Abrocitinib
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Edzel Lorraine Co, DMD, MD[2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS, MORTALITY, MALIGNANCY, MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS (MACE), and THROMBOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Increased risk of serious bacterial, fungal, viral and opportunistic infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis (TB). Discontinue treatment with CIBINQO if serious or opportunistic infection occurs. Test for latent TB before and during therapy; treat latent TB prior to use. Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even patients with initial negative latent TB test. • Higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. CIBINQO is not approved for use in RA patients. • Malignancies have occurred with CIBINQO. Higher rate of lymphomas and lung cancers with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in RA patients. • MACE has occurred with CIBINQO. Higher rate of MACE (defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke) with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in RA patients. • Thrombosis has occurred with CIBINQO. Increased incidence of pulmonary embolism, venous and arterial thrombosis with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers. |
Overview
Abrocitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with refractory, moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with other systemic drug products, including biologics, or when use of those therapies is inadvisable. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include (≥1% with CIBINQO 100 mg) are nasopharyngitis, nausea, headache, herpes simplex, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, dizziness, urinary tract infection, fatigue, acne, vomiting, impetigo, oropharyngeal pain, hypertension, influenza, gastroenteritis, and dermatitis contact;
(≥1% with CIBINQO 200 mg and greater than CIBINQO 100 mg) are nausea, headache, herpes simplex, increased blood creatine kinase, dizziness, urinary tract infection, acne, vomiting, gastroenteritis, upper abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, herpes zoster, and thrombocytopenia..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Use the lowest efficacious dose to maintain response.
CIBINQO can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible unless it is less than 12 hours before the next dose, in which case skip the missed dose. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
Administer CIBINQO with or without food at approximately the same time each day.
Swallow CIBINQO tablets whole with water. Do not crush, split, or chew CIBINQO tablets.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
• 50 mg: Pink, oval, film-coated tablet debossed with "PFE" on one side and "ABR 50" on the other. • 100 mg: Pink, round, film-coated tablet debossed with "PFE" on one side and "ABR 100" on the other. • 200 mg: Pink, oval, film-coated tablet debossed with "PFE" on one side and "ABR 200" on the other.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Abrocitinib FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Contraindications
CIBINQO is contraindicated in:
- Patients taking antiplatelet therapies, except for low-dose aspirin (≤81 mg daily), during the first 3 months of treatment
Warnings
|
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS, MORTALITY, MALIGNANCY, MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS (MACE), and THROMBOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Increased risk of serious bacterial, fungal, viral and opportunistic infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis (TB). Discontinue treatment with CIBINQO if serious or opportunistic infection occurs. Test for latent TB before and during therapy; treat latent TB prior to use. Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even patients with initial negative latent TB test. • Higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. CIBINQO is not approved for use in RA patients. • Malignancies have occurred with CIBINQO. Higher rate of lymphomas and lung cancers with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in RA patients. • MACE has occurred with CIBINQO. Higher rate of MACE (defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke) with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers in RA patients. • Thrombosis has occurred with CIBINQO. Increased incidence of pulmonary embolism, venous and arterial thrombosis with another JAK inhibitor vs. TNF blockers. |
- Serious Infections
The most frequent serious infections reported in clinical studies with CIBINQO for atopic dermatitis were herpes simplex, herpes zoster, and pneumonia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Serious infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis and bacterial, invasive fungal, viral, and other opportunistic infections, have occurred in patients receiving JAK inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions.
Avoid use of CIBINQO in patients with active, serious infection including localized infections.
Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating CIBINQO in patients:
• with chronic or recurrent infection • who have been exposed to tuberculosis • with a history of a serious or an opportunistic infection • who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses • with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with CIBINQO. If a patient develops a serious or opportunistic infection, discontinue CIBINQO. Initiate complete diagnostic testing and appropriate antimicrobial therapy. The risks and benefits of treatment with CIBINQO should be carefully considered prior to reinitiating therapy with CIBINQO.
Tuberculosis
Evaluate and test patients for TB before starting CIBINQO therapy and consider yearly screening for patients in highly endemic areas for TB. CIBINQO is not recommended for use in patients with active TB. For patients with a new diagnosis of latent TB or prior untreated latent TB, or for patients with a negative test for latent TB but who are at high risk for TB infection, start preventive therapy for latent TB prior to initiation of CIBINQO. Monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of TB, including patients who were tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy.
Viral Reactivation
Viral reactivation, including herpes virus reactivation (e.g., herpes zoster, herpes simplex), was reported in clinical trials with CIBINQO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If a patient develops herpes zoster, consider interrupting CIBINQO until the episode resolves.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported in patients receiving JAK inhibitors. Perform viral hepatitis screening in accordance with clinical guidelines before starting therapy and monitor for reactivation during therapy with CIBINQO. CIBINQO is not recommended for use in patients with active hepatitis B or hepatitis C [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor patients with inactive HBV for expression of HBV DNA during therapy with CIBINQO. If HBV DNA is detected during therapy with CIBINQO, consult a liver specialist.
- Mortality
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety trial of another JAK inhibitor in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, a higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, was observed in subjects treated with the JAK inhibitor compared with TNF blockers. CIBINQO is not approved for use in RA.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with CIBINQO.
- Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Malignancies, including non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC), were observed in clinical trials with CIBINQO for atopic dermatitis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Perform periodic skin examination for patients who are at increased risk for skin cancer. Exposure to sunlight and UV light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using broad-spectrum sunscreen.
Malignancies, including lymphomas, have occurred in patients receiving JAK inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions. In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety trial of another JAK inhibitor in RA subjects, a higher rate of malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC)) was observed in subjects treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. CIBINQO is not approved for use in RA. A higher rate of lymphomas was observed in subjects treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. A higher rate of lung cancers was observed in current or past smokers treated with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. In this trial, current or past smokers had an additional increased risk of overall malignancies.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with CIBINQO, particularly in patients with a known malignancy (other than a successfully treated NMSC), patients who develop a malignancy when on treatment, and patients who are current or past smokers.
- Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
Major adverse cardiovascular events were reported in clinical trials of CIBINQO for atopic dermatitis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety trial of another JAK inhibitor in RA subjects 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and non-fatal stroke was observed with the JAK inhibitor compared to those treated with TNF blockers. CIBINQO is not approved for use in RA. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with CIBINQO, particularly in patients who are current or past smokers and patients with other cardiovascular risk factors. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious cardiovascular events and the steps to take if they occur. Discontinue CIBINQO in patients that have experienced a myocardial infarction or stroke
- Thrombosis
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) were observed in subjects receiving CIBINQO in the clinical trials for atopic dermatitis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Thrombosis, including DVT, PE, and arterial thrombosis have been reported in patients receiving JAK inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions. Many of these adverse reactions were serious and some resulted in death.
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety trial of another JAK inhibitor in RA subjects 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, higher rates of overall thrombosis, DVT, and PE were observed compared to those treated with TNF blockers. CIBINQO is not approved for use in RA.
Avoid CIBINQO in patients that may be at increased risk of thrombosis. If symptoms of thrombosis occur, discontinue CIBINQO and evaluate and treat patients appropriately.
- Laboratory Abnormalities
Hematologic Abnormalities
Treatment with CIBINQO was associated with an increased incidence of thrombocytopenia and lymphopenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Prior to CIBINQO initiation, perform a CBC [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. CBC evaluations are recommended at 4 weeks after initiation and 4 weeks after dose increase of CIBINQO. Discontinuation of CIBINQO therapy is required for certain laboratory abnormalities [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Lipid Elevations
Dose-dependent increase in blood lipid parameters were reported in subjects treated with CIBINQO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Lipid parameters should be assessed approximately 4 weeks following initiation of CIBINQO therapy and thereafter patients should be managed according to clinical guidelines for hyperlipidemia. The effect of these lipid parameter elevations on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
- Immunizations
Prior to initiating CIBINQO, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines, including prophylactic herpes zoster vaccinations. Avoid vaccination with live vaccines immediately prior to, during and immediately after CIBINQO therapy.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Serious Infections • Mortality • Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders • Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events • Thrombosis • Laboratory Abnormalities
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Abrocitinib Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Effects of Other Drugs on CIBINQO
- Strong CYP2C19 Inhibitors
- Clinical Impact: Coadministration of CIBINQO with strong CYP2C19 inhibitors increases the combined exposure of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2 which may increase the adverse reactions of CIBINQO
- Intervention: Dosage reduction of CIBINQO is recommended when coadministered with strong CYP2C19 inhibitors
- Moderate to Strong Inhibitors of both CYP2C19 and CYP2C9
- Clinical Impact: Coadministration of CIBINQO with drugs that are moderate to strong inhibitors of both CYP2C19 and CYP2C9 increases the exposure of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2 which may increase the adverse reactions of CIBINQO
- Intervention: Avoid concomitant use of CIBINQO with drugs that are moderate to strong inhibitors of both CYP2C19 and CYP2C9.
- Strong CYP2C19 or CYP2C9 Inducers
- Clinical Impact: Coadministration of CIBINQO with strong CYP2C19 or CYP2C9 inducers decreases the combined exposure of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2, which may result in loss of or reduced clinical response
- Intervention: Avoid concomitant use of CIBINQO with strong CYP2C19 or CYP2C9 inducers.
- Strong CYP2C19 Inhibitors
- Effects of CIBINQO on Other Drugs
- P-gp Substrate Where Small Concentration Changes May Lead to Serious or Life-threatening Toxicities
- Clinical Impact: Coadministration of CIBINQO with P-gp substrate increases plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates and may result in potential adverse reactions of the P-gp substrate where small concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities (e.g., digoxin)
- Intervention: Monitor appropriately or dose titrate P-gp substrate where small concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities when coadministered with CIBINQO.
- Antiplatelet Therapy Drugs
- Clinical Impact: Coadministration of CIBINQO with antiplatelet therapy drugs may increase the risk of bleeding with thrombocytopenia.
- Intervention: Antiplatelet drugs, except for low-dose aspirin (≤81 mg daily), during the first 3 months of treatment are contraindicated with CIBINQO.
- P-gp Substrate Where Small Concentration Changes May Lead to Serious or Life-threatening Toxicities
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Abrocitinib in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Abrocitinib in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to CIBINQO during pregnancy. Pregnant women exposed to CIBINQO and health care providers are encouraged to call 1-877-311-3770.
Risk Summary
Available data from pregnancies reported in clinical trials with CIBINQO are not sufficient to establish a drug‑associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of abrocitinib to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at exposure 11 or 4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on AUC comparison, respectively, resulted in maternal dystocia and skeletal variations in rats and no adverse effects in rabbits (see Data).
The background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. All pregnancies carry some risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risks in the U.S. general population of major birth defects and miscarriages are 2–4% and 15–20% of clinically recognized pregnancies, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryofetal development study, abrocitinib was administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of 10, 30, or 60 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. No fetal malformations were observed. Abrocitinib increased the incidence of skeletal variations of short 13th ribs at 30 mg/kg/day (11 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Increased embryofetal lethality and additional skeletal variations (cervical arches with reduced ventral processes, thickened ribs, and unossified metatarsals) were noted at 60 mg/kg/day (17 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In an embryofetal development study, abrocitinib was administered orally to pregnant rabbits at doses of 10, 30, or 75 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. No abrocitinib-related maternal or developmental toxicity was noted at doses up to 75 mg/kg/day (4 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In a prenatal and postnatal development study, abrocitinib was administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of 10, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day beginning on gestation day 6 and continuing through lactation day 20. Dystocia with prolonged parturition and reduced offspring body weights were noted at 30 mg/kg/day (11 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Postnatal survival was markedly decreased at 60 mg/kg/day (17 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No maternal toxicity was observed at 10 mg/kg/day (2.4 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). No abrocitinib-related effects on postnatal developmental, neurobehavioral, or reproductive performance of offspring was noted at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (11 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
Nursing Mothers
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of abrocitinib in human milk, the effects on the breast-fed infant, or the effects on milk production. Abrocitinib was secreted in milk of lactating rats (see Data). When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. Because of the serious adverse findings in adults, including risks of serious infections, malignancy, and thrombosis, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with CIBINQO and for one day after the last dose (approximately 5–6 elimination half-lives).
Data
Animal Data
Lactating female rats were orally administered a single dose of 10 mg/kg abrocitinib on lactation day 12. Abrocitinib AUC was approximately 5 times greater in milk than in plasma.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CIBINQO in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with atopic dermatitis have been established.
In trials Trial-AD-1 and Trial-AD-2, 124 pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years old weighing 25 kg or more with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis were enrolled and randomized to receive either CIBINQO 100 mg (N=51), 200 mg (N=48), or matching placebo (N=25) in monotherapy. Additional 284 pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age weighing 25 kg or more with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, were enrolled and randomized to receive either CIBINQO 100 mg (N=95) or 200 mg (N=94) or matching placebo (N=95) in combination with topical corticosteroids in Trial-AD-4. Efficacy and adverse reaction profile were comparable between the pediatric patients and adults.
The safety and effectiveness of CIBINQO have not been established in pediatric patients below 12 years of age.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data In a juvenile animal toxicity study, abrocitinib was administered orally to juvenile rats at doses of 5, 25, and 75 mg/kg/day from postnatal day 10 (approximately equivalent to a human infant) through postnatal day 63 (approximately equivalent to an adolescent). Abrocitinib caused a reversible, dose‑related decrease in the primary spongiosa in the metaphysis of the proximal tibia and distal femur and adverse effects on bone development at all dose levels. Abrocitinib caused irreversible dose-related small or misshapen femoral heads at doses ≥5 mg/kg/day (0.8 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison); irreversibly decreased femur size and caused paw malrotation and limb impairment at doses ≥25 mg/kg/day (7.2 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison); and fractures at 75 mg/kg/day (27 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison).
In a follow-up study, abrocitinib (25 mg/kg/day, at least 4.5 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) was orally administered to juvenile rats from postnatal day (PND) 10, 15, 21, or 30 through PND day 63. Administration beginning PND 10 caused adverse macroscopic and microscopic bone findings consistent with the previous juvenile animal study. However, administration beginning PND 15 (approximately equivalent to a 6- to 12-month old infant) caused non-adverse reversible microscopic bone findings. No bone findings were noted when administration began on PND 21 or 30 (approximately equivalent to 2- and 6-year old children, respectively).
Geriatic Use
A total of 145 (4.6%) subjects 65 years of age and older, while 25 (0.8%) were 75 years of age and older, were enrolled in CIBINQO clinical trials. Clinical trials of CIBINQO did not include sufficient numbers of subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
A higher proportion of subjects 65 years of age and older discontinued from clinical trials compared to younger subjects. Among all subjects exposed to CIBINQO, including the long-term extension trial, confirmed ALC <500/mm3 occurred only in subjects 65 years of age and older. A higher proportion of subjects 65 years of age and older had platelet counts <75,000/mm3. The incidence rate of herpes zoster in subjects 65 years of age and older treated with CIBINQO (7.40 per 100 patient-years) was higher than that of subjects 18 to less than 65 years of age (3.44 per 100 patient-years).
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Abrocitinib with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Abrocitinib with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
In patients with severe (eGFR <30 mL/min) and moderate (eGFR 30–59 mL/min) renal impairment, the combined exposure (AUCinf,u) of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2, is increased compared to patients with normal renal function (eGFR ≥90 mL/min). This may increase the risk of adverse reactions such as infections.
CIBINQO is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment and ESRD including those on renal replacement therapy.
A dosage reduction in patients with moderate renal impairment is recommended. No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild renal impairment (eGFR 60–89 mL/min).
CIBINQO has not been studied in subjects on renal replacement therapy. In Phase 3 clinical trials, CIBINQO was not evaluated in subjects with atopic dermatitis with baseline creatinine clearance values less than 40 mL/min.
Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use of CIBINQO in patients with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment. In clinical trials, CIBINQO was not evaluated in subjects with severe (Child Pugh C) hepatic impairment.
Dosage adjustment is not required in patients with mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment based on similar combined exposure (AUCinf,u) of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2 compared to patients with normal hepatic function.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
Females
Based on the findings in rats, oral administration of CIBINQO may impair female fertility. Impaired fertility in female rats was reversible 1 month after cessation of abrocitinib oral administration
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Abrocitinib in patients who are immunocompromised.
CYP2C19 Poor Metabolizers
In patients who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers, the AUC of abrocitinib is increased compared to CYP2C19 normal metabolizers due to reduced metabolic clearance. Dosage reduction of CIBINQO is recommended in patients who are known or suspected to be CYP2C19 poor metabolizers based on genotype or previous history/experience with other CYP2C19 substrates.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Abrocitinib Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Abrocitinib Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Abrocitinib and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is no experience regarding human overdosage with CIBINQO. There is no specific antidote for overdose with CIBINQO. In case of an overdose, call Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 for latest recommendations.
Pharmacology

Mechanism of Action
Abrocitinib reversibly inhibits JAK1 by blocking the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding site. In a cell-free isolated enzyme assay, abrocitinib was selective for JAK1 over JAK2 (28-fold), JAK3 (>340-fold), and tyrosine kinase (TYK) 2 (43-fold), as well as the broader kinome. The relevance of inhibition of specific JAK enzymes to therapeutic effectiveness is not currently known. Both the parent compound and the active metabolites inhibit JAK1 activity in vitro with similar levels of selectivity.
Structure
CIBINQO (abrocitinib) tablets contain the free base of abrocitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, for oral administration.
Abrocitinib is a white to pale colored powder with the following chemical name: N-((1s,3s)-3-(methyl(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)cyclobutyl)propane-1-sulfonamide
The solubility of abrocitinib in water is 0.04 mg/mL at 25ºC.
Abrocitinib has a molecular weight of 323.42 g/mol and a molecular formula of C14H21N5O2S.
Pharmacodynamics
Treatment with CIBINQO was associated with dose-dependent reduction in serum markers of inflammation, including high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), interleukin-31 (IL-31) and thymus and activation regulated chemokine (TARC). These changes returned to near baseline within 4 weeks of drug discontinuation.
Effect on Platelet Count
Treatment with CIBINQO was also associated with a transient, dose-dependent decrease in platelet count with the nadir occurring at a median of 24 days after continuous administration of abrocitinib 200 mg once daily. The percent change from baseline of the nadir increases with decreasing baseline platelet counts (-41.2%, -33.4%, and -26.5% for baseline platelet counts of 170, 220, and 270 × 103/mm3, respectively). Partial recovery of platelet count (~40% recovery in platelet count by 12 weeks) occurred without discontinuation of the treatment.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose 3 times the maximum approved recommended dose, abrocitinib does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
Abrocitinib plasma Cmax and AUC increased dose proportionally up to 200 mg. Steady-state plasma concentrations of abrocitinib are achieved within 48 hours after once daily administration.
Absorption
Abrocitinib is absorbed with over 91% extent of oral absorption and absolute oral bioavailability of approximately 60%. The peak plasma concentrations of abrocitinib are reached within 1 hour.
Effect of Food
Coadministration of CIBINQO with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (total 916 calories, with approximate distribution of 55% fat, 29% carbohydrates, and 16% protein) had no clinically relevant effect on abrocitinib exposures (AUC and Cmax of abrocitinib increased by approximately 26% and 29%, respectively, and Tmax was prolonged by 2 hours).
Distribution
After intravenous administration, the volume of distribution of abrocitinib is approximately 100 L. Approximately 64%, 37% and 29% of circulating abrocitinib and its active metabolites M1 and M2, respectively, are bound to plasma proteins. Abrocitinib and its active metabolites M1 and M2 bind predominantly to albumin and distribute equally between red blood cells and plasma.
Elimination
Abrocitinib is eliminated primarily by metabolic clearance mechanisms. The mean elimination half-lives of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2, range 3 to 5 hours.
Metabolism
The metabolism of abrocitinib is mediated by multiple CYP enzymes, CYP2C19 (~53%), CYP2C9 (~30%), CYP3A4 (~11%) and CYP2B6 (~6%). In a human radiolabeled study, abrocitinib was the most prevalent circulating species, with two active polar mono-hydroxylated metabolites identified as M1 (3-hydroxypropyl), and M2 (2-hydroxypropyl). Metabolite M1 is less active than abrocitinib while metabolite M2 is as active as the parent. The pharmacologic activity of abrocitinib is attributable to the unbound exposure of parent molecule (~60%) as well as M1 (~10%) and M2 (~30%) in systemic circulation. The sum of unbound exposures of abrocitinib, M1 and M2, each expressed in molar units and adjusted for relative potencies, is referred to as the combined exposure of abrocitinib and its two active metabolites, M1 and M2.
Excretion
After a single radiolabeled abrocitinib dose, less than 1% of the dose was excreted in urine as unchanged drug. The metabolites of abrocitinib, M1 and M2 are excreted predominantly in urine, and are substrates of OAT3 transporter.
Nonclinical Toxicology
In a 2-year oral carcinogenicity study in rats, abrocitinib increased the incidence of benign thymomas in female rats at doses of 10 and 30 mg/kg/day (2.8 and 14 times the MRHD, respectively, based on AUC comparison). Abrocitinib was not carcinogenic in female rats at 3 mg/kg/day (0.6 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) or male rats at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (14 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Abrocitinib was not carcinogenic in Tg.rasH2 mice at oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day in males and 75 mg/kg/day in females.
Abrocitinib was not mutagenic in the bacterial mutagenicity assay (Ames assay). Although abrocitinib was aneugenic in the in vitro TK6 micronucleus assay, abrocitinib was not aneugenic or clastogenic in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Abrocitinib did not impair male fertility at doses up to 70 mg/kg/day (26 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison) or female fertility at 10 mg/kg/day (2 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Abrocitinib impaired female fertility (reducing fertility index, corpora lutea, and implantation sites) at 70 mg/kg/day (29 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison). Impaired fertility in female rats reversed 1 month after cessation of abrocitinib administration.
Clinical Studies
The efficacy of CIBINQO as monotherapy and in combination with background topical corticosteroids was evaluated in 4 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials [Trial-AD-1 (NCT03349060), Trial-AD-2 (NCT03575871), Trial-AD-3 (NCT03720470), and Trial-AD-4 (NCT03796676)] in 1900 subjects (see Table 8). Trial-AD-1 and Trial-AD-2 enrolled adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older. Trial-AD-3 enrolled only adults (≥18 years of age) and Trial-AD-4 enrolled only pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age. The trials enrolled subjects with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis as defined by Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score ≥3, Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score ≥16, body surface area (BSA) involvement ≥10%, and Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS) ≥4 at the baseline visit prior to randomization.
Baseline Characteristics
In Trial-AD-1, Trial-AD-2, and Trial-AD-3, 53% of subjects were male, 69% of subjects were white, 64% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 3 (moderate AD), and 36% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 4 (severe AD). The baseline mean EASI score was 30. The baseline mean age was 36 years old with 8% of subjects 12 to less than 18 years old and 92% of subjects 18 years of age or older. Subjects in these trials were those who had inadequate response to previous topical therapy or were subjects for whom topical treatments were medically inadvisable or who had received systemic therapies including dupilumab. In each of the trials, over 40% of subjects had prior exposure to systemic therapy. In Trial-AD-1 and Trial-AD-2, 6% of the subjects had received dupilumab, whereas prior use of dupilumab was not allowed in Trial-AD-3.
In Trial-AD-4, 49% of subjects were female, 56% of subjects were White, 33% of subjects were Asian and 6% of subjects were Black. The median age was 15 years and the proportion of subjects with severe atopic dermatitis (IGA of 4) was 38%.
Trial Designs and Endpoints
Trial-AD-1, Trial-AD-2, Trial-AD-3, and Trial-AD-4 assessed the co-primary endpoints of IGA and EASI-75 responses at Week 12.
Clinical Response
Monotherapy Trials
- The proportion of subjects achieving PP-NRS4 at Week 2 (defined as an improvement of ≥4 points from baseline in PP-NRS) was higher in subjects treated with CIBINQO monotherapy 200 mg once daily (28% in Trial-AD-1 and 24% in Trial-AD-2) and 100 mg once daily (11% in both trials) compared to placebo (2% in both trials).
- A higher proportion of subjects in the CIBINQO monotherapy 100 mg or 200 mg once daily arms compared to placebo achieved improvement in itching at Week 12.
Combination Therapy Trials
- The proportions of subjects achieving PP-NRS4 at Week 2 was higher in subjects treated with CIBINQO 200 mg once daily (30%) and 100 mg once daily (14%) in combination with background medicated topical therapies compared to placebo (8%).
- The proportion of pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age achieving PP-NRS4 at Week 2 in Trial-AD-4 was higher with CIBINQO 200 mg once daily (25%) and 100 mg once daily (13%) compared to placebo (8%).
- A higher proportion of subjects in the CIBINQO 200 mg once daily arm compared to placebo achieved improvement in itching at Week 12.
Subgroup Analysis (Monotherapy Trials and the Combination Therapy Trial in Subjects 18 Years of Age and Older)
Examination of age, gender, race, weight, and previous systemic AD therapy treatment did not identify differences in response to CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg once daily among these subgroups in Trial-AD-1, Trial-AD-2, and Trial-AD-3.
How Supplied

Storage
Store CIBINQO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Keep in original package. The container closure system is child resistant.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Abrocitinib |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Tablet Bottle Label ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer NDC 0069-0235-30
CIBINQO™ (abrocitinib) tablets
50 mg
Do not crush, split, or chew the tablets.
30 Tablets Rx only

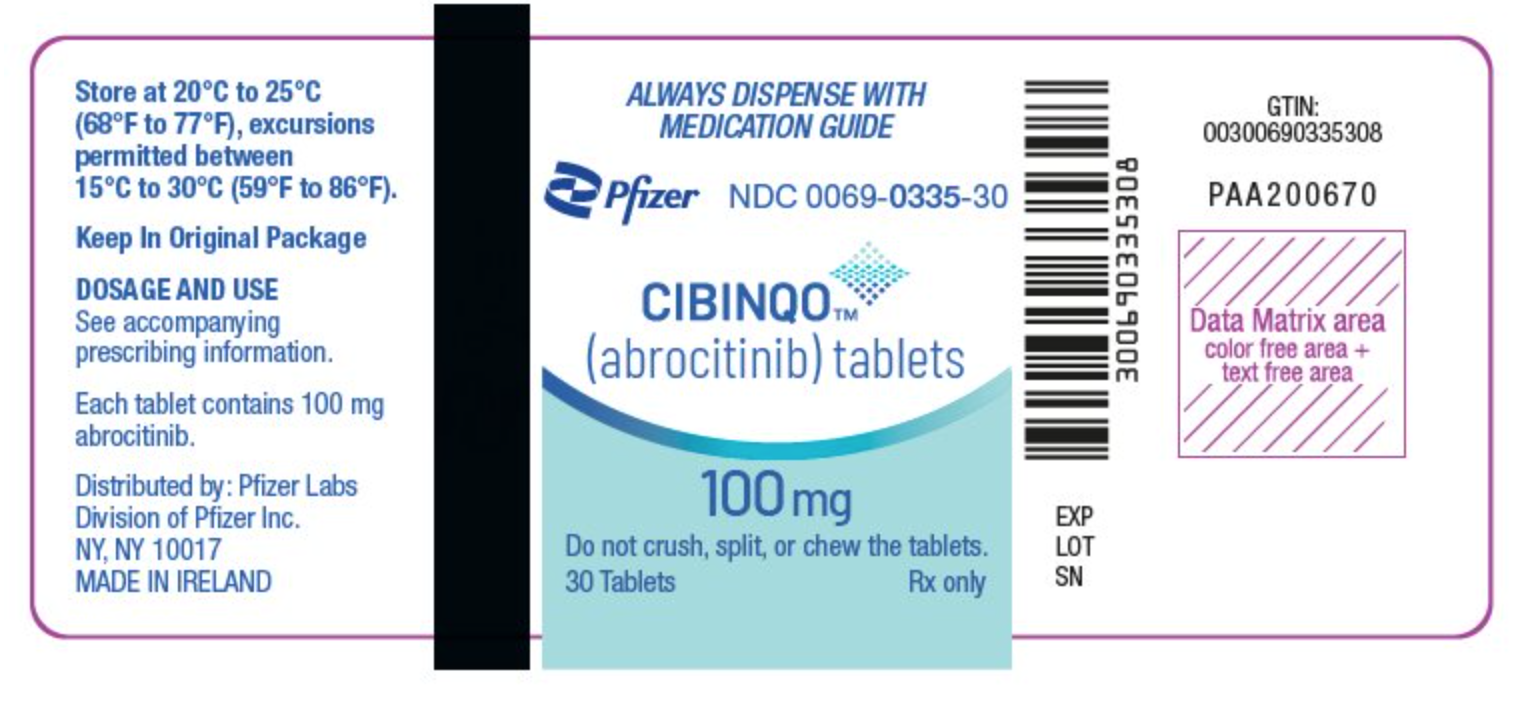
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Tablet Bottle Label ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer NDC 0069-0335-30
CIBINQO™ (abrocitinib) tablets
100 mg
Do not crush, split, or chew the tablets.
30 Tablets Rx only
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg Tablet Bottle Label ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer NDC 0069-0435-30
CIBINQO™ (abrocitinib) tablets
200 mg
Do not crush, split, or chew the tablets.
30 Tablets Rx only

{{#ask: Label Page::Abrocitinib |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Pregnancy Registry
Advise patients to report their pregnancy to 1-877-311-3770/
Serious Infections
Inform patients that they may develop infections when taking CIBINQO. Instruct patients to tell their healthcare provider if they develop any signs or symptoms of an infection.
Advise patients that the risk of herpes zoster is increased in patients treated with CIBINQO and some cases can be serious [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Malignancies
Inform patients that CIBINQO may increase their risk of certain cancers, including skin cancers. Periodic skin examinations are recommended while using CIBINQO. Advise patients that exposure to sunlight and UV light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen.
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
Inform patients that CIBINQO may increase their risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular death. Instruct all patients, especially current or past smokers or patients with other cardiovascular risk factors, to be alert for the development of signs and symptoms of cardiovascular events.
Thrombosis
Advise patients that events of DVT and PE have been reported in clinical trials with CIBINQO. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention if they develop any signs or symptoms of a DVT or PE.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Inform patients that CIBINQO may affect certain lab tests, and that blood tests are required before and during CIBINQO treatment.
Immunizations
Advise patients that vaccination with live vaccines is not recommended during CIBINQO treatment and immediately prior to or after CIBINQO treatment. Instruct patients to inform the healthcare practitioner that they are taking CIBINQO prior to a potential vaccination.
Retinal Detachment
Inform patients that retinal detachment has been reported in clinical trials for atopic dermatitis in patients who received CIBINQO. Advise patients to immediately inform their healthcare provider if they develop any sudden changes in vision while receiving CIBINQO.
Infertility
Advise patients who can become pregnant that CIBINQO may impair fertility.
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with CIBINQO.
Administration
Advise patients not to chew, crush, or split CIBINQO tablets.
This product's labeling may have been updated. For the most recent prescribing information, please visit www.pfizer.com.
For Medical Information about CIBINQO, please visit www.pfizermedinfo.com or call 1-800-438-1985.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Abrocitinib interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
CIBINQO
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Abrocitinib Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib supply.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib 50mg.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib 100mg.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib 200mg.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib supply.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib 50mg.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib 100mg.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Abrocitinib
|Pill Name=Abrocitinib 200mg.png
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}