Lymphangiomyomatosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
'''For patient information, click [[Lymphangiomyomatosis (patient information)|here]].''' | '''For patient information, click [[Lymphangiomyomatosis (patient information)|here]].''' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 7: | ||
{{SK}} Lymphangioleiomyomatosis; LAM; pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis; pulmonary lymphangiomyomatosis | {{SK}} Lymphangioleiomyomatosis; LAM; pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis; pulmonary lymphangiomyomatosis | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
* Lymphangiomyocytosis is defined as a multifocal neoplasm with differentiation of the perivascular epithelioid cell and has a female prepondrance, especially females of child-bearing age. Lymphangiomyomatosis is the result of disorderly smooth muscle proliferation throughout the bronchioles, alveolar septa, perivascular spaces, and lymphatics, resulting in the obstruction of small airways (leading to pulmonary cyst formation and [[pneumothorax]]) and [[lymphatic system|lymphatics]] (leading to [[chyle|chylous]] [[pleural effusion]]). LAM occurs in a sporadic form, which only affects females, who are usually of childbearing age. Lymphangiomyocytosis also occurs in patients who have [[tuberous sclerosis]]. | * Lymphangiomyocytosis is defined as a multifocal neoplasm with differentiation of the perivascular epithelioid cell and has a female prepondrance, especially females of child-bearing age. | ||
*The | * Lymphangiomyomatosis is the result of disorderly smooth muscle proliferation throughout the bronchioles, alveolar septa, perivascular spaces, and lymphatics, resulting in the obstruction of small airways (leading to pulmonary cyst formation and [[pneumothorax]]) and [[lymphatic system|lymphatics]] (leading to [[chyle|chylous]] [[pleural effusion]]). LAM occurs in a sporadic form, which only affects females, who are usually of childbearing age. Lymphangiomyocytosis also occurs in patients who have [[tuberous sclerosis]]. | ||
*The ''tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)'' gene mutation has been associated with the development of lymphangiomyomatosis. | |||
*On gross pathology, [feature1], [feature2], and [feature3] are characteristic findings of [disease name]. | *On gross pathology, [feature1], [feature2], and [feature3] are characteristic findings of [disease name]. | ||
*On microscopic histopathological analysis, smooth muscle and epithelioid cells and by the proliferation of lymphatic vessels are characteristic findings of lmphangiomyomatosis. | *On microscopic histopathological analysis, smooth muscle and epithelioid cells and by the proliferation of lymphatic vessels are characteristic findings of lmphangiomyomatosis.<ref name="pmid11031360">{{cite journal| author=Ferrans VJ, Yu ZX, Nelson WK, Valencia JC, Tatsuguchi A, Avila NA et al.| title=Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): a review of clinical and morphological features. | journal=J Nippon Med Sch | year= 2000 | volume= 67 | issue= 5 | pages= 311-29 | pmid=11031360 | doi= | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11031360 }} </ref> | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
* There are no established causes for lymphangiomyomatosis. | * There are no established causes for lymphangiomyomatosis. | ||
==Differentiating Lymphangiomyomatosis from other Diseases== | ==Differentiating Lymphangiomyomatosis from other Diseases== | ||
* Lymphangiomyomatosis must be differentiated from other diseases that cause similar clinical features, such as: | * Lymphangiomyomatosis must be differentiated from other diseases that cause similar clinical features, such as: | ||
:*Asthma | :*[[Asthma]] | ||
:*Spontaneous pneumothorax | :*Spontaneous pneumothorax | ||
:*Emphysema | :*[[Emphysema]] | ||
:*Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis | :*[[Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis]] | ||
:*Eosinophilic granuloma (EG) | :*[[Eosinophilic granuloma]] (EG) | ||
:*Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome | :*Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome | ||
:*Lymphangiomas | :*[[Lymphangiomas]] | ||
:*Pulmonary lymphangiectasis | :*Pulmonary lymphangiectasis | ||
:*Leiomyosarcoma | :*[[Leiomyosarcoma]] | ||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
* Till date, 1500 cases of sporadic cases of lymphangiomyomatosis was estimated to be in United States. | * Till date, 1500 cases of sporadic cases of lymphangiomyomatosis was estimated to be in United States. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 34: | ||
===Race=== | ===Race=== | ||
*There is no racial predilection for lymphangiomyomatosis. | *There is no racial predilection for lymphangiomyomatosis. | ||
== Natural History, Complications and Prognosis== | == Natural History, Complications and Prognosis== | ||
*Common complications of lymphangiomyomatosis include ascitis, chylous pleural effusion, pneumothorax, hemoptysis, chyloptysis, chyluria, hematuria, pericardial effusion, pneumoperitoneum, lymphedema, respiratory failure, osteoporosis, and meningioma. | *Common complications of lymphangiomyomatosis include [[ascitis]], chylous pleural effusion, [[pneumothorax]], [[hemoptysis]], chyloptysis, chyluria, hematuria, pericardial effusion, pneumoperitoneum, lymphedema, respiratory failure, osteoporosis, and meningioma. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
=== Symptoms === | === Symptoms === | ||
*Symptoms of lymphangiomyomatosis may include the following: | *Symptoms of lymphangiomyomatosis may include the following: | ||
:*Constipation | :*[[Constipation]] | ||
:*Dyspnea | :*[[Dyspnea]] | ||
:*Cough | :*[[Cough]] | ||
=== Physical Examination === | === Physical Examination === | ||
*Physical examination may be remarkable for: | *Physical examination may be remarkable for: | ||
:*Crackles | :*Crackles | ||
:*Wheezes | :*Wheezes | ||
:*Pleural effusion | :*[[Pleural effusion]] | ||
:*Pneumothorax | :*[[Pneumothorax]] | ||
:*Ascites | :*[[Ascites]] | ||
:*Facial angiofibromas | :*Facial angiofibromas | ||
:*Periungual fibromas | :*Periungual fibromas | ||
| Line 76: | Line 57: | ||
=== Laboratory Findings === | === Laboratory Findings === | ||
*There are no specific laboratory findings associated with lymphangiomyomatosis. | *There are no specific laboratory findings associated with lymphangiomyomatosis. | ||
===Imaging Findings=== | ===Imaging Findings=== | ||
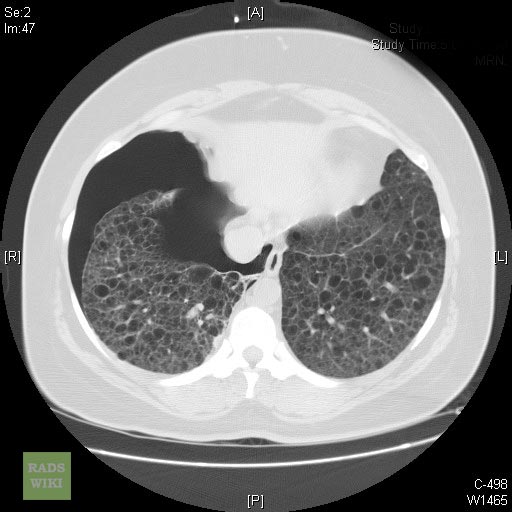
* High-resolution [[computed tomography|CT]] of the chest is both more specific than chest x ray for the diagnosis, as well as better able to assess the degree of pulmonary involvement. | * High-resolution [[computed tomography|CT]] of the chest is both more specific than chest x ray for the diagnosis, as well as better able to assess the degree of pulmonary involvement. | ||
| Line 84: | Line 64: | ||
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis 003.jpg</gallery> | Lymphangioleiomyomatosis 003.jpg</gallery> | ||
* With lmphangiomyomatosis, there is diffuse replacement of the pulmonary parenchyma by thin-walled cysts measuring 2-20 mm in diameter, with equal involvement of upper and lower lung zones. On chest X-rays, superimposition of the cysts gives a reticulonodular pattern of [[interstitial lung disease]]. | * With lmphangiomyomatosis, there is diffuse replacement of the pulmonary parenchyma by thin-walled cysts measuring 2-20 mm in diameter, with equal involvement of upper and lower lung zones. On chest X-rays, superimposition of the cysts gives a reticulonodular pattern of [[interstitial lung disease]]. | ||
=== Other Diagnostic Studies === | === Other Diagnostic Studies === | ||
*Lymphangiomyomatosis may also be diagnosed using immunohistochemistry. | *Lymphangiomyomatosis may also be diagnosed using immunohistochemistry. | ||
*Findings on immunohistochemistry include Flt-4 (VEGFR-3). | *Findings on immunohistochemistry include Flt-4 (VEGFR-3). | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
=== Medical Therapy === | === Medical Therapy === | ||
*The mainstay of therapy for lymphangiomyomatosisis include sirolimus, medroxyprogesterone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and tamoxifen. | *The mainstay of therapy for lymphangiomyomatosisis include [[sirolimus]], medroxyprogesterone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and [[tamoxifen]]. | ||
=== Surgery === | === Surgery === | ||
*Surgical intervention can only be performed for patients with receuurent lymphangiomyomatosis resitant to medical therapy. | *Surgical intervention can only be performed for patients with receuurent lymphangiomyomatosis resitant to medical therapy. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 13 May 2016
For patient information, click here.
Template:Lymphangiomyomatosis Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S. [2] Ammu Susheela, M.D. [3]
Synonyms and keywords: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis; LAM; pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis; pulmonary lymphangiomyomatosis
Overview
Pathophysiology
- Lymphangiomyocytosis is defined as a multifocal neoplasm with differentiation of the perivascular epithelioid cell and has a female prepondrance, especially females of child-bearing age.
- Lymphangiomyomatosis is the result of disorderly smooth muscle proliferation throughout the bronchioles, alveolar septa, perivascular spaces, and lymphatics, resulting in the obstruction of small airways (leading to pulmonary cyst formation and pneumothorax) and lymphatics (leading to chylous pleural effusion). LAM occurs in a sporadic form, which only affects females, who are usually of childbearing age. Lymphangiomyocytosis also occurs in patients who have tuberous sclerosis.
- The tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) gene mutation has been associated with the development of lymphangiomyomatosis.
- On gross pathology, [feature1], [feature2], and [feature3] are characteristic findings of [disease name].
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, smooth muscle and epithelioid cells and by the proliferation of lymphatic vessels are characteristic findings of lmphangiomyomatosis.[1]
Causes
- There are no established causes for lymphangiomyomatosis.
Differentiating Lymphangiomyomatosis from other Diseases
- Lymphangiomyomatosis must be differentiated from other diseases that cause similar clinical features, such as:
- Asthma
- Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Emphysema
- Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
- Eosinophilic granuloma (EG)
- Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome
- Lymphangiomas
- Pulmonary lymphangiectasis
- Leiomyosarcoma
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Till date, 1500 cases of sporadic cases of lymphangiomyomatosis was estimated to be in United States.
Age
- Lymphangiomyomatosis is more commonly observed among femele patients aged 15-45 years old.
Gender
- Lymphangiomyomatosis affects women exclusively who are of reproductive age group.
Race
- There is no racial predilection for lymphangiomyomatosis.
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- Common complications of lymphangiomyomatosis include ascitis, chylous pleural effusion, pneumothorax, hemoptysis, chyloptysis, chyluria, hematuria, pericardial effusion, pneumoperitoneum, lymphedema, respiratory failure, osteoporosis, and meningioma.
Diagnosis
Symptoms
- Symptoms of lymphangiomyomatosis may include the following:
Physical Examination
- Physical examination may be remarkable for:
- Crackles
- Wheezes
- Pleural effusion
- Pneumothorax
- Ascites
- Facial angiofibromas
- Periungual fibromas
- Hypomelanotic macules, ash-leaf spots
- Shagreen patch
- Forehead plaque
- Retinal hamartoma
Laboratory Findings
- There are no specific laboratory findings associated with lymphangiomyomatosis.
Imaging Findings
- High-resolution CT of the chest is both more specific than chest x ray for the diagnosis, as well as better able to assess the degree of pulmonary involvement.
- With lmphangiomyomatosis, there is diffuse replacement of the pulmonary parenchyma by thin-walled cysts measuring 2-20 mm in diameter, with equal involvement of upper and lower lung zones. On chest X-rays, superimposition of the cysts gives a reticulonodular pattern of interstitial lung disease.
Other Diagnostic Studies
- Lymphangiomyomatosis may also be diagnosed using immunohistochemistry.
- Findings on immunohistochemistry include Flt-4 (VEGFR-3).
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- The mainstay of therapy for lymphangiomyomatosisis include sirolimus, medroxyprogesterone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, and tamoxifen.
Surgery
- Surgical intervention can only be performed for patients with receuurent lymphangiomyomatosis resitant to medical therapy.
References
- ↑ Ferrans VJ, Yu ZX, Nelson WK, Valencia JC, Tatsuguchi A, Avila NA; et al. (2000). "Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): a review of clinical and morphological features". J Nippon Med Sch. 67 (5): 311–29. PMID 11031360.