Hamartoma MRI: Difference between revisions
(→MRI) |
Farima Kahe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Hamartoma}} | {{Hamartoma}} | ||
{{CMG}}{{AE}}{{MV}} | {{CMG}}{{AE}}{{MV}} {{VKG}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
MRI is the modality of choice for assessment of hypothalamic, [[spleen]], [[kidney]], and other abdominal hamartomas. On MRI, hamartoma is characterized by a heterogeneous signal in [[T1]] and high signal due to fat and cartilaginous components in T2. | [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] is the modality of choice for assessment of [[hypothalamic]], [[spleen]], [[kidney]], and other abdominal [[hamartomas]]. On [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], [[hamartoma]] is characterized by a [[heterogeneous]] signal in [[T1]] and high signal due to fat and [[cartilaginous]] components in [[T2 phage|T2]]. | ||
==MRI== | ==MRI== | ||
MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of [[hamartomas]]. Findings on MRI suggestive of [[hamartomas]] include:<ref name="radio">Hypothalamic hamartoma.Dr Donna D'Souza et al. Radiopedia.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/pulmonary-hamartoma-1 Accessed on December 09, 2015</ref><ref name="pmid27936889">{{cite journal |vauthors=Leiter Herrán F, Restrepo CS, Alvarez Gómez DI, Suby-Long T, Ocazionez D, Vargas D |title=Hamartomas from head to toe: an imaging overview |journal=Br J Radiol |volume=90 |issue=1071 |pages=20160607 |date=March 2017 |pmid=27936889 |pmc=5601532 |doi=10.1259/bjr.20160607 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17620469">{{cite journal |vauthors=Saleem SN, Said AH, Lee DH |title=Lesions of the hypothalamus: MR imaging diagnostic features |journal=Radiographics |volume=27 |issue=4 |pages=1087–108 |date=2007 |pmid=17620469 |doi=10.1148/rg.274065123 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*T1: isointense to cerebral cortex | * | ||
*T1 contrast: no contrast enhancement | *[[T1]]: isointense to [[cerebral cortex]] | ||
*T2: iso to hyperintense to [[cerebral cortex]], the higher the proportion of glial cells, the higher the [[T2]] signal. | *[[T1]] contrast: no contrast enhancement | ||
*MR spectroscopy | *T2: iso to hyperintense to [[cerebral cortex]], the higher the proportion of [[Glial cell|glial]] cells, the higher the [[T2]] signal. | ||
*[[Mitral regurgitation|MR]] [[spectroscopy]] | |||
**Reduced NAA/C | **Reduced NAA/C | ||
**Increased | **Increased myo [[inositol]] | ||
**Increased Cho/Cr compared to the [[amygdala]] has also been reported. | **Increased Cho/Cr compared to the [[amygdala]] has also been reported. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
Image:Biliary-hamartomas-MR-05.jpg|Biliary hamartomas([http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]) | Image:Biliary-hamartomas-MR-05.jpg|Biliary hamartomas([http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<br style="clear:left" /> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 04:20, 5 April 2019
|
Hamartoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hamartoma MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hamartoma MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [2] Vamsikrishna Gunnam M.B.B.S [3]
Overview
MRI is the modality of choice for assessment of hypothalamic, spleen, kidney, and other abdominal hamartomas. On MRI, hamartoma is characterized by a heterogeneous signal in T1 and high signal due to fat and cartilaginous components in T2.
MRI
MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of hamartomas. Findings on MRI suggestive of hamartomas include:[1][2][3]
- T1: isointense to cerebral cortex
- T1 contrast: no contrast enhancement
- T2: iso to hyperintense to cerebral cortex, the higher the proportion of glial cells, the higher the T2 signal.
- MR spectroscopy
Gallery
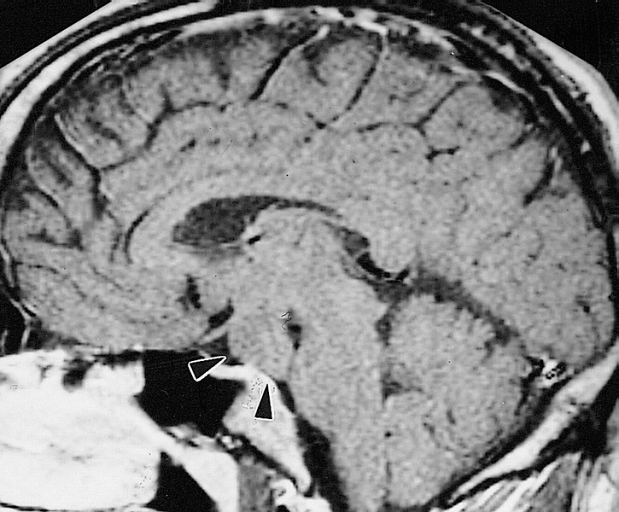
Hypothalamic Hamartoma
-
MRI showing hypothalamic hamartoma(Images courtesy of RadsWiki)
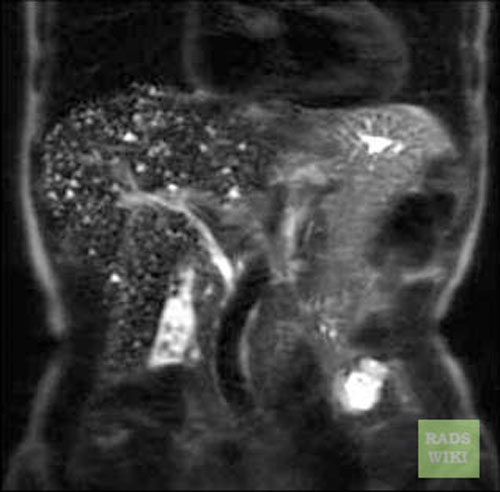
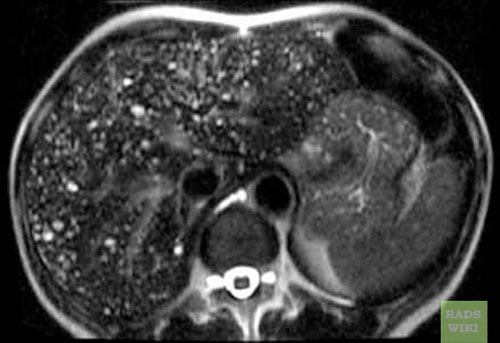
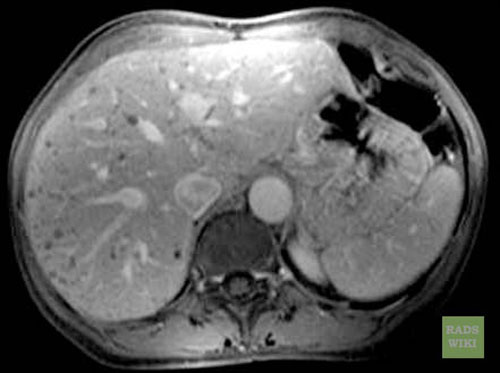
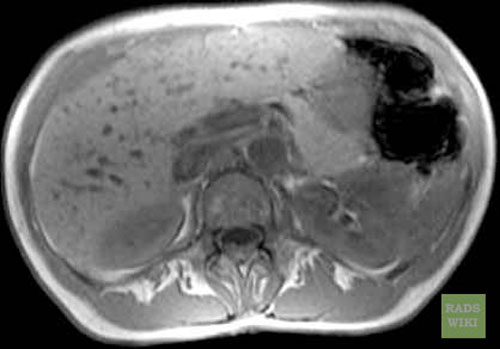
Biliar Hamartomas
-
Biliary hamartomas(Images courtesy of RadsWiki)
-
Biliary hamartomas(Images courtesy of RadsWiki)
-
Biliary hamartomas(Images courtesy of RadsWiki)
-
Biliary hamartomas(Images courtesy of RadsWiki)
References
- ↑ Hypothalamic hamartoma.Dr Donna D'Souza et al. Radiopedia.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/pulmonary-hamartoma-1 Accessed on December 09, 2015
- ↑ Leiter Herrán F, Restrepo CS, Alvarez Gómez DI, Suby-Long T, Ocazionez D, Vargas D (March 2017). "Hamartomas from head to toe: an imaging overview". Br J Radiol. 90 (1071): 20160607. doi:10.1259/bjr.20160607. PMC 5601532. PMID 27936889.
- ↑ Saleem SN, Said AH, Lee DH (2007). "Lesions of the hypothalamus: MR imaging diagnostic features". Radiographics. 27 (4): 1087–108. doi:10.1148/rg.274065123. PMID 17620469.