Famciclovir adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Adverse Reactions
Acute renal failure is discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
The most common adverse events reported in at least 1 indication by >10% of adult patients treated with FAMVIR are headache and nausea.
Clinical Trials Experience in Adult Patients
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Immunocompetent patients: The safety of FAMVIR has been evaluated in active- and placebo-controlled clinical studies involving 816 FAMVIR-treated patients with herpes zoster (FAMVIR, 250 mg three times daily to 750 mg three times daily); 163 FAMVIR-treated patients with recurrent genital herpes (FAMVIR, 1000 mg twice daily); 1,197 patients with recurrent genital herpes treated with FAMVIR as suppressive therapy (125 mg once daily to 250 mg three times daily) of which 570 patients received FAMVIR (open-labeled and/or double-blind) for at least 10 months; and 447 FAMVIR-treated patients with herpes labialis (FAMVIR, 1500 mg once daily or 750 mg twice daily). Table 2 lists selected adverse events.
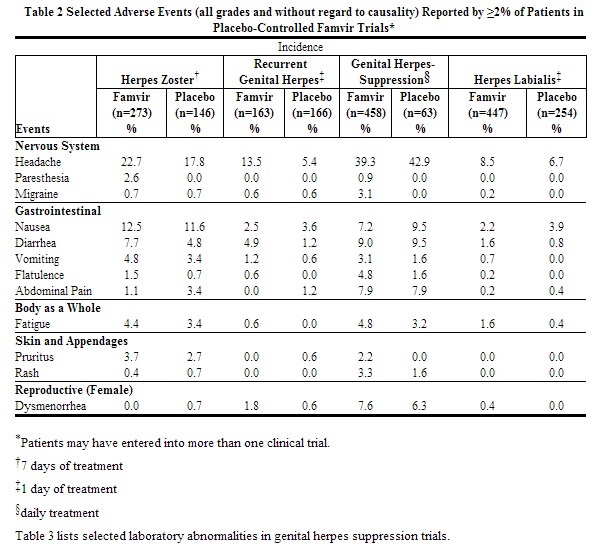 |
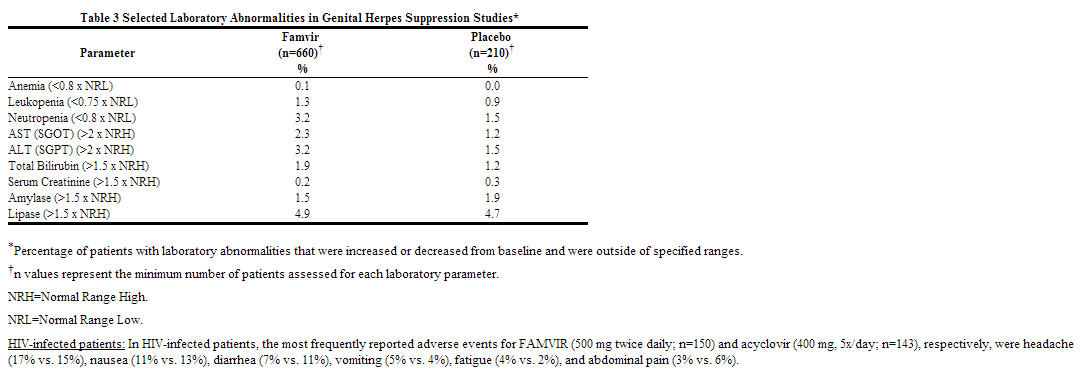 |
Postmarketing Experience
The adverse events listed below have been reported during postapproval use of FAMVIR. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Thrombocytopenia
Hepatobiliary disorders: Abnormal liver function tests, cholestatic jaundice
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness, somnolence
Psychiatric disorders: Confusion (including delirium, disorientation, and confusional state occurring predominantly in the elderly), hallucinations
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Urticaria, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, angioedema (e.g., face, eyelid, periorbital, and pharyngeal edema), leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Cardiac disorders: Palpitations[1]
References
- ↑ "http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/020363s037lbl.pdf" (PDF). External link in
|title=(help)
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.