Clofibrate: Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Drugbox | ||
| IUPAC_name | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| image | | verifiedrevid = 443529702 | ||
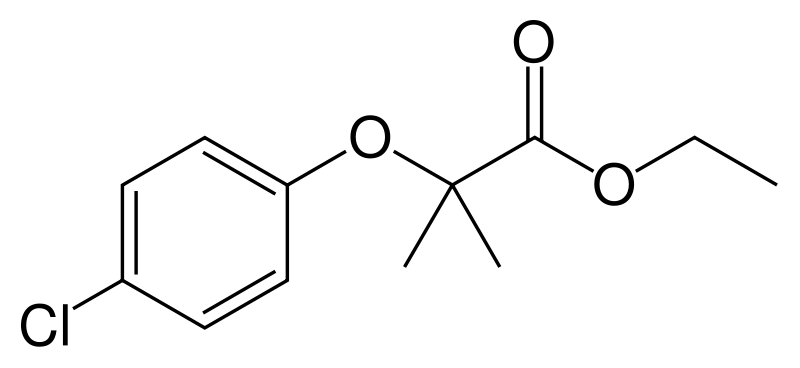
| IUPAC_name = ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate | |||
| | | image = Clofibrate.svg | ||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| | | tradename = | ||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CONS|clofibrate}} | |||
| pregnancy_AU = B1 | |||
| pregnancy_US = C | |||
| pregnancy_category = | |||
| legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S3 / S4 / S5 / S6 / S7 / S8 / S9 --> | |||
| legal_CA = <!-- / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| | | legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD / Class A, B, C --> | ||
| pregnancy_AU | | legal_US = Discontinued | ||
| pregnancy_US | | legal_status = | ||
| pregnancy_category= | |||
| legal_AU | |||
| legal_CA | |||
| legal_UK | |||
Class A, B, C --> | |||
| legal_US | |||
| legal_status | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral | | routes_of_administration = Oral | ||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = | |||
| protein_bound = Variable, 92–97% at therapeutic concentrations | |||
| metabolism = [[Hydrolysis|Hydrolyzed]] to [[clofibric acid]]; [[liver|hepatic]] [[glucuronidation]] | |||
| elimination_half-life = Highly variable; average 18–22 hours. Prolonged in [[renal failure]] | |||
| excretion = [[Kidney|Renal]], 95 to 99% | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| CAS_number = 637-07-0 | |||
| ATC_prefix = C10 | |||
| ATC_suffix = AB01 | |||
| PubChem = 2796 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = DB00636 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 2694 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = HPN91K7FU3 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D00279 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 3750 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 565 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
== | | C=12 | H=15 | Cl=1 | O=3 | ||
| molecular_weight = 242.698 g/mol | |||
| smiles = Clc1ccc(OC(C(=O)OCC)(C)C)cc1 | |||
| InChI = 1/C12H15ClO3/c1-4-15-11(14)12(2,3)16-10-7-5-9(13)6-8-10/h5-8H,4H2,1-3H3 | |||
| InChIKey = KNHUKKLJHYUCFP-UHFFFAOYAE | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C12H15ClO3/c1-4-15-11(14)12(2,3)16-10-7-5-9(13)6-8-10/h5-8H,4H2,1-3H3 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = KNHUKKLJHYUCFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| boiling_point = 148 | |||
}} | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{SI}} | |||
{{CMG}} | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''Clofibrate''' (tradename '''Atromid-S''') is an [[organic compound]]. It is marketed as a [[fibrate]]. It is a lipid-lowering agent used for controlling the high cholesterol and [[triacylglyceride]] level in the blood. It increases [[lipoprotein lipase]] activity to promote the conversion of [[VLDL]] to [[LDL]], and hence reduce the level of VLDL. It can increase the level of [[High Density Lipoprotein|HDL]] as well. | |||
==Complications and controversies== | |||
It can induce [[syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone hypersecretion|SIADH]], syndrome of inappropriate secretion of [[vasopressin|antidiuretic hormone ADH]] (vasopressin). | |||
== | The [[World Health Organization]] Cooperative Trial on Primary Prevention of [[Ischaemic Heart Disease]] using clofibrate to lower serum [[cholesterol]] observed excess mortality in the clofibrate-treated group despite successful cholesterol lowering (47% more deaths during treatment with clofibrate and 5% after treatment with clofibrate) than the non-treated high cholesterol group. These deaths were due to a wide variety of causes other than heart disease, and remain "unexplained".<ref>{{cite journal |author= |title=WHO cooperative trial on primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease with clofibrate to lower serum cholesterol: final mortality follow-up. Report of the Committee of Principal Investigators |journal=Lancet |volume=2 |issue=8403 |pages=600–4 |date=September 1984 |pmid=6147641 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
Clofibrate was discontinued in 2002 due to adverse affects. | |||
== | ==Synthesis== | ||
[[File:Clofibrate synthesis.png|thumb||center|700px|Clofibrate synthesis.<ref>http://drugsynthesis.blogspot.co.uk/2012/04/laboratory-synthesis-of-clofibrate.html</ref>]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
{{Lipid modifying agents}} | {{Lipid modifying agents}} | ||
[[Category:Fibrates]] | [[Category:Fibrates]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | |||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 21:56, 23 July 2014
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Variable, 92–97% at therapeutic concentrations |
| Metabolism | Hydrolyzed to clofibric acid; hepatic glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | Highly variable; average 18–22 hours. Prolonged in renal failure |
| Excretion | Renal, 95 to 99% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 242.698 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Boiling point | 148 °C (298.4 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Clofibrate |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Clofibrate |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Clofibrate at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Clofibrate at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Clofibrate
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Clofibrate Discussion groups on Clofibrate Patient Handouts on Clofibrate Directions to Hospitals Treating Clofibrate Risk calculators and risk factors for Clofibrate
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Clofibrate |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Clofibrate (tradename Atromid-S) is an organic compound. It is marketed as a fibrate. It is a lipid-lowering agent used for controlling the high cholesterol and triacylglyceride level in the blood. It increases lipoprotein lipase activity to promote the conversion of VLDL to LDL, and hence reduce the level of VLDL. It can increase the level of HDL as well.
Complications and controversies
It can induce SIADH, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone ADH (vasopressin).
The World Health Organization Cooperative Trial on Primary Prevention of Ischaemic Heart Disease using clofibrate to lower serum cholesterol observed excess mortality in the clofibrate-treated group despite successful cholesterol lowering (47% more deaths during treatment with clofibrate and 5% after treatment with clofibrate) than the non-treated high cholesterol group. These deaths were due to a wide variety of causes other than heart disease, and remain "unexplained".[1]
Clofibrate was discontinued in 2002 due to adverse affects.
Synthesis

References
- ↑ "WHO cooperative trial on primary prevention of ischaemic heart disease with clofibrate to lower serum cholesterol: final mortality follow-up. Report of the Committee of Principal Investigators". Lancet. 2 (8403): 600–4. September 1984. PMID 6147641.
- ↑ http://drugsynthesis.blogspot.co.uk/2012/04/laboratory-synthesis-of-clofibrate.html