Neuroendocrine tumors other imaging findings
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
Neuroendocrine tumors Microchapters |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Other Imaging Findings
Octreoscan
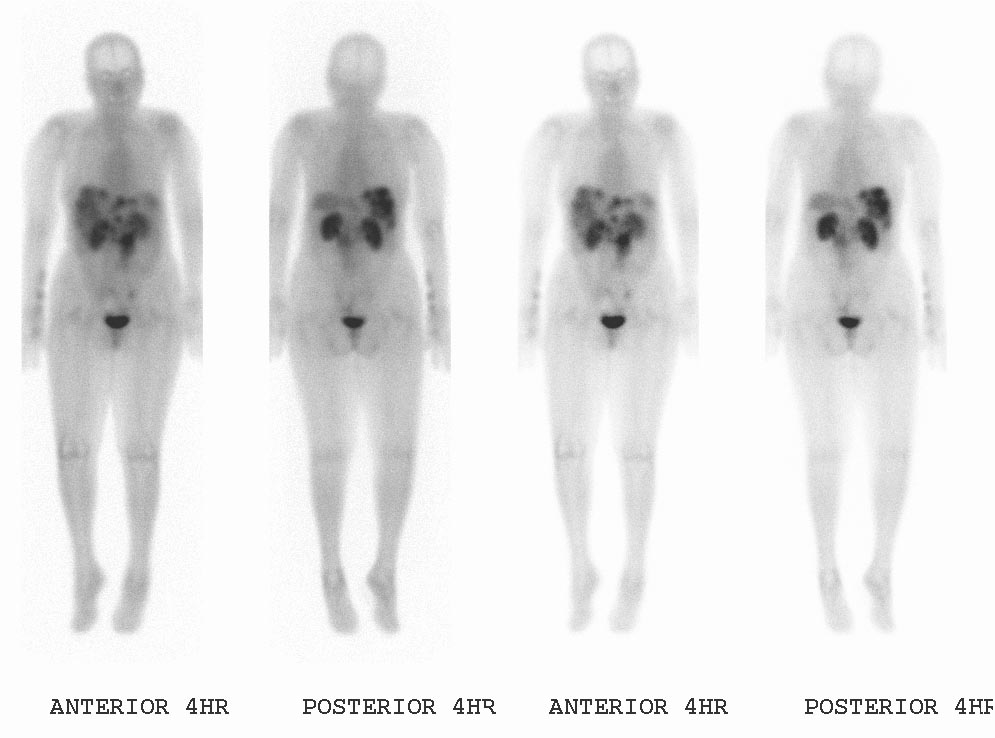
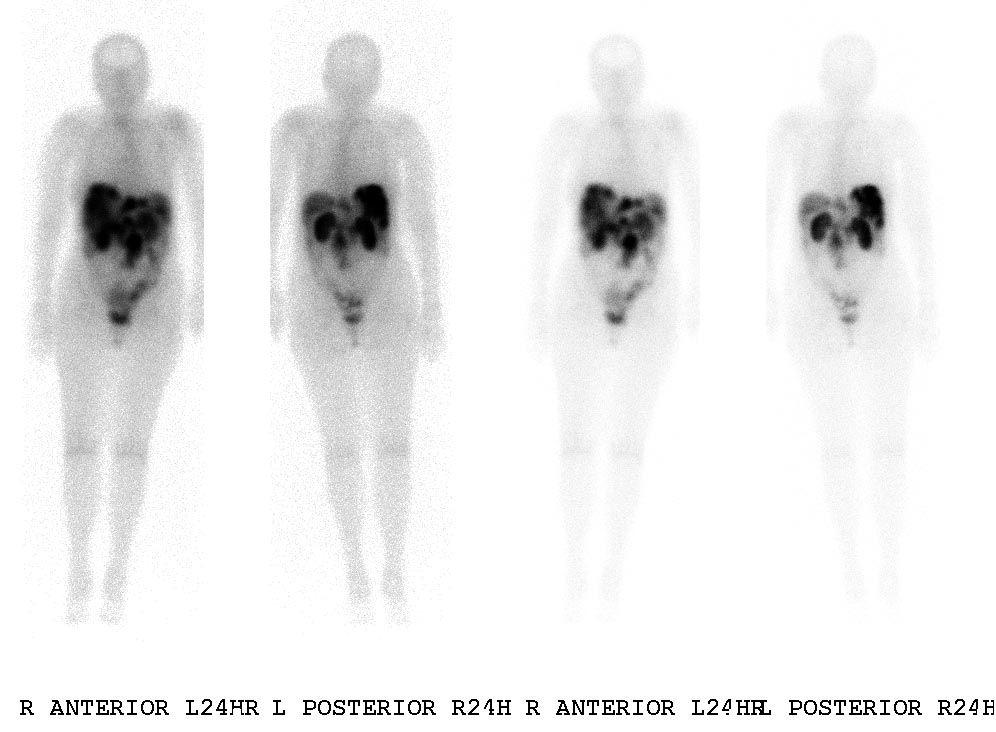
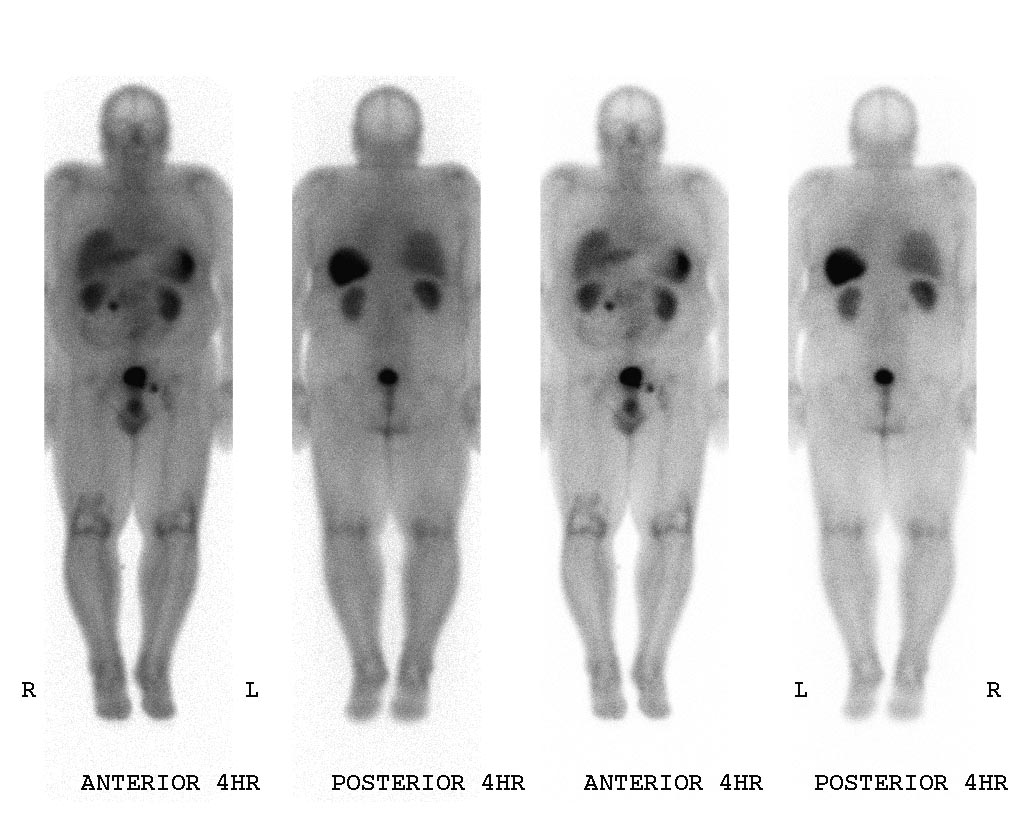
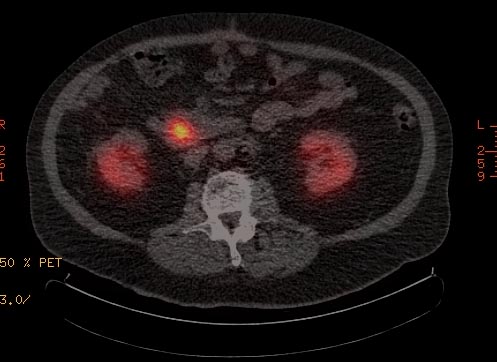
The diagnostic procedure that utilizes a somatostatin analog is the OctreoScan, also called somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS or SSRS): a patient is injected with octreotide chemically bound to a radioactive substance, often indium-111; for those patients whose tumor cells are avid for octreotide, a radiation-sensitive scan can then indicate the locations of the larger lesions.
An OctreoScan is a relatively crude test that generates subjective results.