Basilic vein
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss Basilic vein further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
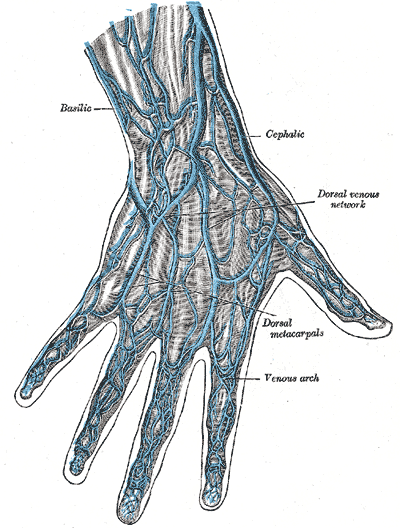
In human anatomy, the basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of hand and forearm. It originates on the medial (ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand, and it travels up the base of the forearm and arm. Most of its course is superficial; it generally travels in the fat and other fasciae that lie superficial to the muscles of the upper extremity. Because of this, it is usually visible through the skin.
Near the region anterior to the cubital fossa, in the bend of the elbow joint, the basilic vein usually connects with the other large superficial vein of the upper extremity, the cephalic vein, via the median cubital vein. The layout of superficial veins in the forearm is highly variable from person to person, and there are generally a variety of other unnamed superficial veins that the basilic vein communicates with.
About halfway up the arm proper (the part between the shoulder and elbow), the basilic vein goes deep, travelling under the muscles. There, around the lower border of the teres major muscle, it joins the brachial veins to form the axillary vein.
Along with other superficial veins in the forearm, the basilic vein is a possible site for venipuncture.
Additional images
-
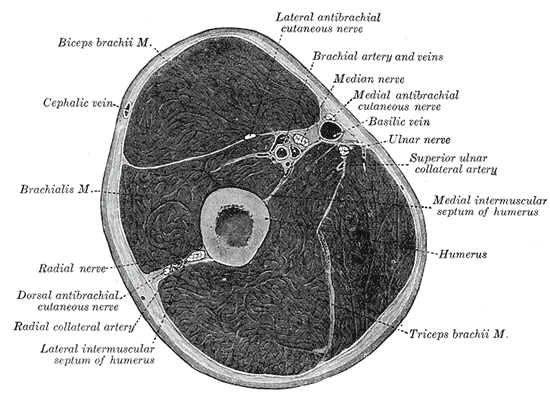
Cross-section through the middle of upper arm.
-
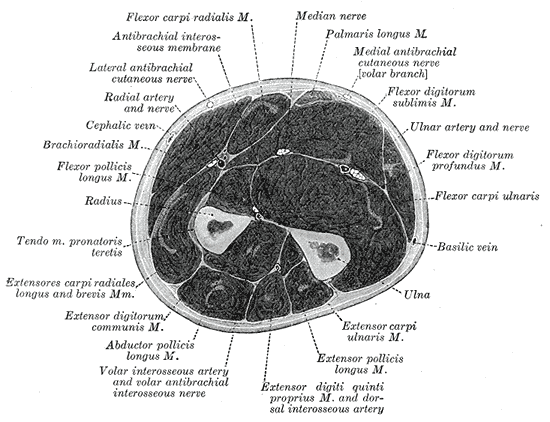
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
-
The brachial artery.
-
The veins on the dorsum of the hand.