Thymoma differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
(Mahshid) |
(I have edited and rearranged the differential diagnosis of thymoma in table form.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Thymoma}} | {{Thymoma}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{AM}} {{AAM}} | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{AM}} {{AAM}} Nouman M.K, M.D.[4] | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases such as [[thymic carcinoma]], | Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases such as [[thymic carcinoma]], [[mediastinal germ cell tumor]],thymic masses,[[lymphoma]] and substernal [[Thyroid disease|thyroid]]. | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases | Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases as<ref name="pmid18417872">{{cite journal| author=Desai F, Shah M, Patel S, Shukla SN| title=Fine needle aspiration cytology of anterior mediastinal masses. | journal=Indian J Pathol Microbiol | year= 2008 | volume= 51 | issue= 1 | pages= 88-90 | pmid=18417872 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18417872 }}</ref>: | ||
* | {| | ||
:* | |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | ||
! rowspan="2" |Diseases | |||
:* | !Site | ||
:* | ! colspan="4" |Histology Findings and Lab Tests | ||
:* | ! colspan="3" |Clinical Features | ||
:* | |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | ||
!Mediastinal Part | |||
!Cell Organization | |||
!Tumor Cells | |||
!Lymphoid Cells | |||
!Additional Tests | |||
!General Symptoms | |||
!Obstructive symptoms | |||
!Additional Features | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinal germ cell tumor|Mediastinal Germ Cell Tumor]] | |||
|Anterior | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Non-adhesive | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Cell with large nuclei and prominent nucleoli | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Mature looking,small | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* PLAP+ | |||
* Serum AFP | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Chest pain, cough and dyspnea|Chest pain]], | |||
* [[Cough]] | |||
* [[Dyspnea|Difficulty breathing]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Superior vena cava syndrome]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Post obstructive pneumonia | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Thymic masses]] | |||
|Anterior | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Varies | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Depend on mass type | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Varies with type | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Depend on type | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Fever and cough|Fever]] | |||
* [[Night sweats]] | |||
* Weight loss(depend on mass type) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Stridor | |||
* Superior vena cava syndrome | |||
* Facial Swelling | |||
* [[Odynophagia]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Obstructive effect can cause [[Horner syndrome]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Lymphoma]] | |||
|Anterior,middle | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Non-adhesive | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Immature lymphoid cells([[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma]]), | |||
* | * Classical Reed Sternberg Cell and its variant(Hodgkin Lymphoma) | ||
: | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
* Immature([[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]]) | |||
* Mature,small(Hodgkin lymphoma) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* LCA+, | |||
* Light chain restriction in B-NHL, | |||
::* | * CD15+,CD30+ in Hodgkin Lymphoma | ||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Fever and cough|Fever]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
:* | * [[Night sweats]] | ||
* [[Shortness of breath while lying down|Shortness of breath]] | |||
* | | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | ||
: | * Phrenic nerve palsy | ||
:* | * [[Hoarseness]] | ||
* Superior vena cava syndrome | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Pleural Effusion | |||
* [[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Thyroid]] | |||
|Anterior | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Varies | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Hurtle cells,prominent nucleoli,abundant cytoplasm | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* [[Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma|Non-Hodgkin]] type is more common in Thyroid lymphoma | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Antithyroid peroxidase antibodies, | |||
* Antithyroglobulin antibodies | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Symptoms of [[hypothyroidism]](cold intolerance,weight gain,constipation etc) or | |||
* [[Hyperthyroidism]] (heat intolerance,weight loss,diarrhea etc) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Positional dyspnea | |||
* Choking sensation | |||
* [[Wheezing]] | |||
* Superior vena cava syndrome | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* Vocal cord palsy | |||
* Horner Syndrome | |||
|} | |||
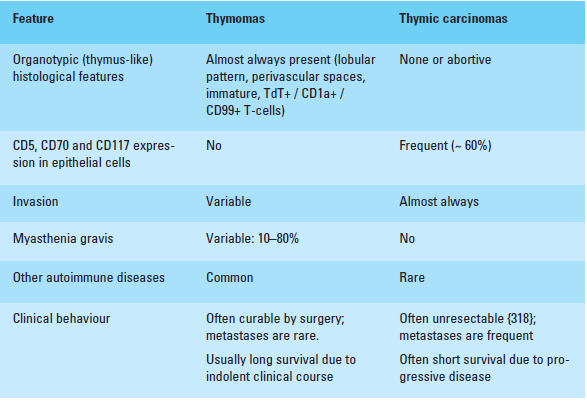
* The following table shows the important differences between thymomas and thymic carcinomas: | |||
{| | {| | ||
| [[File:diff.png|800px|thumb|Differential diagnosis of thymomas types A, AB, B and [[Thymic cancer|thymic carcinomas]]. | | [[File:diff.png|800px|thumb|Differential diagnosis of thymomas types A, AB, B and [[Thymic cancer|thymic carcinomas]].]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Other differentials== | ==Other differentials== | ||
Thymoma must be differentiated from other similar conditions which lead to multiple endocrine disorders such as [[autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome]], [[POEMS syndrome]], Hirata syndrome, [[Kearns–Sayre syndrome]] and [[Wolfram syndrome|Wolfram syndromes]]. | Thymoma must be differentiated from other similar conditions which lead to multiple endocrine disorders such as [[autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome]], [[POEMS syndrome]], Hirata syndrome, [[Kearns–Sayre syndrome]] and [[Wolfram syndrome|Wolfram syndromes]]. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 96: | Line 179: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Types of cancer]] | [[Category:Types of cancer]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 1 August 2018
|
Thymoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Case Studies |
|
Thymoma differential diagnosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Thymoma differential diagnosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Thymoma differential diagnosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Amr Marawan, M.D. [2] Ahmad Al Maradni, M.D. [3] Nouman M.K, M.D.[4]
Overview
Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases such as thymic carcinoma, mediastinal germ cell tumor,thymic masses,lymphoma and substernal thyroid.
Differential Diagnosis
Thymoma must be differentiated from other diseases as[1]:
| Diseases | Site | Histology Findings and Lab Tests | Clinical Features | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediastinal Part | Cell Organization | Tumor Cells | Lymphoid Cells | Additional Tests | General Symptoms | Obstructive symptoms | Additional Features | |
| Mediastinal Germ Cell Tumor | Anterior | Non-adhesive |
|
|
|
| ||
| Thymic masses | Anterior | Varies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lymphoma | Anterior,middle | Non-adhesive |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Thyroid | Anterior | Varies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- The following table shows the important differences between thymomas and thymic carcinomas:
 |
Other differentials
Thymoma must be differentiated from other similar conditions which lead to multiple endocrine disorders such as autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome, POEMS syndrome, Hirata syndrome, Kearns–Sayre syndrome and Wolfram syndromes.
| Disease | Addison's disease | Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Hypothyroidism | Other disorders present |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS type 1 | + | Less common | Less common | Hypoparathyroidism Candidiasis Hypogonadism |
| APS type 2 | + | + | + | Hypogonadism Malabsorption |
| APS type 3 | - | + | + | Malabsorption |
| Thymoma | + | - | + | Myasthenia gravis Cushing syndrome |
| Chromosomal abnormalities (Turner syndrome, Down's syndrome) |
- | + | + | Cardiac dysfunction |
| Kearns–Sayre syndrome | - | + | - | Myopathy Hypoparathyroidism Hypogonadism |
| Wolfram syndrome | - | + | - | Diabetes insipidus Optic atrophy Deafness |
| POEMS syndrome | - | + | - | Polyneuropathy Hypogonadism Plasma cell dyscrasias |
References
- ↑ Desai F, Shah M, Patel S, Shukla SN (2008). "Fine needle aspiration cytology of anterior mediastinal masses". Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 51 (1): 88–90. PMID 18417872.