Trace amine
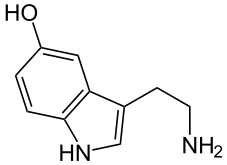
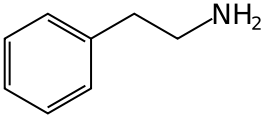
Trace amines are endogenous compounds structurally related to classical biogenic amines, such as catecholamines, serotonin and histamine. Trace amines include p-tyramine, β-phenylethylamine, tryptamine, octopamine, and 3-iodothyronamine, and are found in the nervous systems of animals from insects to mammals. Also the entheogenic DMT is created in small amounts by the human body during normal metabolism[1] by the enzyme tryptamine-N-methyltransferase.
Trace amines overlap substantially with classical biogenic amines neurotransmitters regarding to chemical properties, synthesis, and breakdown; trace amines commonly colocalize in neurons with these neurotransmitters.
Psychiatric disorders such as depression and schizophrenia have been linked to irregular levels of trace amines.
See also
References
- ↑ Barker SA, Monti JA and Christian ST (1981). N,N-Dimethyltryptamine: An endogenous hallucinogen. In International Review of Neurobiology, vol 22, pp. 83-110; Academic Press, Inc.
| Stub icon | This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |