Tongue cancer pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
| (18 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Tongue cancer}} | {{Tongue cancer}} | ||
{{CMG}}{{AE}}{{Simrat}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Simrat}} {{MAD}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Genes involved in the pathogenesis of tongue cancer include ''[[TP53]]'', ''[[c-myc]]'', and ''erb-b1''. | [[Leukoplakia]] and [[erythroplakia]] have the greatest potential for [[malignant]] transformation in tongue cancer. World Health Organization classified oral cancer into mild, moderate, and severe dysplasia. Genes involved in the pathogenesis of tongue cancer include ''[[TP53]]'', ''[[c-myc]]'', and ''erb-b1''. On gross pathology, exophytic, ulcerative, and infiltarative growth patterns are characteristic findings of tongue cancer. Tongue cancer constitutes of highly differentiated squamous cells lacking frank cytologic criteria of [[malignancy]] with rare mitoses. The surface of the lesion is covered with compressed invaginating folds of [[keratin]] layers. A stroma-like inflammatory reaction and a blunt pushing margin may be seen. | ||
On gross pathology, exophytic, ulcerative, and infiltarative growth patterns are characteristic findings of tongue cancer. | |||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
===Pathogenesis=== | |||
*The two most common types of [[Premalignant condition|precancerous conditions]] on the tongue are called [[leukoplakia]] and [[erythroplakia]] and they can usually be easily spotted by a dentist. | |||
*[[Leukoplakia]] and [[erythroplakia]] have the greatest potential for [[malignant]] transformation into tongue cancer.<ref name="pmid1807482">{{cite journal| author=Abbey LM| title=Precancerous lesions of the mouth. | journal=Curr Opin Dent | year= 1991 | volume= 1 | issue= 6 | pages= 773-6 | pmid=1807482 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1807482 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Leukoplakia]] is defined as a white patch of the [[Mucosal|mucosa]] that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease. | |||
*[[Leukoplakia]] is considered a [[premalignant condition]] from the chronic irritation of the [[mucous membranes]], resulting in increased rates of [[epithelial]] and [[connective tissue]] proliferation. | |||
*[[Leukoplakia]] usually occurs after the age of 40 years, with the peak incidence before age 50 years. | |||
*[[Leukoplakia]] is 2-3 times more common in men than in women. | |||
*The rates of [[malignant]] transformation of [[leukoplakia]] lesions range from less than 1% to as high as 17.5%, averaging 4.5-6%. | |||
*Erythroleukoplakia and nodular [[leukoplakia]] exhibit the highest rate of [[malignant]] transformation. | |||
*[[Erythroplakia]] is defined as a red, velvety plaque found on the oral mucosa that cannot be ascribed to any other predetermined condition. | |||
*No sex predilection is recognized in erythroplakia and it is rarely found on the tongue compared with other sites in the oral cavity. | |||
*[[Erythroplakia]] is considered as the earliest sign of asymptomatic cancer by Mashberg.<ref name="aaa">{{Cite journal | author = [[A. Mashberg]] | title = Erythroplasia: the earliest sign of asymptomatic oral cancer | journal = [[Journal of the American Dental Association (1939)]] | volume = 96 | issue = 4 | pages = 615–620 | year = 1978 | pmid = 0273632}}</ref> | |||
=== World Health Organization grading for oral cancer dysplasia: === | |||
* Mild [[dysplasia]]: Abnormal cytological features largely confined to the '''lower third''' of the [[epithelium]].<ref name="pmid26166107">{{cite journal| author=Lee CC, Ho HC, Su YC, Yu CH, Yang CC| title=Modified Tumor Classification With Inclusion of Tumor Characteristics Improves Discrimination and Prediction Accuracy in Oral and Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients Who Underwent Surgery. | journal=Medicine (Baltimore) | year= 2015 | volume= 94 | issue= 27 | pages= e1114 | pmid=26166107 | doi=10.1097/MD.0000000000001114 | pmc=4504658 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26166107 }}</ref> | |||
* Moderate dysplasia: The dysplastic process extends into the '''middle third''' of the epithelium. | |||
* Severe dysplasia: Extension of the dysplasia into the '''upper third''' of the epithelium. | |||
* [[Carcinoma in situ|Carcinoma in-situ]]: '''Full thickness''' involvement is present in the absence of invasion. | |||
=== Tumor spread === | |||
==== Local spread ==== | |||
* '''Floor of mouth SCC''' spreads superficially without invading into the [[mylohyoid muscle]] or the sublingual gland until a late stage. | |||
* Tumor involving '''the lateral margin of tongue''' tends to spread in depth. | |||
* The '''intrinsic muscles of tongue''' run in all directions. | |||
* Tumors of palate spread superficially rather than in depth. | |||
==== Lymphatic spread ==== | |||
* The mechanism of spread from the primary site to [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] is almost always by [[embolism]] or by permeation. | |||
* Spread to local [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] worsens the prognosis in oral and oropharyngeal cancer. | |||
* The [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]] in the neck are divided into levels. Levels at high risk for metastasis from oral cavity SCC are Levels I, II and III, and to a lesser extent Level IV. | |||
==== Hematogenous spread ==== | |||
* Hematogenous spread is less important than local and [[Lymphatic drainage|lymphatic spread]]. | |||
* The best predictor of the likelihood of this spread is involvement of the neck at multiple levels. | |||
* This suggests that the route of entry of [[Tumor|tumors]] into the circulation is most often via the large [[veins]] in the neck and that hematogenous spread is in effect tertiary spread following extracapsular spread from neck [[Lymph node|lymph nodes]]. | |||
===Genetics=== | ===Genetics=== | ||
* Genes involved in the pathogenesis of tongue cancer include ''[[TP53]]'', which is located on [[chromosome 17]].<ref name="pmid17321451">{{cite journal| author=Abbas NF, Labib El-Sharkawy S, Abbas EA, Abdel Monem El-Shaer M| title=Immunohistochemical study of p53 and angiogenesis in benign and preneoplastic oral lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma. | journal=Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod | year= 2007 | volume= 103 | issue= 3 | pages= 385-90 | pmid=17321451 | doi=10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.11.008 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17321451 }}</ref> | |||
* The [[carcinogens]] in tobacco smoke, for example, increase the [[prevalence]] and spectrum of [[TP53 (gene)|TP53]] [[mutations]].<ref name="pmid20534998">{{cite journal| author=Stelow EB, Jo VY, Stoler MH, Mills SE| title=Human papillomavirus-associated squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract. | journal=Am J Surg Pathol | year= 2010 | volume= 34 | issue= 7 | pages= e15-24 | pmid=20534998 | doi=10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181e21478 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20534998 }}</ref> | |||
* Other [[oncogenes]] associated with squamous cell cancers of the tongue include ''[[c-myc]]'' and ''[[ErbB|erb -b1]]''. | |||
* More than 50% of [[Oropharyngeal carcinoma|oropharyngeal carcinomas]] harbour integrated [[Human papillomavirus|HPV]] [[DNA]]. | |||
* The E6 and E7 viral oncoproteins bind and inactivate the [[TP53 (gene)|TP53]] and [[Retinoblastoma-like protein 1|retinoblastoma gene]] products respectively, disengaging two of the more critical pathways involved in [[cell cycle]] regulation. | |||
* Local tumor recurrence reflects extension of genetically damaged cells beyond the clinical and microscopic boundaries of [[carcinoma]] to the margins of surgical resection.<ref name="pmid21572401">{{cite journal| author=Schlecht NF, Brandwein-Gensler M, Nuovo GJ, Li M, Dunne A, Kawachi N et al.| title=A comparison of clinically utilized human papillomavirus detection methods in head and neck cancer. | journal=Mod Pathol | year= 2011 | volume= 24 | issue= 10 | pages= 1295-305 | pmid=21572401 | doi=10.1038/modpathol.2011.91 | pmc=3157570 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21572401 }}</ref> | |||
* Head and neck SCC have been identified by circulating [[plasma]] or serum changes which can be used for follow-up and screening. | |||
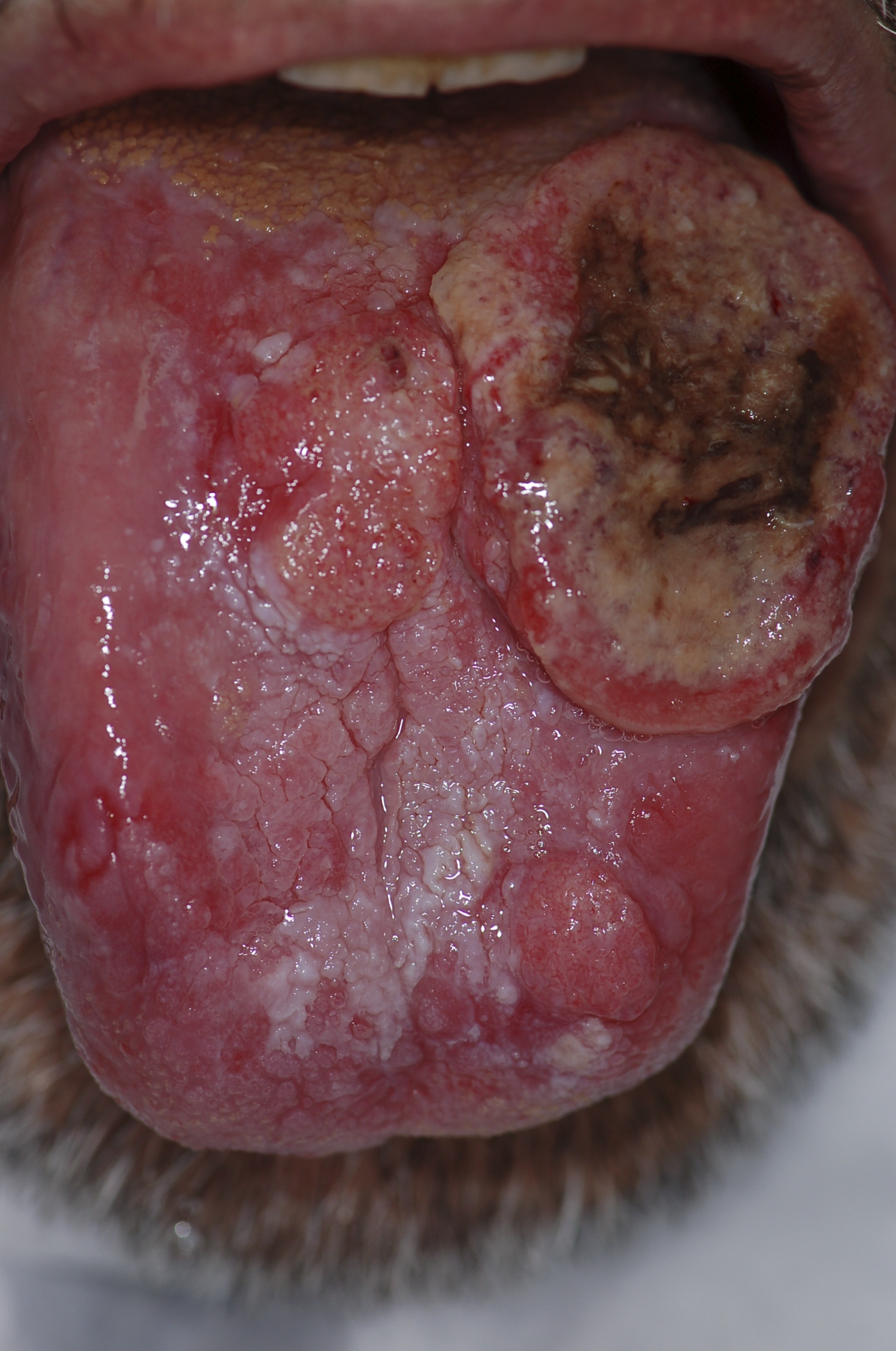
===Gross pathology=== | ===Gross pathology=== | ||
[[Squamous cell carcinoma]] is the most common malignancy of the tongue. It typically has three gross morphologic growth patterns: exophytic, ulcerative, and infiltrative. | * [[Squamous cell carcinoma]] is the most common malignancy of the tongue. | ||
The infiltrative and ulcerative are the types most commonly observed on the tongue.The macroscopic appearance of tongue cancer depends on the following: | * It typically has three gross morphologic growth patterns: exophytic, [[Ulcerated lesion|ulcerative]], and infiltrative. | ||
*Duration of the [[lesion]] | * The infiltrative and [[Ulceral|ulcerative]] are the types most commonly observed on the tongue. | ||
*The amount of [[keratinization]] | * The macroscopic appearance of tongue cancer depends on the following: | ||
*The changes in the adjoining mucosa | |||
A fully developed tongue lesion appears as an exophytic bulky lesion that is gray to grayish-red and has a rough, shaggy, or papillomatous surface. | **Duration of the [[lesion]] | ||
**The amount of [[keratinization]] | |||
**The changes in the adjoining [[Mucosal|mucosa]] | |||
**A fully developed tongue lesion appears as an exophytic bulky lesion that is gray to grayish-red and has a rough, shaggy, or [[Papilloma|papillomatous]] surface. | |||
[[File:PLoS oral cancer.png|300px|center|thumb|Gross pathology of oral SCC, source: By Luca Pastore, Maria Luisa Fiorella, Raffaele Fiorella, Lorenzo Lo Muzio - http://www.plosmedicine.org/article/showImageLarge.action?uri=info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pmed.0050212.g001, CC BY 2.5, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=15252632]] | |||
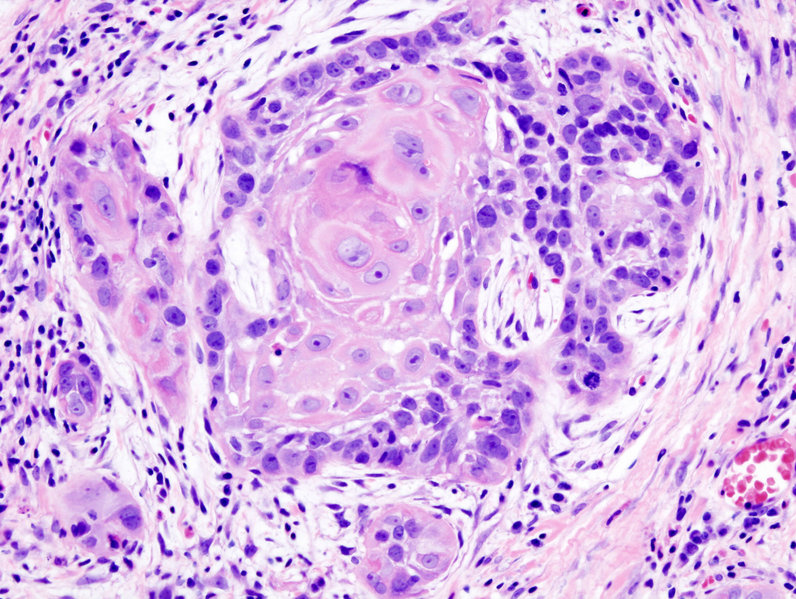
===Microscopic Pathology=== | ===Microscopic Pathology=== | ||
*Microscopically, tongue cancers are broadly based and invasive through papillary fronds. | *Microscopically, tongue cancers are broadly based and invasive through [[papillary]] fronds. | ||
*Tongue cancer constitutes of highly differentiated squamous cells lacking frank cytologic criteria of malignancy with rare mitoses. The surface of the lesion is covered with compressed invaginating folds of [[keratin]] layers. A stroma-like inflammatory reaction and a blunt pushing margin may be seen. | *Tongue cancer constitutes of highly differentiated squamous cells lacking frank cytologic criteria of [[malignancy]] with rare mitoses. | ||
*The surface of the lesion is covered with compressed invaginating folds of [[keratin]] layers. A stroma-like inflammatory reaction and a blunt pushing margin may be seen. | |||
=== | * SCC is subdivided by the WHO into:<ref name="pmid23015393">{{cite journal| author=Peterson BR, Nelson BL| title=Nonkeratinizing undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. | journal=Head Neck Pathol | year= 2013 | volume= 7 | issue= 1 | pages= 73-5 | pmid=23015393 | doi=10.1007/s12105-012-0401-4 | pmc=3597164 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=23015393 }}</ref> | ||
**[[Keratinized|Keratinizing]] type: Worst prognosis. | |||
*[[ | **Undifferentiated type: Intermediate prognosis, [[Epstein Barr virus|EBV]] association.<ref name="pmid7778675">{{cite journal| author=Pathmanathan R, Prasad U, Chandrika G, Sadler R, Flynn K, Raab-Traub N| title=Undifferentiated, nonkeratinizing, and squamous cell carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Variants of Epstein-Barr virus-infected neoplasia. | journal=Am J Pathol | year= 1995 | volume= 146 | issue= 6 | pages= 1355-67 | pmid=7778675 | doi= | pmc=1870892 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7778675 }}</ref> | ||
**Nonkeratinizing type: Good prognosis, [[Epstein Barr virus|EBV]] association. | |||
[[File:Oral cancer (1) squamous cell carcinoma histopathology.jpg|300px|center|thumb|Microscopic picture of oral SCC, source: By No machine-readable author provided. KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=486166]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
{{ | {{WH}} | ||
{{ | {{WS}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:08, 23 January 2018
|
Tongue cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Tongue cancer pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Tongue cancer pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Tongue cancer pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Simrat Sarai, M.D. [2] Mohammed Abdelwahed M.D[3]
Overview
Leukoplakia and erythroplakia have the greatest potential for malignant transformation in tongue cancer. World Health Organization classified oral cancer into mild, moderate, and severe dysplasia. Genes involved in the pathogenesis of tongue cancer include TP53, c-myc, and erb-b1. On gross pathology, exophytic, ulcerative, and infiltarative growth patterns are characteristic findings of tongue cancer. Tongue cancer constitutes of highly differentiated squamous cells lacking frank cytologic criteria of malignancy with rare mitoses. The surface of the lesion is covered with compressed invaginating folds of keratin layers. A stroma-like inflammatory reaction and a blunt pushing margin may be seen.
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis
- The two most common types of precancerous conditions on the tongue are called leukoplakia and erythroplakia and they can usually be easily spotted by a dentist.
- Leukoplakia and erythroplakia have the greatest potential for malignant transformation into tongue cancer.[1]
- Leukoplakia is defined as a white patch of the mucosa that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease.
- Leukoplakia is considered a premalignant condition from the chronic irritation of the mucous membranes, resulting in increased rates of epithelial and connective tissue proliferation.
- Leukoplakia usually occurs after the age of 40 years, with the peak incidence before age 50 years.
- Leukoplakia is 2-3 times more common in men than in women.
- The rates of malignant transformation of leukoplakia lesions range from less than 1% to as high as 17.5%, averaging 4.5-6%.
- Erythroleukoplakia and nodular leukoplakia exhibit the highest rate of malignant transformation.
- Erythroplakia is defined as a red, velvety plaque found on the oral mucosa that cannot be ascribed to any other predetermined condition.
- No sex predilection is recognized in erythroplakia and it is rarely found on the tongue compared with other sites in the oral cavity.
- Erythroplakia is considered as the earliest sign of asymptomatic cancer by Mashberg.[2]
World Health Organization grading for oral cancer dysplasia:
- Mild dysplasia: Abnormal cytological features largely confined to the lower third of the epithelium.[3]
- Moderate dysplasia: The dysplastic process extends into the middle third of the epithelium.
- Severe dysplasia: Extension of the dysplasia into the upper third of the epithelium.
- Carcinoma in-situ: Full thickness involvement is present in the absence of invasion.
Tumor spread
Local spread
- Floor of mouth SCC spreads superficially without invading into the mylohyoid muscle or the sublingual gland until a late stage.
- Tumor involving the lateral margin of tongue tends to spread in depth.
- The intrinsic muscles of tongue run in all directions.
- Tumors of palate spread superficially rather than in depth.
Lymphatic spread
- The mechanism of spread from the primary site to lymph nodes is almost always by embolism or by permeation.
- Spread to local lymph nodes worsens the prognosis in oral and oropharyngeal cancer.
- The lymph nodes in the neck are divided into levels. Levels at high risk for metastasis from oral cavity SCC are Levels I, II and III, and to a lesser extent Level IV.
Hematogenous spread
- Hematogenous spread is less important than local and lymphatic spread.
- The best predictor of the likelihood of this spread is involvement of the neck at multiple levels.
- This suggests that the route of entry of tumors into the circulation is most often via the large veins in the neck and that hematogenous spread is in effect tertiary spread following extracapsular spread from neck lymph nodes.
Genetics
- Genes involved in the pathogenesis of tongue cancer include TP53, which is located on chromosome 17.[4]
- The carcinogens in tobacco smoke, for example, increase the prevalence and spectrum of TP53 mutations.[5]
- Other oncogenes associated with squamous cell cancers of the tongue include c-myc and erb -b1.
- More than 50% of oropharyngeal carcinomas harbour integrated HPV DNA.
- The E6 and E7 viral oncoproteins bind and inactivate the TP53 and retinoblastoma gene products respectively, disengaging two of the more critical pathways involved in cell cycle regulation.
- Local tumor recurrence reflects extension of genetically damaged cells beyond the clinical and microscopic boundaries of carcinoma to the margins of surgical resection.[6]
- Head and neck SCC have been identified by circulating plasma or serum changes which can be used for follow-up and screening.
Gross pathology
- Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common malignancy of the tongue.
- It typically has three gross morphologic growth patterns: exophytic, ulcerative, and infiltrative.
- The infiltrative and ulcerative are the types most commonly observed on the tongue.
- The macroscopic appearance of tongue cancer depends on the following:
- Duration of the lesion
- The amount of keratinization
- The changes in the adjoining mucosa
- A fully developed tongue lesion appears as an exophytic bulky lesion that is gray to grayish-red and has a rough, shaggy, or papillomatous surface.
Microscopic Pathology
- Microscopically, tongue cancers are broadly based and invasive through papillary fronds.
- Tongue cancer constitutes of highly differentiated squamous cells lacking frank cytologic criteria of malignancy with rare mitoses.
- The surface of the lesion is covered with compressed invaginating folds of keratin layers. A stroma-like inflammatory reaction and a blunt pushing margin may be seen.
- SCC is subdivided by the WHO into:[7]
- Keratinizing type: Worst prognosis.
- Undifferentiated type: Intermediate prognosis, EBV association.[8]
- Nonkeratinizing type: Good prognosis, EBV association.
References
- ↑ Abbey LM (1991). "Precancerous lesions of the mouth". Curr Opin Dent. 1 (6): 773–6. PMID 1807482.
- ↑ A. Mashberg (1978). "Erythroplasia: the earliest sign of asymptomatic oral cancer". Journal of the American Dental Association (1939). 96 (4): 615–620. PMID 0273632.
- ↑ Lee CC, Ho HC, Su YC, Yu CH, Yang CC (2015). "Modified Tumor Classification With Inclusion of Tumor Characteristics Improves Discrimination and Prediction Accuracy in Oral and Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients Who Underwent Surgery". Medicine (Baltimore). 94 (27): e1114. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001114. PMC 4504658. PMID 26166107.
- ↑ Abbas NF, Labib El-Sharkawy S, Abbas EA, Abdel Monem El-Shaer M (2007). "Immunohistochemical study of p53 and angiogenesis in benign and preneoplastic oral lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma". Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 103 (3): 385–90. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.11.008. PMID 17321451.
- ↑ Stelow EB, Jo VY, Stoler MH, Mills SE (2010). "Human papillomavirus-associated squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract". Am J Surg Pathol. 34 (7): e15–24. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181e21478. PMID 20534998.
- ↑ Schlecht NF, Brandwein-Gensler M, Nuovo GJ, Li M, Dunne A, Kawachi N; et al. (2011). "A comparison of clinically utilized human papillomavirus detection methods in head and neck cancer". Mod Pathol. 24 (10): 1295–305. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.91. PMC 3157570. PMID 21572401.
- ↑ Peterson BR, Nelson BL (2013). "Nonkeratinizing undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma". Head Neck Pathol. 7 (1): 73–5. doi:10.1007/s12105-012-0401-4. PMC 3597164. PMID 23015393.
- ↑ Pathmanathan R, Prasad U, Chandrika G, Sadler R, Flynn K, Raab-Traub N (1995). "Undifferentiated, nonkeratinizing, and squamous cell carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Variants of Epstein-Barr virus-infected neoplasia". Am J Pathol. 146 (6): 1355–67. PMC 1870892. PMID 7778675.