Trimethaphan
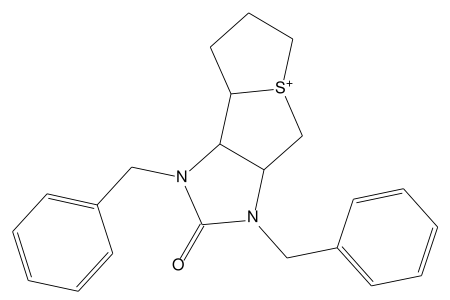 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25N2OS |
| Molar mass | 365.513 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Trimethaphan |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Trimethaphan Most cited articles on Trimethaphan |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Trimethaphan |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Trimethaphan at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Trimethaphan at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Trimethaphan
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Trimethaphan Discussion groups on Trimethaphan Patient Handouts on Trimethaphan Directions to Hospitals Treating Trimethaphan Risk calculators and risk factors for Trimethaphan
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Trimethaphan |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Trimethaphan is a drug that counteracts cholinergic transmission at the nicotinic receptors of the autonomic ganglia and therefore blocks both the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. It acts as a non-depolarizing competitive antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, is short-acting, and is given intravenously.
Effects
Trimethaphan is a quaternary amine and therefore carries a positive charge. Being charged, it cannot cross lipid cell membranes, such as those that comprise the blood-brain barrier. Due to this, trimethaphan does not have any effect on the central nervous system.
The ciliary muscle of the eye functions to round the lens for accommodation and is controlled mainly by parasympathetic system input. With administration of a ganglion-blocking drug, the ciliary muscle cannot contract (cycloplegia) and the patient loses the ability to focus their eyes.
Trimethaphan has a strong effect on the cardiovascular system. The size of blood vessels is primarily controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. Loss of sympathetic system input to the blood vessels causes them to get larger (vasodilation) which has the effect of lowering blood pressure. Postural hypotension is a common side effect of such drugs. Effects on the heart include a decreased force of contraction and an increase in heart rate (tachycardia). Although it is important to note that this reflexive tachycardia can be diminished or undetected due to the fact that Trimethaphan is also blocking the sympathetic ganglia innervating the heart.
The motility of the gastrointestinal tract is regulated by the parasympathetic system, and blockage of this input results in diminished motility and constipation.
Therapeutic Uses
The therapeutic uses of trimethaphan are very limited due to the competition from newer drugs that are more selective in their actions and effects produced. It is occasionally used to treat a hypertensive crisis and dissecting aortic aneurysm, to treat pulmonary edema, and to reduce bleeding during neurosurgery.
Adverse Effects
The adverse effects are due to its nonselective ganglion block and are described in the "Effects" section above. The side effects are severe enough to limit this drugs use to emergency and acute situations.
References
- "Ganglion-blocking Drugs." Drug Benefits and Risks: International Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology. (2001). ISBN 0-471-89927-5
- Katzung, Bertram G. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 9th ed. (2004). ISBN 0-07-141092-9
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Antihypertensive agents
- Cardiovascular Drugs
- Drug