Thymoma differential diagnosis
|
Thymoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Case Studies |
|
Thymoma differential diagnosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Thymoma differential diagnosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Thymoma differential diagnosis |
+
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Amr Marawan, M.D. [2] Ahmad Al Maradni, M.D. [3] Nouman M.K, M.D.[4]
Overview
Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases such as thymic carcinoma, mediastinal germ cell tumor,thymic masses,lymphoma and substernal thyroid.
Differential Diagnosis
Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases as:
| Diseases | Site | Histology Findings and Lab Tests | Clinical Features | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediastinal Part | Cell Organization | Tumor Cells | Lymphoid Cells | Additional Tests | General Symptoms | Obstructive symptoms | Additional Features | |
| Mediastinal Germ Cell Tumor | Anterior | Non-adhesive |
|
|
|
| ||
| Thymic masses | Anterior | Varies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lymphoma | Anterior,middle | Non-adhesive |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Thyroid | Anterior | Varies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thymomas Vs Thymic Carcinomas:
- The following table shows the important differences between thymomas and thymic carcinomas:
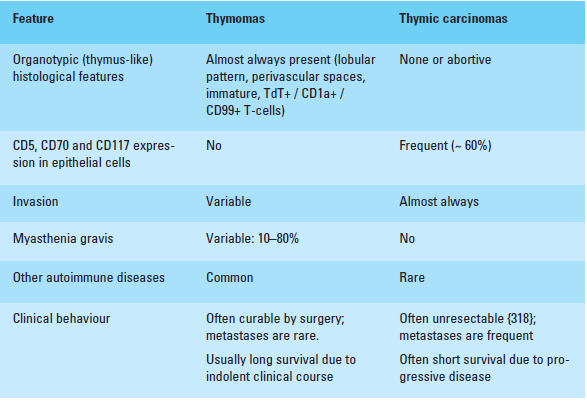 |
Other differentials
Thymoma must be differentiated from other similar conditions which lead to multiple endocrine disorders such as autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome, POEMS syndrome, Hirata syndrome, Kearns–Sayre syndrome and Wolfram syndromes.
| Disease | Addison's disease | Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Hypothyroidism | Other disorders present |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS type 1 | + | Less common | Less common | Hypoparathyroidism Candidiasis Hypogonadism |
| APS type 2 | + | + | + | Hypogonadism Malabsorption |
| APS type 3 | - | + | + | Malabsorption |
| Thymoma | + | - | + | Myasthenia gravis Cushing syndrome |
| Chromosomal abnormalities (Turner syndrome, Down's syndrome) |
- | + | + | Cardiac dysfunction |
| Kearns–Sayre syndrome | - | + | - | Myopathy Hypoparathyroidism Hypogonadism |
| Wolfram syndrome | - | + | - | Diabetes insipidus Optic atrophy Deafness |
| POEMS syndrome | - | + | - | Polyneuropathy Hypogonadism Plasma cell dyscrasias |