Aducanumab-avwa
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Tejasvi Aryaputra
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Aducanumab-avwa is an amyloid beta-directed antibody that is FDA approved for the treatment of treat Alzheimer’s disease. Common adverse reactions include ARIA-H microhemorrhage, fall, ARIA-Edema, ARIA-H superficial siderosis, and headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
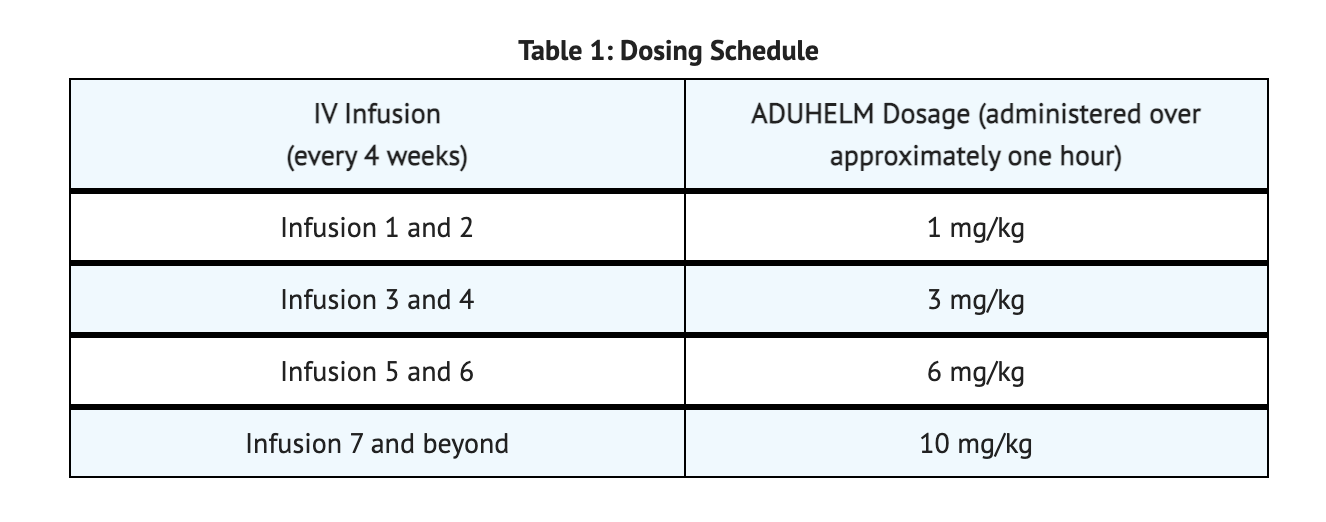
- 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa after initial titration.
- Administered as an intravenous (IV) infusion given for one hour every 4 weeks which is at a minimum 21 days apart.
- Give dose immediately or as soon as possible if scheduled time for dosing of Aducanumab-avwa is missed.
Table 1 summarizes Dosing Schedule of Aducanumab-avwa.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Aducanumab-avwa in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Aducanumab-avwa in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Aducanumab-avwa in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Aducanumab-avwa in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa Contraindications in the drug label.
Warnings
Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities
- Amyloid related imaging abnormalities-edema may be observed in patients taking Aducanumab-avwa as MRI's reveal.
- Amyloid related imaging abnormalities-hemosiderin deposition may be observed in patients taking Aducanumab-avwa.
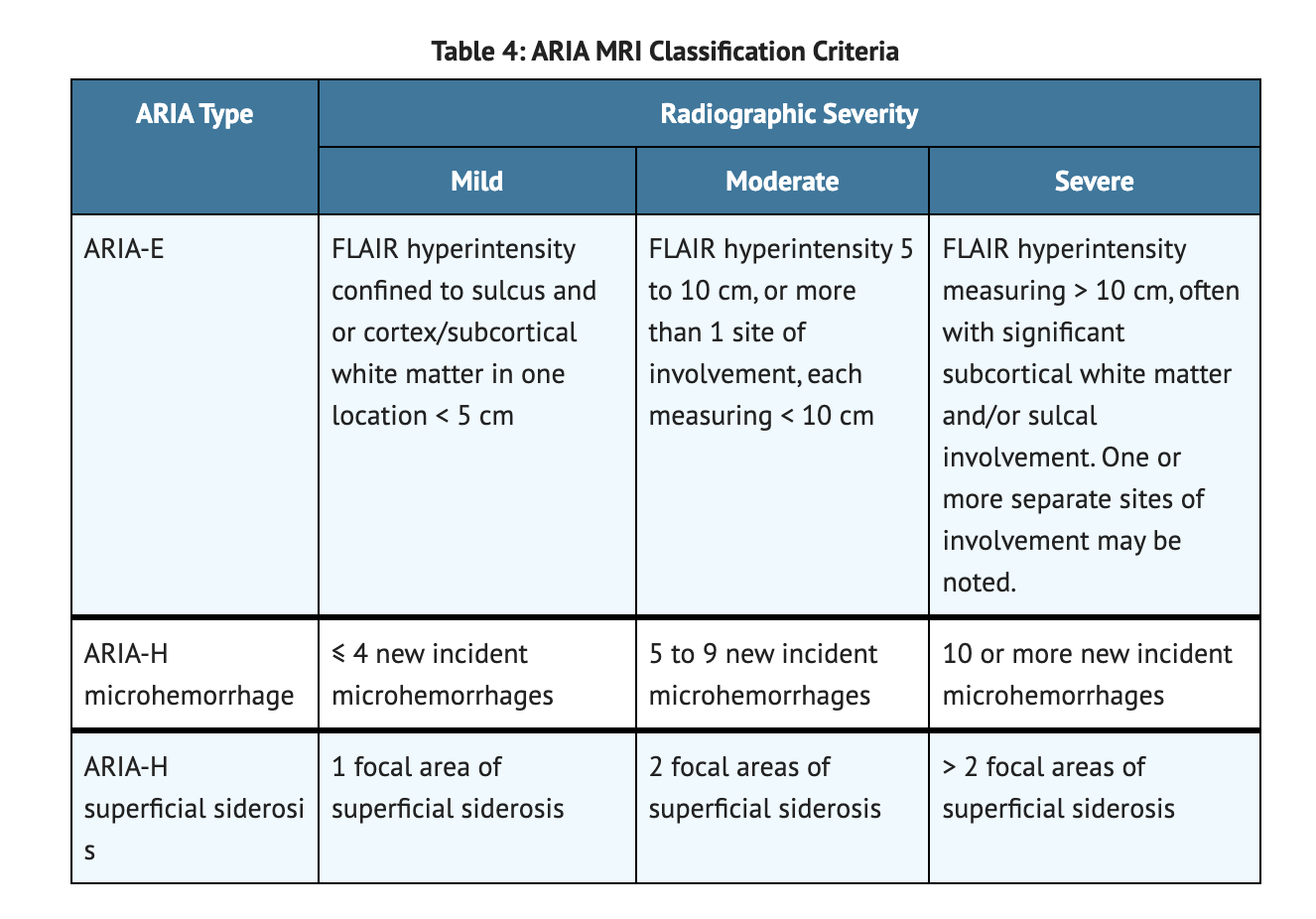
Table 4 summarized ARIA MRI Classification Criteria.
ARIA E and H
- 41% of patients in clinical studies taking 10 mg/kg Aducanumab-avwa displayed ARIA E and/or H.
- 10% of patients in clinical studies taking a placebo displayed ARIA E and/or H.
- 35% of patients in clinical studies taking 10 mg/kg Aducanumab-avwa displayed ARIA E compared to the 3% patients who experienced ARIA E when taking a placebo.
- There were 16% of patients in clinical studies 1 and 2 who were part of the Aducanumab-avwa group that were ApoE ε4 homozygotes.
- There were 51% of patients in clinical studies 1 and 2 who were part of the Aducanumab-avwa group that were ApoE ε4 heterozygotes.
- There were 32% of patients in clinical studies 1 and 2 who were part of the Aducanumab-avwa group that were ApoE ε4 non-carriers.
- ApoE ε4 carriers patients had more occurrences of ARIA-E than ApoE ε4 non-carriers patients.
- 11% of homozygotes displayed severe radiographic ARIA-E compared to the 4% and 2% seen in hetrozygotes and non-carriers, respectively.
- Intervention of serious adverse reactions with ARIA-E were similar in patients that are ApoE ε4 carriers vs. non-carriers when given Aducanumab-avwa.
- Management of ARIA does not differ in patients that are ApoE ε4 carriers vs. non-carriers when given Aducanumab-avwa.
- ApoE ε4 carrier status should be taken into consideration when treating a patient with Aducanumab-avwa.
- ARIA-E radiographic events was observed mostly during the early stages of treatment, first 8 doses, in comparison to the duration of the rest of the treatment.
- 13% of patients that had ARIA-E due to Aducanumab-avwa treatment displayed severe radiographic severity.
- 58% of patients that had ARIA-E due to Aducanumab-avwa treatment displayed moderate radiographic severity.
- 30% of patients that had ARIA-E due to Aducanumab-avwa treatment displayed mild radiographic severity.
- ARIA-E resolution in patients who had it occurred in 68% by 12 weeks.
- ARIA-E resolution in patients who had it occurred in 91% by 20 weeks.
- ARIA-E resolution in patients who had it occurred in 98% after detection.
- One episode of ARIA-E was seen in 10% of all patients who received 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa.
- Three or more episodes of ARIA-E was seen in 1% of all patients who received 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa.
- 21% of patients in clinical studies displayed ARIA-H when given 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa in comparison to the 1% of patients that displayed ARIA-H when given a placebo.
- A greater than 1 cm in diameter intracerebral hemorrhage was reported by 0.5% of patients after Aducanumab-avwa treatment.
- A greater than 1 cm in diameter intracerebral hemorrhage was reported by 0.4% of patients after placebo treatment.
- Clinical studies showed no indications that patients taking antithrombotic medication increased a risk for ARIA or intracerebral hemorrhage when treated with Aducanumab-avwa.
- 24% of patients treated with Aducanumab-avwa displayed clinical symptoms who had ARIA E or/and H when compared the 5% of patients who were given a placebo.
- Headache was the most common symptom of ARIA observed in patients who had ARIA when treated with Aducanumab-avwa.
- Dizziness/vertigo, nausea, confusion/delirium/altered mental status/disorientation, and visual disturbance were other symptoms associated with ARIA that were observed in patients who had ARIA when treated with Aducanumab-avwa.
- 0.3% of patients with ARIA during Aducanumab-avwa treatment displayed serious symptoms associated with ARIA.
- Seizures were reported by patients that had ARIA.
- Independent of ARIA, 0.5% of patients receiving 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa reported seizures when compared to the 0.8% from the placebo group.
- Status epilepticus was also reported by patients that were receiving 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa.
Monitoring for ARIA-E and ARIA-H
- Advise patients to have an MRI of the brain prior to starting Aducanumab-avwa.
- Monitor symptoms for ARIA very closely during the first 8 doses of treatment, specifically during the titration step, of Aducanumab-avwa.
- Advise patients to have a clinical evaluation if experiencing symptoms associated with ARIA.
- During the 5th, 7th, 9th, and 12th infusion, obtain a brain MRI scan of the patient to make sure there is no asymptomatic ARIA present.
ARIA-E Management
- Patients that experienced symptomatic or asymptomatic ARIA-E had their Aducanumab-avwa dosing suspended.
- Dosing of Aducanumab-avwa for patients with ARIA-E is based on clinical symptoms and radiographic severity displayed by the patient.
ARIA-H Management
- Patients that experienced symptomatic or asymptomatic ARIA-H had their Aducanumab-avwa dosing suspended.
- Dosing of Aducanumab-avwa for patients with ARIA-E is based on ARIA-H type and radiographic severity displayed by the patient.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- During Aducanumab-avwa infusion, urticaria and angioedema was reported by 1 patient during clinical studies.
- Advise patients to discontinue Aducanumab-avwa infusion immediately upon any signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions and durations of follow up, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- 3,078 patients were part of the clinical study to look into the safety of Aducanumab-avwa.
- 1105 patients of the patient population had received 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa who were mostly females (52%) and Whites (76%) with a mean age of 70.
- 5% of patients given Aducanumab-avwa withdrew from the clinical study due to an adverse reaction.
- ARIA-H superficial siderosis was the most common adverse reaction that caused withdrawal from the clinical study.
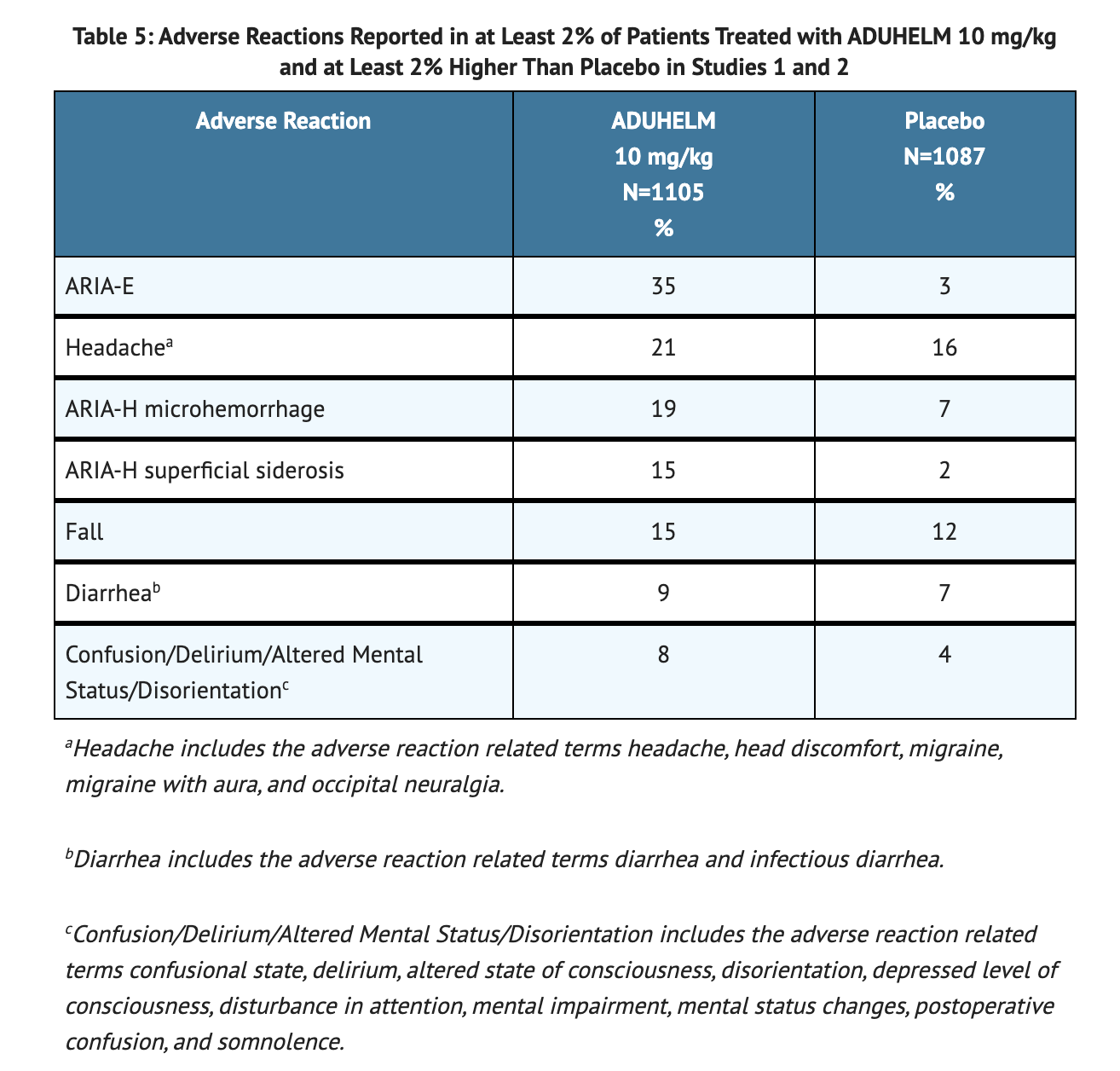
Table 5 summarizes adverse reactions that were reported in at least 2% of patients treated with ADUHELM and at least 2% more frequently than in patients on placebo.
Immunogenicity
- A vitro assay was used to detect binding anti-aducanumab-avwa antibodies.
- 0.6% of patients receiving Aducanumab-avwa during the clinical studies displayed anti-aducanumab-avwa antibodies.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
No adequate data have been found to look at if Aducanumab-avwa causes major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes in humans. In female rat studies, there were no signs of an adverse effect on embryofetal development or pre/postnatal development when given 0, 100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg/week of Aducanumab-avwa.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Aducanumab-avwa in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Aducanumab-avwa during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
No current data has been done on the effects of Aducanumab-avwa on the breastfed infant and the effects on milk production in women when treated with Aducanumab-avwa. Advise nursing females to consider the potential adverse risks/developmental and health benefits of Aducanumab-avwa treatment.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aducanumab-avwa in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
No significant differences of adverse reactions from Aducanumab-avwa in patients whose age ranged from 50 to 85 years. There were no indications from clinical studies that there are additional safety concerns for patients who are 65 years of age or older.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aducanumab-avwa with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aducanumab-avwa with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aducanumab-avwa in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aducanumab-avwa in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Aducanumab-avwa in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Aducanumab-avwa in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Dilution Instructions
- Aseptic technique should be used to prepare Aducanumab-avwa diluted solution for infusion.
- Use a patients body weight to calculate dose, total volume of Aducanumab-avwa, and the number vials used.
- Aducanumab-avwa should be colorless to yellow solution as well as clear to opalescent.
- Infusion bag of 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP should be used.
- Insert required volume of Aducanumab-avwa dosage into the infusion bag.
- Mix infusion solution and Aducanumab-avwa gently by inverting the infusion bag gently.
- Aducanumab-avwa solution can be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C for 3 days if not used immediately.
- Aducanumab-avwa solution can be stored at room temperature for 24 hours if not used immediately.
- Aducanumab-avwa solution should be at room temperature before being infused into a patient.
Administration Instructions
- Do not infuse Aducanumab-avwa solution if there is discoloration or foreign particles are detected.
- Utilize a sterile, low-protein binding to infuse Aducanumab-avwa intravenously over a 1 hour timespan.
- Advise patients to stop infusion Aducanumab-avwa immediately if signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity-type reaction are observed.
Monitoring
Monitoring and Dosing Interruptions for Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities
- Advise patients to receive a brain MRI prior to Aducanumab-avwa.
- Patients should also receive a MRI scan of the brain before the 5th, 7th, 9th, and 12th infusion.
- Stop Aducanumab-avwa treatment if the patient develops intracerebral hemorrhage greater than 1 cm in diameter.
- Either permanently discontinue or resume Aducanumab-avwa treatment based on the clinical symptoms a patient displays.
Table 2 summarizes dosing interruptions for patients with ARIA-E.
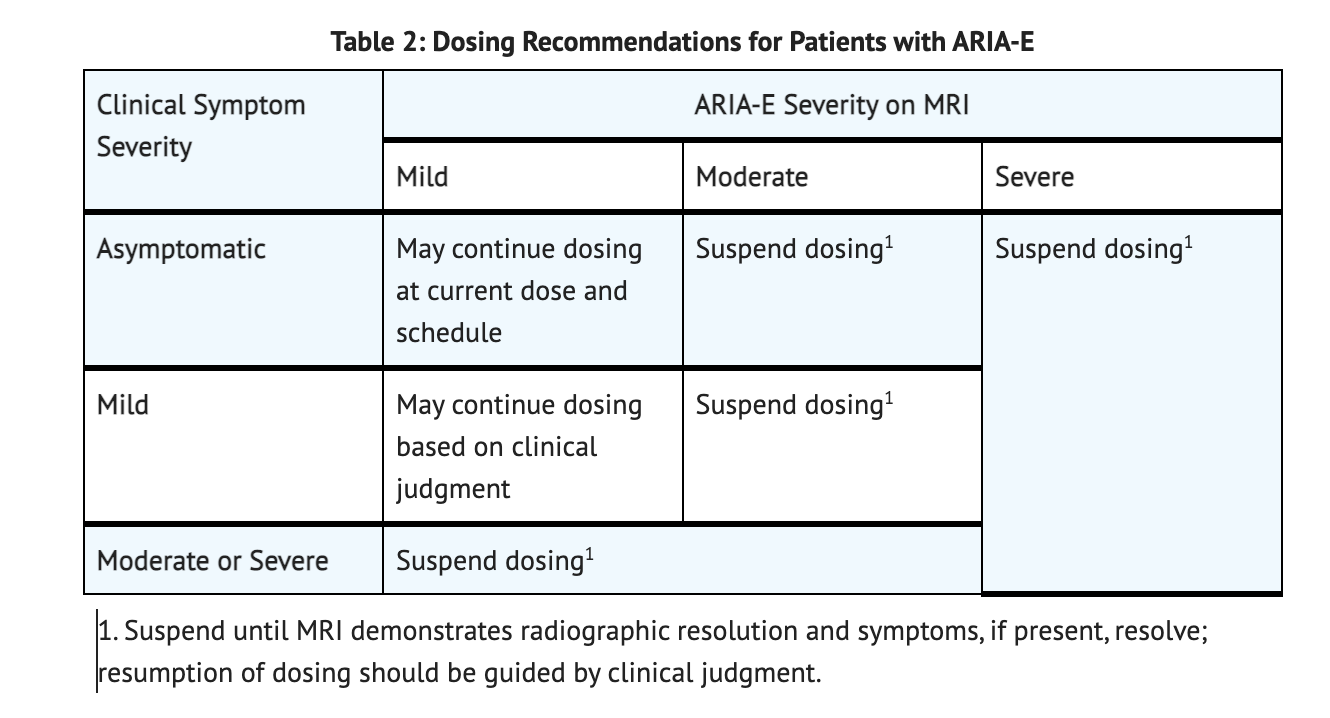
Table 3 summarizes dosing interruptions for patients with ARIA-H.

IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Aducanumab-avwa and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
Aducanumab-avwa?
| |
| Therapeutic monoclonal antibody | |
| Source | u |
| Target | Amyloid beta |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | N06 |
| PubChem | ? |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Synonyms | Aducanumab-avwa, BIIB037, BIIB-037 |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | 24.8 days[1] |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | Intravenous |
Mechanism of Action
- Aducanumab-avwa is a human, immunoglobulin gamma 1 monoclonal antibody.
- Aducanumab-avwa is directed against insoluble forms and aggregated soluble of amyloid beta.
- Aducanumab-avwa reduces amyloid beta plaques.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
Effect of ADUHELM on Amyloid Beta Pathology
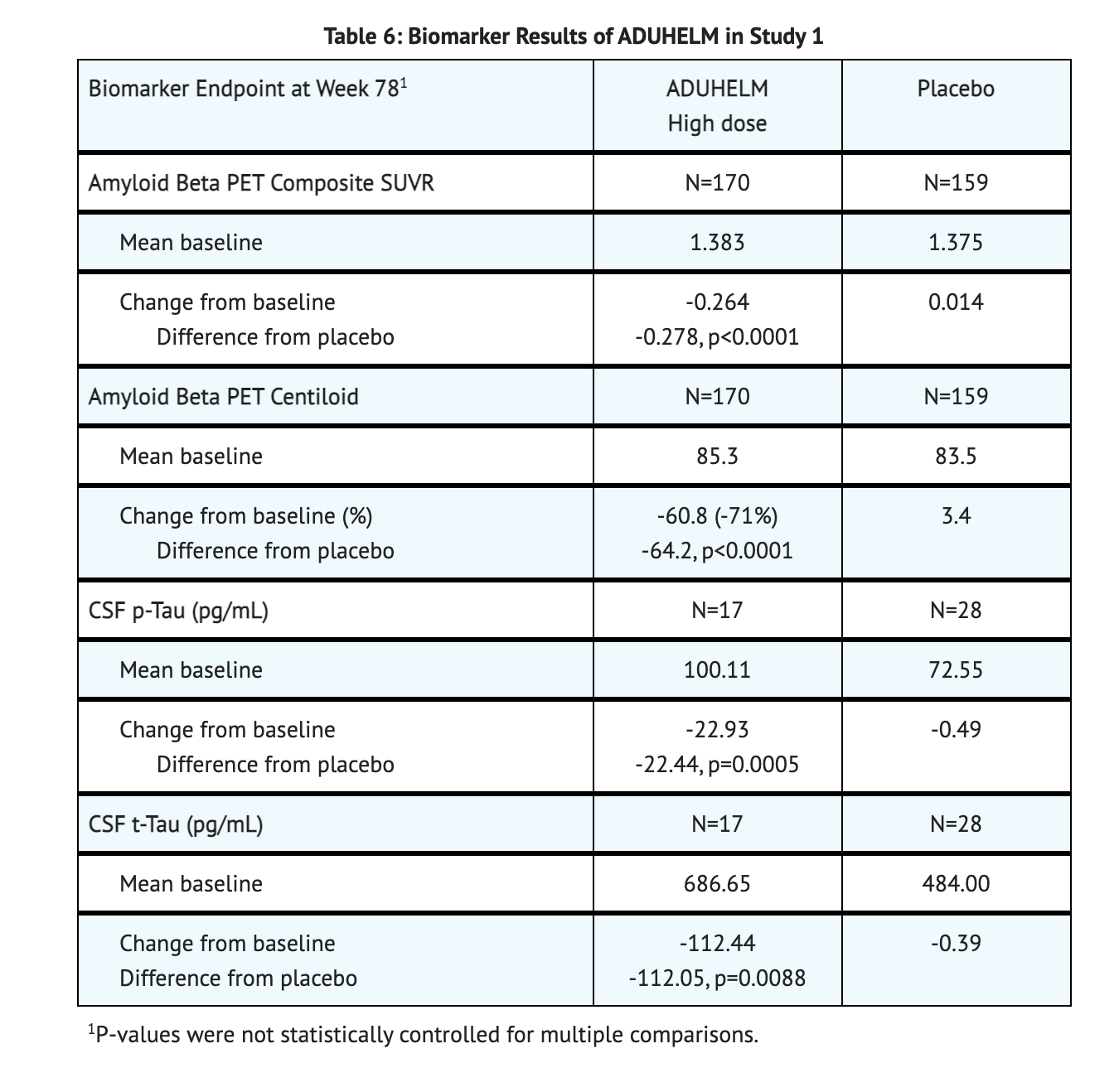
- Amyloid beta plaque was reduced by Aducanumab-avwa over a dose- and time-dependent manner.
- In the brain, reduced amyloid beta plaque levels were seen at both low and high dose Aducanumab-avwa at both Weeks 26 and 78 in clinical studies 1 and 2.
- At week 132, there was continued to decrease of amyloid beta plaque levels in the brain for clinical studies 1 and 2.
- A statistically significant dose- and time-dependent reductions in clinical study 3 led to a decrease in amyloid beta plaque levels when patients were given 3 mg/kg, 6 mg/kg, and 10 mg/kg of Aducanumab-avwa at Weeks 26 and 54 when compared to the placebo.
- At week 222, there was continued to decrease of amyloid beta plaque levels in the brain for clinical study 3 in a time- and dose-dependent manner.
Effect of ADUHELM on Tau Pathophysiology
- Neurodegeneration and tau pathophysiology markers were reduced by Aducanumab-avwa in clinical studies 1 and 2.
- CSF levels of p-Tau were reduced by Aducanumab-avwa in clinical studies 1 and 2.
- At week 78, Aducanumab-avwa low and high doses was favored in comparison to the placebo group when looking at adjusted mean change from baseline in CSF p-Tau levels in Study 1.
- Data from study 2 favored Aducanumab-avwa, but were not statistically significant.
- CSF levels of t-Tau were reduced by Aducanumab-avwa in clinical studies 1 and 2.
- At week 78, Aducanumab-avwa low and high doses was favored in comparison to the placebo group when looking at adjusted mean change from baseline in CSF t-Tau levels in Study 1.
- Data from study 2 favored Aducanumab-avwa, but were not statistically significant.
- Aducanumab-avwa high doses were favored when looking at adjusted mean change from baseline in tau PET SUVR when compared to the placebo in the medial temporal, frontal, and temporal brain region.
Exposure-Response Relationships
- CDR-SB, ADAS-Cog13, and ADCS-ADL-MCI declines had greater reduction when associated with higher exposure of Aducanumab-avwa.
- Declines in amyloid beta plaque were associated with higher exposure of Aducanumab-avwa.
Pharmacokinetics
- 2961 patients with Alzheimer's disease were used to understand the pharmacokinetics of Aducanumab-avwa.
- By 16 weeks of a 4-week regimen, steady state concentrations of Aducanumab-avwa was reached.
- Increased dose proportionally of Aducanumab-avwa from 1 to 10 mg/kg every 4 weeks led to peak AUCss, Cmax, and Cmin.
Distribution
- For volume of distribution at steady state, 9.63 L is the mean value.
Elimination
- Catabolic pathways will lead to Aducanumab-avwa degradation into small peptides and amino acids.
- 0.0159 L/hr is the Aducanumab-avwa clearance.
- 24.8 days is the terminal half-life of Aducanumab-avwa.
Specific Populations
- Age, body weight, sex, and race have an impact on Aducanumab-avwa exposure which is not clinically significant.
- Metabolism by hepatic enzymes and renal elimination is not expected to occur to Aducanumab-avwa.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis
- No studies have been conducted on carcinogenesis.
Mutagenesis
- No studies have been conducted on genotoxicity.
Impairment of Fertility
- No adverse effects of reproductive performance and fertility was observed in rats given 0, 100, 300, or 1000 mg/kg/week of Aducanumab-avwa prior to and during mating and continuing in females to gestation day 7.
Clinical Studies
- Two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group studies (1 and 2) were conducted on Alzheimer patients to look into the efficacy of Aducanumab-avwa.
- A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study (3) was also conducted on Alzheimer patients to look into the efficacy of Aducanumab-avwa.
- In studies 1 and 2, patients either received a placebo, Aducanumab-avwa low dose (3 or 6 mg/kg for ApoE ε4 carriers and noncarriers, respectively), or Aducanumab-avwa high dose (10 mg/kg).
Study 1
- 71 years of age was the mean age for the patient population in study 1.
Figure 1 displays results from the amyloid beta PET and CSF biomarker substudies of Study 1.
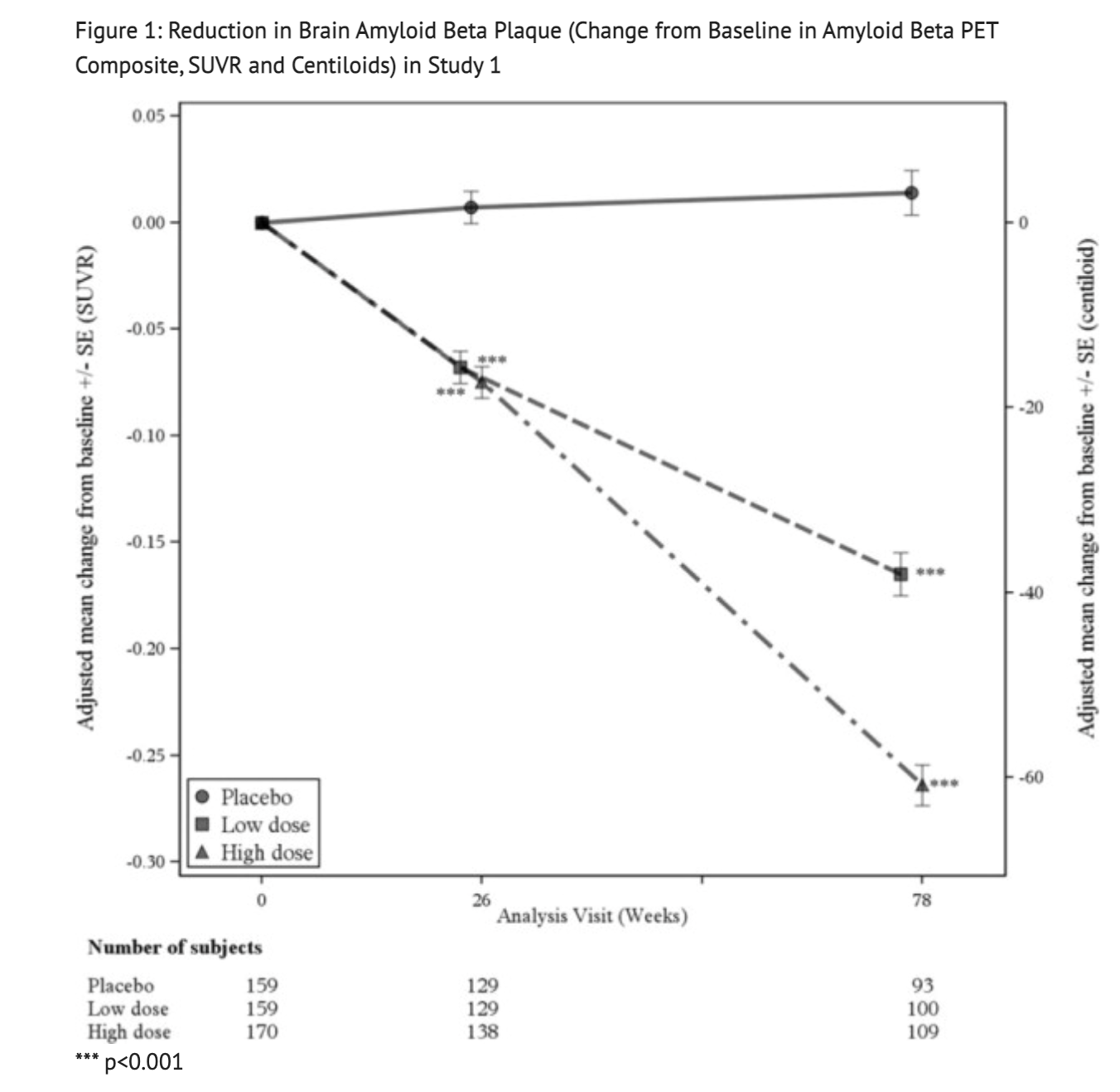
Table 6 summarizes Biomarker Results of Aducanumab-avwa in Study 1.
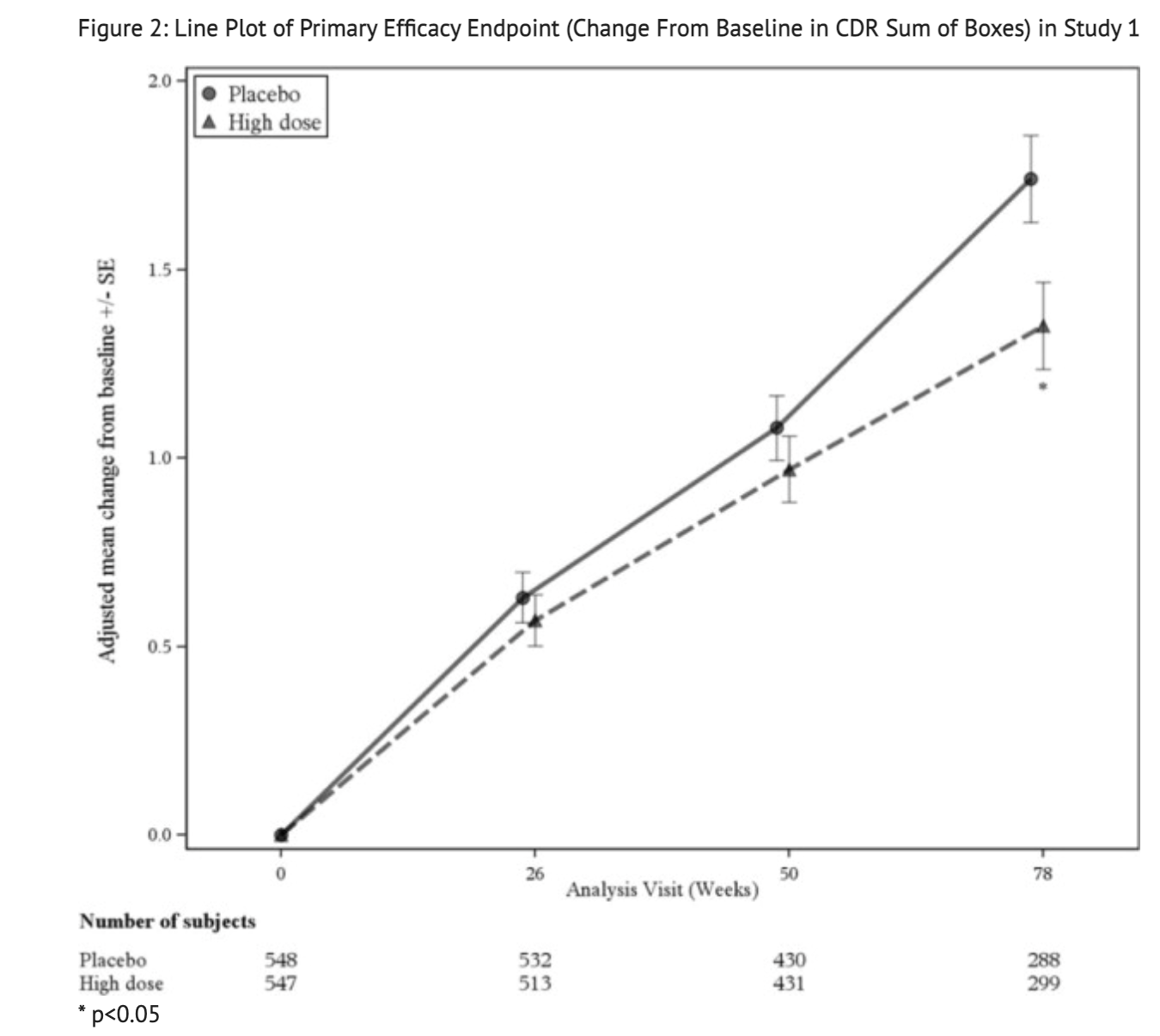
- Change from baseline on the CDR-SB at week 78 was the primary efficacy endpoint.
Figure 2 summarizes the Change From Baseline in CDR Sum of Boxes for Study 1.
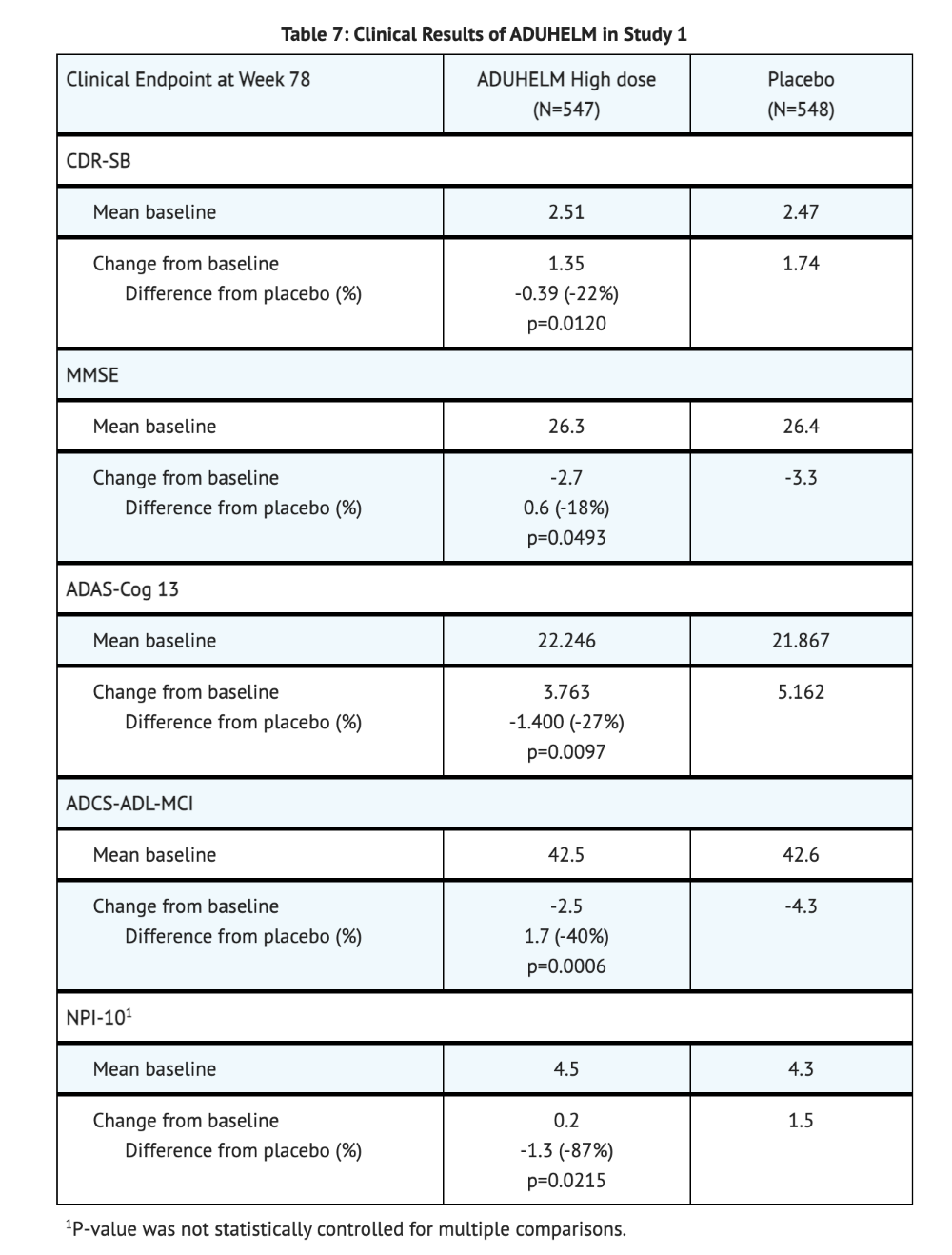
- Change from baseline in the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale at week 78, change from baseline in MMSE score at Week 78, and the change from baseline in the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study – Activities of Daily Living Inventory score at week 28 were the secondary efficacy endpoints for Study 1.
- When comparing Aducanumab-avwa high dose to the placebo, statistically significant differences were observed.
- For secondary efficacy endpoints, Aducanumab-avwa treatment was favored.
Table 7 summarizes clinical results of the Aducanumab-avwa high dose group compared to the placebo group for Study 1.
Study 2
- 71 years of age was the mean age for the patient population in study 2.
Figure 3 displays the Reduction in Brain Amyloid Beta Plaque for Study 2.
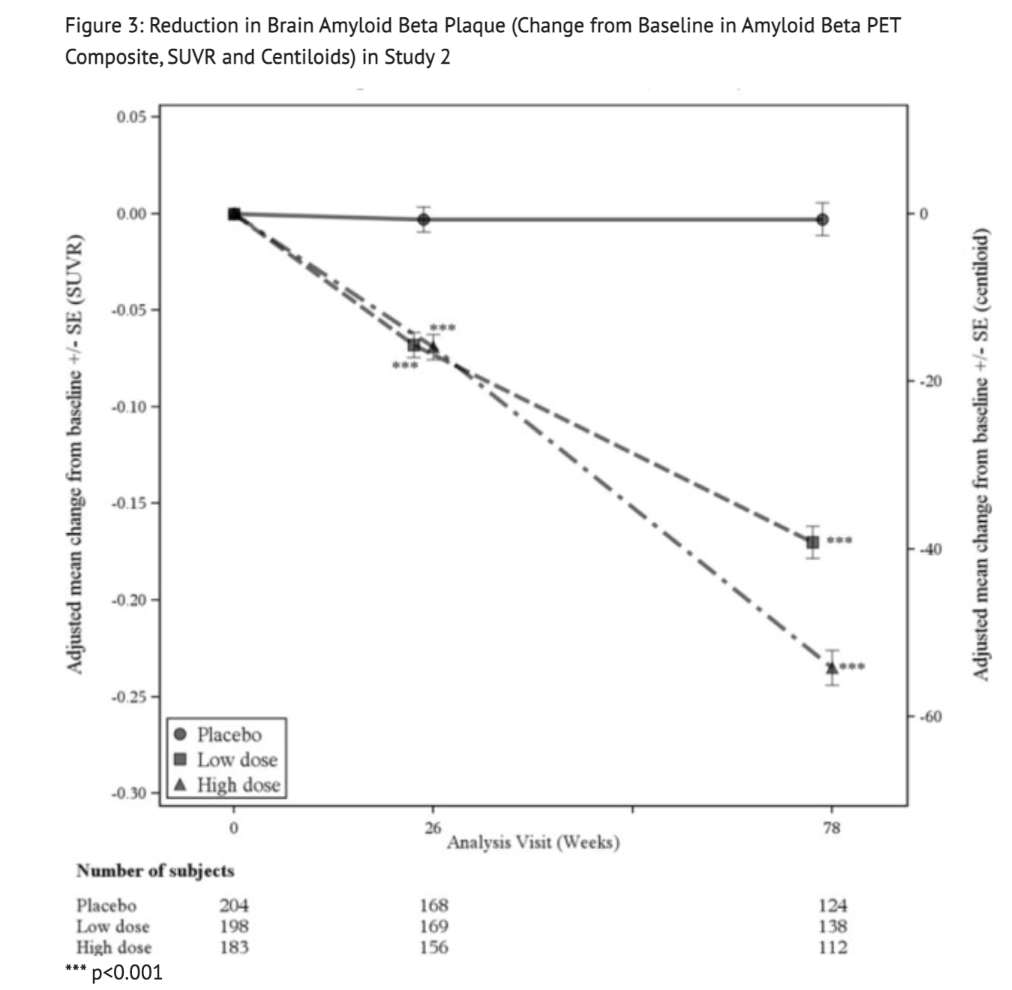
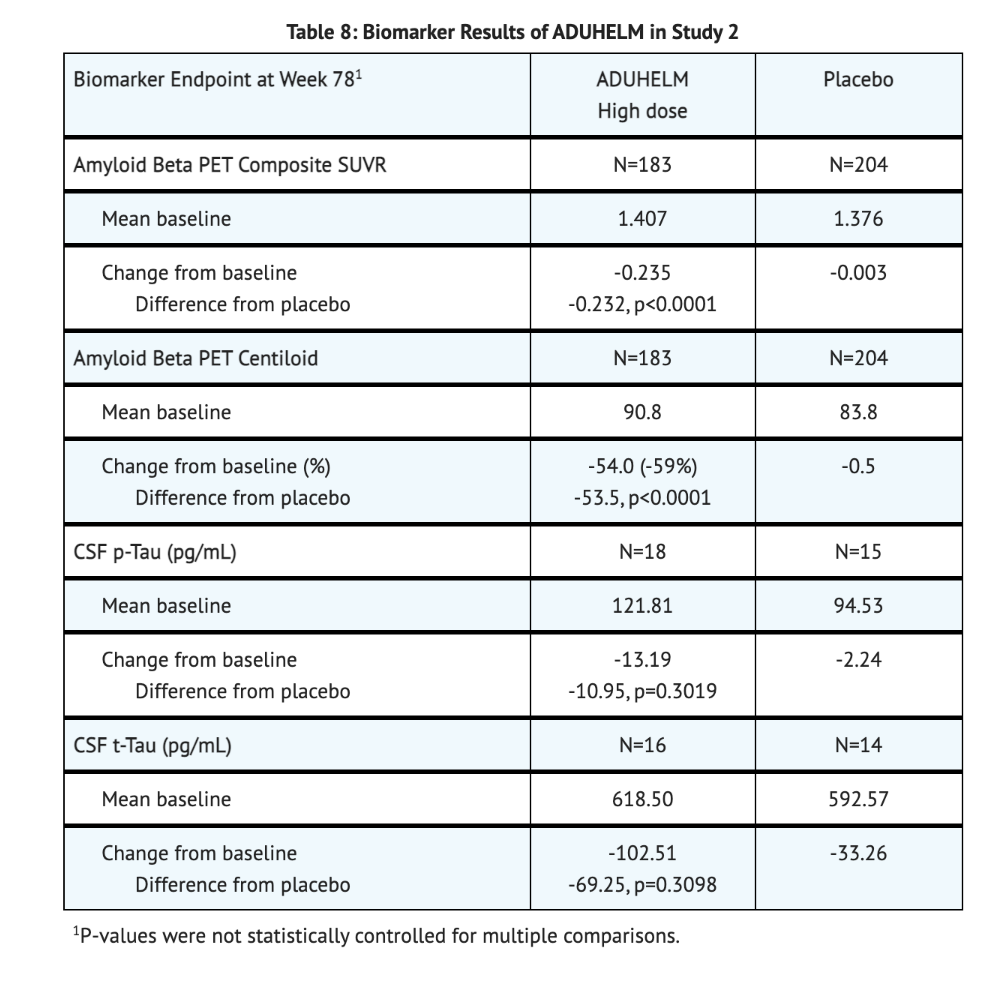
Table 8 summarizes Biomarker Results of Aducanumab-avwa in Study 2.
Study 3
- 73 years of age was the mean age for the patient population in study 3.
- Patients in this study either received 1, 3, 6, or 10 mg/kg of a fixed dosage of Aducanumab-avwa over 44 weeks, titration of 10 mg/kg Aducanumab-avwa, or a placebo for 12 months.
Figure 4 summarizes Reduction in Brain Amyloid Beta Plaque in Study 3.
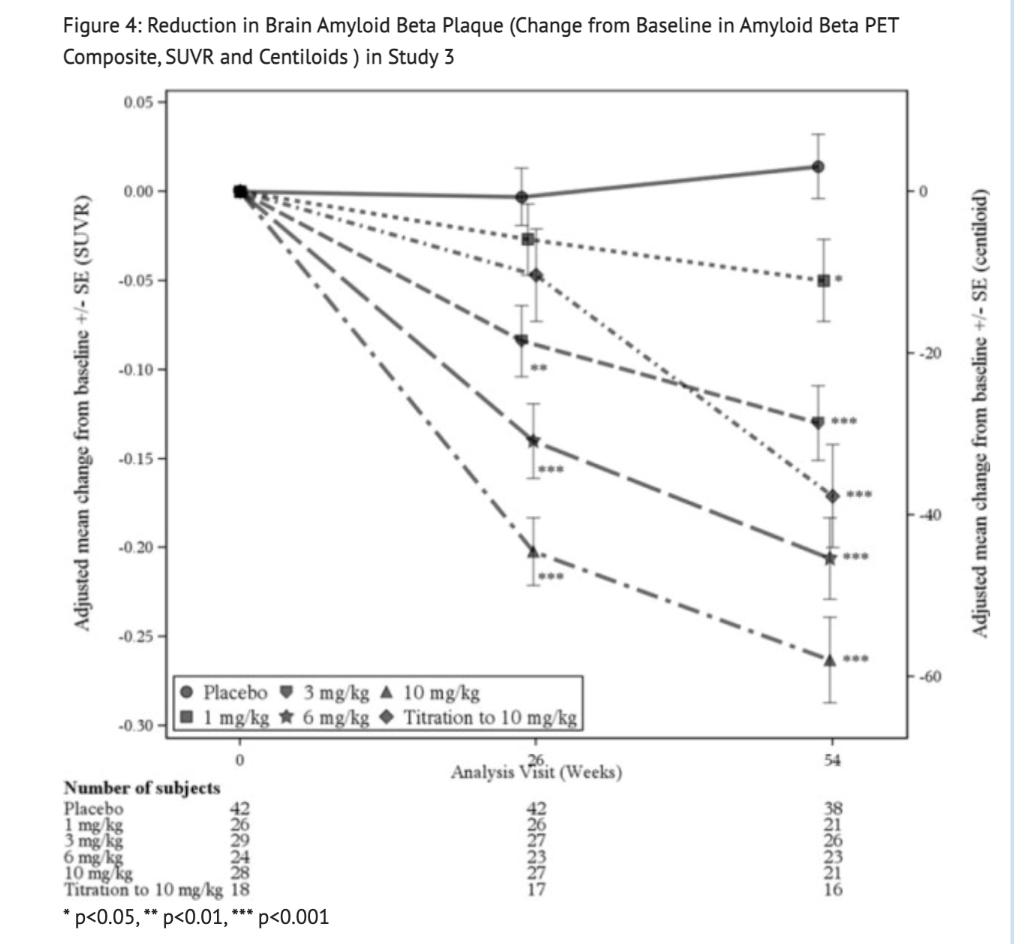
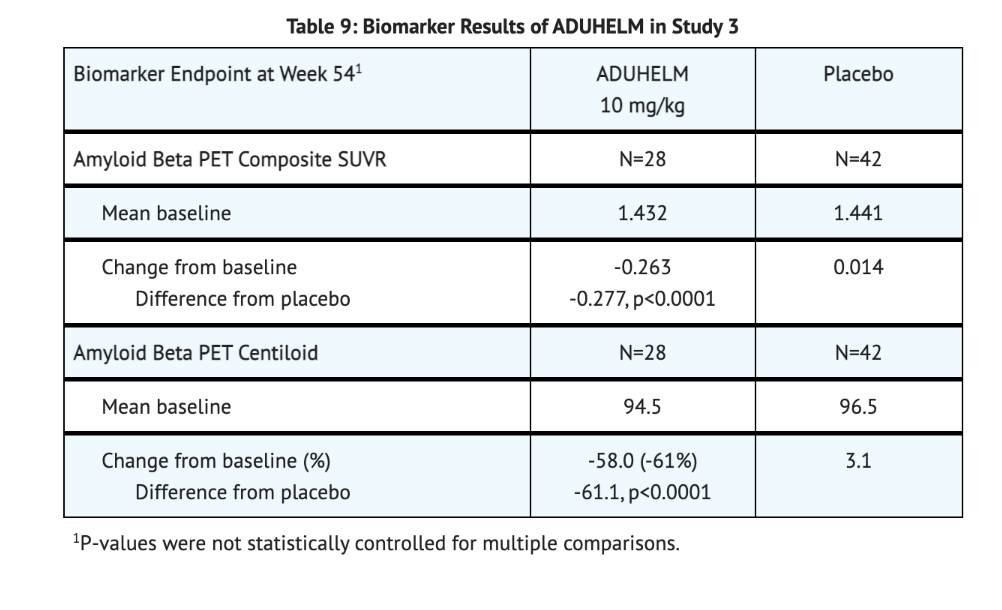
Table 9 summarizes Biomarker Results of Aducanumab-avwa in Study 3.
How Supplied
- A injection containing a colorless to yellow solution, which is also clear to opalescent.
- 2 different single dose vial options for Aducanumab-avwa.
- First option: Single dose vial option could contain 170 mg/1.7 mL of Aducanumab-avwa.
- Second optionL: Single dose vial option could contain 300 mg/3 mL of Aducanumab-avwa.
Storage
- To protect from light, store in original carton.
- Refrigerate from 2°C to 8°C.
- Avoid freezing or shaking Aducanumab-avwa vials.
- Aducanumab-avwa unopened from carton may be stored at 25°C for up to 3 days.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Aducanumab-avwa |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


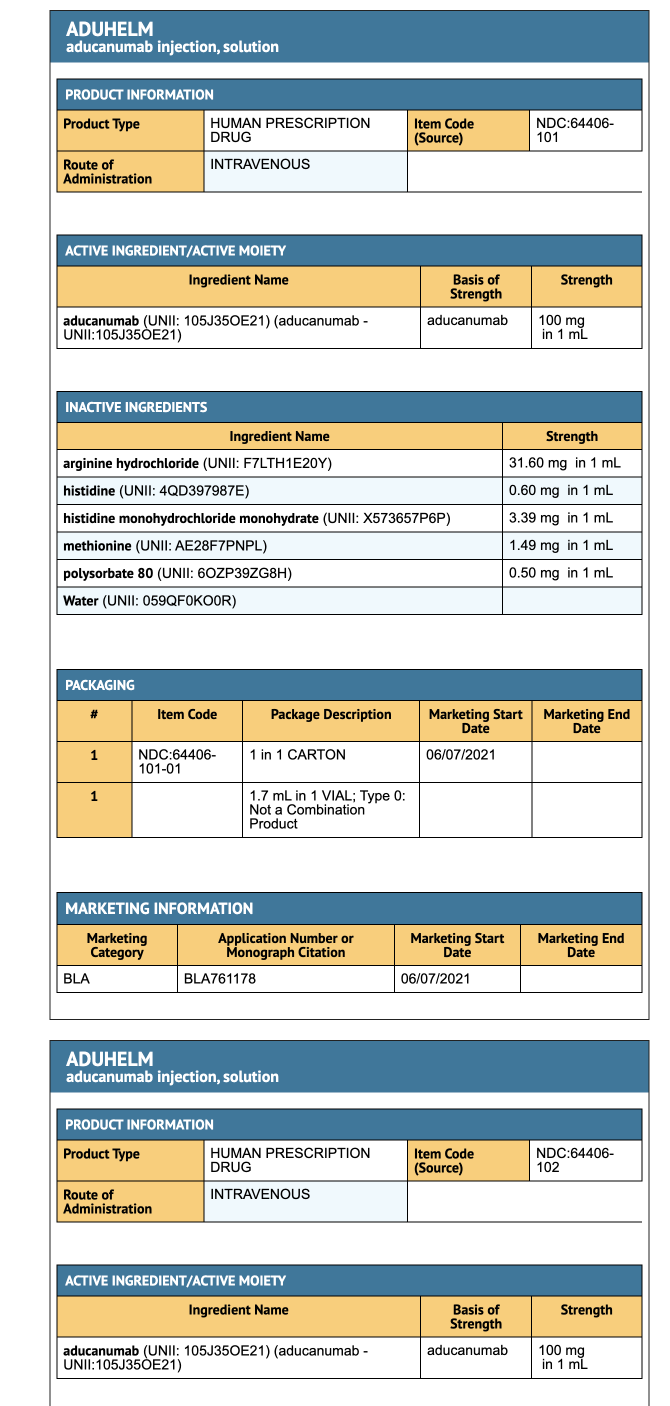
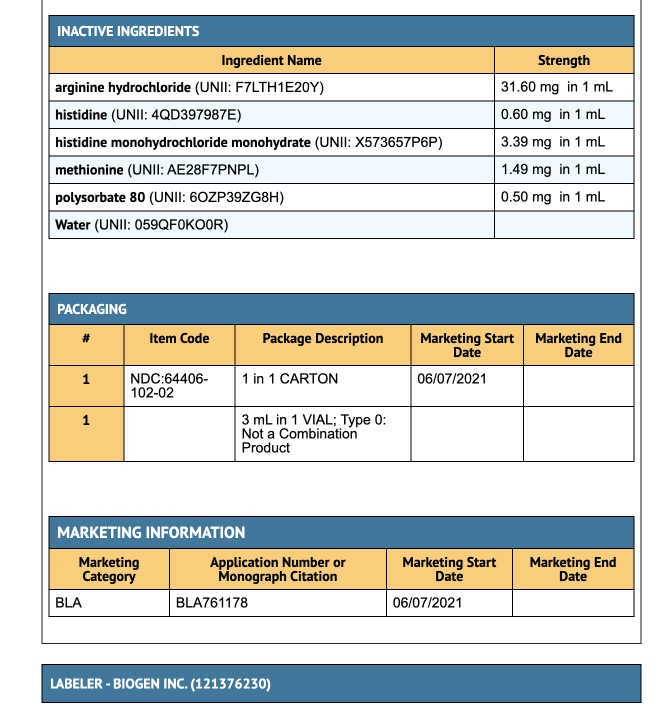
{{#ask: Label Page::Aducanumab-avwa |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Amyloid Related Imaging Abnormalities
- Advise patients that ARIA may occur when taking Aducanumab-avwa.
- ARIA can cause temporary swelling of the brain which eventually resolves.
- Advise patients that bleeding may occur in or on surface of brain in small amounts.
- Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience confusion, dizziness, nausea, headache, seizure, or vision changes.
- Advise patients that MRI's may be used to detect whether ARIA is present or absent.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Urticaria and angioedema are some of the hypersensitivity reactions that may occur in patients taking Aducanumab-avwa.
- Seek medical attention if experiencing signs or symptoms associated with hypersensitivity reactions.
Package Insert
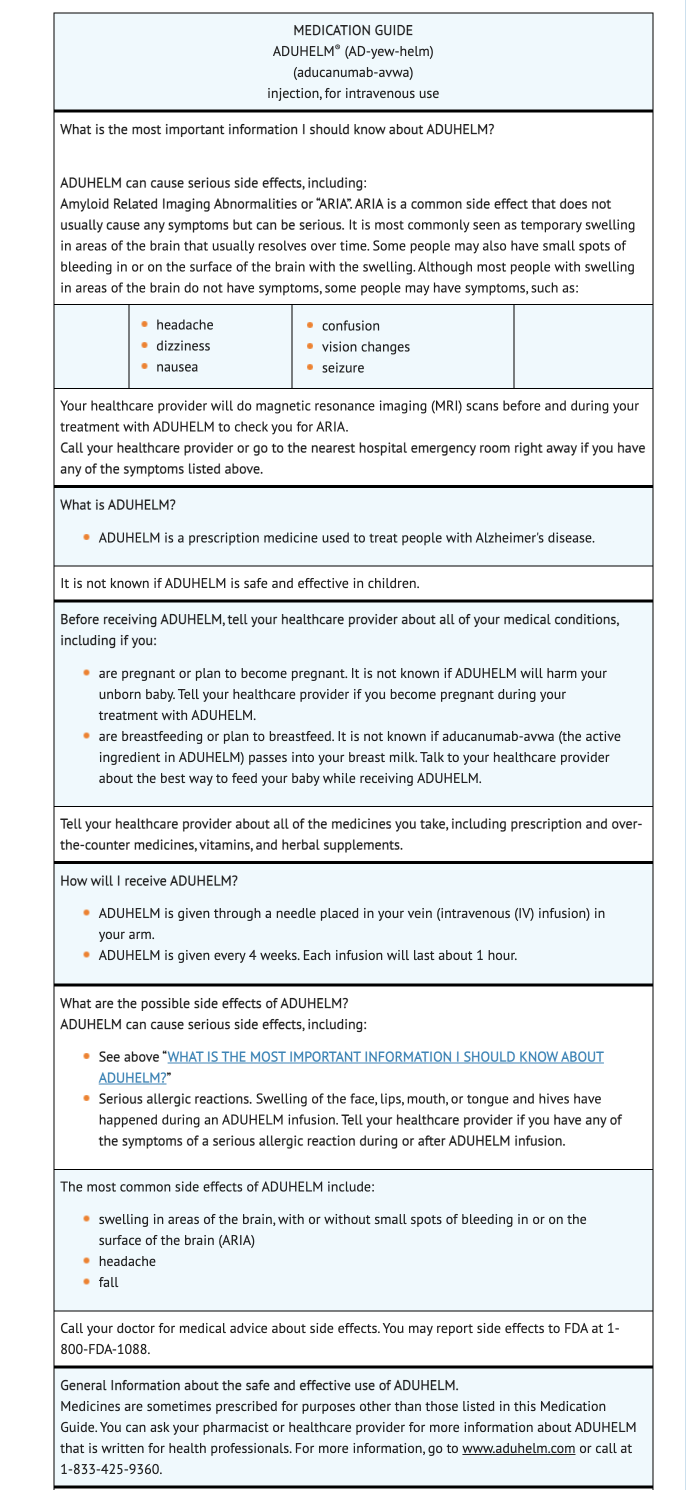

Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Aducanumab-avwa interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Aduhelm
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Aducanumab-avwa Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Aduhelm- aducanumab injection, solution". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 14 June 2021. Retrieved 14 June 2021. Unknown parameter
|url-status=ignored (help)