Mitral regurgitation chest x-ray: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Mitral regurgitation}} | {{Mitral regurgitation}} | ||
{{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}}; [[Varun Kumar]], M.B.B.S.; [[Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan]], M.B.B.S. | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}}; [[Varun Kumar]], M.B.B.S.; [[Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan]], M.B.B.S. | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
The chest [[x-ray]] in individuals with chronic [[mitral regurgitation]] is characterized by enlargement of the [[left atrium]] and the [[left ventricle]]. In acute mitral regurgitation, [[pulmonary edema]] is present, but the heart is not enlarged. | The chest [[x-ray]] in individuals with chronic [[mitral regurgitation]] is characterized by enlargement of the [[left atrium]] and the [[left ventricle]]. In acute mitral regurgitation, [[pulmonary edema]] is present, but the heart is not enlarged. | ||
== | ==Chest X-ray == | ||
[[Image:mitral-valve02.jpg||250px|left|Calcification of the mitral annulus]]<br clear="left"/> | [[Image:mitral-valve02.jpg||250px|left|Calcification of the mitral annulus]]<br clear="left"/> | ||
*The pulmonary vascular markings are typically normal in chronic compensated mitral regurgitation, since the pulmonary venous pressures are usually not significantly elevated. | *The pulmonary vascular markings are typically normal in chronic compensated mitral regurgitation, since the pulmonary venous pressures are usually not significantly elevated. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 19:30, 28 August 2012
|
Mitral Regurgitation Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Mitral regurgitation chest x-ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Mitral regurgitation chest x-ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Mitral regurgitation chest x-ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.; Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan, M.B.B.S.
Overview
The chest x-ray in individuals with chronic mitral regurgitation is characterized by enlargement of the left atrium and the left ventricle. In acute mitral regurgitation, pulmonary edema is present, but the heart is not enlarged.
Chest X-ray
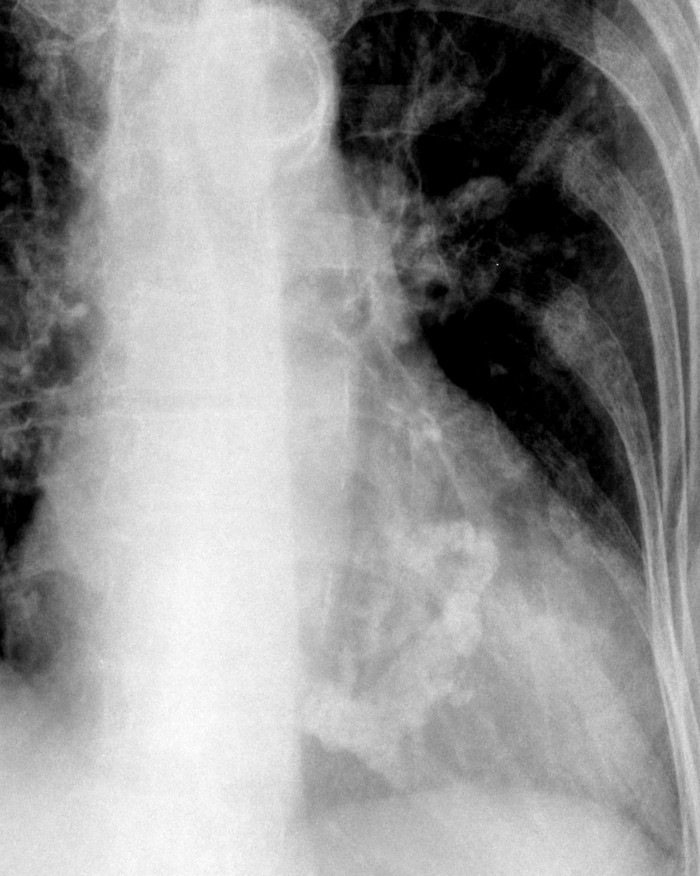
- The pulmonary vascular markings are typically normal in chronic compensated mitral regurgitation, since the pulmonary venous pressures are usually not significantly elevated.
- Calcification of the mitral annulus is not infrequent, and is seen in up to 35% of elderly patients on echocardiography which is more sensitive than CXR. It typically begins around the margins of the posterior leaflet forming a “C” (as in this case) - eventually with anterior leaflet involvement the “C” closes forming an “O”.
- As opposed to aortic valve calcification, calcification of the mitral annulus is not significantly associated with stenosis of the valve and contrary to previous thought, nor is it associated with strokes - when other factors are adjusted for in multivariate models.
- Mitral valve calcification can be associated with impaired AV nodal conduction and can be associated with varying degrees of heart block.
- The left main sten bronchus can be pushed up by an enlarged left atrium
- Pathologically it is important to distinguish annular calcification, which is not on the leaflet, and is covered with intact endothelium, from leaflet calcification in stenotic valves secondary to rheumatic fever.
- If there is no enlargement of the cardiac silhouette and pulmonary edema is present, this suggests acute disruption of the valve apparatus.