Alcoholic liver disease pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
* Late complications of cirrhosis or liver failure include [[portal hypertension]], [[coagulopathy|coagulation disorders]], [[ascites]] and other complications including [[hepatic encephalopathy]] and the [[hepatorenal syndrome]]. | * Late complications of cirrhosis or liver failure include [[portal hypertension]], [[coagulopathy|coagulation disorders]], [[ascites]] and other complications including [[hepatic encephalopathy]] and the [[hepatorenal syndrome]]. | ||
* [[Cirrhosis]] also has number of other causes, such as hepatitis and toxins. The late stages of cirrhosis (say from viral hepatitis or alcohol) may look similar. This phenomenon is termed a "final common pathway" for a disease. | * [[Cirrhosis]] also has number of other causes, such as hepatitis and toxins. The late stages of cirrhosis (say from viral hepatitis or alcohol) may look similar. This phenomenon is termed a "final common pathway" for a disease. | ||
[[Image:Pathogenesis alcoholic liver injury.jpg | [[Image:Pathogenesis alcoholic liver injury.jpg|center|Pathogenesis of alcohol induced liver injury]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 07:35, 28 October 2012
|
Alcoholic liver disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Alcoholic liver disease pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Alcoholic liver disease pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Alcoholic liver disease pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Pathophysiology
Alcoholic liver disease usually occurs after years of excessive drinking. The longer the alcohol use and the more alcohol that was consumed, the greater the likelihood of developing liver disease.
Acute alcoholic hepatitis can result from binge drinking. It may be life-threatening if severe.
People who drink excessively can become malnourished because of the empty calories from alcohol, reduced appetite, and poor absorption (malabsorption) of nutrients in the intestines. Malnutrition contributes to liver disease.
Other factors that contribute to the development of alcoholic liver disease:
- Genetic factors
- Personal susceptibility to alcohol-induced liver disease
- Toxicity of alcohol (ethanol) to the liver
Alcoholic liver disease does not affect all heavy drinkers. Women may be more susceptible than men. It is not necessary to get drunk for the disease to develop.
Fatty change and alcoholic hepatitis are probably reversible. The later stages of fibrosis and cirrhosis tend to be irreversible but can usually be quite well managed for long periods of time.
The cause of fatty change are:
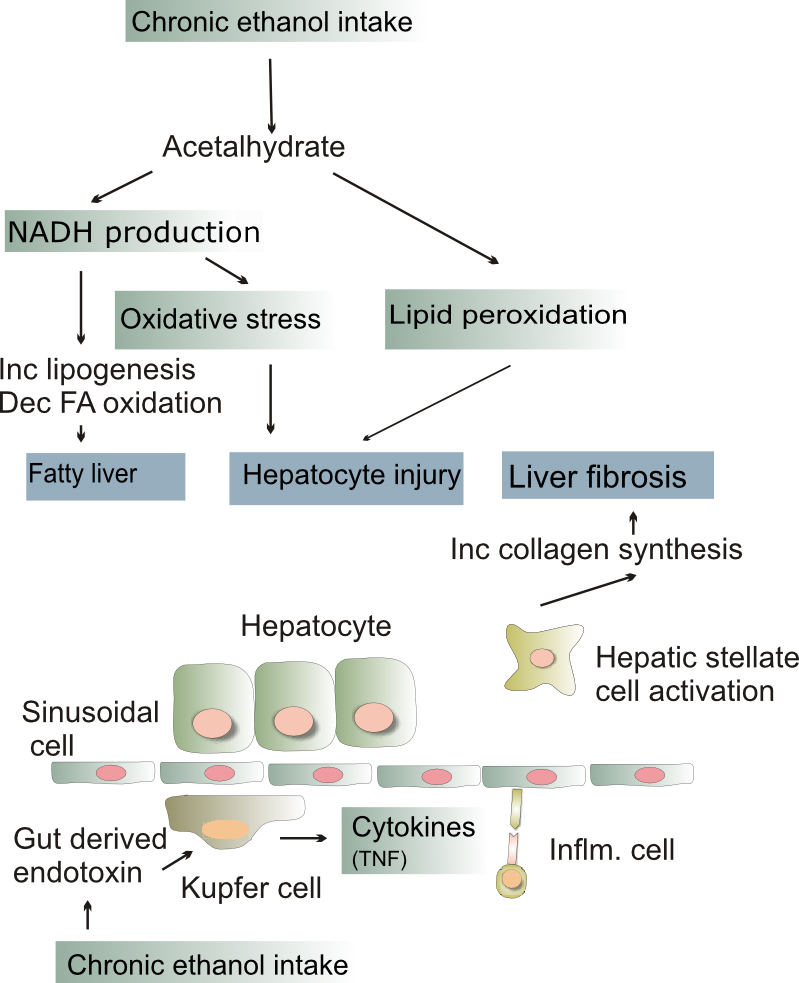
- The excess generation of NAD by the enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase which cause shunting of normal substrates from catabolism towards lipid biosynthesis.
- Impaired assembly and secretion of lipoproteins and increased peripheral lipid catabolism may also contribute
The cause of alcoholic hepatitis are:
- Acetaldehyde formed from alcohol induces lipid peroxidation and acetaldehyde protein adduct formation which disrupt cytoskeleton
- Directly affect microtubule organization, mitochondrial function and membrane fluidity
- Generation of ROS
- Neutrophil attack at the site of hepatocyte necrosis
Fatty change
- Fatty change, or steatosis is the accumulation of fat in liver cells which can be seen as fatty globules under the microscope.
- Alcoholism causes large fatty globules (macrovesicular steatosis).
- Other causes of macrovesicular steatosis include diabetes, obesity and starvation.
- Alcoholic fatty change is probably dose related.
- Small fatty globules have different causes.
Alcoholic hepatitis
- Some people get an acute hepatitis or inflammatory reaction to the cells affected by fatty change. This is not directly related to the dose of alcohol.
- Some people seem more prone to this reaction than others. This is called alcoholic steatonecrosis and the inflammation probably predisposes to liver fibrosis.
Liver fibrosis
- Liver fibrosis, in itself, is largely asymptomatic but as it progresses it can turn into cirrhosis, where the fibrosis alters the architecture and impairs the function of the liver.
Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis is a late stage of liver disease marked by fibrosis and altered liver architecture.
- It is often progressive and may eventually lead to liver failure.
- Late complications of cirrhosis or liver failure include portal hypertension, coagulation disorders, ascites and other complications including hepatic encephalopathy and the hepatorenal syndrome.
- Cirrhosis also has number of other causes, such as hepatitis and toxins. The late stages of cirrhosis (say from viral hepatitis or alcohol) may look similar. This phenomenon is termed a "final common pathway" for a disease.