Degarelix: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|indicationType=treatment | |indicationType=treatment | ||
|indication=patients with advanced [[prostate cancer]]. | |indication=patients with advanced [[prostate cancer]]. | ||
|adverseReactions=injection site reactions (e.g., [[pain]], [[erythema]], [[swelling]], or [[induration]]), hot flashes, increased weight, fatigue, and increases in serum levels of transaminases and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT),asthenia, fever, night sweats, Nausea, Dizziness, headache and insomnia<!--Black Box Warning--> | |adverseReactions=injection site reactions (e.g., [[pain]], [[erythema]], [[swelling]], or [[induration]]), [[hot flashes]], increased weight, [[fatigue]], and increases in serum levels of transaminases and [[gamma-glutamyltransferase]] (GGT),[[asthenia]], [[fever]], [[night sweats]], [[Nausea]], [[Dizziness]], [[headache]] and [[insomnia]]<!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle=Title | |blackBoxWarningTitle=Title | ||
|blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;"> </span></i> | |blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;"> </span></i> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
|fdaLIADAdult=====Prostate cancer===== | |fdaLIADAdult=====Prostate cancer===== | ||
* | *Degarelix is a [[GnRH]] receptor antagonist indicated for treatment of patients with advanced [[prostate cancer]] | ||
=====Dosing Information===== | =====Dosing Information===== | ||
*Degarelix is for subcutaneous administration only and is not to be administered intravenously. | *Degarelix is for subcutaneous administration only and is not to be administered intravenously. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
:*Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the reconstituted product can no longer be used. Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose for the patient). | :*Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the reconstituted product can no longer be used. Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose for the patient). | ||
| Line 84: | Line 81: | ||
<!--Contraindications--> | <!--Contraindications--> | ||
|contraindications=*Degarelix is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to degarelix or to any of the product components. | |contraindications=*Degarelix is contraindicated in patients with known [[hypersensitivity]] to degarelix or to any of the product components. | ||
*Degarelix is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. Degarelix can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Degarelix given to rabbits during organogenesis at doses that were 0.02% of the clinical loading dose (240 mg) on a mg/m2 basis caused embryo/fetal lethality and abortion. When degarelix was given to female rats during organogenesis, at doses that were just 0.036% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis, there was an increase post implantation loss and a decrease in the number of live fetuses. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. | *Degarelix is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. Degarelix can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Degarelix given to rabbits during organogenesis at doses that were 0.02% of the clinical loading dose (240 mg) on a mg/m2 basis caused embryo/fetal lethality and abortion. When degarelix was given to female rats during organogenesis, at doses that were just 0.036% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis, there was an increase post implantation loss and a decrease in the number of live fetuses. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. | ||
| Line 90: | Line 87: | ||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
|warnings======Effect on QT/QTc Interval===== | |warnings======Effect on QT/QTc Interval===== | ||
*Long-term androgen deprivation therapy prolongs the QT interval. Physicians should consider whether the benefits of androgen deprivation therapy outweigh the potential risks in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, electrolyte abnormalities, or congestive heart failure and in patients taking Class IA (e.g. quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g. amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications. | *Long-term [[androgen]] deprivation therapy prolongs the [[QT interval]]. Physicians should consider whether the benefits of androgen deprivation therapy outweigh the potential risks in patients with [[congenital long QT syndrome]], electrolyte abnormalities, or [[congestive heart failure]] and in patients taking Class IA (e.g. [[quinidine]], [[procainamide]]) or Class III (e.g. [[amiodarone]], [[sotalol]]) [[antiarrhythmic]] medications. | ||
*In the randomized, active-controlled trial comparing Degarelix to leuprolide, periodic electrocardiograms were performed. Seven patients, three (<1%) in the pooled degarelix group and four (2%) patients in the leuprolide 7.5 mg group, had a QTcF > 500 msec. From baseline to end of study the median change for Degarelix was 12.3 msec and for leuprolide was 16.7 msec. | *In the randomized, active-controlled trial comparing Degarelix to [[leuprolide]], periodic electrocardiograms were performed. Seven patients, three (<1%) in the pooled degarelix group and four (2%) patients in the [[leuprolide]] 7.5 mg group, had a QTcF > 500 msec. From baseline to end of study the median change for Degarelix was 12.3 msec and for [[leuprolide]] was 16.7 msec. | ||
=====Laboratory Testing===== | =====Laboratory Testing===== | ||
*Therapy with Degarelix results in suppression of the pituitary gonadal system. Results of diagnostic tests of the pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal functions conducted during and after Degarelix may be affected. The therapeutic effect of Degarelix should be monitored by measuring serum concentrations of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) periodically. If PSA increases, serum concentrations of testosterone should be measured. | *Therapy with Degarelix results in suppression of the pituitary gonadal system. Results of diagnostic tests of the pituitary [[gonadotropic]] and gonadal functions conducted during and after Degarelix may be affected. The therapeutic effect of Degarelix should be monitored by measuring serum concentrations of [[prostate-specific antigen]] (PSA) periodically. If [[PSA]] increases, serum concentrations of [[testosterone]] should be measured. | ||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | <!--Adverse Reactions--> | ||
| Line 100: | Line 97: | ||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | <!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | ||
|clinicalTrials=*Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. | |clinicalTrials=*Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. | ||
*A total of 1325 patients with prostate cancer received Degarelix either as a monthly treatment (60-160 mg) or as a single dose (up to 320 mg). A total of 1032 patients (78%) were treated for at least 6 months and 853 patients (64%) were treated for one year or more. The most commonly observed adverse reactions during Degarelix therapy included injection site reactions (e.g., pain, erythema, swelling, or induration), hot flashes, increased weight, fatigue, and increases in serum levels of transaminases and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT). The majority of the adverse reactions were Grade 1 or 2, with Grade 3/4 adverse reaction incidences of 1% or less. | *A total of 1325 patients with prostate cancer received Degarelix either as a monthly treatment (60-160 mg) or as a single dose (up to 320 mg). A total of 1032 patients (78%) were treated for at least 6 months and 853 patients (64%) were treated for one year or more. The most commonly observed adverse reactions during Degarelix therapy included injection site reactions (e.g., [[pain]], [[erythema]], [[swelling]], or [[induration]]), hot flashes, increased weight, fatigue, and increases in serum levels of [[transaminases]] and [[gamma-glutamyltransferase]] (GGT). The majority of the adverse reactions were Grade 1 or 2, with Grade 3/4 adverse reaction incidences of 1% or less. | ||
*Degarelix was studied in an active-controlled trial (N = 610) in which patients with prostate cancer were randomized to receive Degarelix (subcutaneous) or leuprolide (intramuscular) monthly for 12 months. Adverse reactions reported in 5% of patients or more are shown in Table 1. | *Degarelix was studied in an active-controlled trial (N = 610) in which patients with prostate cancer were randomized to receive Degarelix (subcutaneous) or [[leuprolide]] (intramuscular) monthly for 12 months. Adverse reactions reported in 5% of patients or more are shown in Table 1. | ||
[[File:Degarelix03.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | [[File:Degarelix03.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
*The most frequently reported adverse reactions at the injection sites were pain (28%), erythema (17%), swelling (6%), induration (4%) and nodule (3%). These adverse reactions were mostly transient, of mild to moderate intensity, occurred primarily with the starting dose and led to few discontinuations (<1%). Grade 3 injection site reactions occurred in 2% or less of patients receiving degarelix. | *The most frequently reported adverse reactions at the injection sites were [[pain]] (28%), [[erythema]] (17%), [[swelling]] (6%), [[induration]] (4%) and nodule (3%). These adverse reactions were mostly transient, of mild to moderate intensity, occurred primarily with the starting dose and led to few discontinuations (<1%). Grade 3 injection site reactions occurred in 2% or less of patients receiving degarelix. | ||
*Hepatic laboratory abnormalities were primarily Grade 1 or 2 and were generally reversible. Grade 3 hepatic laboratory abnormalities occurred in less than 1% of patients. | *Hepatic laboratory abnormalities were primarily Grade 1 or 2 and were generally reversible. Grade 3 hepatic laboratory abnormalities occurred in less than 1% of patients. | ||
*In 1-5% of patients the following adverse reactions, not already listed, were considered related to Degarelix by the investigator: | *In 1-5% of patients the following adverse reactions, not already listed, were considered related to Degarelix by the investigator: | ||
*Body as a whole: Asthenia, fever, night sweats; Digestive system: Nausea; Nervous system: Dizziness, headache, insomnia. | *Body as a whole: [[Asthenia]], [[fever]], [[night sweats]]; Digestive system: [[Nausea]]; Nervous system: [[Dizziness]], [[headache]], [[insomnia]]. | ||
*The following adverse reactions, not already listed, were reported to be drug-related by the investigator in ≥1% of patients: erectile dysfunction, gynecomastia, hyperhidrosis, testicular atrophy, and diarrhea. | *The following adverse reactions, not already listed, were reported to be drug-related by the investigator in ≥1% of patients: [[erectile dysfunction]], [[gynecomastia]], [[hyperhidrosis]], [[testicular atrophy]], and [[diarrhea]]. | ||
*Changes in bone density: | *Changes in [[bone density]]: | ||
:*Decreased bone density has been reported in the medical literature in men who have had orchiectomy or who have been treated with a GnRH agonist. It can be anticipated that long periods of medical castration in men will result in decreased bone density. | :*Decreased bone density has been reported in the medical literature in men who have had [[orchiectomy]] or who have been treated with a [[GnRH agonist]]. It can be anticipated that long periods of medical castration in men will result in decreased bone density. | ||
*Anti-degarelix antibody development has been observed in 10% of patients after treatment with Degarelix for 1 year. There is no indication that the efficacy or safety of Degarelix treatment is affected by antibody formation. | *Anti-degarelix antibody development has been observed in 10% of patients after treatment with Degarelix for 1 year. There is no indication that the efficacy or safety of Degarelix treatment is affected by antibody formation. | ||
|postmarketing=There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of Degarelix in the drug label. | |postmarketing=There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of Degarelix in the drug label. | ||
| Line 118: | Line 115: | ||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | <!--Drug Interactions--> | ||
|drugInteractions=*No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted. | |drugInteractions=*No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted. | ||
*Degarelix is not a substrate for the human CYP450 system. Degarelix is not an inducer or inhibitor of the CYP450 system in vitro. Therefore, clinically significant CYP450 pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions are unlikely. | *Degarelix is not a substrate for the human [[CYP450]] system. Degarelix is not an inducer or inhibitor of the [[CYP450]] system in vitro. Therefore, clinically significant [[CYP450]] pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions are unlikely. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
|FDAPregCat=X | |FDAPregCat=X | ||
|useInPregnancyFDA=*Women who are or may become pregnant should not take Degarelix . When degarelix was given to rabbits during early organogenesis at doses of 0.002 mg/kg/day (about 0.02% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in early post-implantation loss. Degarelix given to rabbits during mid and late organogenesis at doses of 0.006 mg/kg/day (about 0.05% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused embryo/fetal lethality and abortion. When degarelix was given to female rats during early organogenesis, at doses of 0.0045 mg/kg/day (about 0.036% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in early post-implantation loss. When degarelix was given to female rats during mid and late organogenesis, at doses of 0.045 mg/kg/day (about 0.36% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in the number of minor skeletal abnormalities and variants. | |useInPregnancyFDA=*Women who are or may become pregnant should not take Degarelix . When degarelix was given to rabbits during early organogenesis at doses of 0.002 mg/kg/day (about 0.02% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in early post-implantation loss. Degarelix given to rabbits during mid and late organogenesis at doses of 0.006 mg/kg/day (about 0.05% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused embryo/fetal lethality and [[abortion]]. When degarelix was given to female rats during early organogenesis, at doses of 0.0045 mg/kg/day (about 0.036% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in early post-implantation loss. When degarelix was given to female rats during mid and late organogenesis, at doses of 0.045 mg/kg/day (about 0.36% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in the number of minor skeletal abnormalities and variants. | ||
|useInPregnancyAUS=* | |useInPregnancyAUS=* | ||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Degarelix in women who are pregnant. | There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Degarelix in women who are pregnant. | ||
|useInLaborDelivery=There is no FDA guidance on use of Degarelix during labor and delivery. | |useInLaborDelivery=There is no FDA guidance on use of Degarelix during labor and delivery. | ||
| Line 133: | Line 129: | ||
|useInRace=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix with respect to specific racial populations. | |useInRace=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix with respect to specific racial populations. | ||
|useInRenalImpair=*No pharmacokinetic studies in renally impaired patients have been conducted. At least 20-30% of a given dose of degarelix is excreted unchanged in the urine. | |useInRenalImpair=*No pharmacokinetic studies in renally impaired patients have been conducted. At least 20-30% of a given dose of degarelix is excreted unchanged in the urine. | ||
*A population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from the randomized study demonstrated that there is no significant effect of mild renal impairment [creatinine clearance (CrCL) 50-80 mL/min] on either the degarelix concentration or testosterone concentration. Data on patients with moderate or severe renal impairment is limited and therefore degarelix should be used with caution in patients with CrCL < 50 mL/min. | *A population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from the randomized study demonstrated that there is no significant effect of mild renal impairment [[[creatinine clearance]] (CrCL) 50-80 mL/min] on either the degarelix concentration or [[testosterone]] concentration. Data on patients with moderate or severe [[renal impairment]] is limited and therefore degarelix should be used with caution in patients with [[CrCL]] < 50 mL/min. | ||
|useInHepaticImpair=*Patients with hepatic impairment were excluded from the randomized trial. | |useInHepaticImpair=*Patients with hepatic impairment were excluded from the randomized trial. | ||
*A single dose of 1 mg degarelix administered as an intravenous infusion over 1 hour was studied in 16 non-prostate cancer patients with either mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment. Compared to non-prostate cancer patients with normal liver function, the exposure of degarelix decreased by 10% and 18% in patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, respectively. Therefore, dose adjustment is not necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. However, since hepatic impairment can lower degarelix exposure, it is recommended that in patients with hepatic impairment testosterone concentrations should be monitored on a monthly basis until medical castration is achieved. Once medical castration is achieved, an every-other-month testosterone monitoring approach could be considered. | *A single dose of 1 mg degarelix administered as an intravenous infusion over 1 hour was studied in 16 non-prostate cancer patients with either mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment. Compared to non-prostate cancer patients with normal liver function, the exposure of degarelix decreased by 10% and 18% in patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, respectively. Therefore, dose adjustment is not necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. However, since hepatic impairment can lower degarelix exposure, it is recommended that in patients with hepatic impairment testosterone concentrations should be monitored on a monthly basis until medical castration is achieved. Once medical castration is achieved, an every-other-month testosterone monitoring approach could be considered. | ||
*Patients with severe hepatic dysfunction have not been studied and caution is therefore warranted in this group. | *Patients with severe hepatic dysfunction have not been studied and caution is therefore warranted in this group. | ||
|useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix in women of reproductive potentials and males. | |useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix in women of reproductive potentials and males. | ||
|useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of Degarelix in patients who are immunocompromised. | |useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of Degarelix in patients who are [[immunocompromised]]. | ||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | <!--Administration and Monitoring--> | ||
| Line 158: | Line 154: | ||
<!--Drug box 2--> | <!--Drug box 2--> | ||
|drugBox=<!--Mechanism of Action--> | |drugBox=<!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
|mechAction=*Degarelix is a GnRH receptor antagonist. It binds reversibly to the pituitary GnRH receptors, thereby reducing the release of gonadotropins and consequently testosterone. | |mechAction=*Degarelix is a GnRH receptor antagonist. It binds reversibly to the pituitary [[GnRH]] receptors, thereby reducing the release of [[gonadotropins]] and consequently [[testosterone]]. | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
|structure=*Degarelix is a sterile lyophilized powder for injection containing degarelix (as the acetate) and mannitol. Degarelix is a synthetic linear decapeptide amide containing seven unnatural amino acids, five of which are D-amino acids. The acetate salt of degarelix is a white to off-white amorphous powder of low density as obtained after lyophilization. | |structure=*Degarelix is a sterile lyophilized powder for injection containing degarelix (as the acetate) and [[mannitol]]. Degarelix is a synthetic linear decapeptide amide containing seven unnatural amino acids, five of which are D-amino acids. The acetate salt of degarelix is a white to off-white amorphous powder of low density as obtained after lyophilization. | ||
*The chemical name of degarelix is D-Alaninamide, N-acetyl-3-(2-naphthalenyl)-D-alanyl-4-chloro-D-phenylalanyl-3-(3-pyridinyl)-D-alanyl-L-seryl-4-[(4S)-hexahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidinyl]carbonyl]amino]-L phenylalanyl-4-[(aminocarbonyl)amino]-D-phenylalanyl-L leucyl-N6–(1-methylethyl)-L-lysyl-L-prolyl. It has an empirical formula of C82H103N18O16Cl and a molecular weight of 1632.3 Da. | *The chemical name of degarelix is D-Alaninamide, N-acetyl-3-(2-naphthalenyl)-D-alanyl-4-chloro-D-phenylalanyl-3-(3-pyridinyl)-D-alanyl-L-seryl-4-[(4S)-hexahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidinyl]carbonyl]amino]-L phenylalanyl-4-[(aminocarbonyl)amino]-D-phenylalanyl-L leucyl-N6–(1-methylethyl)-L-lysyl-L-prolyl. It has an empirical formula of C82H103N18O16Cl and a molecular weight of 1632.3 Da. | ||
*Degarelix has the following structural formula: | *Degarelix has the following structural formula: | ||
[[File:Degarelix01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | [[File:Degarelix01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
*Degarelix delivers degarelix acetate, equivalent to 120 mg of degarelix for the starting dose, and 80 mg of degarelix for the maintenance dose. The 80 mg vial contains 200 mg mannitol and the 120 mg vial contains 150 mg mannitol. | *Degarelix delivers degarelix acetate, equivalent to 120 mg of degarelix for the starting dose, and 80 mg of degarelix for the maintenance dose. The 80 mg vial contains 200 mg [[mannitol]] and the 120 mg vial contains 150 mg [[mannitol]]. | ||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
|PD=*A single dose of 240 mg Degarelix causes a decrease in the plasma concentrations of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and subsequently testosterone. | |PD=*A single dose of 240 mg Degarelix causes a decrease in the plasma concentrations of [[luteinizing hormone]] (LH) and [[follicle stimulating hormone]] (FSH), and subsequently [[testosterone]]. | ||
*Degarelix is effective in achieving and maintaining testosterone suppression below the castration level of 50 ng/dL. | *Degarelix is effective in achieving and maintaining [[testosterone]] suppression below the castration level of 50 ng/dL. | ||
[[File:Degarelix04.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | [[File:Degarelix04.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | <!--Pharmacokinetics--> | ||
|PK=====Absorption===== | |PK=====Absorption===== | ||
*Degarelix forms a depot upon subcutaneous administration, from which degarelix is released to the circulation. Following administration of Degarelix 240 mg at a product concentration of 40 mg/mL, the mean Cmax was 26.2 ng/mL (coefficient of variation, CV 83%) and the mean AUC was 1054 ng•day/mL (CV 35%). Typically Cmax occurred within 2 days after subcutaneous administration. In prostate cancer patients at a product concentration of 40 mg/mL, the pharmacokinetics of degarelix were linear over a dose range of 120 to 240 mg. The pharmacokinetic behavior of the drug is strongly influenced by its concentration in the injection solution. | *Degarelix forms a depot upon subcutaneous administration, from which degarelix is released to the circulation. Following administration of Degarelix 240 mg at a product concentration of 40 mg/mL, the mean [[Cmax]] was 26.2 ng/mL ([[coefficient of variation]], CV 83%) and the mean [[AUC]] was 1054 ng•day/mL (CV 35%). Typically [[Cmax]] occurred within 2 days after subcutaneous administration. In prostate cancer patients at a product concentration of 40 mg/mL, the pharmacokinetics of degarelix were linear over a dose range of 120 to 240 mg. The pharmacokinetic behavior of the drug is strongly influenced by its concentration in the injection solution. | ||
=====Distribution===== | =====Distribution===== | ||
| Line 178: | Line 174: | ||
=====Metabolism===== | =====Metabolism===== | ||
*Degarelix is subject to peptide hydrolysis during the passage of the hepato-biliary system and is mainly excreted as peptide fragments in the feces. No quantitatively significant metabolites were detected in plasma samples after subcutaneous administration. In vitro studies have shown that degarelix is not a substrate, inducer or inhibitor of the CYP450 or p-glycoprotein transporter systems. | *Degarelix is subject to peptide hydrolysis during the passage of the hepato-biliary system and is mainly excreted as peptide fragments in the feces. No quantitatively significant metabolites were detected in plasma samples after subcutaneous administration. In vitro studies have shown that degarelix is not a substrate, inducer or inhibitor of the CYP450 or p-[[glycoprotein]] transporter systems. | ||
=====Excretion===== | =====Excretion===== | ||
| Line 193: | Line 189: | ||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | <!--Clinical Studies--> | ||
|clinicalStudies=*The safety and efficacy of Degarelix were evaluated in an open-label, multi-center, randomized, parallel-group study in patients with prostate cancer. A total of 620 patients were randomized to receive one of two Degarelix dosing regimens or leuprolide for one year: | |clinicalStudies=*The safety and efficacy of Degarelix were evaluated in an open-label, multi-center, randomized, parallel-group study in patients with [[prostate cancer]]. A total of 620 patients were randomized to receive one of two Degarelix dosing regimens or [[leuprolide]] for one year: | ||
:*Degarelix at a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/mL) followed by monthly doses of 160 mg (40 mg/mL) subcutaneously, | :*Degarelix at a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/mL) followed by monthly doses of 160 mg (40 mg/mL) subcutaneously, | ||
:*Degarelix at a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/mL) followed by monthly doses of 80 mg (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously, | :*Degarelix at a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/mL) followed by monthly doses of 80 mg (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously, | ||
:*Leuprolide 7.5 mg intramuscularly monthly. | :*[[Leuprolide]] 7.5 mg intramuscularly monthly. | ||
*Serum levels of testosterone were measured at screening, on Day 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 in the first month, and then monthly until the end of the study. | *Serum levels of [[testosterone]] were measured at screening, on Day 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 in the first month, and then monthly until the end of the study. | ||
*The clinical trial population (n=610) across all treatment arms had an overall median age of approximately 73 (range 50 to 98). The ethnic/racial distribution was 84% white, 6% black, and 10% others. Disease stage was distributed approximately as follows: 20% metastatic, 29% locally advanced (T3/T4 Nx M0 or N1 M0), 31% localized (T1 or T2 N0 M0), and 20% classified as other (including patients whose disease metastatic status could not be determined definitively - or patients with PSA relapse after primary curative therapy). In addition, the median testosterone baseline value across treatment arms was approximately 400 ng/dL. | *The clinical trial population (n=610) across all treatment arms had an overall median age of approximately 73 (range 50 to 98). The ethnic/racial distribution was 84% white, 6% black, and 10% others. Disease stage was distributed approximately as follows: 20% metastatic, 29% locally advanced (T3/T4 Nx M0 or N1 M0), 31% localized (T1 or T2 N0 M0), and 20% classified as other (including patients whose disease metastatic status could not be determined definitively - or patients with PSA relapse after primary curative therapy). In addition, the median [[testosterone]] baseline value across treatment arms was approximately 400 ng/dL. | ||
*The primary objective was to demonstrate that Degarelix is effective with respect to achieving and maintaining testosterone suppression to castration levels (T ≤ 50 ng/dL), during 12 months treatment. The results are shown in Table 2. | *The primary objective was to demonstrate that Degarelix is effective with respect to achieving and maintaining [[testosterone]] suppression to castration levels (T ≤ 50 ng/dL), during 12 months treatment. The results are shown in Table 2. | ||
[[File:Degarelix05.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | [[File:Degarelix05.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
*Percentage changes in testosterone from baseline to Day 28 (median with interquartile ranges) are shown in Figure 2 and the percentages of patients who attained the medical castration of testosterone ≤ 50 ng/dL are summarized in Table 3. | *Percentage changes in testosterone from baseline to Day 28 (median with interquartile ranges) are shown in Figure 2 and the percentages of patients who attained the medical castration of testosterone ≤ 50 ng/dL are summarized in Table 3. | ||
[[File:Degarelix06.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | [[File:Degarelix06.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
*In the clinical trial, PSA levels were monitored as a secondary endpoint. PSA levels were lowered by 64% two weeks after administration of Degarelix , 85% after one month, 95% after three months, and remained suppressed throughout the one year of treatment. These PSA results should be interpreted with caution because of the heterogeneity of the patient population studied. No evidence has shown that the rapidity of PSA decline is related to a clinical benefit. | *In the clinical trial, [[PSA]] levels were monitored as a secondary endpoint. [[PSA]] levels were lowered by 64% two weeks after administration of Degarelix , 85% after one month, 95% after three months, and remained suppressed throughout the one year of treatment. These [[PSA]] results should be interpreted with caution because of the heterogeneity of the patient population studied. No evidence has shown that the rapidity of [[PSA]] decline is related to a clinical benefit. | ||
<!--How Supplied--> | <!--How Supplied--> | ||
|howSupplied=*Degarelix is available as: | |howSupplied=*Degarelix is available as: | ||
| Line 246: | Line 242: | ||
:*The common side effects include: | :*The common side effects include: | ||
:*hot flashes | :*hot flashes | ||
:*injection site pain, redness, and swelling, especially with the first dose | :*injection site [[pain]], [[redness]], and [[swelling]], especially with the first dose | ||
:*weight gain | :*weight gain | ||
:*increase in some liver enzymes | :*increase in some liver enzymes | ||
:*tiredness | :*[[tiredness]] | ||
:*hypertension | :*[[hypertension]] | ||
:*back and joint pain | :*back and [[joint pain]] | ||
:*chills | :*[[chills]] | ||
:*urinary tract infection | :*[[urinary tract infection]] | ||
:*decreased sex drive and trouble with erectile function (impotence) | :*decreased sex drive and trouble with erectile function ([[impotence]]) | ||
*These are not all the possible side effects. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. | *These are not all the possible side effects. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. | ||
*Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. | *Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. | ||
| Line 264: | Line 260: | ||
*What are the ingredients in Degarelix ? | *What are the ingredients in Degarelix ? | ||
:*Active ingredient: degarelix (as acetate) | :*Active ingredient: degarelix (as acetate) | ||
:*Inactive ingredient: mannitol | :*Inactive ingredient: [[mannitol]] | ||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | <!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | ||
|alcohol=* Alcohol-Degarelix interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |alcohol=* Alcohol-Degarelix interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 4 February 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Degarelix is an anti -neoplastic agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of patients with advanced prostate cancer.. Common adverse reactions include injection site reactions (e.g., pain, erythema, swelling, or induration), hot flashes, increased weight, fatigue, and increases in serum levels of transaminases and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT),asthenia, fever, night sweats, Nausea, Dizziness, headache and insomnia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Prostate cancer=
- Degarelix is a GnRH receptor antagonist indicated for treatment of patients with advanced prostate cancer
Dosing Information
- Degarelix is for subcutaneous administration only and is not to be administered intravenously.
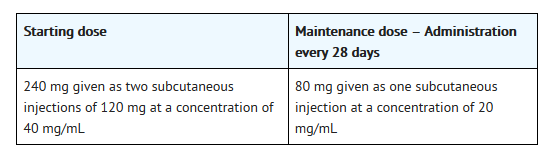
- Degarelix is administered as a subcutaneous injection in the abdominal region. As with other drugs administered by subcutaneous injection, the injection site should vary periodically. Injections should be given in areas of the abdomen that will not be exposed to pressure, e.g. not close to waistband or belt nor close to the ribs.
- Degarelix is supplied as a powder to be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP (WFI). The reconstitution procedure needs to be carefully followed. Administration of other concentrations is not recommended. See Instructions for Proper Use.
Instructions for Proper Use
- NOTE:
- Gloves should be worn during preparation and administration
- Reconstituted drug must be administered within one hour after addition of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (WFI)
- Keep the vials vertical at all times
- Do not shake the vials
- Follow aseptic technique
Degarelix 120 mg
- The Treatment Initiation pack contains 2 vials of Degarelix 120 mg that must be prepared for 2 subcutaneous injections. Hence, the instructions here below need to be repeated a second time.
- Prepare Degarelix 120 mg for reconstitution by gathering the following:
- 6 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (WFI); Do not use Bacteriostatic Water for Injection
- 2 reconstitution needles – 21G / 2 inch
- 2 administration needles for subcutaneous injection – 27G / 1-1/4 inch
- 2 injection syringes (5 mL)
- Draw up 3 mL WFI with a reconstitution needle (21G / 2 in).
- Inject the WFI slowly into the Degarelix 120 mg vial. To keep the product and syringe sterile, do not remove the syringe and the needle.
- Keeping the vial in an upright position, swirl it very gently until the liquid looks clear and without undissolved powder or particles. If the powder adheres to the vial over the liquid surface, the vial can be tilted slightly to dissolve powder. Avoid shaking to prevent foam formation. A ring of small air bubbles on the surface of the liquid is acceptable. The reconstitution procedure may take up to 15 minutes.
- Tilt the vial slightly and keep the needle in the lowest part of the vial. Withdraw 3 mL of Degarelix 120 mg without turning the vial upside down.
- Exchange the reconstitution needle with the administration needle for deep subcutaneous injection (27G / 1-1/4 in). Remove any air bubbles.
- Inject 3 mL of Degarelix 120 mg subcutaneously immediately after reconstitution.
- Grasp the skin of the abdomen, elevate the subcutaneous tissue. Insert the needle deeply at an angle of not less than 45 degrees.
- Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the reconstituted product can no longer be used. Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose for the patient).
- Repeat reconstitution procedure for the second dose. Choose a different injection site and inject 3 mL.
Degarelix 80 mg
- The Treatment Maintenance pack contains 1 vial of Degarelix 80 mg that must be prepared for subcutaneous injection.
- Prepare Degarelix 80 mg for reconstitution by gathering the following:
- 4.2 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (WFI); Do not use Bacteriostatic Water for Injection
- 1 reconstitution needle – 21G / 2 inch
- 1 administration needle for subcutaneous injection – 27G / 1-1/4 inch
- 1 injection syringe (5 mL)
- Draw up 4.2 mL WFI with the reconstitution needle (21G / 2 in).
- Inject the WFI slowly into the Degarelix 80 mg vial. To keep the product and syringe sterile, do not remove the syringe and the needle.
- Keeping the vial in an upright position, swirl it very gently until the liquid looks clear and without undissolved powder or particles. If the powder adheres to the vial over the liquid surface, the vial can be tilted slightly to dissolve powder. Avoid shaking to prevent foam formation. A ring of small air bubbles on the surface of the liquid is acceptable. The reconstitution procedure may take up to 15 minutes.
- Tilt the vial slightly and keep the needle in the lowest part of the vial. Withdraw 4 mL of Degarelix 80 mg without turning the vial upside down.
- Exchange the reconstitution needle with the administration needle for deep subcutaneous injection (27G / 1-1/4 in). Remove any air bubbles.
- Inject 4 mL of Degarelix 80 mg subcutaneously immediately after reconstitution:
- Grasp the skin of the abdomen, elevate the subcutaneous tissue. Insert the needle deeply at an angle of not less than 45 degrees.
- Gently pull back the plunger to check if blood is aspirated. If blood appears in the syringe, the reconstituted product can no longer be used. Discontinue the procedure and discard the syringe and the needle (reconstitute a new dose for the patient).
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Degarelix in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Degarelix in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Contraindications
- Degarelix is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to degarelix or to any of the product components.
- Degarelix is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. Degarelix can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Degarelix given to rabbits during organogenesis at doses that were 0.02% of the clinical loading dose (240 mg) on a mg/m2 basis caused embryo/fetal lethality and abortion. When degarelix was given to female rats during organogenesis, at doses that were just 0.036% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis, there was an increase post implantation loss and a decrease in the number of live fetuses. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Warnings
Effect on QT/QTc Interval
- Long-term androgen deprivation therapy prolongs the QT interval. Physicians should consider whether the benefits of androgen deprivation therapy outweigh the potential risks in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, electrolyte abnormalities, or congestive heart failure and in patients taking Class IA (e.g. quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g. amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications.
- In the randomized, active-controlled trial comparing Degarelix to leuprolide, periodic electrocardiograms were performed. Seven patients, three (<1%) in the pooled degarelix group and four (2%) patients in the leuprolide 7.5 mg group, had a QTcF > 500 msec. From baseline to end of study the median change for Degarelix was 12.3 msec and for leuprolide was 16.7 msec.
Laboratory Testing
- Therapy with Degarelix results in suppression of the pituitary gonadal system. Results of diagnostic tests of the pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal functions conducted during and after Degarelix may be affected. The therapeutic effect of Degarelix should be monitored by measuring serum concentrations of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) periodically. If PSA increases, serum concentrations of testosterone should be measured.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- A total of 1325 patients with prostate cancer received Degarelix either as a monthly treatment (60-160 mg) or as a single dose (up to 320 mg). A total of 1032 patients (78%) were treated for at least 6 months and 853 patients (64%) were treated for one year or more. The most commonly observed adverse reactions during Degarelix therapy included injection site reactions (e.g., pain, erythema, swelling, or induration), hot flashes, increased weight, fatigue, and increases in serum levels of transaminases and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT). The majority of the adverse reactions were Grade 1 or 2, with Grade 3/4 adverse reaction incidences of 1% or less.
- Degarelix was studied in an active-controlled trial (N = 610) in which patients with prostate cancer were randomized to receive Degarelix (subcutaneous) or leuprolide (intramuscular) monthly for 12 months. Adverse reactions reported in 5% of patients or more are shown in Table 1.
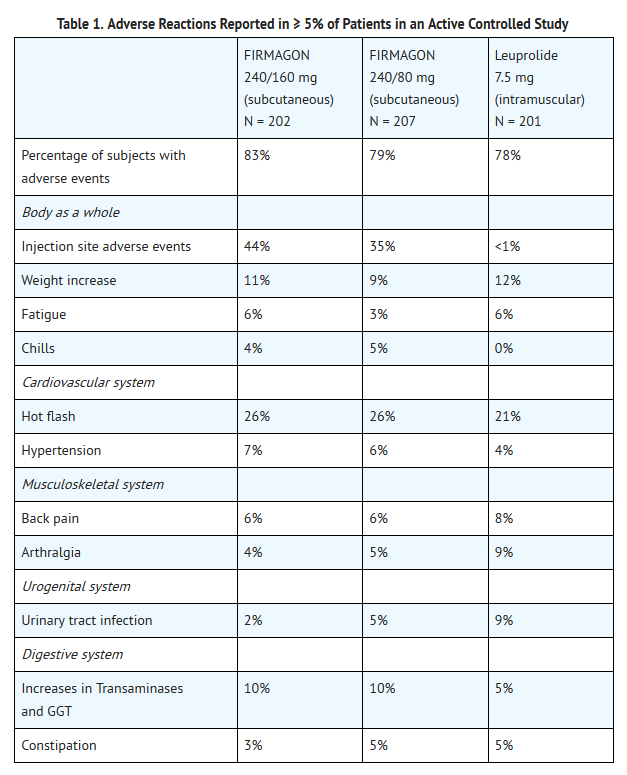
- The most frequently reported adverse reactions at the injection sites were pain (28%), erythema (17%), swelling (6%), induration (4%) and nodule (3%). These adverse reactions were mostly transient, of mild to moderate intensity, occurred primarily with the starting dose and led to few discontinuations (<1%). Grade 3 injection site reactions occurred in 2% or less of patients receiving degarelix.
- Hepatic laboratory abnormalities were primarily Grade 1 or 2 and were generally reversible. Grade 3 hepatic laboratory abnormalities occurred in less than 1% of patients.
- In 1-5% of patients the following adverse reactions, not already listed, were considered related to Degarelix by the investigator:
- Body as a whole: Asthenia, fever, night sweats; Digestive system: Nausea; Nervous system: Dizziness, headache, insomnia.
- The following adverse reactions, not already listed, were reported to be drug-related by the investigator in ≥1% of patients: erectile dysfunction, gynecomastia, hyperhidrosis, testicular atrophy, and diarrhea.
- Changes in bone density:
- Decreased bone density has been reported in the medical literature in men who have had orchiectomy or who have been treated with a GnRH agonist. It can be anticipated that long periods of medical castration in men will result in decreased bone density.
- Anti-degarelix antibody development has been observed in 10% of patients after treatment with Degarelix for 1 year. There is no indication that the efficacy or safety of Degarelix treatment is affected by antibody formation.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Degarelix in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted.
- Degarelix is not a substrate for the human CYP450 system. Degarelix is not an inducer or inhibitor of the CYP450 system in vitro. Therefore, clinically significant CYP450 pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions are unlikely.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Women who are or may become pregnant should not take Degarelix . When degarelix was given to rabbits during early organogenesis at doses of 0.002 mg/kg/day (about 0.02% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in early post-implantation loss. Degarelix given to rabbits during mid and late organogenesis at doses of 0.006 mg/kg/day (about 0.05% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused embryo/fetal lethality and abortion. When degarelix was given to female rats during early organogenesis, at doses of 0.0045 mg/kg/day (about 0.036% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in early post-implantation loss. When degarelix was given to female rats during mid and late organogenesis, at doses of 0.045 mg/kg/day (about 0.36% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increase in the number of minor skeletal abnormalities and variants.
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Degarelix in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Degarelix during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Degarelix is not indicated for use in women and is contraindicated in women who are or who may become pregnant. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from degarelix, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of Degarelix , 82% were age 65 and over, while 42% were age 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- No pharmacokinetic studies in renally impaired patients have been conducted. At least 20-30% of a given dose of degarelix is excreted unchanged in the urine.
- A population pharmacokinetic analysis of data from the randomized study demonstrated that there is no significant effect of mild renal impairment [[[creatinine clearance]] (CrCL) 50-80 mL/min] on either the degarelix concentration or testosterone concentration. Data on patients with moderate or severe renal impairment is limited and therefore degarelix should be used with caution in patients with CrCL < 50 mL/min.
Hepatic Impairment
- Patients with hepatic impairment were excluded from the randomized trial.
- A single dose of 1 mg degarelix administered as an intravenous infusion over 1 hour was studied in 16 non-prostate cancer patients with either mild (Child Pugh A) or moderate (Child Pugh B) hepatic impairment. Compared to non-prostate cancer patients with normal liver function, the exposure of degarelix decreased by 10% and 18% in patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, respectively. Therefore, dose adjustment is not necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. However, since hepatic impairment can lower degarelix exposure, it is recommended that in patients with hepatic impairment testosterone concentrations should be monitored on a monthly basis until medical castration is achieved. Once medical castration is achieved, an every-other-month testosterone monitoring approach could be considered.
- Patients with severe hepatic dysfunction have not been studied and caution is therefore warranted in this group.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Degarelix in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Degarelix in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Degarelix in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Degarelix in the drug label.
Overdosage
- There have been no reports of overdose with Degarelix . In the case of overdose, however, discontinue Degarelix , treat the patient symptomatically, and institute supportive measures.
- As with all prescription drugs, this medicine should be kept out of the reach of children.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Degarelix Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Degarelix is a GnRH receptor antagonist. It binds reversibly to the pituitary GnRH receptors, thereby reducing the release of gonadotropins and consequently testosterone.
Structure
- Degarelix is a sterile lyophilized powder for injection containing degarelix (as the acetate) and mannitol. Degarelix is a synthetic linear decapeptide amide containing seven unnatural amino acids, five of which are D-amino acids. The acetate salt of degarelix is a white to off-white amorphous powder of low density as obtained after lyophilization.
- The chemical name of degarelix is D-Alaninamide, N-acetyl-3-(2-naphthalenyl)-D-alanyl-4-chloro-D-phenylalanyl-3-(3-pyridinyl)-D-alanyl-L-seryl-4-[(4S)-hexahydro-2,6-dioxo-4-pyrimidinyl]carbonyl]amino]-L phenylalanyl-4-[(aminocarbonyl)amino]-D-phenylalanyl-L leucyl-N6–(1-methylethyl)-L-lysyl-L-prolyl. It has an empirical formula of C82H103N18O16Cl and a molecular weight of 1632.3 Da.
- Degarelix has the following structural formula:
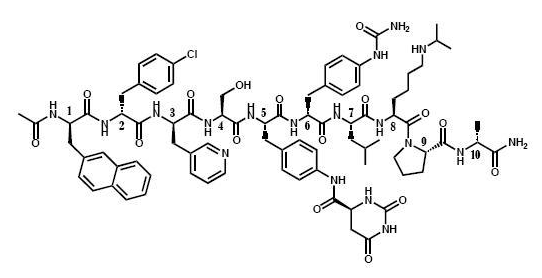
- Degarelix delivers degarelix acetate, equivalent to 120 mg of degarelix for the starting dose, and 80 mg of degarelix for the maintenance dose. The 80 mg vial contains 200 mg mannitol and the 120 mg vial contains 150 mg mannitol.
Pharmacodynamics
- A single dose of 240 mg Degarelix causes a decrease in the plasma concentrations of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and subsequently testosterone.
- Degarelix is effective in achieving and maintaining testosterone suppression below the castration level of 50 ng/dL.
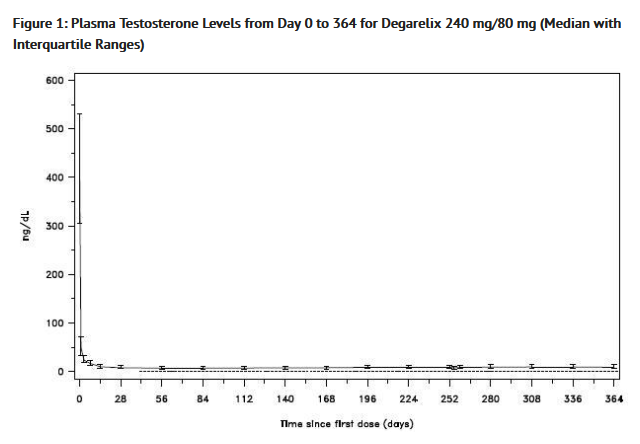
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption=
- Degarelix forms a depot upon subcutaneous administration, from which degarelix is released to the circulation. Following administration of Degarelix 240 mg at a product concentration of 40 mg/mL, the mean Cmax was 26.2 ng/mL (coefficient of variation, CV 83%) and the mean AUC was 1054 ng•day/mL (CV 35%). Typically Cmax occurred within 2 days after subcutaneous administration. In prostate cancer patients at a product concentration of 40 mg/mL, the pharmacokinetics of degarelix were linear over a dose range of 120 to 240 mg. The pharmacokinetic behavior of the drug is strongly influenced by its concentration in the injection solution.
Distribution
- The distribution volume of degarelix after intravenous (> 1 L/kg) or subcutaneous administration (> 1000L) indicates that degarelix is distributed throughout total body water. In vitro plasma protein binding of degarelix is estimated to be approximately 90%.
Metabolism
- Degarelix is subject to peptide hydrolysis during the passage of the hepato-biliary system and is mainly excreted as peptide fragments in the feces. No quantitatively significant metabolites were detected in plasma samples after subcutaneous administration. In vitro studies have shown that degarelix is not a substrate, inducer or inhibitor of the CYP450 or p-glycoprotein transporter systems.
Excretion
- Following subcutaneous administration of 240 mg Degarelix at a concentration of 40 mg/mL to prostate cancer patients, degarelix is eliminated in a biphasic fashion, with a median terminal half-life of approximately 53 days. The long half-life after subcutaneous administration is a consequence of a very slow release of degarelix from the Degarelix depot formed at the injection site(s). Approximately 20-30% of a given dose of degarelix was renally excreted, suggesting that approximately 70-80% is excreted via the hepato-biliary system in humans. Following subcutaneous administration of degarelix to prostate cancer patients the clearance is approximately 9 L/hr.
Effect of Age, Weight and Race
- There was no effect of age, weight, or race on the degarelix pharmacokinetic parameters or testosterone concentration.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility=
- Degarelix was administered subcutaneously to rats every 2 weeks for 2 years at doses of 2, 10 and 25 mg/kg (about 9, 45 and 120% of the recommended human loading dose on a mg/m2 basis). Long term treatment with degarelix at 25 mg/kg caused an increase in the combined incidence of benign hemangiomas plus malignant hemangiosarcomas in females.
- Degarelix was administered subcutaneously to mice every 2 weeks for 2 years at doses of 2, 10 and 50 mg/kg (about 5, 22 and 120% of the recommended human loading dose [240 mg] on a mg/m2 basis). There was no statistically significant increase in tumor incidence associated with this treatment.
- Degarelix did not cause genetic damage in standard in vitro assays (bacterial mutation, human lymphocyte chromosome aberration) nor in in vivo rodent bone marrow micronucleus tests.
- Single degarelix doses of ≥ 1 mg/kg (about 5% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused reversible infertility in male rats. Single doses of ≥ 0.1 mg/kg (about 0.5% of the clinical loading dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused a decrease in fertility in female rats.
Clinical Studies
- The safety and efficacy of Degarelix were evaluated in an open-label, multi-center, randomized, parallel-group study in patients with prostate cancer. A total of 620 patients were randomized to receive one of two Degarelix dosing regimens or leuprolide for one year:
- Degarelix at a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/mL) followed by monthly doses of 160 mg (40 mg/mL) subcutaneously,
- Degarelix at a starting dose of 240 mg (40 mg/mL) followed by monthly doses of 80 mg (20 mg/mL) subcutaneously,
- Leuprolide 7.5 mg intramuscularly monthly.
- Serum levels of testosterone were measured at screening, on Day 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 in the first month, and then monthly until the end of the study.
- The clinical trial population (n=610) across all treatment arms had an overall median age of approximately 73 (range 50 to 98). The ethnic/racial distribution was 84% white, 6% black, and 10% others. Disease stage was distributed approximately as follows: 20% metastatic, 29% locally advanced (T3/T4 Nx M0 or N1 M0), 31% localized (T1 or T2 N0 M0), and 20% classified as other (including patients whose disease metastatic status could not be determined definitively - or patients with PSA relapse after primary curative therapy). In addition, the median testosterone baseline value across treatment arms was approximately 400 ng/dL.
- The primary objective was to demonstrate that Degarelix is effective with respect to achieving and maintaining testosterone suppression to castration levels (T ≤ 50 ng/dL), during 12 months treatment. The results are shown in Table 2.
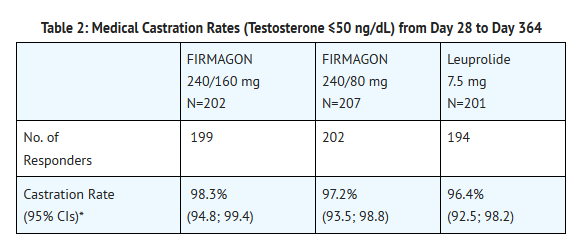
- Percentage changes in testosterone from baseline to Day 28 (median with interquartile ranges) are shown in Figure 2 and the percentages of patients who attained the medical castration of testosterone ≤ 50 ng/dL are summarized in Table 3.
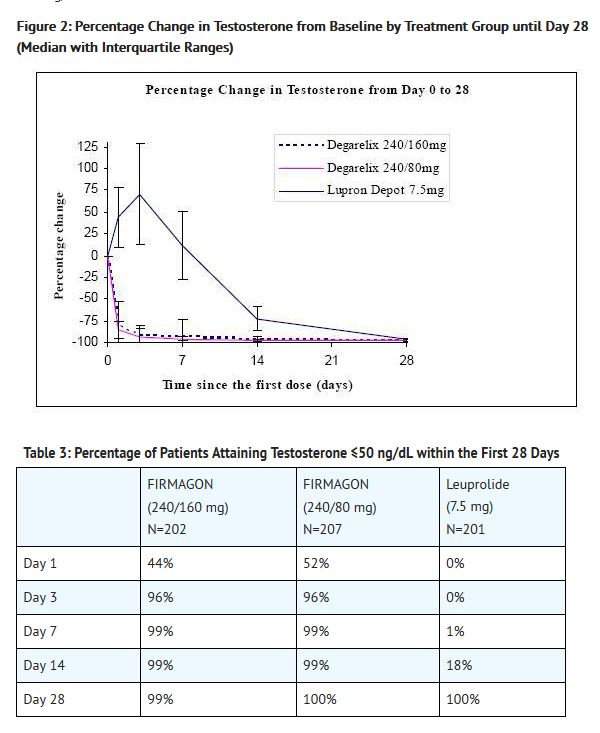
- In the clinical trial, PSA levels were monitored as a secondary endpoint. PSA levels were lowered by 64% two weeks after administration of Degarelix , 85% after one month, 95% after three months, and remained suppressed throughout the one year of treatment. These PSA results should be interpreted with caution because of the heterogeneity of the patient population studied. No evidence has shown that the rapidity of PSA decline is related to a clinical benefit.
How Supplied
- Degarelix is available as:
- NDC 55566-8401-1, Starting dose – One carton contains:Two vials each with 120 mg powder for injection
- NDC 55566-8301-1, Maintenance dose – One carton contains:One vial with 80 mg powder for injection
Storage
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
- Caution should be exercised in handling and preparing the solution of Degarelix . Several guidelines on proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs have been published.1-4 To minimize the risk of dermal exposure, always wear impervious gloves when handling Degarelix . If Degarelix solution contacts the skin, immediately wash the skin thoroughly with soap and water. If Degarelix contacts mucous membranes, the membranes should be flushed immediately and thoroughly with water
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Degarelix |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Degarelix |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Information
- Patients should be instructed to read the Patient Labeling carefully.
- Patients should be informed of the possible side effects of androgen deprivation therapy, including hot flashes, flushing of the skin, increased weight, decreased sex drive, and difficulties with erectile function. Possible side effects related to therapy with Degarelix include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site; these are usually mild, self limiting, and decrease within three days.
FDA-approved Patient Labeling
- Degarelix (FIRM-uh-gahn)
- (degarelix for injection)
- Read this patient information leaflet before you start taking Degarelix and each time you get a refill.There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
- What is Degarelix ?
- Degarelix is a prescription medicine used in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
- It is not known if Degarelix is safe or effective in children.
- Who should not use Degarelix ?
- Degarelix should not be given to:
- people who are allergic to any ingredient in Degarelix . See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Degarelix
- women who are pregnant or may become pregnant
- Talk to your healthcare provider before getting Degarelix if you have any of these conditions.
- What should I tell my healthcare provider before receiving Degarelix ?
- Before receiving Degarelix , tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have any heart problems
- have problems with balance of your body salts or electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium
- have kidney or liver problems
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if Degarelix passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Degarelix or breast-feed. You should not do both without talking with your healthcare provider.
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you are taking or have taken any medicines for your heart.
- Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
- How should I receive Degarelix ?
- You will receive an injection of Degarelix from your healthcare provider.
- The injection site will always be in the abdominal area but will change within that area with the next doses of Degarelix .
- The injected medicine gives you a continuous release of Degarelix over one month.
- Two injections are given as a first dose and the following monthly doses are one injection.
- Make sure your injection site is free of any pressure from belts, waistbands or other types of clothing.
- Always set up an appointment for your next injection.
- If you miss a dose of Degarelix , or if you think you forgot to get your monthly dose of Degarelix , talk to your healthcare provider about how to get your next dose.
- What are the possible side effects of Degarelix ?
- The common side effects include:
- hot flashes
- injection site pain, redness, and swelling, especially with the first dose
- weight gain
- increase in some liver enzymes
- tiredness
- hypertension
- back and joint pain
- chills
- urinary tract infection
- decreased sex drive and trouble with erectile function (impotence)
- These are not all the possible side effects. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
- Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
- General information about the safe and effective use of Degarelix .
- Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in the patient leaflet. Do not use Degarelix for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Degarelix to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
- This patient information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Degarelix . If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Degarelix that is written for health professionals.
- For more information, go to WWW.Degarelix .COM or call 1-888-FERRING (1-888-337-7464).
- What are the ingredients in Degarelix ?
- Active ingredient: degarelix (as acetate)
- Inactive ingredient: mannitol
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Degarelix interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Degarelix
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Degarelix |Label Name=Degarelix10.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Degarelix |Label Name=Degarelix11.png
}}