Cirrhosis MRI: Difference between revisions
(→MRI) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
==MRI== | ==MRI== | ||
Magnetic resonance imaging: The role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the diagnosis of cirrhosis is unclear. Despite much enthusiasm about the potential of MRI in the evaluation of the cirrhotic patient, its use today is limited by expense, patient intolerability, and the ability to obtain information provided by MRI through other means. | |||
Some authors report that MRI can accurately diagnose cirrhosis and provide correlation with its severity. <ref name="pmid10470885">{{cite journal |author=Ito K, Mitchell DG, Hann HW, Kim Y, Fujita T, Okazaki H, Honjo K, Matsunaga N |title=Viral-induced cirrhosis: grading of severity using MR imaging |journal=[[AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology]] |volume=173 |issue=3 |pages=591–6 |year=1999 |month=September |pmid=10470885 |doi= |url=http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10470885 |accessdate=2012-09-06}}</ref><ref name="pmid10352597">{{cite journal |author=Ito K, Mitchell DG, Gabata T, Hussain SM |title=Expanded gallbladder fossa: simple MR imaging sign of cirrhosis |journal=[[Radiology]] |volume=211 |issue=3 |pages=723–6 |year=1999 |month=June |pmid=10352597 |doi= |url=http://radiology.rsnajnls.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10352597 |accessdate=2012-09-06}}</ref><ref name="pmid9609897">{{cite journal |author=Ito K, Mitchell DG, Hann HW, Outwater EK, Kim Y, Fujita T, Okazaki H, Honjo K, Matsunaga N |title=Progressive viral-induced cirrhosis: serial MR imaging findings and clinical correlation |journal=[[Radiology]] |volume=207 |issue=3 |pages=729–35 |year=1998 |month=June |pmid=9609897 |doi= |url=http://radiology.rsnajnls.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9609897 |accessdate=2012-09-06}}</ref> One study found the sensitivity and specificity of an MRI scoring system in distinguishing Child-Pugh grade A cirrhosis from other grades to be 93 and 82 percent, respectively. MRI may also reveal iron overload and provide an estimate of the hepatic iron concentration. MR angiography is more sensitive than ultrasonography in diagnosing complications of cirrhosis such as portal vein thrombosis. <ref name="pmid8273643">{{cite journal |author=Finn JP, Kane RA, Edelman RR, Jenkins RL, Lewis WD, Muller M, Longmaid HE |title=Imaging of the portal venous system in patients with cirrhosis: MR angiography vs duplex Doppler sonography |journal=[[AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology]] |volume=161 |issue=5 |pages=989–94 |year=1993 |month=November |pmid=8273643 |doi= |url=http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=8273643 |accessdate=2012-09-06}}</ref> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 6 September 2012
|
Cirrhosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Cirrhosis MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cirrhosis MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Govindavarjhulla, M.B.B.S. [2]
Overview
MRI
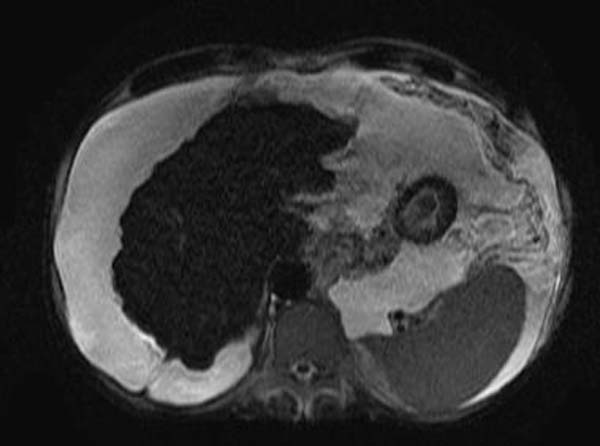
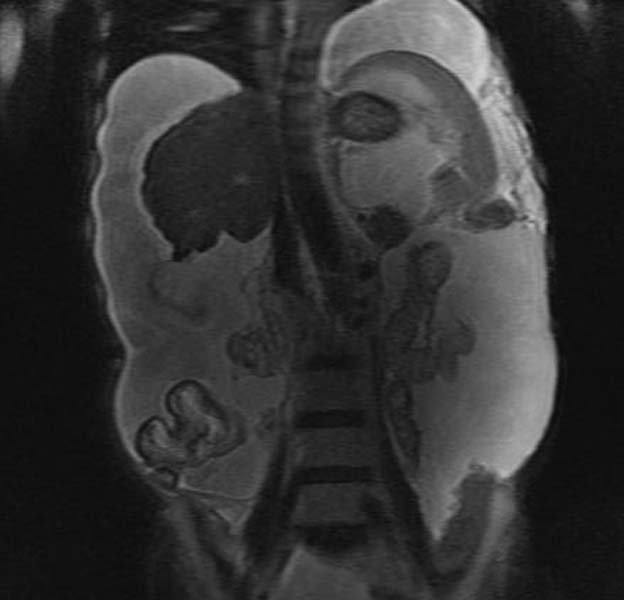
Magnetic resonance imaging: The role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the diagnosis of cirrhosis is unclear. Despite much enthusiasm about the potential of MRI in the evaluation of the cirrhotic patient, its use today is limited by expense, patient intolerability, and the ability to obtain information provided by MRI through other means.
Some authors report that MRI can accurately diagnose cirrhosis and provide correlation with its severity. [1][2][3] One study found the sensitivity and specificity of an MRI scoring system in distinguishing Child-Pugh grade A cirrhosis from other grades to be 93 and 82 percent, respectively. MRI may also reveal iron overload and provide an estimate of the hepatic iron concentration. MR angiography is more sensitive than ultrasonography in diagnosing complications of cirrhosis such as portal vein thrombosis. [4]
-
T2
-
T2
References
- ↑ Ito K, Mitchell DG, Hann HW, Kim Y, Fujita T, Okazaki H, Honjo K, Matsunaga N (1999). "Viral-induced cirrhosis: grading of severity using MR imaging". AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 173 (3): 591–6. PMID 10470885. Retrieved 2012-09-06. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ito K, Mitchell DG, Gabata T, Hussain SM (1999). "Expanded gallbladder fossa: simple MR imaging sign of cirrhosis". Radiology. 211 (3): 723–6. PMID 10352597. Retrieved 2012-09-06. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ito K, Mitchell DG, Hann HW, Outwater EK, Kim Y, Fujita T, Okazaki H, Honjo K, Matsunaga N (1998). "Progressive viral-induced cirrhosis: serial MR imaging findings and clinical correlation". Radiology. 207 (3): 729–35. PMID 9609897. Retrieved 2012-09-06. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Finn JP, Kane RA, Edelman RR, Jenkins RL, Lewis WD, Muller M, Longmaid HE (1993). "Imaging of the portal venous system in patients with cirrhosis: MR angiography vs duplex Doppler sonography". AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 161 (5): 989–94. PMID 8273643. Retrieved 2012-09-06. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)