Bambuterol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 20% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, extensive Further metabolized to terbutaline by plasma cholinesterase |
| Elimination half-life | 13 hours (bambuterol) 21 hours (terbutaline) |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
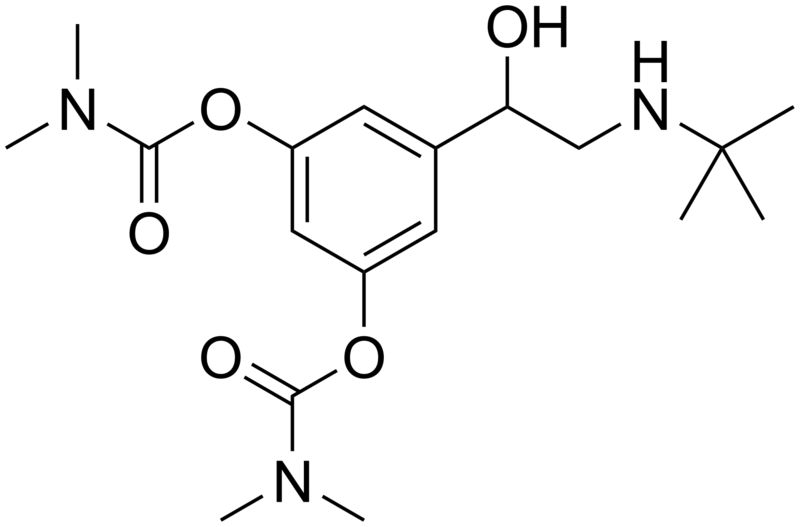
| Formula | C18H29N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 367.44 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Bambuterol |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Bambuterol |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Bambuterol at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Bambuterol at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Bambuterol
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Bambuterol Discussion groups on Bambuterol Patient Handouts on Bambuterol Directions to Hospitals Treating Bambuterol Risk calculators and risk factors for Bambuterol
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Bambuterol |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Bambuterol is a long acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist (LABA) used in the treatment of asthma; it also is a prodrug of terbutaline. Commercially, the AstraZeneca pharmaceutical company produces and markets bambuterol as Bambec and Oxeol (INN).[1]
Indications
As other LABAs, bambuterol is used in the long-term management of persistent asthma.[1] It should not be used as a rescue medication for short-term relief of asthma symptoms.
Contraindications
Bambuterol is contraindicated in pregnancy and in people with seriously impaired liver function. It can be used by people with renal impairment, but dose adjustments are necessary.[1]
Adverse effects
The adverse effect profile of bambuterol is similar to that of salbutamol, and may include fatigue, nausea, palpitations, headache, dizziness and tremor.[1]
Interactions
Concomitant administration of bambuterol with corticosteroids, diuretics, and xanthine derivatives (such as theophylline) increases the risk of hypokalemia (decreased levels of potassium in the blood).[2]
Bambuterol acts as a cholinesterase inhibitor, and can prolong the duration of action of suxamethonium (succinylcholine) and other drugs whose breakdown in the body depends on cholinesterase function.[1] Butyrylcholinesterase activity returns to normal approximately two weeks after bambuterol is stopped.[3] It can also enhance the effects of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers, such as vecuronium bromide.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Sweetman, Sean C., ed. (2009). "Bronchodilators and Anti-asthma Drugs". Martindale: The complete drug reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. pp. 1115–16. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sweetman (2009), pp. 1132–33.
- ↑ Sitar DS (October 1996). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of bambuterol". Clin Pharmacokinet. 31 (4): 246–56. doi:10.2165/00003088-199631040-00002. PMID 8896942.
- Pages with script errors
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Articles with changed DrugBank identifier
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Infobox drug articles with non-default infobox title
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Beta-adrenergic agonists
- Prodrugs
- Phenethylamines
- Drug
- Carbamates