Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Turky Alkathery, M.D. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) is an an amide local anesthetic that is FDA approved for the procedure of localized anesthesia in periodontal pockets during scaling and/or root planing. Common adverse reactions include application site reactions including pain, soreness, irritation, numbness, ulcerations, vesicles, edema, abscess and/or redness.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine is an amide local anesthetic indicated for adults who require localized anesthesia in periodontal pockets during scaling and/or root planing.
Dosage
General Dosing Information
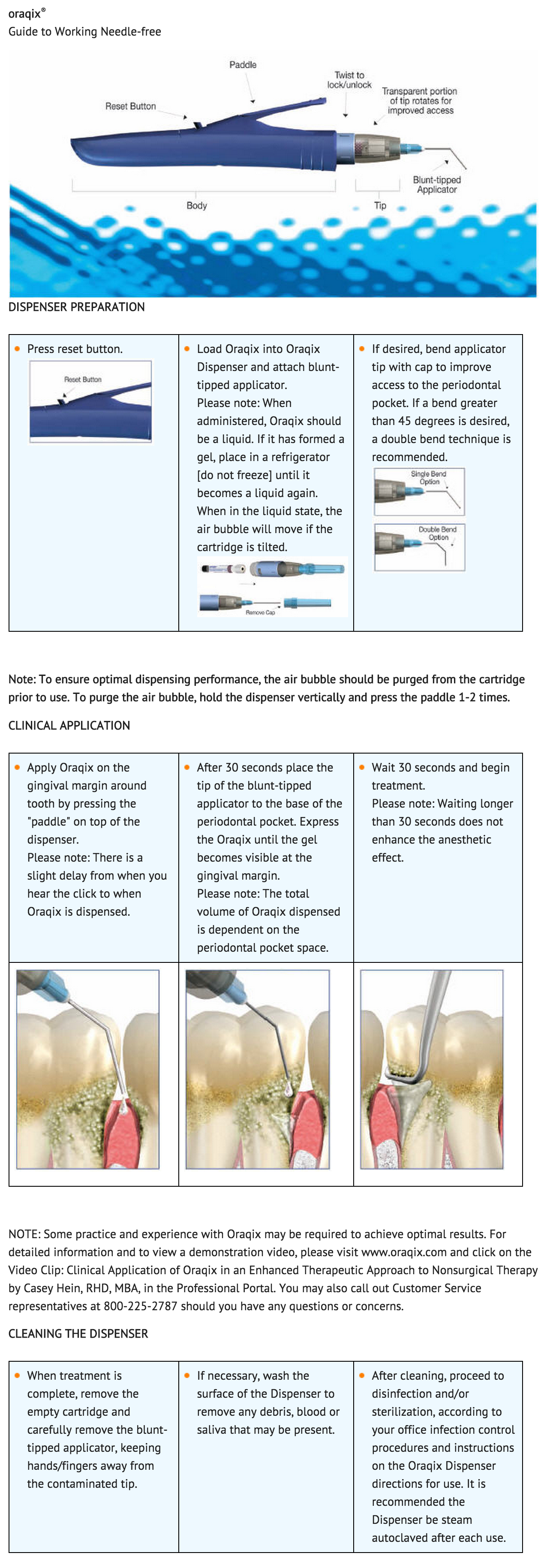
- Apply Lidocaine/Prilocaine on the gingival margin around the selected teeth using the blunt-tipped applicator included in the package. Wait 30 seconds, and then fill the periodontal pockets with Lidocaine/Prilocaine using the blunt-tipped applicator until the gel becomes visible at the gingival margin. Wait another 30 seconds before starting treatment. A longer waiting time does not enhance the anesthesia. Anesthetic effect, as assessed by probing of pocket depths, has a duration of approximately 20 minutes (individual overall range 14 – 31 minutes). If the anesthesia starts to wear off, Lidocaine/Prilocaine may be re-applied if needed.
- Typically, 1 cartridge (1.7g) or less of Lidocaine/Prilocaine will be sufficient for one quadrant of the dentition.
- When administered, Lidocaine/Prilocaine should be a liquid. If it has formed a gel, it should be placed in a refrigerator (do not freeze) until it becomes a liquid again. When in the liquid state, the air bubble visible in the cartridge will move if the cartridge is tilted.
Maximum Recommended Dosage
- The maximum recommended dose of Lidocaine/Prilocaine at one treatment session is 5 cartridges, i.e., 8.5g gel.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine is contraindicated in patients with a known history of hypersensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type or to any other component of the product.
Warnings
Methemoglobinemia
- Prilocaine in Lidocaine/Prilocaine can cause elevated methemoglobin levels particularly in conjunction with methemoglobin-inducing agents. Methemoglobinemia has also been reported in a few cases in association with lidocaine treatment. Patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency or congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia are more susceptible to drug-induced methemoglobinemia. Lidocaine/Prilocaine should not be used in those patients with congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia and in infants under the age of twelve months who are receiving treatment with methemoglobin-inducing agents. Signs and symptoms of methemoglobinemia may be delayed some hours after exposure. Initial signs and symptoms of methemoglobinemia are characterized by a slate grey cyanosis seen in, e.g., buccal mucous membranes, lips and nail beds. In severe cases symptoms may include central cyanosis, headache, lethargy, dizziness, fatigue, syncope, dyspnea, CNS depression, seizures, dysrhythmia and shock. Methemoglobinemia should be considered if central cyanosis unresponsive to oxygen therapy occurs, especially if metHb-inducing agents have been used. Calculated oxygen saturation and pulse oximetry are inaccurate in the setting of methemoglobinemia. The diagnosis can be confirmed by an elevated methemoglobin level measured with co-oximetry. Normally, metHb levels are <1%, and cyanosis may not be evident until a level of at least 10% is present. The development of methemoglobinemia is generally dose related. The individual maximum level of metHb in blood ranged from 0.8% to 1.7% following administration of the maximum dose of 8.5g Lidocaine/Prilocaine.
- Management of methemoglobinemia: Clinically significant symptoms of methemoglobinemia should be treated with a standard clinical regimen such as a slow intravenous infection of methylene blue at a dosage of 1to 2 mg/kg given over a five minute period.
- Patients taking drugs associated with drug-induced methemoglobinemia such as sulfonamides, acetaminophen, acetanilide, aniline dyes, benzocaine, chloroquine, dapsone, naphthalene, nitrates and nitrites, nitrofurantoin, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, pamaquine, para-aminosalicylic acid, phenacetin, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primaquine, and quinine are also at greater risk for developing methemoglobinemia. Treatment with Lidocaine/Prilocaine should be avoided in patients with any of the above conditions or with a previous history of problems in connection with prilocaine treatment.
Do Not Inject
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine should not be used with standard dental syringes. Only use this product with the Lidocaine/Prilocaine blunt-tipped applicator, which is available from DENTSPLY Pharmaceutical.
Allergic/anaphylactic reactions
- Allergic and anaphylactic reactions associated with lidocaine or prilocaine in Lidocaine/Prilocaine can occur. These reactions may be characterized by urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm, and shock. If these reactions occur they should be managed by conventional means.
Avoid Contact with Eyes
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine coming in contact with the eye should be avoided because animal studies have demonstrated severe eye irritation. A loss of protective reflexes may allow corneal irritation and potential abrasion. If eye contact occurs, immediately rinse the eye with water or saline and protect it until normal sensation returns. In addition, the patient should be evaluated by an ophthalmologist, as indicated.
History of Drug Sensitivity
- Patients allergic to paraminobenzoic acid derivatives (procaine, tetracaine, benzocaine, etc.) have not shown cross sensitivity to lidocaine and/or prilocaine. However, Lidocaine/Prilocaine should be used with caution in patients with a history of drug sensitivities, especially if the etiologic agent is uncertain.
Severe Hepatic Disease
- Patients with severe hepatic disease, because of their inability to metabolize local anesthetics normally, are at greater risk of developing toxic plasma concentrations of lidocaine and prilocaine.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- Although no major differences in adverse events between Lidocaine/Prilocaine and placebo-treated subjects were observed, all patients in the placebo-controlled studies received either Lidocaine/Prilocaine or a placebo gel (consisting of the vehicle in Lidocaine/Prilocaine without lidocaine or prilocaine). Therefore, it is not possible to determine if adverse events in each treatment group were attributable to the inactive ingredients comprising the Lidocaine/Prilocaine or vehicle or if adverse event rates were higher than expected background rates. Therefore, a causal relationship between the reported adverse reactions and Lidocaine/Prilocaine could neither be established nor ruled out.
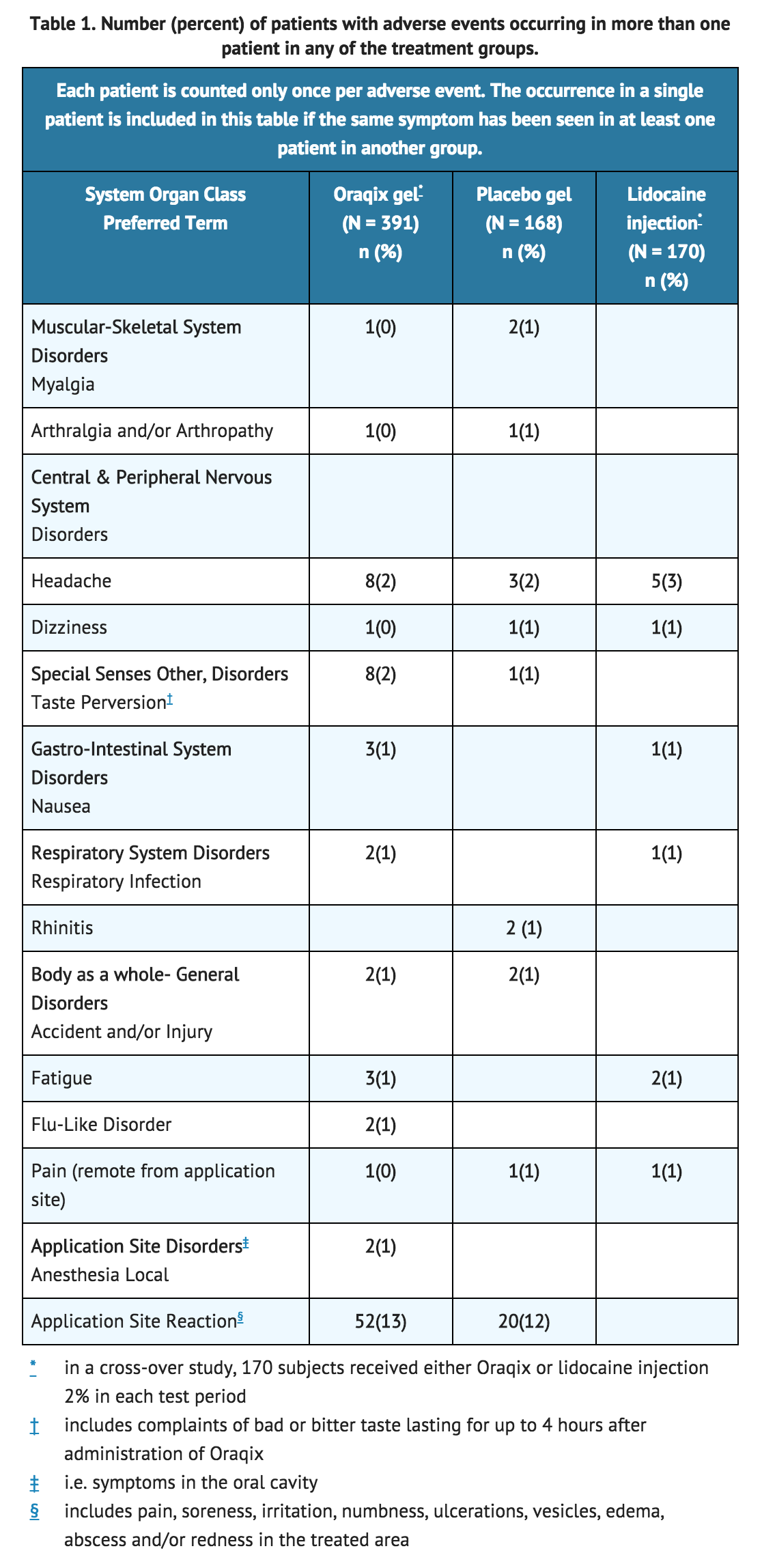
- Following SRP treatment with Lidocaine/Prilocaine in 391 patients, the most frequent adverse events were local reactions in the oral cavity (see following TABLE). These events, which occurred in approximately 15% of patients, included pain, soreness, irritation, numbness, vesicles, ulcerations, edema and/or redness in the treated area. Of the 391 patients treated with Lidocaine/Prilocaine, five developed ulcerative lesions and two developed vesicles of mild to moderate severity near the site of SRP. In addition, ulcerative lesions in or near the treated area were also reported for three out of 168 patients who received placebo. Other symptoms reported in more than one patient were headache, taste perversion, nausea, fatigue, flu, respiratory infection, musculoskeletal pain and accident/injury.
Postmarketing Experience
- There is limited information regarding postmarketing experience.
Drug Interactions
Other Local Anesthetics or Agents Structurally Related to Local Anesthetics
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine should be used with caution in combination with dental injection anesthesia, other local anesthetics, or agents structurally related to local anesthetics, e.g., Class 1 antiarrhythmics such as tocainide and mexiletine, as the toxic effects of these drugs are likely to be additive and potentially synergistic.
Drugs inducing Methemoglobinemia
- Patients taking drugs associated with drug-induced methemoglobinemia such as sulfonamides, acetaminophen, acetanilide, aniline dyes, benzocaine, chloroquine, dapsone, naphthalene, nitrates and nitrites, nitrofurantoin, nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, pamaquine, para-aminosalicylic acid, phenacetin, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primaquine, and quinine are also at greater risk for developing methemoglobinemia.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Reproduction studies have been performed in rats with lidocaine, prilocaine and a 1:1 (weight:weight) mixture of the two compounds. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus at subcutaneous doses of up to 30 mg/kg lidocaine (estimated exposure was approximately equivalent to the expected lidocaine exposure at the maximum recommended human dose of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (lidocaine and prilocaine periodontal gel) 2.5% / 2.5% on a mg/m2 basis). Following intramuscular prilocaine doses of up to 300 mg/kg (estimated exposure was approximately 11 times the expected prilocaine exposure at the maximum recommended human dose of Lidocaine/Prilocaine gel on a mg/m2 basis), there was no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus. Similarly, subcutaneous administration of a lidocaine and prilocaine mixture of 40 mg/kg of each compound (estimated exposures were approximately 1.5 times the expected lidocaine and prilocaine exposures at the maximum recommended human dose of Lidocaine/Prilocaine gel on a mg/m2 basis) produced no teratogenic, embryotoxic, or fetotoxic effects. Reproductive toxicology studies of lidocaine were also conducted in rabbits. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus at a dose of 5 mg/kg, s.c. (60 mg/m2). Treatment of rabbits with 15 mg/kg (180 mg/m2) produced evidence of maternal toxicity and evidence of delayed fetal development, including a non-significant decrease in fetal weight (7%) and an increase in minor skeletal anomalies (skull and sternebral defects, reduced ossification of the phalanges). The effects of lidocaine and prilocaine on post-natal development was examined in rats treated for 8 months with 10 or 30 mg/kg, s.c. lidocaine or prilocaine (60mg/m2 and 180 mg/m2 on a body surface area basis, respectively up to 1.4-fold the maximum recommended exposure for a single procedure). This time period encompassed 3 mating periods. There was no evidence of altered post-natal development in any offspring; however, both doses of either drug reduced the average number of pups per litter surviving until weaning of offspring from the first 2 mating periods. In a separate study, the effect of prilocaine on pre- and postnatal development was examined in rats treated with up to 60 mg/kg, s.c. (up to 2.8 times the maximum recommended human dose of prilocaine in Lidocaine/Prilocaine gel on a mg/m2 basis) from Day 6 of gestation to weaning. There was no evidence of altered post-natal development, viability, or reproductive capacity in any offspring. All the above calculations of exposure are assuming 100% bioavailability of lidocaine and prilocaine after Lidocaine/Prilocaine administration. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Lidocaine/Prilocaine should be used during pregnancy only if the benefits outweigh the risks.
- Reproduction studies on the Lidocaine/Prilocaine drug product, including the inactive ingredients, have not been conducted.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Lidocaine and, possibly, prilocaine are excreted in breast milk. Caution should be exercised when Lidocaine/Prilocaine is administered to nursing women.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Very young children are more susceptible to methemoglobinemia. There have been reports of clinically significant methemoglobinemia in infants and children following excessive applications of lidocaine 2.5% topical cream.
Geriatic Use
- Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of Lidocaine/Prilocaine, 7% were aged 65 and over, while 1% were aged 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
- Dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Periodontal.
Monitoring
- There is limited information regarding drug monitoring.
IV Compatibility
- There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility.
Overdosage
Lidocaine/Prilocaine Local anesthetic toxicity emergency
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine used at the recommended doses is not likely to cause toxic plasma levels of lidocaine or prilocaine. However, if other local anesthetics are administered at the same time, e.g. topically or by injection, the toxic effects are thought to be additive and could result in an overdose with systemic toxic reactions. There is generally an increase in severity of symptoms with increasing plasma concentrations of lidocaine and/or prilocaine. Systemic CNS toxicity may occur over a range of plasma concentrations of local anesthetics. CNS toxicity may typically be found around 5000 ng/mL of lidocaine; however a small number of patients reportedly may show signs of toxicity at approximately 1000 ng/mL.
- Pharmacological thresholds for prilocaine are poorly defined. Central nervous system (CNS) symptoms usually precede cardiovascular manifestations. The plasma level of lidocaine observed after the maximum recommended dose (5 cartridges) of Lidocaine/Prilocaine in 11 patients exposed over 3 hours ranged from 157to 552 ng/mL with a mean of 284 ng/mL ± 122 SD. The corresponding figure for prilocaine was 53-181 ng/mL with a mean of 106 ± 45 SD.
- Systemic adverse effects of lidocaine and/or prilocaine are manifested by central nervous system and/or cardiovascular symptoms.
- Clinical symptoms of systemic toxicity include CNS excitation and/or depression (light-headedness, hyperacusis, visual disturbances, muscular tremors, and general convulsions). Lidocaine and/or prilocaine may cause decreases in cardiac output, total peripheral resistance and mean arterial pressure. These changes may be attributable to direct depressant effects of these local anesthetic agents on the cardiovascular system. Cardiovascular manifestations may include hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmia, and cardiovascular collapse.
Management of Lidocaine/Prilocaine Local Anesthetic Emergencies
- Should severe CNS or cardiovascular symptoms occur, these may be treated symptomatically by, for example, the administration of anticonvulsive drugs, respiratory support and/or cardiovascular resuscitation as necessary.
Methemoglobinemia
- For detailed information on methemoglobinemia causes, symptoms, and treatment, see WARNINGS.
- For additional information about overdose treatment, call a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
Pharmacology
Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival)
| |
| Combination of | |
| Lidocaine | anesthetic |
| Prilocaine | anesthetic |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- Lidocaine and prilocaine belong to the amide class of local anesthetics. Both lidocaine and prilocaine block sodium ion channels required for the initiation and conduction of neuronal impulses, resulting in local anesthesia.
Structure
- Lidocaine/Prilocaine 2.5%/2.5% is a microemulsion in which the oil phase is a eutectic mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine in a ratio of 1:1 by weight. This eutectic mixture has a melting point below room temperature; therefore, both local anesthetics exist as liquid oils rather than as crystals. Lidocaine/Prilocaine contains poloxamer excipients, which show reversible temperature-dependent gelation. Together with the lidocaine-prilocaine 1:1 mixture, the poloxamers form a low-viscosity fluid system at room temperature and an elastic gel in the periodontal pocket. Lidocaine/Prilocaine is administered into periodontal pockets, by means of the supplied special applicator. Gelation occurs at body temperature, followed by release of the local anesthetics, lidocaine and prilocaine. The Lidocaine/Prilocaine single-use glass cartridges deliver up to 1.7g (1.7mL) of gel (42.5 mg of lidocaine and 42.5 mg of prilocaine). Prilocaine base and lidocaine base are both relatively hydrophilic amino-amides.
- The structural formulas are:

- Lidocaine is chemically designated as 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-acetamide and has an octanol:water partition ratio of 43 at pH 7.4. The pKa of lidocaine is 7.86. Prilocaine is chemically designated as N-(2-methyl-phenyl)-2 (propylamino)-propanamide and has an octanol:water partition ratio of 25 at pH 7.4. The pKa of prilocaine is 7.89.
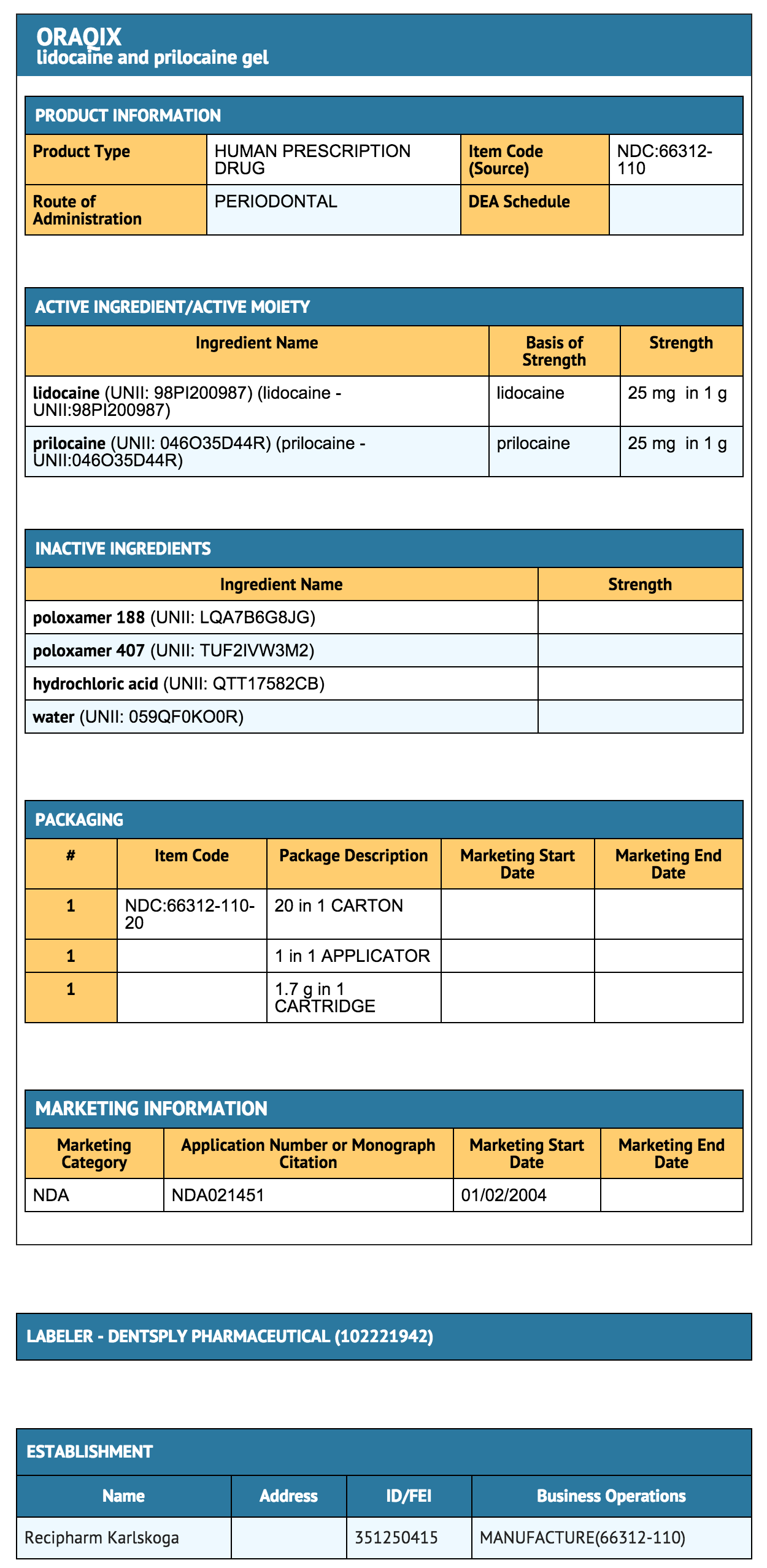
- Each gram of Lidocaine/Prilocaine contains 25-mg lidocaine base and 25-mg prilocaine base. The gel also contains thermosetting agents (poloxamer 188 purified, poloxamer 407 purified), hydrochloric acid (pH adjustment), and purified water. The pH of Lidocaine/Prilocaine is 7.5-8.0.
Pharmacodynamics
- After application of Lidocaine/Prilocaine on the gingival margin and a waiting period of 30 seconds, additional Lidocaine/Prilocaine is applied directly into periodontal pockets to provide localized anesthesia. The onset of local anesthetic effect after application of Lidocaine/Prilocaine into the periodontal pocket occurs by 30 seconds and a longer waiting time does not enhance the anesthetic affect. Anesthetic effect, as assessed by probing of pocket depths, lasted for about 20 minutes (individual overall range 14 to 31 minutes).
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Lidocaine and prilocaine are absorbed from Lidocaine/Prilocaine via the oral mucous membranes. After a single application of 0.9to 3.5 g Lidocaine/Prilocaine, the mean (±SD) lidocaine and prilocaine Cmax values were 182 (±53) and 77 (±27) ng/mL, respectively. After a total of 8 to 8.5 g Lidocaine/Prilocaine administered as repeated applications over 3 hours, the mean (±SD) lidocaine Cmax was 284 (±122) ng/mL, ranging between 157 and 552 ng/mL. The mean lidocaine AUC∞ was 84,000 ng.min/mL. The mean (±SD) prilocaine Cmax was 106 (±45) ng/mL, ranging between 53 and 181 ng/mL. The mean prilocaine AUC∞ was 26,000 ng.min/mL.
- The increase in Cmax of both lidocaine and prilocaine is proportional (or less than proportional) to the dose after single application of Lidocaine/Prilocaine. The Cmax after a cumulative dose of 8.5 g Lidocaine/Prilocaine administered as repeated applications over 3 hours, (i.e. the highest recommended dose, corresponding to 212.5 mg each of lidocaine and prilocaine base), is lower than that extrapolated from the proportional increase in plasma concentrations at lower doses.
- The median Tmax of lidocaine and prilocaine was 30 minutes, ranging between 20 and 40 min., after the start of a single application of 0.9 to 3.5 g Lidocaine/Prilocaine, and 200 minutes, ranging between 120 and 200 min., after a cumulative dose of 8.5g Lidocaine/Prilocaine administered as repeated applications over 3 hours.
- The toxicities of lidocaine and prilocaine are thought to be additive. Systemic CNS toxicity may occur over a range of plasma concentrations of local anesthetics. CNS toxicity may typically be found around 5000 ng/mL of lidocaine, however a small number of patients reportedly may show signs of toxicity at approximately 1000 ng/mL. Pharmacological thresholds for prilocaine are poorly defined.
- Distribution: Lidocaine and prilocaine have an intermediate degree of plasma protein binding, mainly to 1-acid glycoprotein, with a protein binding of 70% and 40%, respectively. When administered intravenously, the mean volume of distribution (for 60 kg person) at steady state for lidocaine and prilocaine were 90 L and 156 L, respectively. Lidocaine/Prilocaine is not intended for intravenous administration. Both lidocaine and prilocaine cross the placental and blood brain barriers, presumably by passive diffusion.
- Metabolism: Lidocaine and prilocaine are mainly metabolized in the liver. Prilocaine and lidocaine are not metabolized by plasma esterases.
- The main metabolism of lidocaine is through N-dealkylation to monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and glycinexylidide (GX), which is mainly mediated by CYP3A4. These metabolites are hydrolyzed to 2,6-xylidine, which is converted to 4-hydroxy-2,6-xylidine (mediated by CYP2A6), the major urinary metabolite in man. After a total of 8 to 8.5g Lidocaine/Prilocaine administered as repeated applications over 3 hours, the mean (+SD) 2,6-xylidine Cmax was 18 (+8.4) ng/mL ranging between 8 and 32 ng/mL. The mean 2,6-xylidine AUC∞ was 9800 ng.min/mL (±6370), ranging between 3480 to 24,580 ng/min/mL). MEGX has an antiarrhythmic and convulsant activity similar to that of lidocaine and a somewhat longer half-life. GX has a weak antiarrhythmic effect but lacks convulsant activity and has a half-life of about 10 h.
- Prilocaine is split at the amide linkage to o-toluidine, which is converted further to 4- and 6- hydroxytoluidine. The prilocaine metabolite o-toluidine and the hydroxylated metabolites of o-toluidine are excreted mainly in the urine. o-Toluidine has been shown to be carcinogenic in several animal models. After a total of 8 to 8.5g Lidocaine/Prilocaine was administered as repeated applications over 3 hours, the mean (±SD) o-toluidine Cmax was 25 (±11) ng/mL ranging between 13 and 44 ng/mL. The mean o-toluidine AUC∞ was 9200 ng.min/mL. The median Tmax was 220 minutes, ranging between 90 and 240 min. In addition, o-Toluidine can cause the formation of methemoglobin (metHb) following treatment with prilocaine. Individual maximum blood concentrations of metHb increased from 0 to 1.1% up to 0.8 to 1.7% following administration of the maximum recommended dose of 8.5g Lidocaine/Prilocaine administrated as repeated applications over 3 hours. The Tmax of metHb ranged from 1 to 4 hours. Normally, <1 % of the total hemoglobin is in the form of metHb. Patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiencies, and patients taking oxidizing drugs such as antimalarials and sulfonamides are more susceptible to drug-induced methemoglobinemia.
- Elimination: Lidocaine and prilocaine have systemic clearances of 0.95 and 2.37 L/min, respectively, after intravenous administration as single agents. The terminal half-life of both drugs after intravenous administration as single agents is 1.6 h. Lidocaine/Prilocaine is not intended for intravenous administration.
- However, after application of Lidocaine/Prilocaine to the periodontal pockets the mean (±SD) terminal lidocaine half-life was 3.6 (±1.3) hours, ranging between 2.2 and 6.5 h. The mean (±SD) terminal prilocaine half-life was 2.8 (±1.0) hours, ranging between 2.0 to 5.7 h. For the metabolite o-toluidine the mean terminal half-life was 4.0 (±1.1) hours, ranging between 2.0 and 5.7 hours. For the metabolite 2,6-xylidine the mean terminal half-life was 8.0 (±4.0) hours, ranging between 3.7 and 18.3 hours.
- Pediatrics: The pharmacokinetics of lidocaine and prilocaine after Lidocaine/Prilocaine administration have not been studied in pediatric patients.
- Geriatrics: The pharmacokinetics of lidocaine and prilocaine after Lidocaine/Prilocaine administration have not been studied in geriatric patients. However, intravenous studies, the elimination half-life of lidocaine was statistically significantly longer in elderly patients (2.5 hours) than in younger patients (1.5 hours). No studies in the intravenous pharmacokinetics of prilocaine in elderly patients have been performed.
- Special populations: No pharmacokinetic studies were conducted to specifically address special populations.
- Renal Impairment: Lidocaine and prilocaine and their metabolites are known to be excreted by the kidney, and the metabolites may accumulate in patients with impaired renal function.
- Hepatic Impairment: The half-life of lidocaine may be prolonged two-fold or more in patients with liver dysfunction. Liver dysfunction may also alter prilocaine pharmacokinetics. Because of their inability to metabolize local anesthetics normally, patients with severe hepatic disease, are at a greater risk of developing toxic plasma concentrations of lidocaine and prilocaine.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Carcinogenesis - Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of either lidocaine or prilocaine. Chronic oral toxicity studies of o-toluidine, a metabolite of prilocaine, have shown that this compound is a carcinogen in both mice and rats. The tumors associated with o-toluidine included hepatocarcinomas/ adenomas in female mice, multiple occurrences of hemangiosarcomas/hemangiomas in both sexes of mice, sarcomas of multiple organs, transitional-cell carcinomas/papillomas of urinary bladder in both sexes of rats, subcutaneous fibromas/fibrosarcomas and mesotheliomas in male rats, and mammary gland fibroadenomas/adenomas in female rats. These findings were observed at the lowest tested dose of 150 mg/kg/day or greater over two years (estimated daily exposures in mice and rats were approximately 6 and 12 times, respectively, the estimated exposure to o-toluidine at the maximum recommended human dose of 8.5g of Lidocaine/Prilocaine gel on a mg/m2 basis). Thus, the no effect dose is less than 6 to 12 times the estimated exposure to o-toluidine at the maximum recommended human dose, assuming 100% bioavailability of prilocaine from the Lidocaine/Prilocaine gel. Complete conversion of prilocaine to its metabolite o-toluidine on a molar basis is assumed. This gives a conversion on a weight basis of about 50% for prilocaine base (dependent on the molecular weights, i.e. 220 for prilocaine base and 107 for o-toluidine).
- Mutagenesis - The mutagenic potentials of lidocaine and prilocaine have been tested in the Ames Salmonella reverse mutation assay, an in vitro chromosome aberrations assay in human lymphocytes and in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. There was no indication of any mutagenic effects for either compound in these studies.
- o-Toluidine, metabolite of prilocaine, was positive in Escherichia coli DNA repair and phage-induction assays. Urine concentrates from rats treated orally with 300 mg/kg o-toluidine were mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium in the presence of metabolic activation. Several other tests on o-toluidine, including reverse mutations in five different Salmonella typhimurium strains with or without metabolic activation, and single strand breaks in DNA of V79 Chinese hamster cells, were negative.
- Impairment of Fertility: The effect of lidocaine on fertility was examined in the rat model. Administration of 30 mg/kg, s.c. (180 mg/m2 or 1.4 fold the maximum recommended human oral dose for one treatment session assuming 100% bioavailability of lidocaine) to the mating pair did not produce alterations in fertility or general reproductive performance of rats. There are no studies that examine the effect of lidocaine or prilocaine on sperm parameters. The effects of prilocaine on fertility was examined in rats treated for 8 months with 10 or 30 mg/kg, s.c. lidocaine or prilocaine (60 mg/m2 and 180 mg/m2 on a body surface area basis, respectively up to 1.4-fold the maximum recommended exposure for a single procedure assuming 100% bioavailability of lidocaine and prilocaine). This time period encompassed 3 mating periods. There was no evidence of altered fertility.
Clinical Studies
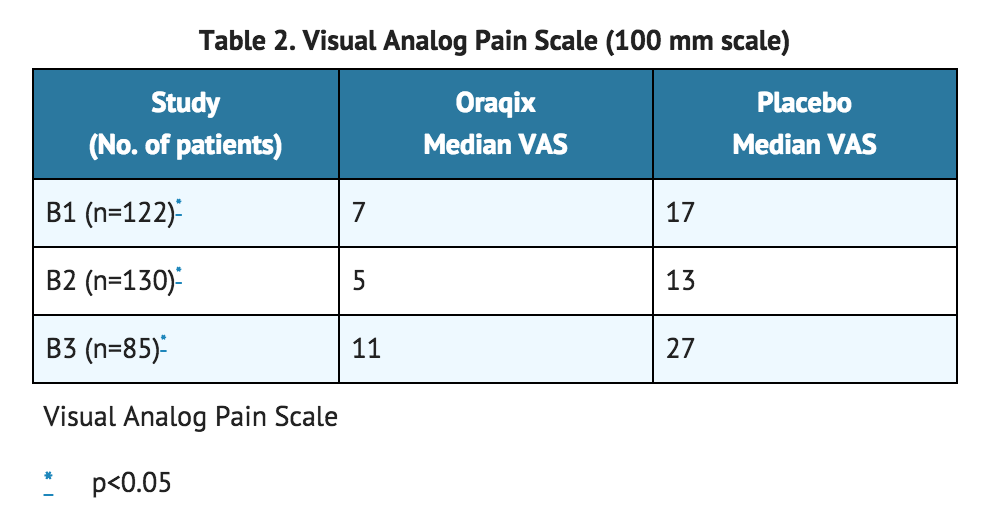
- A total of 337 patients (146 men and 191 women; 169 Lidocaine/Prilocaine and 168 placebo) were studied in three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Patients received a median dose of approximately 1 cartridge (1.7g gel), ranging from ¼ to 2½ cartridges per quadrant treated. The analgesic effect of Lidocaine/Prilocaine was assessed by asking patients to rate their pain on a continuous visual analog scale (VAS) from 0 (no pain) to 100 mm (worst pain imaginable). Patients were asked to report overall procedural pain 5 minutes following manual scaling and/or root planing (SRP) in a single quadrant that had been pre-treated with Lidocaine/Prilocaine or placebo (vehicle only, without lidocaine or prilocaine). In all three studies, patients were given Lidocaine/Prilocaine or placebo (vehicle only, without lidocaine or prilocaine). In all three studies, patients who were given Lidocaine/Prilocaine reported lower VAS scores during the procedure than those given placebo. Study B3 recruited patients with a known sensitivity to mechanical probing of dental pockets, whereas in studies B1 and B2, this was not a requirement. *Results of B1, B2 and B3 are summarized below.
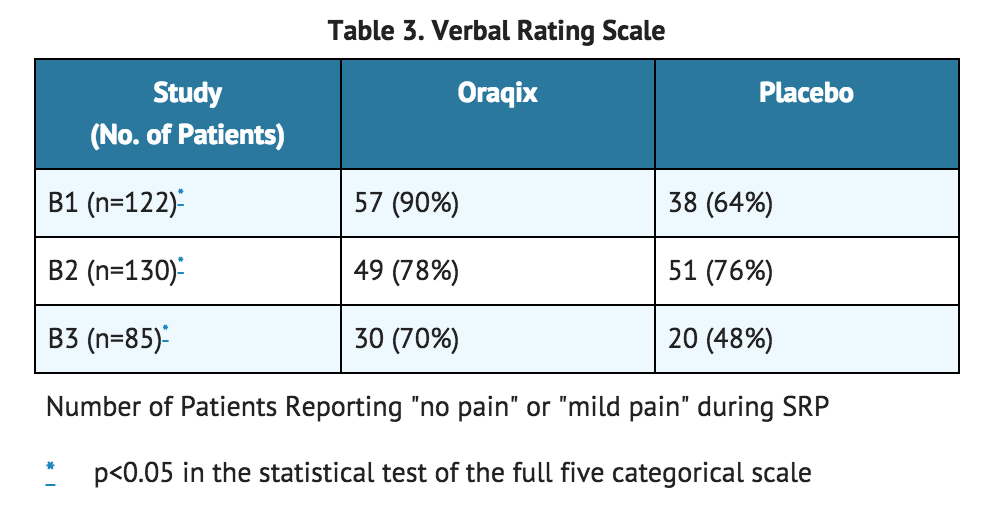
- The trial also compared individual patient estimates of pain on a 5-step categorical Verbal Rating Scale (VRS) which included the following categories: no pain, mild pain, moderate pain, severe pain, and very severe pain. The results of those who reported no pain or mild pain are shown in the test table.
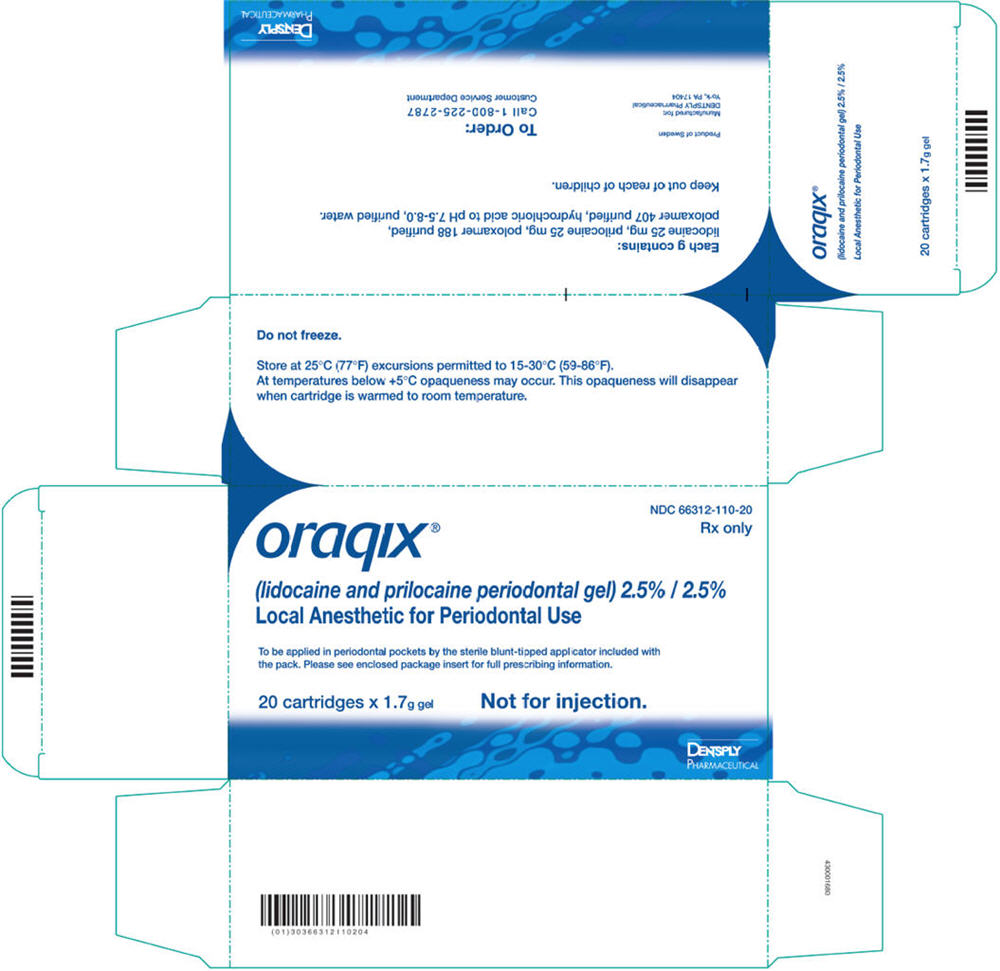
How Supplied
- Oraqix (lidocaine and prilocaine periodontal gel), 2.5%/2.5%, is supplied in dental cartridges that provide 1.7g gel.
- Individually blister-packaged cartridges of Oraqix are distributed in a carton of 20 (NDC 66312-110-20). Each individual blister package also contains a sterile blunt-tipped applicator. Each blunt-tipped applicator is for single use only.
Storage
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
- At temperatures below +5°C Oraqix may become opaque. This opacity will disappear when the cartridge is warmed to room temperature.
- DO NOT FREEZE. Some components of Oraqix may precipitate if cartridges are frozen. Cartridges should not be used if they contain a precipitate.
- Do not use dental cartridge warmers with Oraqix. The heat will cause the product to gel.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

{{#ask: Label Page::Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients should be cautioned to avoid injury to the treated area, or exposure to extreme hot or cold temperatures, until complete sensation has returned.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Lidocaine/Prilocaine (subgengival) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ORAQIX®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- There is limited information regarding Look-Alike Drug Names.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.