Pericarditis in malignancy pathophysiology
|
Pericarditis in malignancy Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Pericarditis in malignancy from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Case Studies |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.; Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan, M.B.B.S.
Overview
The pericardium may be involved by direct local spread from neoplasms such as breast and lung carcinomas or by metastatic spread via blood stream and lymphatics as in melanomas, lymphomas and leukemias.
Pericardial effusion in such situations may occur either secondary to pericardial inflammation or obstruction of lymphatic drainage by enlarged mediastinal nodes.[1][2][3]
Pathophysiology
Gross Pathology
-
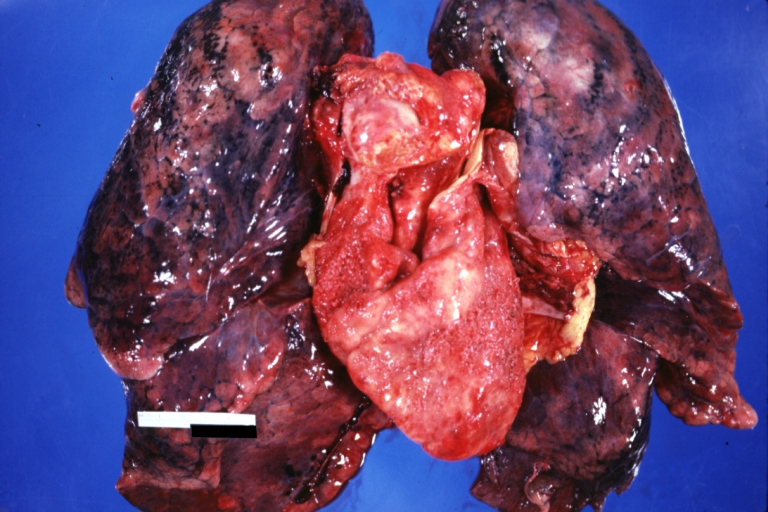
Neoplastic pericarditis: Gross, natural color, shaggy pericarditis. Primer is adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Microscopic Pathology
-
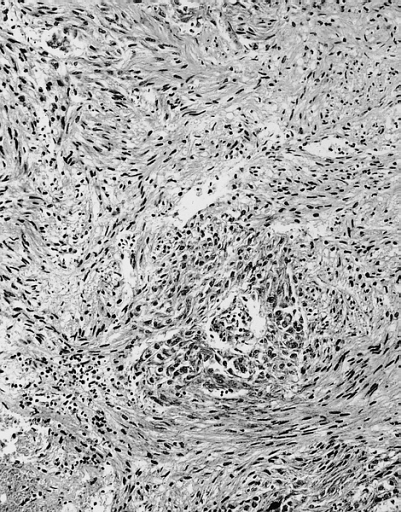
Malignant Mesothelioma, Biphasic Type: Pericardium: This tumor has epithelioid cells (lower half) surrounded by spindled cells. The patient was a 46-year-old woman with constrictive pericarditis; the pericardium was studded with coalescing tumor nodules.
References
- ↑ Maisch B, Seferović PM, Ristić AD, Erbel R, Rienmüller R, Adler Y; et al. (2004). "Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases executive summary; The Task force on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases of the European society of cardiology". Eur Heart J. 25 (7): 587–610. doi:10.1016/j.ehj.2004.02.002. PMID 15120056.
- ↑ Ben-Horin S, Bank I, Guetta V, Livneh A (2006). "Large symptomatic pericardial effusion as the presentation of unrecognized cancer: a study in 173 consecutive patients undergoing pericardiocentesis". Medicine (Baltimore). 85 (1): 49–53. doi:10.1097/01.md.0000199556.69588.8e. PMID 16523053.
- ↑ Imazio M, Demichelis B, Parrini I, Favro E, Beqaraj F, Cecchi E; et al. (2005). "Relation of acute pericardial disease to malignancy". Am J Cardiol. 95 (11): 1393–4. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.01.094. PMID 15904655.