ lymphocytes or NK cells.<ref name="pmid97102282">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fiorillo MT, Greco G, Maragno M, Potolicchio I, Monizio A, Dupuis ML, Sorrentino R |title=The naturally occurring polymorphism Asp116-->His116, differentiating the ankylosing spondylitis-associated HLA-B*2705 from the non-associated HLA-B*2709 subtype, influences peptide-specific CD8 T cell recognition |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=28 |issue=8 |pages=2508–16 |date=August 1998 |pmid=9710228 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* 90% of the time HLA B27 shows strong genetic association with AS, But only 5% of the patients who are positive for HLA B27 are going to develop ankylosing spondylitis (AS). | * 90% of the time HLA B27 shows strong [[genetic]] association with AS, But only 5% of the patients who are positive for HLA B27 are going to develop [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS). | ||
* HLA-B27 was found to have at least 25 allele subtypes which encode for 25 different gene products. Among all the 25 different alleles B*2705 is most common subtype which is thought to be a parent molecule and associated with higher risk of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). | * [[HLA-B27]] was found to have at least 25 [[allele]] subtypes which encode for 25 different gene products. Among all the 25 different alleles B*2705 is most common subtype which is thought to be a parent [[molecule]] and associated with higher risk of [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS). | ||
* B*2701, B*2702, B*2704, and B*2707 are the other subtypes which confer disease susceptibility.<ref name="pmid14734527">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B |title=Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=271–81 |date=January 2004 |pmid=14734527 |pmc=2211767 |doi=10.1084/jem.20031690 |url=}}</ref> | * B*2701, B*2702, B*2704, and B*2707 are the other subtypes which confer disease susceptibility.<ref name="pmid14734527">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B |title=Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=271–81 |date=January 2004 |pmid=14734527 |pmc=2211767 |doi=10.1084/jem.20031690 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* In peripheral blood mononuclear cells HLA–B27 has been found to be more highly expressed, than in healthy HLA-B27+ individuals. Furthermore, B*2705 expression levels were found to be higher in AS patients.<ref name="pmid2187471">{{cite journal |vauthors=Benjamin R, Parham P |title=Guilt by association: HLA-B27 and ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Immunol. Today |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=137–42 |date=April 1990 |pmid=2187471 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * In peripheral blood [[mononuclear cells]] HLA–B27 has been found to be more highly expressed, than in healthy HLA-B27+ individuals. Furthermore, B*2705 expression levels were found to be higher in AS patients.<ref name="pmid2187471">{{cite journal |vauthors=Benjamin R, Parham P |title=Guilt by association: HLA-B27 and ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Immunol. Today |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=137–42 |date=April 1990 |pmid=2187471 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Many theories have been postulated with regard to the molecular pathogenesis role of HLA-B27 in AS which include arthritogenic peptides, aberrant folding, HLA-B27 misfolding, and increased intracellular microbial survival.<ref name="pmid147345272">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B |title=Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=271–81 |date=January 2004 |pmid=14734527 |pmc=2211767 |doi=10.1084/jem.20031690 |url=}}</ref> | * Many theories have been postulated with regard to the [[molecular]] [[pathogenesis]] role of HLA-B27 in AS which include arthritogenic [[Peptide|peptides]], aberrant folding, HLA-B27 misfolding, and increased [[intracellular]] [[microbial]] survival.<ref name="pmid147345272">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B |title=Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=271–81 |date=January 2004 |pmid=14734527 |pmc=2211767 |doi=10.1084/jem.20031690 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Single amino acid changes from aspartate in the B*2705 allele to histidine in the B*2709 allele results in loss of the association with AS.<ref name="pmid8089488">{{cite journal |vauthors=Del Porto P, D'Amato M, Fiorillo MT, Tuosto L, Piccolella E, Sorrentino R |title=Identification of a novel HLA-B27 subtype by restriction analysis of a cytotoxic gamma delta T cell clone |journal=J. Immunol. |volume=153 |issue=7 |pages=3093–100 |date=October 1994 |pmid=8089488 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid147345273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B |title=Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=271–81 |date=January 2004 |pmid=14734527 |pmc=2211767 |doi=10.1084/jem.20031690 |url=}}</ref> | * Single [[amino acid]] changes from [[aspartate]] in the B*2705 allele to [[histidine]] in the B*2709 allele results in loss of the association with AS.<ref name="pmid8089488">{{cite journal |vauthors=Del Porto P, D'Amato M, Fiorillo MT, Tuosto L, Piccolella E, Sorrentino R |title=Identification of a novel HLA-B27 subtype by restriction analysis of a cytotoxic gamma delta T cell clone |journal=J. Immunol. |volume=153 |issue=7 |pages=3093–100 |date=October 1994 |pmid=8089488 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid147345273">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B |title=Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide |journal=J. Exp. Med. |volume=199 |issue=2 |pages=271–81 |date=January 2004 |pmid=14734527 |pmc=2211767 |doi=10.1084/jem.20031690 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* A common feature shared by the two caucasoid AS-associated subtypes (B*2702 and B*2705) but different from B*2709, is the presence of a Tyr as peptide C-terminal anchor.<ref name="pmid9045906">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fiorillo MT, Meadows L, D'Amato M, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Appella E, Sorrentino R |title=Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis correlates with the C-terminal residue of peptides presented by various HLA-B27 subtypes |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=368–73 |date=February 1997 |pmid=9045906 |doi=10.1002/eji.1830270205 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7489765">{{cite journal |vauthors=D'Amato M, Fiorillo MT, Carcassi C, Mathieu A, Zuccarelli A, Bitti PP, Tosi R, Sorrentino R |title=Relevance of residue 116 of HLA-B27 in determining susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=25 |issue=11 |pages=3199–201 |date=November 1995 |pmid=7489765 |doi=10.1002/eji.1830251133 |url=}}</ref> | * A common feature shared by the two caucasoid AS-associated subtypes (B*2702 and B*2705) but different from B*2709, is the presence of a Tyr as peptide [[C-terminal]] anchor.<ref name="pmid9045906">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fiorillo MT, Meadows L, D'Amato M, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Appella E, Sorrentino R |title=Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis correlates with the C-terminal residue of peptides presented by various HLA-B27 subtypes |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=368–73 |date=February 1997 |pmid=9045906 |doi=10.1002/eji.1830270205 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7489765">{{cite journal |vauthors=D'Amato M, Fiorillo MT, Carcassi C, Mathieu A, Zuccarelli A, Bitti PP, Tosi R, Sorrentino R |title=Relevance of residue 116 of HLA-B27 in determining susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Eur. J. Immunol. |volume=25 |issue=11 |pages=3199–201 |date=November 1995 |pmid=7489765 |doi=10.1002/eji.1830251133 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* A 9 amino acid fragment of VIPIR (residues 400–408) which is peptide, a sequence highly homologous to an Epstein–Barr virus derived epitope of latent membrane protein 2.<ref name="pmid7533789">{{cite journal |vauthors=Vaughan JH, Nguyen MD, Valbracht JR, Patrick K, Rhodes GH |title=Epstein-Barr virus-induced autoimmune responses. II. Immunoglobulin G autoantibodies to mimicking and nonmimicking epitopes. Presence in autoimmune disease |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=95 |issue=3 |pages=1316–27 |date=March 1995 |pmid=7533789 |pmc=441471 |doi=10.1172/JCI117782 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid2820321">{{cite journal |vauthors=Winrow VR, Perry JD |title=Hyper-responsiveness to EBV in ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Ann. Rheum. Dis. |volume=46 |issue=6 |pages=493–4 |date=June 1987 |pmid=2820321 |pmc=1002175 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * A 9 [[amino acid]] fragment of VIPIR (residues 400–408) which is peptide, a sequence highly [[homologous]] to an [[Epstein Barr virus|Epstein–Barr virus]] derived epitope of latent membrane protein 2.<ref name="pmid7533789">{{cite journal |vauthors=Vaughan JH, Nguyen MD, Valbracht JR, Patrick K, Rhodes GH |title=Epstein-Barr virus-induced autoimmune responses. II. Immunoglobulin G autoantibodies to mimicking and nonmimicking epitopes. Presence in autoimmune disease |journal=J. Clin. Invest. |volume=95 |issue=3 |pages=1316–27 |date=March 1995 |pmid=7533789 |pmc=441471 |doi=10.1172/JCI117782 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid2820321">{{cite journal |vauthors=Winrow VR, Perry JD |title=Hyper-responsiveness to EBV in ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Ann. Rheum. Dis. |volume=46 |issue=6 |pages=493–4 |date=June 1987 |pmid=2820321 |pmc=1002175 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Aggrecan is the another antigen of interest it is proteoglycan of chondroitin sulfate. In some patients a strong cellular immune response is noted with people who are suffering with AS and these patients also show presence of circulating and synovial CD4+ T cells. | * [[Aggrecan]] is the another antigen of interest it is [[proteoglycan]] of [[chondroitin sulfate]]. In some patients a strong [[cellular]] [[Immune system|immune response]] is noted with people who are suffering with AS and these patients also show presence of circulating and synovial [[CD4+ T cells]]. | ||
* Aggrecan is found in anterior uveal tract, aorta, and aortic valve and it is similar proteins such as versican that helps in cyclic compression and relaxation.Immunity to aggrecan in BALB/c mice results in spondylitis and peripheral arthritis.<ref name="pmid19220900">{{cite journal |vauthors=Farkas B, Boldizsar F, Tarjanyi O, Laszlo A, Lin SM, Hutas G, Tryniszewska B, Mangold A, Nagyeri G, Rosenzweig HL, Finnegan A, Mikecz K, Glant TT |title=BALB/c mice genetically susceptible to proteoglycan-induced arthritis and spondylitis show colony-dependent differences in disease penetrance |journal=Arthritis Res. Ther. |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=R21 |date=2009 |pmid=19220900 |pmc=2688253 |doi=10.1186/ar2613 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18650834">{{cite journal |vauthors=Adarichev VA, Vegvari A, Szabo Z, Kis-Toth K, Mikecz K, Glant TT |title=Congenic strains displaying similar clinical phenotype of arthritis represent different immunologic models of inflammation |journal=Genes Immun. |volume=9 |issue=7 |pages=591–601 |date=October 2008 |pmid=18650834 |pmc=3951374 |doi=10.1038/gene.2008.54 |url=}}</ref> | * [[Aggrecan]] is found in [[anterior]] [[Uvea (anatomy)|uveal]] tract, [[aorta]], and [[aortic valve]] and it is similar proteins such as versican that helps in cyclic compression and relaxation.Immunity to aggrecan in BALB/c mice results in [[spondylitis]] and peripheral arthritis.<ref name="pmid19220900">{{cite journal |vauthors=Farkas B, Boldizsar F, Tarjanyi O, Laszlo A, Lin SM, Hutas G, Tryniszewska B, Mangold A, Nagyeri G, Rosenzweig HL, Finnegan A, Mikecz K, Glant TT |title=BALB/c mice genetically susceptible to proteoglycan-induced arthritis and spondylitis show colony-dependent differences in disease penetrance |journal=Arthritis Res. Ther. |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=R21 |date=2009 |pmid=19220900 |pmc=2688253 |doi=10.1186/ar2613 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18650834">{{cite journal |vauthors=Adarichev VA, Vegvari A, Szabo Z, Kis-Toth K, Mikecz K, Glant TT |title=Congenic strains displaying similar clinical phenotype of arthritis represent different immunologic models of inflammation |journal=Genes Immun. |volume=9 |issue=7 |pages=591–601 |date=October 2008 |pmid=18650834 |pmc=3951374 |doi=10.1038/gene.2008.54 |url=}}</ref> | ||
'''Evidence of Other Genetic Associations in Ankylosing spondylitis (AS):''' | '''Evidence of Other Genetic Associations in Ankylosing spondylitis (AS):''' | ||
* There is very significant evidence to prove that other genetic conditions also act to determine which the patients have a increased susceptibility in developing the ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and studies show that HLA-B27+ patients who have a first-degree relative with ankylosing spondylitis(AS) have increased rates of disease development 6–16 times more than those without such a family history with ankylosing spondylitis.<ref name="pmid6606431">{{cite journal |vauthors=Calin A, Marder A, Becks E, Burns T |title=Genetic differences between B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis and B27 positive healthy controls |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=26 |issue=12 |pages=1460–4 |date=December 1983 |pmid=6606431 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6606472">{{cite journal |vauthors=van der Linden S, Valkenburg H, Cats A |title=The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals: a family and population study |journal=Br. J. Rheumatol. |volume=22 |issue=4 Suppl 2 |pages=18–9 |date=November 1983 |pmid=6606472 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6603847">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lochead JA, Chalmers IM, Marshall WH, Larsen B, Skanes VM, Payne RH, Barnard JM |title=HLA-B27 haplotypes in family studies of ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=26 |issue=8 |pages=1011–6 |date=August 1983 |pmid=6603847 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6608352">{{cite journal |vauthors=van der Linden SM, Valkenburg HA, de Jongh BM, Cats A |title=The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals. A comparison of relatives of spondylitis patients with the general population |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=241–9 |date=March 1984 |pmid=6608352 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6604814">{{cite journal |vauthors=LeClercq SA, Chaput L, Russell AS |title=Ankylosing spondylitis: a family study |journal=J. Rheumatol. |volume=10 |issue=4 |pages=629–32 |date=August 1983 |pmid=6604814 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | * There is very significant evidence to prove that other genetic conditions also act to determine which the patients have a increased susceptibility in developing the [[ankylosing spondylitis]] (AS), and studies show that HLA-B27+ patients who have a first-degree relative with ankylosing spondylitis(AS) have increased rates of disease development 6–16 times more than those without such a family history with ankylosing spondylitis.<ref name="pmid6606431">{{cite journal |vauthors=Calin A, Marder A, Becks E, Burns T |title=Genetic differences between B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis and B27 positive healthy controls |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=26 |issue=12 |pages=1460–4 |date=December 1983 |pmid=6606431 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6606472">{{cite journal |vauthors=van der Linden S, Valkenburg H, Cats A |title=The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals: a family and population study |journal=Br. J. Rheumatol. |volume=22 |issue=4 Suppl 2 |pages=18–9 |date=November 1983 |pmid=6606472 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6603847">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lochead JA, Chalmers IM, Marshall WH, Larsen B, Skanes VM, Payne RH, Barnard JM |title=HLA-B27 haplotypes in family studies of ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=26 |issue=8 |pages=1011–6 |date=August 1983 |pmid=6603847 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6608352">{{cite journal |vauthors=van der Linden SM, Valkenburg HA, de Jongh BM, Cats A |title=The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals. A comparison of relatives of spondylitis patients with the general population |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=27 |issue=3 |pages=241–9 |date=March 1984 |pmid=6608352 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid6604814">{{cite journal |vauthors=LeClercq SA, Chaput L, Russell AS |title=Ankylosing spondylitis: a family study |journal=J. Rheumatol. |volume=10 |issue=4 |pages=629–32 |date=August 1983 |pmid=6604814 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Evenmore, the radiographic severity tested with the Bath AS radiographic index has a heritability rate index of 0.62.<ref name="pmid19886979">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brown MA |title=Progress in spondylarthritis. Progress in studies of the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Arthritis Res. Ther. |volume=11 |issue=5 |pages=254 |date=2009 |pmid=19886979 |pmc=2787301 |doi=10.1186/ar2692 |url=}}</ref><ref name="LiBrown2017">{{cite journal|last1=Li|first1=Zhixiu|last2=Brown|first2=Matthew A|title=Progress of genome-wide association studies of ankylosing spondylitis|journal=Clinical & Translational Immunology|volume=6|issue=12|year=2017|pages=e163|issn=2050-0068|doi=10.1038/cti.2017.49 | * Evenmore, the [[Radiography|radiographic]] severity tested with the Bath AS radiographic index has a [[heritability]] rate index of 0.62.<ref name="pmid19886979">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brown MA |title=Progress in spondylarthritis. Progress in studies of the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Arthritis Res. Ther. |volume=11 |issue=5 |pages=254 |date=2009 |pmid=19886979 |pmc=2787301 |doi=10.1186/ar2692 |url=}}</ref><ref name="LiBrown2017">{{cite journal|last1=Li|first1=Zhixiu|last2=Brown|first2=Matthew A|title=Progress of genome-wide association studies of ankylosing spondylitis|journal=Clinical & Translational Immunology|volume=6|issue=12|year=2017|pages=e163|issn=2050-0068|doi=10.1038/cti.2017.49}}</ref> | ||
''HLA-B27 in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis'' | ''HLA-B27 in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis'' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 40: | Line 36: | ||
!Pathogenesis | !Pathogenesis | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Arthritogenic peptides | |Arthritogenic [[Peptide|peptides]] | ||
|Immunological (adaptive immunity) | |[[Immunology|Immunological]] ([[adaptive immunity]]) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Heavy chain of aberrant surface | |[[Heavy chain]] of aberrant surface | ||
|Immunological (innate immunity) | |Immunological ([[innate immunity]]) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Abnormal protein folding | |Abnormal protein folding | ||
|Intracellular (innate immunity) | |[[Intracellular]] (innate immunity) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Enhanced microbial survival | |Enhanced microbial survival | ||
|Intracellular (innate immunity) | |Intracellular (innate immunity) | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Cytokine and Enzymes Effect on AS == | |||
* The immunopathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis(AS) is suspected to involve upregulation of [[proinflammatory]] [[Cytokine|cytokines]] like especially [[Tumor necrosis factor-alpha|tumor necrosis factor]]–a(TNF-a) which is more increased than others in patients with ankylosing spondylitis(AS).<ref name="pmid16583185">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bal A, Unlu E, Bahar G, Aydog E, Eksioglu E, Yorgancioglu R |title=Comparison of serum IL-1 beta, sIL-2R, IL-6, and TNF-alpha levels with disease activity parameters in ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=26 |issue=2 |pages=211–5 |date=February 2007 |pmid=16583185 |doi=10.1007/s10067-006-0283-5 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Increased serum levels of [[IL-6]] and IL-17 shows associate with the development and progression of ankylosing spondylitis.<ref name="pmid165831852">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bal A, Unlu E, Bahar G, Aydog E, Eksioglu E, Yorgancioglu R |title=Comparison of serum IL-1 beta, sIL-2R, IL-6, and TNF-alpha levels with disease activity parameters in ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=26 |issue=2 |pages=211–5 |date=February 2007 |pmid=16583185 |doi=10.1007/s10067-006-0283-5 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26770328">{{cite journal |vauthors=Liu W, Wu YH, Zhang L, Liu XY, Xue B, Wang Y, Liu B, Jiang Q, Kwang HW, Wu DJ |title=Elevated serum levels of IL-6 and IL-17 may associate with the development of ankylosing spondylitis |journal=Int J Clin Exp Med |volume=8 |issue=10 |pages=17362–76 |date=2015 |pmid=26770328 |pmc=4694228 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid7921752">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gratacós J, Collado A, Filella X, Sanmartí R, Cañete J, Llena J, Molina R, Ballesta A, Muñoz-Gómez J |title=Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma) in ankylosing spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease activity and severity |journal=Br. J. Rheumatol. |volume=33 |issue=10 |pages=927–31 |date=October 1994 |pmid=7921752 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
== Gross Pathology == | |||
On gross pathology, The following are the characteristic findings of [[ankylosing spondylitis]](AS). | |||
* Involvement of [[Sacroiliac joint|sacroiliac joints]]. | |||
* [[Synovitis]] which destroys [[articular cartilage]] and results in bony [[ankylosis]]. | |||
* Posterior longitudinal [[ligament]] [[calcification]]. | |||
* Fixed [[kyphosis]] (Bamboo spine). | |||
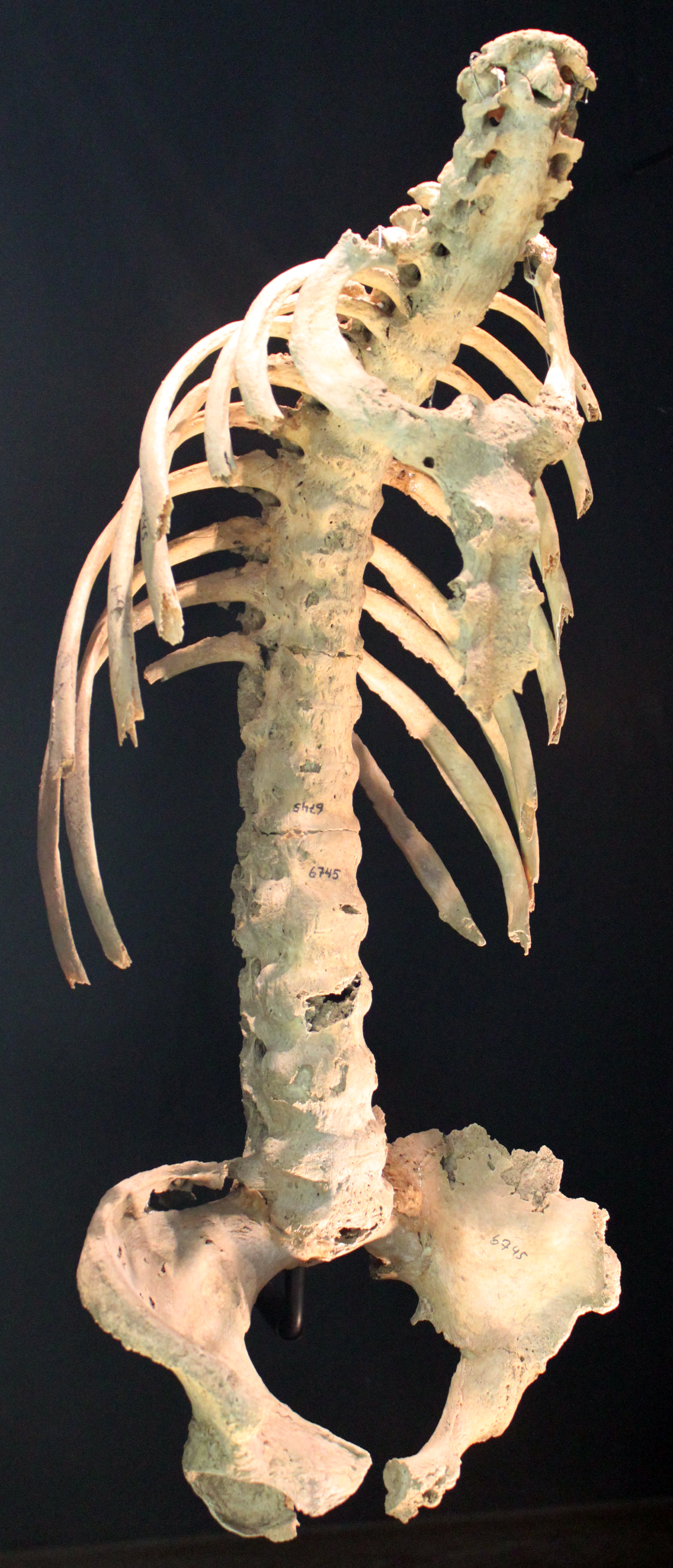
'''''Spine with spondylitis ankylosans'''''[[File:AS Gross Specimen.jpg|center|thumb|https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0510_Spondylitis_ankylosans_(morbus_bechterew)_anagoria.JPG#/media/File:0510_Spondylitis_ankylosans_(morbus_bechterew)_anagoria.JPG]]'''''Anterior flexion in ankylosing spondylitis'''''[[File:Anterior flexion in AS.png|thumb|By Leonard Trask - <nowiki>https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:AS_trask.jpg</nowiki>, Public Domain, <nowiki>https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=52791160</nowiki>|alt=Anterior flexion in AS|center]] | |||
== Microscopic Pathology == | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:05, 30 July 2018
|
Ankylosing spondylitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ankylosing spondylitis pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ankylosing spondylitis pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ankylosing spondylitis pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Manpreet Kaur, MD [2]
Overview
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS), a spondyloarthropathy, is a chronic, multisystem inflammatory disorder involving primarily the sacroiliac (SI) joints and the axial skeleton. The outcome in patients with a spondyloarthropathy, including AS, is generally compared with that in patients with a disease such as rheumatoid arthritis.Mostly the joints where the spine joins the pelvis are also affected.Back pain is one of the most prominent symptoms of the ankylosing spondylitis (AS) which is intermittent in nature.Stiffness in the affected joints gets worse.It is believed that both the combination of genetic and environmental factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and the underlying etiology is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory.
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis[1]
- It is understood that ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is the result of genetic and environmental factors.
- Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect sacroiliac joints and axial skeleton and cause significant functional and structural implications of the affected joints.
- Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) has a familial associations particularly among the patients who are positive for human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–B27 .
Genetics
- Genes involved in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) include Human Leukocyte Antigen–B27(HLA-B27).[2]
- The expression of HLA-B27 is more in the antigen presenting cells.
- HLA-B27 binds to b2 microglobulin after translation and tertiary folding and then loaded with an oligopeptide.
- The complex now passes via Golgi apparatus to the cell surface where the antigenic peptide is presented to either CD8+ lymphocytes or NK cells.[3]
- 90% of the time HLA B27 shows strong genetic association with AS, But only 5% of the patients who are positive for HLA B27 are going to develop ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
- HLA-B27 was found to have at least 25 allele subtypes which encode for 25 different gene products. Among all the 25 different alleles B*2705 is most common subtype which is thought to be a parent molecule and associated with higher risk of ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
- B*2701, B*2702, B*2704, and B*2707 are the other subtypes which confer disease susceptibility.[4]
- In peripheral blood mononuclear cells HLA–B27 has been found to be more highly expressed, than in healthy HLA-B27+ individuals. Furthermore, B*2705 expression levels were found to be higher in AS patients.[5]
- Many theories have been postulated with regard to the molecular pathogenesis role of HLA-B27 in AS which include arthritogenic peptides, aberrant folding, HLA-B27 misfolding, and increased intracellular microbial survival.[6]
- Single amino acid changes from aspartate in the B*2705 allele to histidine in the B*2709 allele results in loss of the association with AS.[7][8]
- A common feature shared by the two caucasoid AS-associated subtypes (B*2702 and B*2705) but different from B*2709, is the presence of a Tyr as peptide C-terminal anchor.[9][10]
- A 9 amino acid fragment of VIPIR (residues 400–408) which is peptide, a sequence highly homologous to an Epstein–Barr virus derived epitope of latent membrane protein 2.[11][12]
- Aggrecan is the another antigen of interest it is proteoglycan of chondroitin sulfate. In some patients a strong cellular immune response is noted with people who are suffering with AS and these patients also show presence of circulating and synovial CD4+ T cells.
- Aggrecan is found in anterior uveal tract, aorta, and aortic valve and it is similar proteins such as versican that helps in cyclic compression and relaxation.Immunity to aggrecan in BALB/c mice results in spondylitis and peripheral arthritis.[13][14]
Evidence of Other Genetic Associations in Ankylosing spondylitis (AS):
- There is very significant evidence to prove that other genetic conditions also act to determine which the patients have a increased susceptibility in developing the ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and studies show that HLA-B27+ patients who have a first-degree relative with ankylosing spondylitis(AS) have increased rates of disease development 6–16 times more than those without such a family history with ankylosing spondylitis.[15][16][17][18][19]
- Evenmore, the radiographic severity tested with the Bath AS radiographic index has a heritability rate index of 0.62.[20][21]
HLA-B27 in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis
| Hypothesis | Pathogenesis |
|---|---|
| Arthritogenic peptides | Immunological (adaptive immunity) |
| Heavy chain of aberrant surface | Immunological (innate immunity) |
| Abnormal protein folding | Intracellular (innate immunity) |
| Enhanced microbial survival | Intracellular (innate immunity) |
Cytokine and Enzymes Effect on AS
- The immunopathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis(AS) is suspected to involve upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines like especially tumor necrosis factor–a(TNF-a) which is more increased than others in patients with ankylosing spondylitis(AS).[22]
- Increased serum levels of IL-6 and IL-17 shows associate with the development and progression of ankylosing spondylitis.[23][24][25]
Gross Pathology
On gross pathology, The following are the characteristic findings of ankylosing spondylitis(AS).
- Involvement of sacroiliac joints.
- Synovitis which destroys articular cartilage and results in bony ankylosis.
- Posterior longitudinal ligament calcification.
- Fixed kyphosis (Bamboo spine).
Spine with spondylitis ankylosans
Anterior flexion in ankylosing spondylitis

Microscopic Pathology
References
- ↑ Shamji, Mohammed F.; Bafaquh, Mohammed; Tsai, Eve (2008). "The pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis". Neurosurgical Focus. 24 (1): E3. doi:10.3171/FOC/2008/24/1/E3. ISSN 1092-0684.
- ↑ Fiorillo MT, Greco G, Maragno M, Potolicchio I, Monizio A, Dupuis ML, Sorrentino R (August 1998). "The naturally occurring polymorphism Asp116-->His116, differentiating the ankylosing spondylitis-associated HLA-B*2705 from the non-associated HLA-B*2709 subtype, influences peptide-specific CD8 T cell recognition". Eur. J. Immunol. 28 (8): 2508–16. PMID 9710228.
- ↑ Fiorillo MT, Greco G, Maragno M, Potolicchio I, Monizio A, Dupuis ML, Sorrentino R (August 1998). "The naturally occurring polymorphism Asp116-->His116, differentiating the ankylosing spondylitis-associated HLA-B*2705 from the non-associated HLA-B*2709 subtype, influences peptide-specific CD8 T cell recognition". Eur. J. Immunol. 28 (8): 2508–16. PMID 9710228.
- ↑ Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B (January 2004). "Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide". J. Exp. Med. 199 (2): 271–81. doi:10.1084/jem.20031690. PMC 2211767. PMID 14734527.
- ↑ Benjamin R, Parham P (April 1990). "Guilt by association: HLA-B27 and ankylosing spondylitis". Immunol. Today. 11 (4): 137–42. PMID 2187471.
- ↑ Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B (January 2004). "Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide". J. Exp. Med. 199 (2): 271–81. doi:10.1084/jem.20031690. PMC 2211767. PMID 14734527.
- ↑ Del Porto P, D'Amato M, Fiorillo MT, Tuosto L, Piccolella E, Sorrentino R (October 1994). "Identification of a novel HLA-B27 subtype by restriction analysis of a cytotoxic gamma delta T cell clone". J. Immunol. 153 (7): 3093–100. PMID 8089488.
- ↑ Hülsmeyer M, Fiorillo MT, Bettosini F, Sorrentino R, Saenger W, Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B (January 2004). "Dual, HLA-B27 subtype-dependent conformation of a self-peptide". J. Exp. Med. 199 (2): 271–81. doi:10.1084/jem.20031690. PMC 2211767. PMID 14734527.
- ↑ Fiorillo MT, Meadows L, D'Amato M, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Appella E, Sorrentino R (February 1997). "Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis correlates with the C-terminal residue of peptides presented by various HLA-B27 subtypes". Eur. J. Immunol. 27 (2): 368–73. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270205. PMID 9045906.
- ↑ D'Amato M, Fiorillo MT, Carcassi C, Mathieu A, Zuccarelli A, Bitti PP, Tosi R, Sorrentino R (November 1995). "Relevance of residue 116 of HLA-B27 in determining susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis". Eur. J. Immunol. 25 (11): 3199–201. doi:10.1002/eji.1830251133. PMID 7489765.
- ↑ Vaughan JH, Nguyen MD, Valbracht JR, Patrick K, Rhodes GH (March 1995). "Epstein-Barr virus-induced autoimmune responses. II. Immunoglobulin G autoantibodies to mimicking and nonmimicking epitopes. Presence in autoimmune disease". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (3): 1316–27. doi:10.1172/JCI117782. PMC 441471. PMID 7533789.
- ↑ Winrow VR, Perry JD (June 1987). "Hyper-responsiveness to EBV in ankylosing spondylitis". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 46 (6): 493–4. PMC 1002175. PMID 2820321.
- ↑ Farkas B, Boldizsar F, Tarjanyi O, Laszlo A, Lin SM, Hutas G, Tryniszewska B, Mangold A, Nagyeri G, Rosenzweig HL, Finnegan A, Mikecz K, Glant TT (2009). "BALB/c mice genetically susceptible to proteoglycan-induced arthritis and spondylitis show colony-dependent differences in disease penetrance". Arthritis Res. Ther. 11 (1): R21. doi:10.1186/ar2613. PMC 2688253. PMID 19220900.
- ↑ Adarichev VA, Vegvari A, Szabo Z, Kis-Toth K, Mikecz K, Glant TT (October 2008). "Congenic strains displaying similar clinical phenotype of arthritis represent different immunologic models of inflammation". Genes Immun. 9 (7): 591–601. doi:10.1038/gene.2008.54. PMC 3951374. PMID 18650834.
- ↑ Calin A, Marder A, Becks E, Burns T (December 1983). "Genetic differences between B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis and B27 positive healthy controls". Arthritis Rheum. 26 (12): 1460–4. PMID 6606431.
- ↑ van der Linden S, Valkenburg H, Cats A (November 1983). "The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals: a family and population study". Br. J. Rheumatol. 22 (4 Suppl 2): 18–9. PMID 6606472.
- ↑ Lochead JA, Chalmers IM, Marshall WH, Larsen B, Skanes VM, Payne RH, Barnard JM (August 1983). "HLA-B27 haplotypes in family studies of ankylosing spondylitis". Arthritis Rheum. 26 (8): 1011–6. PMID 6603847.
- ↑ van der Linden SM, Valkenburg HA, de Jongh BM, Cats A (March 1984). "The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27 positive individuals. A comparison of relatives of spondylitis patients with the general population". Arthritis Rheum. 27 (3): 241–9. PMID 6608352.
- ↑ LeClercq SA, Chaput L, Russell AS (August 1983). "Ankylosing spondylitis: a family study". J. Rheumatol. 10 (4): 629–32. PMID 6604814.
- ↑ Brown MA (2009). "Progress in spondylarthritis. Progress in studies of the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis". Arthritis Res. Ther. 11 (5): 254. doi:10.1186/ar2692. PMC 2787301. PMID 19886979.
- ↑ Li, Zhixiu; Brown, Matthew A (2017). "Progress of genome-wide association studies of ankylosing spondylitis". Clinical & Translational Immunology. 6 (12): e163. doi:10.1038/cti.2017.49. ISSN 2050-0068.
- ↑ Bal A, Unlu E, Bahar G, Aydog E, Eksioglu E, Yorgancioglu R (February 2007). "Comparison of serum IL-1 beta, sIL-2R, IL-6, and TNF-alpha levels with disease activity parameters in ankylosing spondylitis". Clin. Rheumatol. 26 (2): 211–5. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0283-5. PMID 16583185.
- ↑ Bal A, Unlu E, Bahar G, Aydog E, Eksioglu E, Yorgancioglu R (February 2007). "Comparison of serum IL-1 beta, sIL-2R, IL-6, and TNF-alpha levels with disease activity parameters in ankylosing spondylitis". Clin. Rheumatol. 26 (2): 211–5. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0283-5. PMID 16583185.
- ↑ Liu W, Wu YH, Zhang L, Liu XY, Xue B, Wang Y, Liu B, Jiang Q, Kwang HW, Wu DJ (2015). "Elevated serum levels of IL-6 and IL-17 may associate with the development of ankylosing spondylitis". Int J Clin Exp Med. 8 (10): 17362–76. PMC 4694228. PMID 26770328.
- ↑ Gratacós J, Collado A, Filella X, Sanmartí R, Cañete J, Llena J, Molina R, Ballesta A, Muñoz-Gómez J (October 1994). "Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma) in ankylosing spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease activity and severity". Br. J. Rheumatol. 33 (10): 927–31. PMID 7921752.