Phentolamine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Phentolamine is a vasodilator and alpha-adrenergic blocker that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of reversal of the soft-tissue anesthesia. Common adverse reactions include injection site pain, diarrhea, and nasal congestion.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Reversal of the Soft-Tissue Anesthesia
- OraVerse is indicated for reversal of the soft-tissue anesthesia, i.e., anesthesia of the lip and tongue, and the associated functional deficits resulting from an intraoral submucosal injection of a local anesthetic containing a vasoconstrictor. OraVerse is not recommended for use in children less than 6 years of age or weighing less than 15 kg (33 lbs).
- Dosing Information
- The recommended dose of OraVerse is based on the number of cartridges of local anesthetic with vasoconstrictor administered:
- OraVerse should be administered following the dental procedure using the same location(s) and technique(s) (infiltration or block injection) employed for the administration of the local anesthetic.
- Note: Do not administer OraVerse if the product is discolored or contains particulate matter.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Phentolamine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Hypertension
- Dosing Information
- Intravenous phentolamine 5 to 20 milligrams is effective for treating hypertensive crises induced by high levels of circulating catecholamines. conditions which phentolamine may by effective for include pheochromocytoma, clonidine withdrawal, and monoamine oxidase inhibitor interactions.[1]
Sympathetically Maintained Pain
- Phentolamine (1 to 10 milligrams, increasing at 3- to 8-minute intervals up to 25 milligrams) is effective for determining if pain is sympathetically maintained.[2]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Reversal of the Soft-Tissue Anesthesia
- Dosing Information
- In pediatric patients weighing 15-30 kg, the maximum dose of OraVerse recommended is 1/2 cartridge (0.2 mg).
- Note: Use in pediatric patients under 6 years of age or weighing less than 15 kg (33 lbs) is not recommended. A dose of more than 1 cartridge [0.4 mg] of OraVerse has not been studied in children less than 12 years of age.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Phentolamine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Phentolamine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- None (phentolamine mesylate solution for submucosal use)
Warnings
- Cardiovascular Events
- Myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular spasm, and cerebrovascular occlusion have been reported to occur following the parenteral administration of phentolamine. These events usually occurred in association with marked hypotensive episodes producing shock-like states.
- Tachycardia and cardiac arrhythmias may occur with the use of phentolamine or other alpha-adrenergic blocking agents. Although such effects are uncommon after administration of OraVerse, clinicians should be alert to the signs and symptoms of these events, particularly in patients with a prior history of cardiovascular disease.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- In clinical trials, the most common adverse reaction with OraVerse that was greater than the control group was injection site pain.
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- Dental patients were administered a dose of either 0.2, 0.4 or 0.8 mg of OraVerse. The majority of adverse reactions were mild and resolved within 48 hours. There were no serious adverse reactions and no discontinuations due to adverse reactions.
- Table 1 lists adverse reactions where the frequency was greater than or equal to 3% in any OraVerse dose group and was equal to or exceeded that of the control group.
- An examination of population subgroups did not reveal a differential adverse reaction incidence on the basis of age, gender, or race.
- Results from the pain assessments in Study 1 and Study 2, involving mandibular and maxillary procedures, respectively, indicated that the majority of dental patients in both OraVerse and control groups experienced no or mild oral pain, with less than 10% of patients in each group reporting moderate oral pain with a similar distribution between the OraVerse and control groups. No patient experienced severe pain in these studies.
- Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials
- Adverse reactions reported by less than 3% but at least 2 dental patients receiving OraVerse and occurring at a greater incidence than those receiving control, included diarrhea, facial swelling, increased blood pressure/hypertension, injection site reactions, jaw pain, oral pain, paresthesia, pruritus, tenderness, upper abdominal pain and vomiting. The majority of these adverse reactions were mild and resolved within 48 hours. The few reports of paresthesia were mild and transient and resolved during the same time period.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval parenteral use of phentolamine mesylate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Acute and prolonged hypotensive episodes and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported with the use of phentolamine. In addition, weakness, dizziness, flushing, orthostatic hypotension, and nasal stuffiness have occurred.
Drug Interactions
- Lidocaine and Epinephrine
- When OraVerse was administered as an intraoral submucosal injection 30 minutes after injection of a local anesthetic, 2% lidocaine HCl with 1:100,000 epinephrine, the lidocaine concentration increased immediately after OraVerse intraoral injection. Lidocaine AUC and Cmax values were not affected by administration of OraVerse. OraVerse administration did not affect the PK of epinephrine.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. OraVerse should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Oral administration of phentolamine to pregnant rats and mice at doses at least 24 times the recommended dose (based on a 60 kg human) resulted in slightly decreased growth and slight skeletal immaturity of the fetuses. Immaturity was manifested by increased incidence of incomplete or unossified calcaneal and phalangeal nuclei of the hind limb and of incompletely ossified sternebrae. At oral phentolamine doses at least 60 times the recommended dose (based on a 60 kg human), a slightly lower rate of implantation was found in the rat. Phentolamine did not affect embryonic or fetal development in the rabbit at oral doses at least 20 times the recommended dose (based on a 60 kg human). No teratogenic or embryotoxic effects were observed in the rat, mouse, or rabbit studies.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Phentolamine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Phentolamine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether OraVerse is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when OraVerse is administered to a nursing woman. The unknown risks of limited infant exposure to phentolamine through breast milk following a single maternal dose should be weighed against the known benefits of breastfeeding.
Pediatric Use
- In clinical studies, pediatric patients between the ages of 3 and 17 years received OraVerse. The safety and effectiveness of OraVerse have been established in the age group 6-17 years. Effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 6 years has not been established. Use of OraVerse in patients between the ages of 6 and 17 years old is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of OraVerse in adults, with additional adequate and well-controlled studies of OraVerse in pediatric patients ages 12-17 years old [Studies 1 (mandibular procedures) and 2 (maxillary procedures)] and ages 6-11 years old [Study 3 (mandibular and maxillary procedures)]. The safety, but not the efficacy, of OraVerse has been evaluated in pediatric patients under the age of 6 years old. Dosages in pediatric patients may need to be limited based on body weight.
Geriatic Use
- Of the total number of patients in clinical studies of OraVerse, 55 were 65 and over, while 21 were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Phentolamine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Phentolamine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Phentolamine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Phentolamine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Phentolamine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Phentolamine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Submucosal use
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Phentolamine in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Phentolamine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- No deaths due to acute poisoning with phentolamine have been reported.
- Overdosage with parenterally administered phentolamine is characterized chiefly by cardiovascular disturbances, such as arrhythmias, tachycardia, hypotension, and possibly shock. In addition, the following might occur: excitation, headache, sweating, pupillary contraction, visual disturbances, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or hypoglycemia.
Management
- There is no specific antidote; treatment consists of appropriate monitoring and supportive care. Substantial decreases in blood pressure or other evidence of shock-like conditions should be treated vigorously and promptly.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Phentolamine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
| |
| |
Phentolamine
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
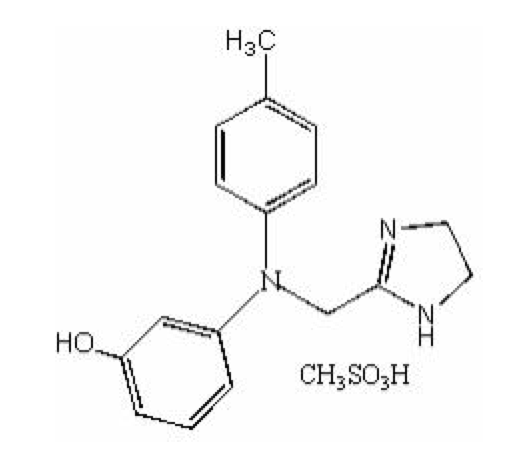
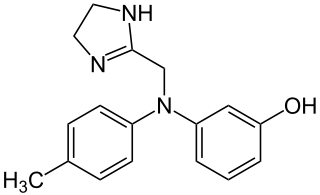
| 3-[(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylmethyl)(4-methylphenyl)amino]phenol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C04 V03AB36 (WHO) |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 281.352 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half life | 19 minutes |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C (U.S.) |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Usually IV or IM |
Mechanism of Action
- The mechanism by which OraVerse accelerates reversal of soft-tissue anesthesia and the associated functional deficits is not fully understood. Phentolamine mesylate, the active ingredient in OraVerse, produces an alpha-adrenergic block of relatively short duration resulting in vasodilatation when applied to vascular smooth muscle. In an animal model, OraVerse increased local blood flow in submucosal tissue of the dog when given after an intraoral injection of lidocaine 2% with 1:100,000 epinephrine.
Structure
- Phentolamine mesylate USP is a white to off-white, odorless crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 377.46. It is sparingly soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in chloroform. The empirical formulation is C 17H19N3O•CH4O3S, and the chemical structure is:
- OraVerse (phentolamine mesylate) Injection is a clear, colorless, sterile, non pyrogenic, isotonic, preservative free solution. Each 1.7 mL cartridge contains 0.4 mg phentolamine mesylate, D-mannitol, edetate disodium, and sodium acetate. Either acetic acid or sodium hydroxide is used as necessary to adjust the pH.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Phentolamine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- Following OraVerse administration, phentolamine is 100% available from the submucosal injection site and peak concentrations are achieved 10-20 minutes after injection. Phentolamine systemic exposure increased linearly after 0.8 mg compared to 0.4 mg OraVerse intraoral submucosal injection. The terminal elimination half-life of phentolamine in the blood was approximately 2-3 hours.
- Pediatrics
- Following OraVerse administration, the phentolamine Cmax was higher (approximately 3.5-fold) in children who weighed between 15 and 30 kg (33 and 66 lbs) than in children who weighed more than 30 kg. However, phentolamine AUC was similar between the two groups. It is recommended that in children weighing 15-30 kg, the maximum dose of OraVerse should be limited to ½ cartridge (0.2 mg).
- The pharmacokinetics of OraVerse in adults and in children who weighed more than 30 kg (66 lbs) are similar after intraoral submucosal injection.
- OraVerse has not been studied in children under 3 years of age or weighing less than 15 kg (33 lbs). The pharmacokinetics of OraVerse after administration of more than 1 cartridge (0.4mg) has not been studied in children.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Carcinogenicity studies with OraVerse have not been conducted.
- Phentolamine was not mutagenic in the in-vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay. In the in-vitro chromosomal aberration study in Chinese hamster ovary cells, numerical aberrations were slightly increased after a 4-hour exposure to phentolamine without metabolic activation and structural aberrations were slightly increased after a 4-hour exposure to phentolamine with metabolic activation only at the highest concentrations tested, but neither numerical nor structural aberrations were increased after a 20-hour exposure without metabolic activation. Phentolamine was not clastogenic in two in-vivo mouse micronucleus assays. At doses up to 150 mg/kg (143 times human therapeutic exposure levels at the Cmax), phentolamine mesylate was shown to have no adverse effects on male fertility in the rat.
Clinical Studies
- The safety and efficacy of OraVerse when used for reversal of soft-tissue anesthesia (STA), i.e., anesthesia of the lips and tongue following a dental procedure that required local anesthesia containing a vasoconstrictor, were evaluated in the following clinical studies. The efficacy of OraVerse on reversal of local anesthesia of the teeth, mandible and maxilla has not been assessed.
- Two Phase 3, double-blinded, randomized, multi-center, controlled studies were conducted in dental patients who had mandibular (Study 1) or maxillary (Study 2) restorative or periodontal maintenance procedures and who had received a local anesthetic that contained a vasoconstrictor. The primary endpoint was time to normal lip sensation as measured by patient reported responses to lip palpation. The secondary endpoints included patients’ perception of altered function, sensation and appearance, and their actual functional deficits in smiling, speaking, drinking and drooling, as assessed by both the patient and an observer blinded to the treatment. In the mandibular study, the time to recovery of tongue sensation was also a secondary endpoint. Patients were stratified by type and amount of anesthetic administered. OraVerse was administered at a cartridge ratio of 1:1 to local anesthetic. The control was a sham injection.
- OraVerse reduced the median time to recovery of normal sensation in the lower lip by 85 minutes (55%) compared to control. The median time to recovery of normal sensation in the upper lip was reduced by 83 minutes (62%). The differences between these times for both studies are depicted in Kaplan-Meier plots for time to normal lip sensation in Figures 1 and 2. Within 1 hour after administration of OraVerse, 41% of patients reported normal lower lip sensation as compared to 7% in the control group, and 59% of patients in the OraVerse group reported normal upper lip sensation as compared to 12% in the control group.
- In Study 1 (mandibular), OraVerse accelerated: a) the recovery of the perception of normal appearance and function by 60 minutes (40%), b) the recovery of normal function by 60 (50%) minutes, and c) the recovery of normal sensation in the tongue by 65 minutes (52%). In Study 2 (maxillary), the recovery of the perception of normal appearance and function was reduced by 60 minutes (50%) and the recovery of normal function was reduced by 45 minutes (43%).
- Study 3, a pediatric, Phase 2, double-blinded, randomized, multi-center, controlled study was conducted in dental patients who had received 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine. Dental patients (n=152, ages 4-11 years) received 1/2 cartridge of local anesthetic if they weighed ≥15 kg but <30 kg, and one-half or one full cartridge if they weighed ≥30 kg at a cartridge ratio of 1:1 to local anesthetic.
- The median time to normal lip sensation in patients 6 to 11 years of age who were trainable in the lip-palpation procedures, for mandibular and maxillary procedures combined, was reduced by 75 minutes (56%). Within 1 hour after administration of OraVerse, 44 patients (61%) reported normal lip sensation, while only 9 patients (21%) randomized to the control group reported normal lip sensation. In this study, neither the patients’ perception of their appearance or ability to function nor their actual ability to function was evaluated.
How Supplied
- OraVerse (phentolamine mesylate) Injection 0.4 mg/1.7 mL is supplied in a dental cartridge, in cartons of 10 and 50 cartridges. Each cartridge is individually packaged in a separate compartment of a 10 cartridge blister pack.
- NDC 1500-0101-01
- NDC 1500-0101-02
- Store at controlled room temperature, 20-25C (68-77F) with brief excursions permitted between 15-30C (59-86F).
- Protect from direct heat and light. Do not permit to freeze.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Phentolamine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Phentolamine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Phentolamine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Phentolamine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Phentolamine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Regitine®
- Oraverse®[3]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- N/A[4]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Kincaid-Smith, P. (1985-04-15). "Vasodilator drugs in the treatment of hypertension". The Medical Journal of Australia. 142 (8): 450–453. ISSN 0025-729X. PMID 3884988.
- ↑ Raja, S. N. (1991-04). "Systemic alpha-adrenergic blockade with phentolamine: a diagnostic test for sympathetically maintained pain". Anesthesiology. 74 (4): 691–698. ISSN 0003-3022. PMID 1848966. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ "Oraverse (phentolamine mesylate)".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Phentolamine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Phentolamine |Label Name=Phentolamine05.png
}}