Angiomyolipoma CT: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==CT Scan== | ==CT Scan== | ||
Abdominal CT scan may be diagnostic for angiomyolipoma. On CT scan, angiomyolipoma is characterized by:<ref name="pmid14990834">{{cite journal| author=Kim JK, Park SY, Shon JH, Cho KS| title=Angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: differentiation from renal cell carcinoma at biphasic helical CT. | journal=Radiology | year= 2004 | volume= 230 | issue= 3 | pages= 677-84 | pmid=14990834 | doi=10.1148/radiol.2303030003 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14990834 }} </ref> | Abdominal CT scan may be diagnostic for angiomyolipoma. On CT scan, angiomyolipoma is characterized by:<ref name="pmid14990834">{{cite journal| author=Kim JK, Park SY, Shon JH, Cho KS| title=Angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: differentiation from renal cell carcinoma at biphasic helical CT. | journal=Radiology | year= 2004 | volume= 230 | issue= 3 | pages= 677-84 | pmid=14990834 | doi=10.1148/radiol.2303030003 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14990834 }} </ref> | ||
*Smooth tumor margin with low intratumoral fat component | |||
*Homogenous enhancement on both corticomedullary and excretory phase scans | *Homogenous enhancement on both corticomedullary and excretory phase scans | ||
*Negative attenuation on unenhanced [[CT scan]] | *Negative attenuation on unenhanced [[CT scan]] | ||
*Rarely [[calcification]] may be present | *Rarely [[calcification]] may be present | ||
Revision as of 17:54, 24 September 2015
|
Angiomyolipoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Angiomyolipoma CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Angiomyolipoma CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
CT Scan
Abdominal CT scan may be diagnostic for angiomyolipoma. On CT scan, angiomyolipoma is characterized by:[1]
- Smooth tumor margin with low intratumoral fat component
- Homogenous enhancement on both corticomedullary and excretory phase scans
- Negative attenuation on unenhanced CT scan
- Rarely calcification may be present
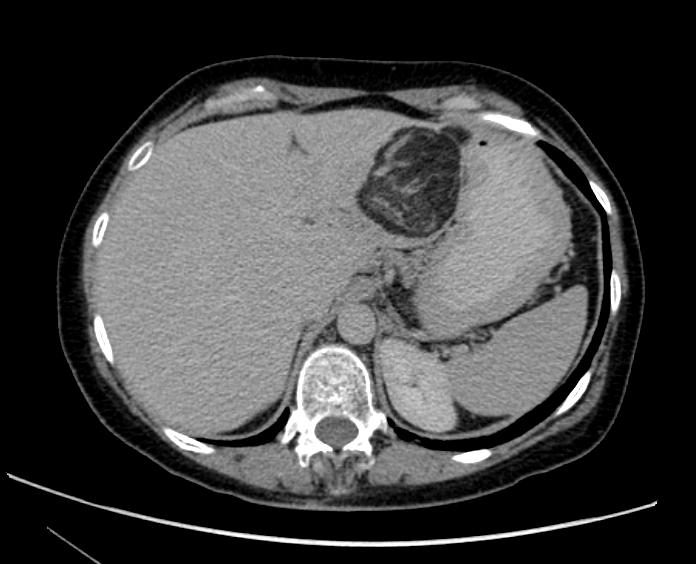
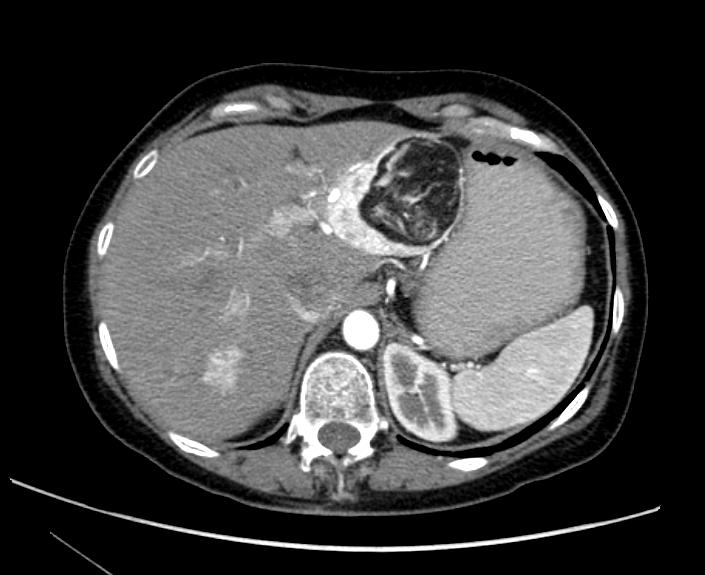
CT images demonstrate a large kidney angiomyolipoma
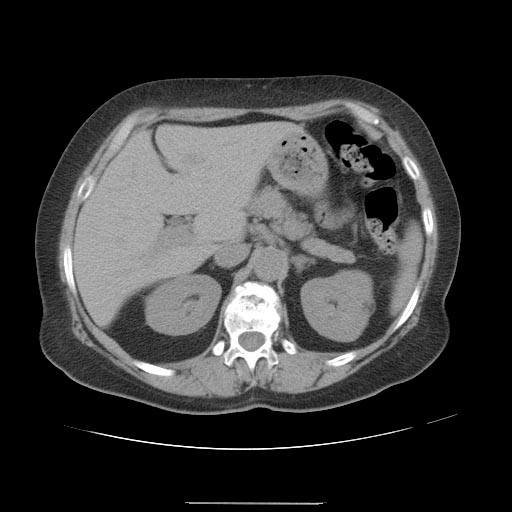
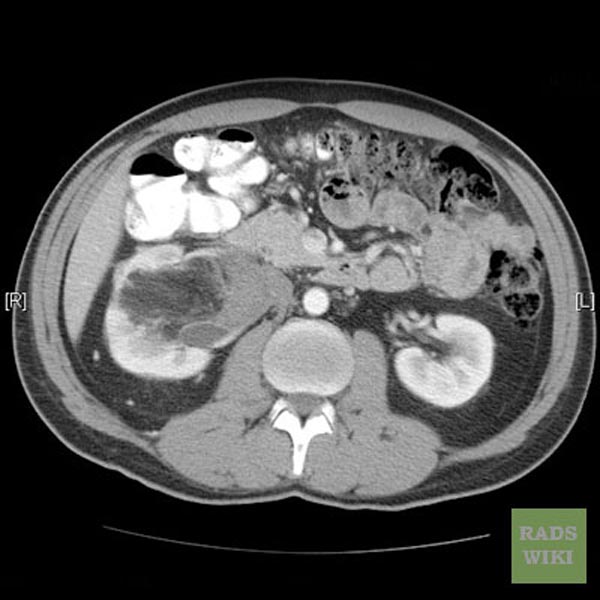
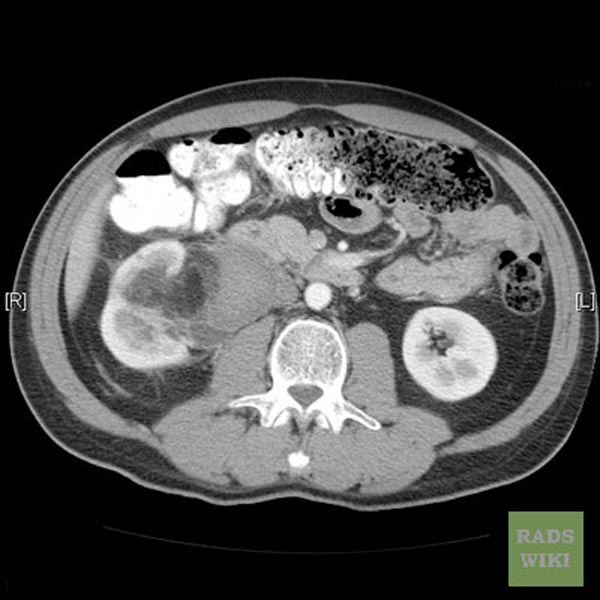
CT images demonstrate a large liver angiomyolipoma
References
- ↑ Kim JK, Park SY, Shon JH, Cho KS (2004). "Angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: differentiation from renal cell carcinoma at biphasic helical CT". Radiology. 230 (3): 677–84. doi:10.1148/radiol.2303030003. PMID 14990834.