Atazanavir microbiology
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohamed Moubarak, M.D. [2]
Microbiology
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
Atazanavir exhibits anti-HIV-1 activity with a mean 50% effective concentration (EC50) in the absence of human serum of 2 to 5 nM against a variety of laboratory and clinical HIV-1 isolates grown in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, macrophages, CEM-SS cells, and MT-2 cells. ATV has activity against HIV-1 Group M subtype viruses A, B, C, D, AE, AG, F, G, and J isolates in cell culture. ATV has variable activity against HIV-2 isolates (1.9 to 32 nM), with EC50 values above the EC50 values of failure isolates. Two-drug combination antiviral activity studies with ATV showed no antagonism in cell culture with NNRTIs (delavirdine, efavirenz, and nevirapine), PIs (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir), NRTIs (abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir, zalcitabine, and zidovudine), the HIV-1 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide, and two compounds used in the treatment of viral hepatitis, adefovir and ribavirin, without enhanced cytotoxicity.
'Resistance
In Cell Culture: HIV-1 isolates with a decreased susceptibility to ATV have been selected in cell culture and obtained from patients treated with ATV or atazanavir/ritonavir (ATV/RTV). HIV-1 isolates with 93- to 183-fold reduced susceptibility to ATV from three different viral strains were selected in cell culture by 5 months. The substitutions in these HIV-1 viruses that contributed to ATV resistance include I50L, N88S, I84V, A71V, and M46I. Changes were also observed at the protease cleavage sites following drug selection. Recombinant viruses containing the I50L substitution without other major PI substitutions were growth impaired and displayed increased susceptibility in cell culture to other PIs (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir). The I50L and I50V substitutions yielded selective resistance to ATV and amprenavir, respectively, and did not appear to be cross-resistant.
Clinical Studies of Treatment-Naive Patients: Comparison of Ritonavir-Boosted REYATAZ vs. Unboosted REYATAZ: Study AI424-089 compared REYATAZ 300 mg once daily with ritonavir 100 mg vs. REYATAZ 400 mg once daily when administered with lamivudine and extended-release stavudine in HIV-infected treatment-naive patients. A summary of the number of virologic failures and virologic failure isolates with ATV resistance in each arm is shown in Table 19.[1]
Clinical Studies of Treatment-Naive Patients Receiving REYATAZ 300 mg With Ritonavir 100 mg: In Phase III study AI424-138, an as-treated genotypic and phenotypic analysis was conducted on samples from patients who experienced virologic failure (HIV-1 RNA ≥400 copies/mL) or discontinued before achieving suppression on ATV/RTV (n=39; 9%) and LPV/RTV (n=39; 9%) through 96 weeks of treatment. In the ATV/RTV arm, one of the virologic failure isolates had a 56-fold decrease in ATV susceptibility emerge on therapy with the development of PI resistance-associated substitutions L10F, V32I, K43T, M46I, A71I, G73S, I85I/V, and L90M. The NRTI resistance-associated substitution M184V also emerged on treatment in this isolate conferring emtricitabine resistance. Two ATV/RTV-virologic failure isolates had baseline phenotypic ATV resistance and IAS-defined major PI resistance-associated substitutions at baseline. The I50L substitution emerged on study in one of these failure isolates and was associated with a 17-fold decrease in ATV susceptibility from baseline and the other failure isolate with baseline ATV resistance and PI substitutions (M46M/I and I84I/V) had additional IAS-defined major PI substitutions (V32I, M46I, and I84V) emerge on ATV treatment associated with a 3-fold decrease in ATV susceptibility from baseline. Five of the treatment failure isolates in the ATV/RTV arm developed phenotypic emtricitabine resistance with the emergence of either the M184I (n=1) or the M184V (n=4) substitution on therapy and none developed phenotypic tenofovir disoproxil resistance. In the LPV/RTV arm, one of the virologic failure patient isolates had a 69-fold decrease in LPV susceptibility emerge on therapy with the development of PI substitutions L10V, V11I, I54V, G73S, and V82A in addition to baseline PI substitutions L10L/I, V32I, I54I/V, A71I, G73G/S, V82V/A, L89V, and L90M. Six LPV/RTV virologic failure isolates developed the M184V substitution and phenotypic emtricitabine resistance and two developed phenotypic tenofovir disoproxil resistance.
Clinical Studies of Treatment-Naive Patients Receiving REYATAZ 400 mg Without Ritonavir: ATV-resistant clinical isolates from treatment-naive patients who experienced virologic failure on REYATAZ 400 mg treatment without ritonavir often developed an I50L substitution (after an average of 50 weeks of ATV therapy), often in combination with an A71V substitution, but also developed one or more other PI substitutions (eg, V32I, L33F, G73S, V82A, I85V, or N88S) with or without the I50L substitution. In treatment-naive patients, viral isolates that developed the I50L substitution, without other major PI substitutions, showed phenotypic resistance to ATV but retained in cell culture susceptibility to other PIs (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir); however, there are no clinical data available to demonstrate the effect of the I50L substitution on the efficacy of subsequently administered PIs.
Clinical Studies of Treatment-Experienced Patients: In studies of treatment-experienced patients treated with ATV or ATV/RTV, most ATV-resistant isolates from patients who experienced virologic failure developed substitutions that were associated with resistance to multiple PIs and displayed decreased susceptibility to multiple PIs. The most common protease substitutions to develop in the viral isolates of patients who failed treatment with ATV 300 mg once daily and RTV 100 mg once daily (together with tenofovir and an NRTI) included V32I, L33F/V/I, E35D/G, M46I/L, I50L, F53L/V, I54V, A71V/T/I, G73S/T/C, V82A/T/L, I85V, and L89V/Q/M/T. Other substitutions that developed on ATV/RTV treatment including E34K/A/Q, G48V, I84V, N88S/D/T, and L90M occurred in less than 10% of patient isolates. Generally, if multiple PI resistance substitutions were present in the HIV-1 virus of the patient at baseline, ATV resistance developed through substitutions associated with resistance to other PIs and could include the development of the I50L substitution. The I50L substitution has been detected in treatment-experienced patients experiencing virologic failure after long-term treatment. Protease cleavage site changes also emerged on ATV treatment but their presence did not correlate with the level of ATV resistance.
Cross-Resistance
Cross-resistance among PIs has been observed. Baseline phenotypic and genotypic analyses of clinical isolates from ATV clinical trials of PI-experienced patients showed that isolates cross-resistant to multiple PIs were cross-resistant to ATV. Greater than 90% of the isolates with substitutions that included I84V or G48V were resistant to ATV. Greater than 60% of isolates containing L90M, G73S/T/C, A71V/T, I54V, M46I/L, or a change at V82 were resistant to ATV, and 38% of isolates containing a D30N substitution in addition to other changes were resistant to ATV. Isolates resistant to ATV were also cross-resistant to other PIs with >90% of the isolates resistant to indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir, and 80% resistant to amprenavir. In treatment-experienced patients, PI-resistant viral isolates that developed the I50L substitution in addition to other PI resistance-associated substitution were also cross-resistant to other PIs.
Baseline Genotype/Phenotype and Virologic Outcome Analyses
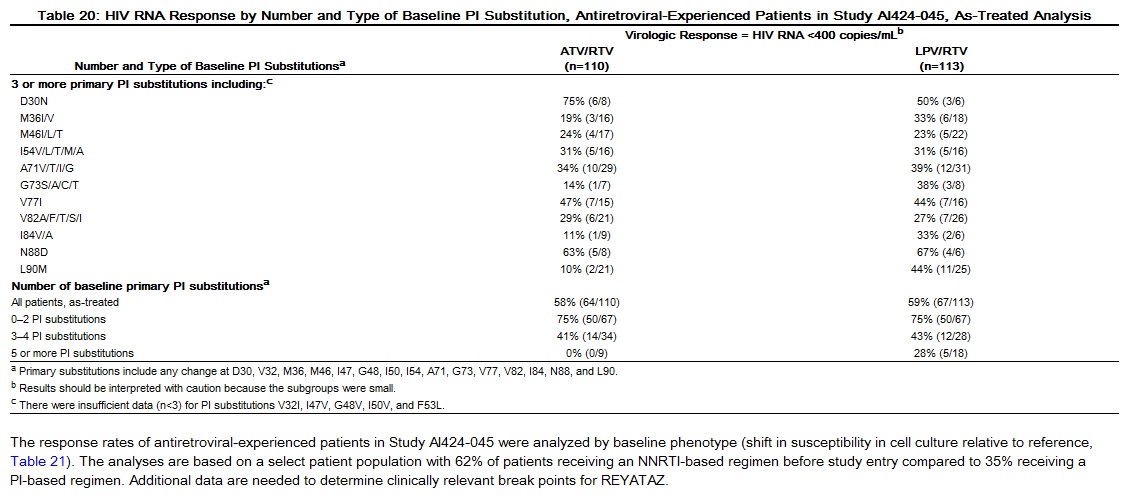
Genotypic and/or phenotypic analysis of baseline virus may aid in determining ATV susceptibility before initiation of ATV/RTV therapy. An association between virologic response at 48 weeks and the number and type of primary PI resistance-associated substitutions detected in baseline HIV-1 isolates from antiretroviral-experienced patients receiving ATV/RTV once daily or lopinavir (LPV)/RTV twice daily in Study AI424-045 is shown in Table 20.
Overall, both the number and type of baseline PI substitutions affected response rates in treatment-experienced patients. In the ATV/RTV group, patients had lower response rates when 3 or more baseline PI substitutions, including a substitution at position 36, 71, 77, 82, or 90, were present compared to patients with 1–2 PI substitutions, including one of these substitutions.
References
- ↑ "REYATAZ (ATAZANAVIR SULFATE) CAPSULE, GELATIN COATED [E.R. SQUIBB & SONS, L.L.C.]". Text " accessdate" ignored (help)
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.