Thrombin human
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gloria Picoy [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Thrombin human is an hemostatic that is FDA approved for the treatment of hemorrhage. Common adverse reactions include prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time, increased INR, lymphocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time and neutrophilia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Is indicated as an aid to hemostasis whenever oozing blood and minor bleeding from capillaries and small venules.
- Apply only on the surface of bleeding tissue
- The amount of thrombin human required depends upon the area of tissue to be treated and the method of application.
- As an approximate guide, volumes up to 10 ml were used in clinical studies where thrombin human was used in conjunction with absorbable gelatin sponge.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Thrombin human in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- Peptic ulcer with hemorrhage
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Apply only on the surface of bleeding tissue
- The amount of thrombin human required depends upon the area of tissue to be treated and the method of application.
- As an approximate guide, volumes up to 10 ml were used in clinical studies where thrombin human was used in conjunction with absorbable gelatin sponge.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Thrombin human in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Thrombin human in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Do not use in individuals known to have anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to human blood products.
- Do not use for the treatment of severe or brisk arterial bleeding.
Warnings
Thrombosis
- Potential risk of thrombosis if absorbed systemically
Transmission of Infectious Agents
- Because this product is made from human plasma, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, such as viruses, and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent.
- The risk of transmitting an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, by testing for the presence of certain current virus infections and by inactivating and removing certain viruses. Despite these measures, such products can still potentially transmit disease.
- There is also the possibility that unknown infectious agents may be present in such products.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
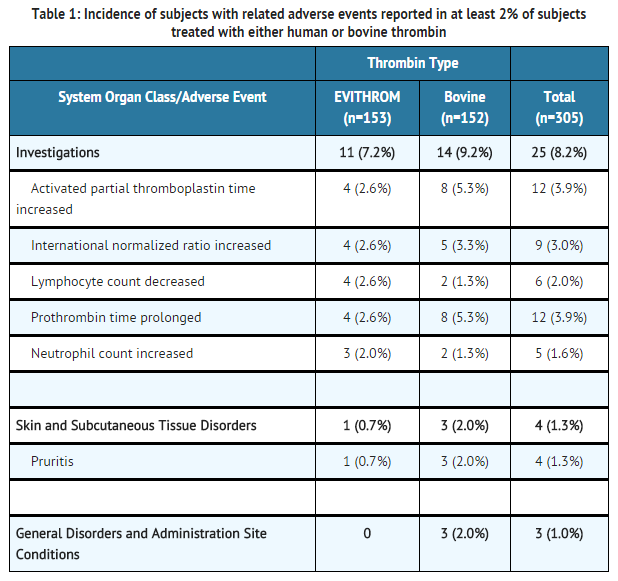
- The most common adverse reactions during clinical trial (reported in at least 2% of subjects treated with thrombin human) were prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time, increased INR, decreased lymphocyte count, prolonged prothrombin time and increased neutrophil count.
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug product cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
- Anaphylactic reactions may occur in rare cases. No adverse events of this type were reported during the conduct of the clinical trials. Mild reactions can be managed with anti-histamines. Severe hypotensive reactions require immediate intervention using current principles of shock therapy.
- In a phase III multicenter, prospective, controlled, randomized, double-blinded study of 305 subjects where thrombin human (n=153) was compared with bovine thrombin (n=152), occurrence of adverse events was not statistically different between the two groups.
- Overall, adverse events occurred in similar proportions of subjects in the two study groups. No clinically significant differences were seen in age (<65 years, >65 years) or gender subgroup analyses of adverse events.
- At least one serious adverse event (SAE) was reported for 26/153 (17%) subjects treated with human thrombin and 17/152 (11%) subjects treated with bovine thrombin. The SAEs reported were associated with post-surgical complications (e.g. wound infection 3/153 for thrombin human and 2/152 for bovine thrombin) and the medical condition of the subject and were not considered related to study drug. Two subjects (1.3%) in thrombin human group experienced a treatment emergent severe adverse event: respiratory arrest and post-procedural hematoma (in one subject) and extradural hematoma. Three subjects in the bovine thrombin group experienced a treatment emergent severe adverse event: hyperhidrosis, pyrexia and post-procedural hematoma.
No deaths were reported during the study period.
Viral serology was not monitored during the study with thrombin human. However, no adverse events indicative of infection with transfusion-transmissible agents were reported.
Immunogenicity
In the clinical study, serum samples were collected at baseline and at 5 weeks post-surgery for evaluation of antibodies to bovine thrombin, bovine Factor V/Va, human thrombin, and human Factor V/Va. Samples were collected at both time points for 81.3% of the subjects. The ELISA data were adjudicated by a panel of experts blinded to treatment assignment. After reviewing all data, the panel used an algorithm for assigning outcomes for each antigen: seroconversion negative or seroconversion positive.
The protocol did not specify any comparative analysis for immunogenicity data, only descriptive statistics. The adjudicated results show that 3.3% of the subjects treated with thrombin human (frozen formulation) developed antibodies to any of the four antigens, compared to 12.7% of the subjects developing antibodies in the control group (bovine thrombin). 7.94% of the subjects treated with bovine thrombin (control group) developed antibodies to bovine thrombin and 9.52% of these subjects developed antibodies to bovine Factor V/Va. A few control subjects had antibodies that cross-reacted with human thrombin, but none had antibodies that cross-reacted with human Factor V/Va. None of the patients treated with thrombin human developed detectable antibodies to human thrombin or to human Factor V/Va.
The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent upon the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. The observed incidence of a positive signal in an assay may be influenced by several factors including timing of sampling, sample handling, concomitant medications, or underlying disease. Therefore, direct comparison of incidence of antibody development to human thrombin, bovine thrombin, human Factor V/Va or bovine Factor V/Va following administration of thrombin human with incidence of antibody development following administration of other products may be misleading and the clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
Postmarketing Experience
No adverse reactions have been identified from spontaneous post-marketing reports.
Drug Interactions
No drug interactions are known.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C
Adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women have not been performed. thrombin human should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the pregnant woman justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Thrombin human in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
The safety of thrombin human for use during labor and delivery has not been established.
Nursing Mothers
The safety of thrombin human for use during breast-feeding has not been established. Use only if clearly needed.
Pediatric Use
Of the 155 patients undergoing liver surgery who were treated in adequate and well-controlled studies of EVICEL Fibrin Sealant (Human), in which thrombin human is a component, eight were pediatric patients. Of these, five were less than 2 years old and three were between 2 and 12 years old. Use of thrombin human in pediatric patients is supported by these data and by extrapolation of findings for safety and efficacy in adults.
Geriatic Use
Sixty three (63) subjects over 65 years of age received thrombin human in the phase III clinical trial. No differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between the elderly and younger patients. Greater susceptibility of older patients to adverse reactions cannot be ruled out.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Thrombin human with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Thrombin human with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Thrombin human in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Thrombin human in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
The effect of thrombin human on fertility has not been evaluated.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Thrombin human in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Topical
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Thrombin human Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Thrombin human and IV administrations.
Overdosage
No case of overdose has been reported.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Thrombin human Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Thrombin (coagulation factor IIa) is a highly specific protease that transforms plasma fibrinogen into fibrin which, in the presence of Factor XIII in the patient's plasma, is cross-linked to form a stable clot. When applied to a surgical wound where bleeding is present, thrombin activates fibrinogen in the patient's plasma to form fibrin, which results in clot formation and hemostasis. The fibrin clot is stabilized by cross-linking occurring as a result of activation of the patient's endogenous factor XIII, which requires the presence of calcium.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Thrombin human Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
Clinical pharmacodynamic studies with human thrombin have not been performed as this would be ethically unacceptable with this type of product.
Pharmacokinetics
Due to the nature of the product, intended for topical application to the surface of tissue at the surgical site, pharmacokinetic studies were not conducted.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of thrombin human due to the human origin of thrombin.
Studies were performed in bacteria to determine mutagenicity of human thrombin alone, and solvent/detergent residues [tri-n-butyl phosphate (TnBP) and Triton X-100, used in the virus inactivation manufacturing step. These studies were negative for both thrombin and for TnBP or Triton X-100 at all concentrations tested. All concentrations of the combination of TnBP and Triton X-100 also tested negative in assays performed to determine mammalian cell mutagenicity, chromosomal aberrations and micronuclei induction.
The effect of thrombin human on fertility has not been evaluated. Reproductive studies were performed in rats with the combination of solvent detergent impurities, TnBP and Triton X-100 at doses up to approximately 600-fold human dose of TnBP (900 μg/kg/day) and 3000-fold human dose of Triton X-100 (4500 μg/kg/day) resulted in increased post-implantation loss and an increased number of late resorptions. Other studies performed with combinations of TnBP (300-fold human dose, 450 μg/kg/day) and Triton X-100 (1500-fold human dose, 2250 μg/kg/day) resulted in increased resorption rates, decreased fetal body weights, and an increased number of runts. No embryo-fetal adverse effects were observed at doses up to 300 μg/kg/day TnBP and 1500 μg/kg/day Triton X-100, 200-fold and 1000-fold the human dose, respectively.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
EVICEL Fibrin Sealant (Human), which includes thrombin human as one of the active components, was classified as non-irritant in the Primary Cutaneous Irritation Test and slightly irritant in the Ocular Irritation test.
Neurotoxicity studies performed with EVITHROM or with EVICEL confirmed that intracerebral application of thrombin was not associated with any evidence of neurotoxicity.
No toxicological effects due to solvent/detergent reagents [tri-n-butyl phosphate (TnBP) and Triton X-100] used in the virus inactivation procedure are expected since the residual levels are less than 5μg/ml.
Clinical Studies
Thrombin human was compared with bovine thrombin in a phase III multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blinded study of 305 subjects at 22 centers in the US. Subjects undergoing elective cardiovascular, neurologic (spinal) or general surgical procedures were randomized (stratified by surgical specialty) when there was oozing or bleeding of mild intensity that could not be controlled by other surgical techniques and the surgeon determined that a topical hemostatic agent was necessary. Bovine thrombin and thrombine human were applied with SURGIFOAM* Absorbable Gelatin Sponge, USP.
Treatment with thrombine human was as successful as treatment with bovine thrombin in achieving the primary efficacy endpoint: hemostasis within 10 minutes of product application and secondary efficacy endpoints: hemostasis within 6 and 3 minutes of product application.
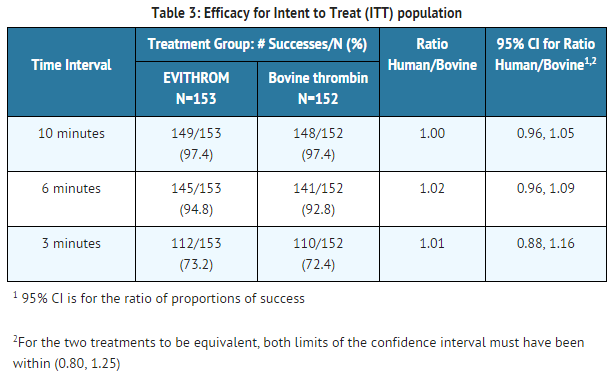
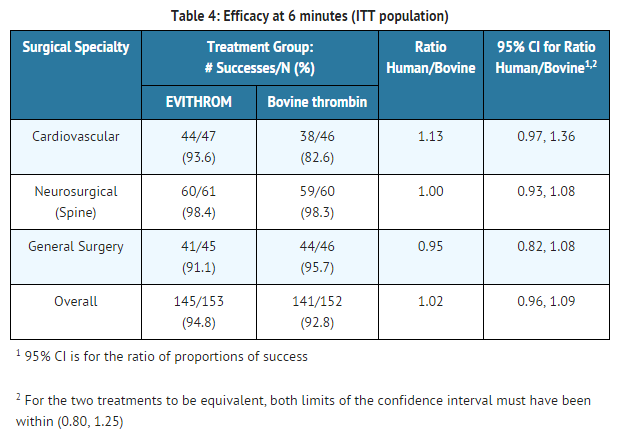
At the 6 minute and 10 minute time points, >90% of subjects from all surgeries in both study groups had achieved hemostasis. The following results were documented for the 3 minute time point as stratified by surgery and study treatment:
- Cardiovascular surgery- human thrombin: 61.7%; bovine thrombin: 63.0%
- Spinal surgery- human thrombin: 83.6%; bovine thrombin: 80.0%
- General surgery- human thrombin: 71.1%; bovine thrombin: 71.7%. for an overall ratio of proportions of 1.01.
How Supplied
- 2 ml vial containing 2000 (1600-2400) units of lyophilized human thrombin powder for reconstitution in 2 ml Water for Injection, USP.
Storage
- At 2- 25°C (36-77°F) for up to 2 years
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Thrombin human |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Thrombin human |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Some viruses such as hepatitis A virus and parvovirus B19 are particularly difficult to remove or inactivate. Parvovirus B19 most seriously affects pregnant women or immune-compromised individuals. Symptoms of parvovirus B19 infection include: fever, drowsiness, chills and runny nose followed about two weeks later by a rash and joint pain. Evidence of hepatitis A may include several days to weeks of poor appetite, fatigue and low-grade fever followed by nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Dark urine and a yellowed complexion are also common symptoms. Consult your physician if such symptoms appear.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Thrombin human interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Evithrom [1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Thrombin human Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Thrombin human |Label Name=Thrombin_human_2000_units.jpg
}}