Colchicine: Difference between revisions
m (Protected "Colchicine": Protecting pages from unwanted edits ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite))) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{DrugProjectFormSinglePage | ||
| | |authorTag= | ||
| | |||
| | {{VP}} | ||
| | |||
| | <!--Overview--> | ||
| | |||
| | |genericName= | ||
| | |||
| | Colchicine | ||
| | |||
| | |aOrAn= | ||
| | |||
| | an | ||
| | |||
| | |drugClass= | ||
| | |||
| | alkaloid | ||
}} | |||
|indication= | |||
gout flares in adults, familial mediterranean fever (FMF) in adults and children 4 years or older | |||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |||
|adverseReactions= | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | |||
|blackBoxWarningTitle= | |||
Title | |||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | |||
* Content | |||
<!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |||
=====Gout Flares===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
*Prophylaxis of Gout Flares: | |||
:*The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for prophylaxis of gout flares for adults and adolescents older than 16 years of age is 0.6 mg once or twice daily. The maximum recommended dose for prophylaxis of gout flares is 1.2 mg/day. | |||
*Treatment of Gout Flares: | |||
:*The recommended dose of COLCRYS for treatment of a gout flare is 1.2 mg (2 tablets) at the first sign of the flare followed by 0.6 mg (1 tablet) one hour later. Higher doses have not been found to be more effective. The maximum recommended dose for treatment of gout flares is 1.8 mg over a 1 hour period. COLCRYS may be administered for treatment of a gout flare during prophylaxis at doses not to exceed 1.2 mg (2 tablets) at the first sign of the flare followed by 0.6 mg (1 tablet) one hour later. Wait 12 hours and then resume the prophylactic dose. | |||
=====Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:*The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for FMF in adults is 1.2 mg to 2.4 mg daily. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Developed by: | |||
* Class of Recommendation: | |||
* Strength of Evidence: | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
|fdaLIADPed= | |||
=====Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for FMF in pediatric patients 4 years of age and older is based on age. The following daily doses may be given as a single or divided dose twice daily: | |||
:**Children 4 – 6 years: 0.3 mg to 1.8 mg daily | |||
:**Children 6 – 12 years: 0.9 mg to 1.8 mg daily | |||
:**Adolescents older than 12 years: 1.2 mg to 2.4 mg daily | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Developed by: | |||
* Class of Recommendation: | |||
* Strength of Evidence: | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Condition1===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
=====Condition2===== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | |||
|contraindications= | |||
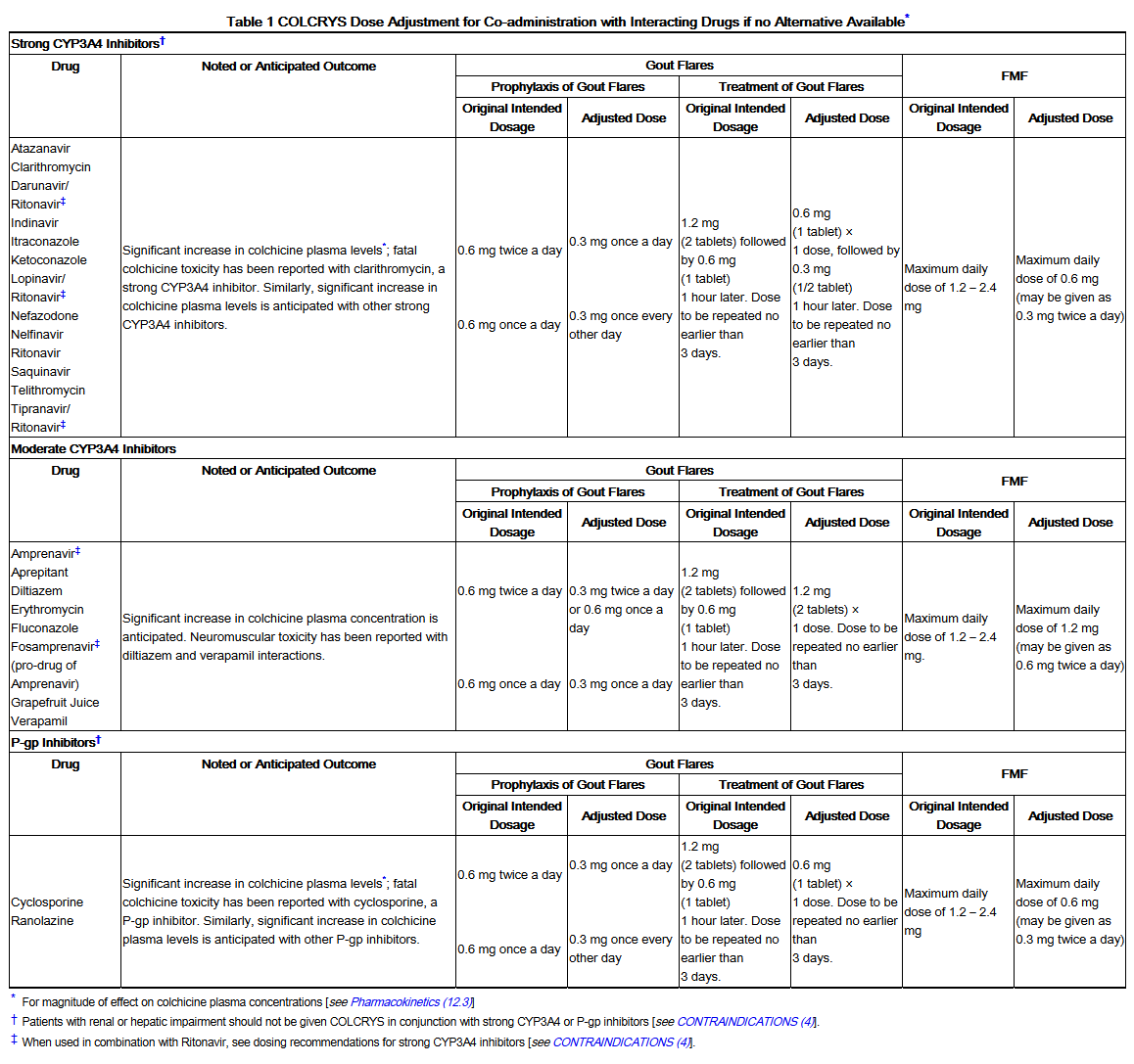
*Patients with renal or hepatic impairment should not be given COLCRYS in conjunction with P-gp or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (this includes all protease inhibitors, except fosamprenavir). In these patients, life-threatening and fatal colchicine toxicity has been reported with colchicine taken in therapeutic doses. | |||
<!--Warnings--> | |||
|warnings= | |||
* Description | |||
====Precautions==== | |||
* Description | |||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | |||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | |||
|clinicalTrials= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Trial Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
=====Body as a Whole===== | |||
=====Cardiovascular===== | |||
=====Digestive===== | |||
=====Endocrine===== | |||
=====Hematologic and Lymphatic===== | |||
=====Metabolic and Nutritional===== | |||
=====Musculoskeletal===== | |||
=====Neurologic===== | |||
=====Respiratory===== | |||
=====Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions===== | |||
=====Special Senses===== | |||
=====Urogenital===== | |||
=====Miscellaneous===== | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | |||
|postmarketing= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
=====Body as a Whole===== | |||
=====Cardiovascular===== | |||
=====Digestive===== | |||
=====Endocrine===== | |||
=====Hematologic and Lymphatic===== | |||
=====Metabolic and Nutritional===== | |||
=====Musculoskeletal===== | |||
=====Neurologic===== | |||
=====Respiratory===== | |||
=====Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions===== | |||
=====Special Senses===== | |||
=====Urogenital===== | |||
=====Miscellaneous===== | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | |||
|drugInteractions= | |||
* Drug | |||
:* Description | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |||
* '''Pregnancy Category''' | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |||
* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | |||
|useInLaborDelivery= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | |||
|useInNursing= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to nursing mothers. | |||
|useInPed= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to pediatric patients. | |||
|useInGeri= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to geriatric patients. | |||
|useInGender= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | |||
|useInRace= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific racial populations. | |||
|useInRenalImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with renal impairment. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with hepatic impairment. | |||
|useInReproPotential= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | |||
|useInImmunocomp= | |||
There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are immunocompromised. | |||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | |||
|administration= | |||
* Oral | |||
* Intravenous | |||
|monitoring= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
* Description | |||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | |||
|IVCompat= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>IV Compatibility</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Overdosage--> | |||
|overdose= | |||
===Acute Overdose=== | |||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | |||
* Description | |||
====Management==== | |||
* Description | |||
===Chronic Overdose=== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Chronic Overdose</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacology--> | |||
<!--Drug box 2--> | |||
|drugBox= | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | |||
|mechAction= | |||
* | |||
<!--Structure--> | |||
|structure= | |||
* | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | |||
|PD= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Pharmacodynamics</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | |||
|PK= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Pharmacokinetics</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | |||
|nonClinToxic= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Nonclinical Toxicology</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | |||
|clinicalStudies= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Studies</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--How Supplied--> | |||
|howSupplied= | |||
* | |||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | |||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Patient Counseling Information</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | |||
|alcohol= | |||
* Alcohol-{{PAGENAME}} interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |||
<!--Brand Names--> | |||
= | |brandNames= | ||
* ®<ref>{{Cite web | title = | url = }}</ref> | |||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | |||
|lookAlike= | |||
=== | * A® — B®<ref name="www.ismp.org">{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://www.ismp.org | url = http://www.ismp.org | publisher = | date = }}</ref> | ||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | |||
|drugShortage= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Pill Image--> | |||
== | {{PillImage | ||
|fileName=No image.jpg|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
|drugName= | |||
|NDC= | |||
|drugAuthor= | |||
|ingredients= | |||
|pillImprint= | |||
|dosageValue= | |||
|dosageUnit= | |||
|pillColor= | |||
|pillShape= | |||
|pillSize= | |||
|pillScore= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Label Display Image--> | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}11.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}11.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
<!--Category--> | |||
[[ | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
Revision as of 19:40, 10 September 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Colchicine is an alkaloid that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of gout flares in adults, familial mediterranean fever (FMF) in adults and children 4 years or older. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Gout Flares
- Dosing Information
- Prophylaxis of Gout Flares:
- The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for prophylaxis of gout flares for adults and adolescents older than 16 years of age is 0.6 mg once or twice daily. The maximum recommended dose for prophylaxis of gout flares is 1.2 mg/day.
- Treatment of Gout Flares:
- The recommended dose of COLCRYS for treatment of a gout flare is 1.2 mg (2 tablets) at the first sign of the flare followed by 0.6 mg (1 tablet) one hour later. Higher doses have not been found to be more effective. The maximum recommended dose for treatment of gout flares is 1.8 mg over a 1 hour period. COLCRYS may be administered for treatment of a gout flare during prophylaxis at doses not to exceed 1.2 mg (2 tablets) at the first sign of the flare followed by 0.6 mg (1 tablet) one hour later. Wait 12 hours and then resume the prophylactic dose.
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
- Dosing Information
- The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for FMF in adults is 1.2 mg to 2.4 mg daily.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Colchicine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Colchicine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
- Dosing Information
- The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for FMF in pediatric patients 4 years of age and older is based on age. The following daily doses may be given as a single or divided dose twice daily:
- Children 4 – 6 years: 0.3 mg to 1.8 mg daily
- Children 6 – 12 years: 0.9 mg to 1.8 mg daily
- Adolescents older than 12 years: 1.2 mg to 2.4 mg daily
- The recommended dosage of COLCRYS for FMF in pediatric patients 4 years of age and older is based on age. The following daily doses may be given as a single or divided dose twice daily:
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Colchicine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Colchicine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Patients with renal or hepatic impairment should not be given COLCRYS in conjunction with P-gp or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (this includes all protease inhibitors, except fosamprenavir). In these patients, life-threatening and fatal colchicine toxicity has been reported with colchicine taken in therapeutic doses.
Warnings
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Colchicine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Colchicine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Colchicine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Colchicine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colchicine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Colchicine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Colchicine in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Colchicine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Colchicine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Colchicine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Colchicine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Colchicine in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Colchicine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Colchicine in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Colchicine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Colchicine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Colchicine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Colchicine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Colchicine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Colchicine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Colchicine |Label Name=Colchicine11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Colchicine |Label Name=Colchicine11.png
}}